Z Technology: A New Era of Innovation
Z technology, a term encompassing a range of emerging technologies, is ushering in a new era of innovation. From artificial intelligence and quantum computing to blockchain and the Internet of […]
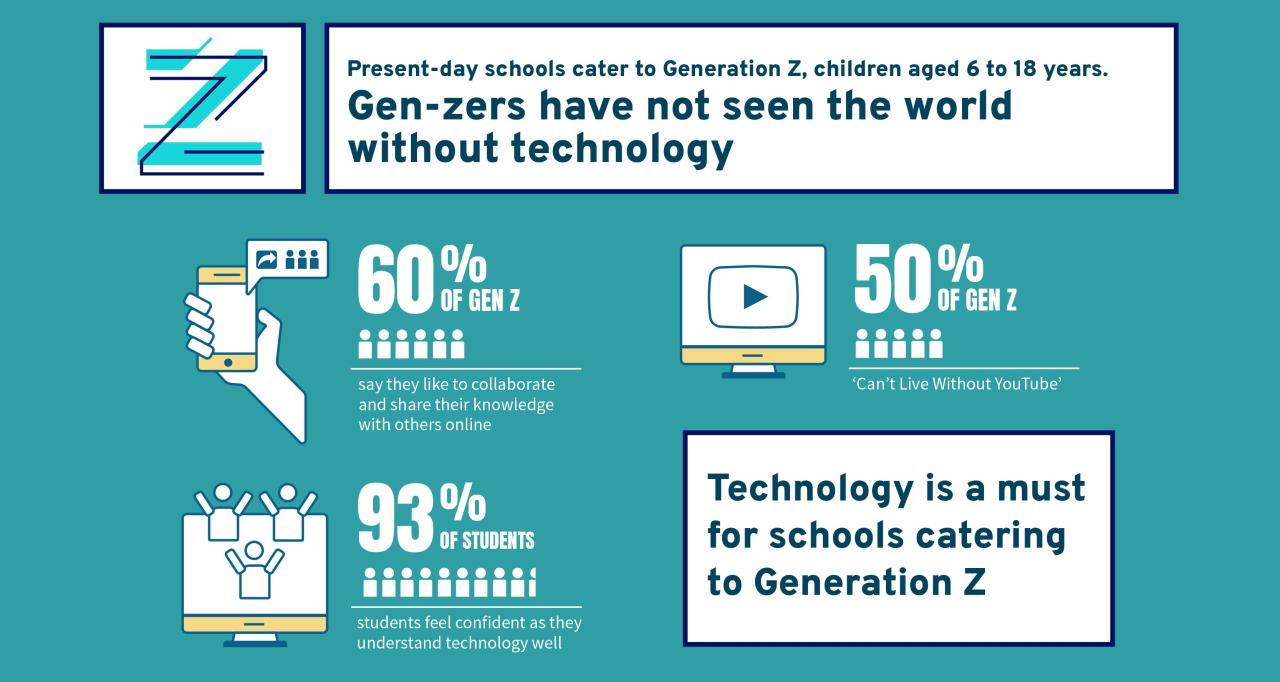
Z technology, a term encompassing a range of emerging technologies, is ushering in a new era of innovation. From artificial intelligence and quantum computing to blockchain and the Internet of Things, these technologies are poised to revolutionize industries, reshape societies, and redefine our daily lives. Z technology is characterized by its ability to process vast amounts of data, automate complex tasks, and connect physical and digital worlds in unprecedented ways.
The potential impact of Z technology is far-reaching. It promises to enhance productivity, improve healthcare, accelerate scientific discovery, and address global challenges such as climate change. However, the adoption of Z technology also presents ethical considerations, raising questions about data privacy, job displacement, and the potential for misuse.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions

The rapid advancement of Z technology presents both immense opportunities and significant ethical challenges. As we navigate this evolving landscape, it is crucial to consider the potential risks and opportunities associated with Z technology’s development and deployment. This section will explore these ethical considerations and delve into potential future directions and emerging trends in the field of Z technology.
Ethical Considerations in Z Technology Development
The development and deployment of Z technology raise various ethical concerns that demand careful consideration. These concerns span a wide range of issues, from data privacy and security to potential biases and societal impacts. It is essential to proactively address these concerns to ensure responsible and equitable development and deployment of Z technology.
- Data Privacy and Security: Z technology often relies on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy and security. It is essential to implement robust data protection measures, such as anonymization techniques and secure data storage solutions, to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
- Algorithmic Bias: Z technology relies on algorithms that can perpetuate existing biases present in the training data. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, particularly in areas like hiring, loan approvals, and criminal justice. Addressing algorithmic bias requires careful selection and preprocessing of training data, as well as ongoing monitoring and evaluation of model performance.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency and accountability are crucial for building trust in Z technology. Users should understand how these technologies work and have access to information about their decision-making processes. Additionally, mechanisms for accountability should be established to address potential misuse or unintended consequences.
- Job Displacement: Z technology has the potential to automate tasks currently performed by humans, raising concerns about job displacement. It is essential to develop strategies for retraining and reskilling the workforce to adapt to the changing job market.
- Social Impact: Z technology can have profound social impacts, influencing our interactions, behaviors, and decision-making. It is crucial to consider the potential consequences of these technologies on society and ensure their development and deployment are aligned with ethical principles and societal values.
Potential Risks and Opportunities
Z technology presents both potential risks and opportunities that require careful consideration. Understanding these risks and opportunities is crucial for navigating the responsible development and deployment of these technologies.
- Risk of Misuse: Z technology can be misused for malicious purposes, such as creating deepfakes, manipulating public opinion, or perpetrating fraud. It is essential to develop safeguards and countermeasures to mitigate these risks.
- Increased Inequality: The benefits of Z technology may not be equally distributed, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities. Addressing this challenge requires efforts to ensure equitable access to these technologies and mitigate potential biases.
- Erosion of Privacy: Z technology can be used to track and monitor individuals, potentially eroding privacy. It is essential to establish clear boundaries and regulations to protect individual privacy.
- Opportunity for Innovation: Z technology holds immense potential for innovation across various sectors, from healthcare and education to manufacturing and finance. These technologies can enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and create new opportunities for growth.
- Potential for Social Good: Z technology can be used to address critical societal challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and disease. These technologies can enable us to develop innovative solutions and improve the well-being of individuals and communities.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
The field of Z technology is rapidly evolving, with numerous emerging trends and future directions shaping its trajectory. Understanding these trends is essential for staying abreast of advancements and opportunities in this dynamic field.
- Advancements in AI: Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are driving significant progress in Z technology. These advancements include improved algorithms, increased computing power, and access to larger datasets, enabling more sophisticated and powerful Z technologies.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Z technology is increasingly being integrated with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and 5G. These integrations create new possibilities and applications for Z technology across various sectors.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of Z technology. As these technologies become more powerful and pervasive, it is essential to develop robust ethical frameworks and guidelines to ensure responsible development and deployment.
- Regulation and Governance: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on regulating Z technology to address ethical concerns and ensure responsible use. This includes developing frameworks for data privacy, algorithmic fairness, and accountability.
- Public Engagement: Public engagement is essential for shaping the future of Z technology. It is crucial to foster dialogue and collaboration between developers, researchers, policymakers, and the public to ensure that these technologies are developed and deployed in a way that benefits society as a whole.
Last Recap: Z Technology

As Z technology continues to evolve, it is crucial to foster responsible innovation, ensuring that its benefits are widely shared and its risks are mitigated. By understanding the opportunities and challenges presented by these emerging technologies, we can harness their transformative power to create a better future for all.
Z technology is rapidly evolving, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. From AI-powered assistants to immersive virtual reality experiences, the impact of Z technology is undeniable. For those who want to stay ahead of the curve, I recommend checking out my technology geeks , a platform dedicated to exploring the latest advancements in Z technology.
Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or just starting to explore the possibilities, this resource will provide valuable insights into the future of Z technology.








