Vendor Technologies: Powering Business Success
Vendor technologies have become an integral part of modern business operations, driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation across industries. From enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, […]
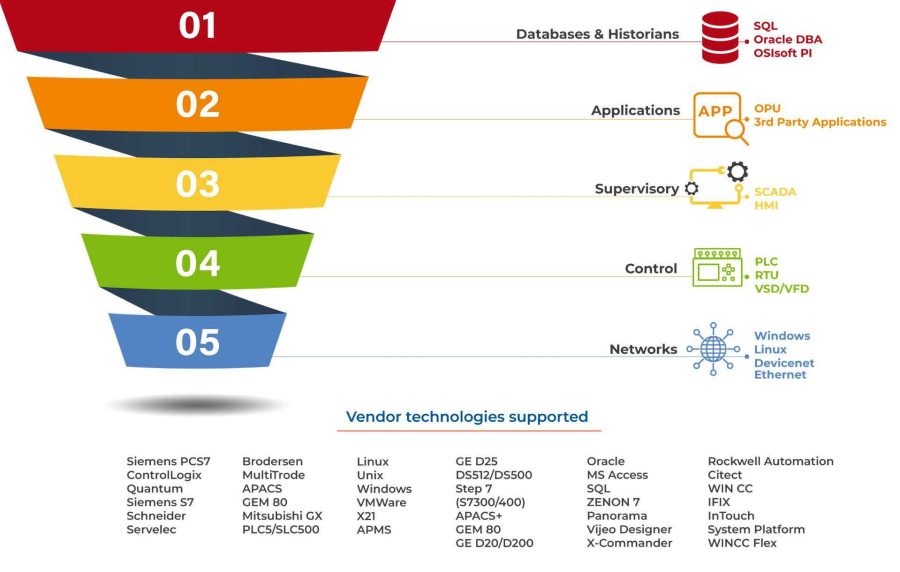
Vendor technologies have become an integral part of modern business operations, driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation across industries. From enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, vendor technologies empower organizations to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive edge.
This exploration delves into the world of vendor technologies, examining their definition, selection considerations, types, impact on businesses, and best practices for implementation. We’ll uncover the critical role they play in shaping the future of business, highlighting key trends and challenges in this dynamic landscape.
Types of Vendor Technologies
Vendor technologies encompass a wide range of tools and services that businesses leverage to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and achieve strategic objectives. These technologies can be categorized based on their functionalities and applications, offering tailored solutions for various business needs.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing platforms provide on-demand access to computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. These platforms are typically delivered through the internet and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud computing offers several advantages, including scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced security.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS providers offer virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing businesses to build and manage their own applications and operating systems. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS providers offer a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without the need for managing the underlying infrastructure. Examples include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS providers offer software applications delivered over the internet, allowing users to access and use the software from any device with an internet connection. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Dropbox.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM systems are designed to manage customer interactions and relationships, providing a centralized platform for tracking customer data, managing sales pipelines, and automating marketing campaigns. These systems enhance customer engagement, improve sales performance, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior.
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform that offers a wide range of features, including sales automation, marketing automation, customer service, and analytics.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A comprehensive CRM solution that integrates with other Microsoft products and services, providing a unified platform for managing customer relationships.
- HubSpot: A popular CRM platform that focuses on inbound marketing and sales, offering tools for lead generation, content marketing, and social media management.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems integrate various business processes, including finance, human resources, supply chain management, and manufacturing, into a single, unified system. These systems streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide real-time insights into business performance.
- SAP: A leading ERP provider that offers a wide range of solutions for various industries, including manufacturing, retail, and finance.
- Oracle: Another major ERP provider that offers a comprehensive suite of applications for managing business processes, including finance, supply chain, and human resources.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: In addition to its CRM capabilities, Microsoft Dynamics 365 also offers ERP solutions for managing financial, supply chain, and operations processes.
Business Intelligence (BI)
BI tools collect, analyze, and visualize data to provide insights into business performance, trends, and customer behavior. These tools empower businesses to make informed decisions, identify opportunities, and optimize operations.
- Tableau: A popular BI tool that offers a user-friendly interface for creating interactive dashboards and visualizations.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s business intelligence platform that integrates with other Microsoft products and services, providing a comprehensive solution for data analysis and reporting.
- Qlik Sense: A self-service BI tool that allows users to explore data and create visualizations without requiring extensive technical expertise.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI technologies are increasingly being adopted by businesses to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance customer experiences. AI-powered solutions can analyze large datasets, predict outcomes, and personalize interactions, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms can learn from data and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. Applications include fraud detection, customer segmentation, and predictive maintenance.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables computers to understand and process human language, enabling applications such as chatbots, sentiment analysis, and automated content generation.
- Computer Vision: Computer vision technologies allow computers to “see” and interpret images and videos, enabling applications such as facial recognition, object detection, and medical imaging analysis.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
The landscape of vendor technologies is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging and shaping the future of business operations.
- Hyperautomation: Automating as many processes as possible using a combination of AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to improve efficiency and reduce human error.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance for applications requiring real-time insights.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting devices and systems to collect and analyze data, enabling smarter and more efficient operations.
- Blockchain: A distributed ledger technology that provides secure and transparent data storage and transactions, enabling applications such as supply chain management and digital identity.
Impact of Vendor Technologies on Businesses
Vendor technologies have significantly impacted businesses across industries, driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation. By leveraging external expertise and resources, companies can access cutting-edge solutions and focus on their core competencies.
Impact on Business Efficiency
Vendor technologies can streamline business processes, automate tasks, and optimize resource allocation, leading to increased efficiency. For example, cloud-based accounting software allows businesses to automate financial tasks, reduce manual errors, and access real-time financial data, improving financial management efficiency. Similarly, customer relationship management (CRM) systems automate customer interactions, personalize marketing campaigns, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior, enhancing sales and marketing efficiency.
Impact on Business Productivity
Vendor technologies empower employees with tools and resources that enhance productivity. Collaboration platforms facilitate seamless communication and teamwork, enabling employees to work effectively regardless of location. Project management tools help businesses track progress, allocate resources efficiently, and ensure timely project completion, boosting productivity.
Impact on Business Innovation
Vendor technologies foster innovation by providing access to new technologies, tools, and platforms. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) platforms enable businesses to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions, driving innovation in areas like product development, customer service, and marketing. Furthermore, cloud computing platforms offer scalable infrastructure and flexible resources, allowing businesses to experiment with new ideas and rapidly deploy innovative solutions.
Case Studies
- Netflix: By leveraging cloud computing services, Netflix can scale its streaming infrastructure on demand, meeting the needs of millions of users worldwide. This has enabled Netflix to deliver a seamless streaming experience and rapidly expand its global reach.
- Amazon: Amazon’s use of AI and ML technologies has revolutionized its operations. From personalized product recommendations to optimized warehouse logistics, AI has significantly enhanced customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Airbnb: Airbnb’s success can be attributed in part to its use of data analytics and machine learning to personalize search results, improve user experience, and optimize pricing strategies.
Potential Risks and Challenges, Vendor technologies
Vendor technologies, while offering numerous benefits, also present potential risks and challenges.
| Risk/Challenge | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Security Breaches | Vendor technologies can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, potentially exposing sensitive data and disrupting business operations. | Implement robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and regular security audits. |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Vendor technologies often involve the collection and storage of sensitive customer data, raising concerns about data privacy and compliance with regulations. | Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and implement data anonymization and encryption techniques. |
| Vendor Lock-in | Businesses may become dependent on a particular vendor, limiting their flexibility and potentially increasing costs in the long run. | Choose vendors with open APIs and standards, and consider using multiple vendors to avoid vendor lock-in. |
| Integration Challenges | Integrating vendor technologies with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming, potentially impacting business operations. | Thoroughly evaluate integration requirements and choose vendors with strong integration capabilities. |
Best Practices for Implementing Vendor Technologies
Implementing vendor technologies effectively is crucial for businesses to maximize their benefits and avoid common pitfalls. A well-structured approach ensures seamless integration, efficient utilization, and optimal return on investment.
Planning
Thorough planning is essential for a successful implementation.
- Define clear objectives and scope: Clearly define the goals you want to achieve with the vendor technology, and Artikel the specific processes or areas it will impact. This will help in selecting the right solution and ensuring alignment with your business needs.
- Conduct a thorough vendor evaluation: Carefully assess potential vendors based on factors like their reputation, experience, technical capabilities, and pricing. Consider conducting proof-of-concept trials to evaluate the technology’s performance in your specific environment.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan: Artikel the steps involved in the implementation, including timelines, resource allocation, and key milestones. This will provide a roadmap for the project and ensure accountability.
- Address potential risks and challenges: Identify potential roadblocks, such as data migration, integration issues, or user adoption challenges. Develop mitigation strategies to address these risks proactively.
Integration
Successful integration is key to ensuring the vendor technology works seamlessly with your existing systems.
- Choose the right integration approach: Consider different integration methods, such as application programming interfaces (APIs), data synchronization, or custom development, based on your specific needs and the vendor’s capabilities.
- Test thoroughly: Conduct comprehensive testing to ensure the integrated system functions as expected and data is transferred accurately. This will help identify and resolve potential issues before going live.
- Document the integration process: Maintain detailed documentation of the integration process, including technical specifications, configuration details, and troubleshooting steps. This will be invaluable for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
Training
Effective training is crucial for users to adopt and utilize the vendor technology efficiently.
- Develop comprehensive training materials: Create user-friendly guides, tutorials, and online resources to explain the technology’s features, functionalities, and best practices.
- Provide hands-on training: Offer practical training sessions that allow users to interact with the technology and learn by doing. This will enhance understanding and facilitate quicker adoption.
- Offer ongoing support: Provide ongoing support channels, such as help desks, online forums, or dedicated support teams, to assist users with any questions or issues they may encounter.
Ongoing Maintenance
Continuous maintenance is essential to ensure the vendor technology remains functional, secure, and up-to-date.
- Establish a maintenance schedule: Develop a regular maintenance schedule for system updates, security patches, and performance monitoring.
- Monitor system performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
- Stay updated on vendor releases: Stay informed about the latest vendor releases and updates to ensure your system is current and benefits from new features and enhancements.
Maximizing Return on Investment (ROI)
To maximize the return on investment from vendor technologies, focus on:
- Clear business objectives: Align technology implementations with specific business goals to ensure measurable outcomes and tangible benefits.
- Data-driven decision making: Track and analyze data to understand the impact of the technology and identify areas for optimization.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly evaluate the technology’s performance and identify opportunities for enhancement or process streamlining.
Evaluating Success
To evaluate the success of a vendor technology implementation, consider:
- Meeting objectives: Assess whether the technology has achieved the defined goals and delivered the expected benefits.
- User adoption: Measure the level of user adoption and satisfaction with the technology.
- Cost savings and efficiency gains: Quantify the cost savings and efficiency improvements realized through the implementation.
- Security and compliance: Evaluate the technology’s security posture and compliance with relevant regulations.
Conclusive Thoughts

As we conclude our journey through the realm of vendor technologies, it’s evident that these solutions are not merely tools but strategic assets that drive business transformation. By carefully considering selection factors, leveraging best practices, and embracing emerging trends, organizations can harness the power of vendor technologies to achieve sustainable growth and thrive in the ever-evolving digital age.
Vendor technologies are constantly evolving, offering new solutions to age-old problems. The swimming pool industry is no exception, with innovations like new swimming pool technology transforming how we maintain and enjoy our pools. This technology, from automated cleaning systems to smart water management, not only simplifies pool ownership but also enhances safety and energy efficiency, demonstrating the power of vendor technologies to improve our lives.