Uniform Technology: Streamlining Industries
Uniform technology, a powerful force reshaping industries, offers a standardized approach to operations. It goes beyond mere standardization, creating a cohesive system that fosters efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. This […]

Uniform technology, a powerful force reshaping industries, offers a standardized approach to operations. It goes beyond mere standardization, creating a cohesive system that fosters efficiency, productivity, and cost savings.
This technology encompasses various tools and processes, all designed to harmonize workflows and ensure consistency across different departments and functions. From manufacturing to healthcare, uniform technology is transforming how businesses operate, driving innovation and improving outcomes.
Defining Uniform Technology
Uniform technology refers to the use of standardized and consistent technologies across different parts of an organization or industry. This standardization aims to achieve efficiency, interoperability, and scalability. It involves implementing common protocols, platforms, and tools to streamline processes and reduce complexity.
Distinguishing Uniform Technology from Standard Technology
Uniform technology is distinct from standard technology in its scope and purpose. While standard technology focuses on defining technical specifications and protocols for a specific technology or component, uniform technology encompasses a broader approach to implementing these standards consistently across an entire system or industry.
For example, a standard for a wireless communication protocol like Wi-Fi defines the technical specifications for transmitting data over wireless networks. In contrast, uniform technology in a manufacturing industry might involve adopting the same Wi-Fi standard for all production lines, ensuring seamless data exchange and consistent network performance across the entire facility.
Examples of Industries Using Uniform Technology
Uniform technology is prevalent in various industries, facilitating seamless operations and data exchange. Here are some examples:
- Manufacturing: Uniform technology is essential for manufacturing companies to maintain consistency in production processes, data collection, and supply chain management. This includes adopting standardized equipment, software, and communication protocols across different facilities and production lines.
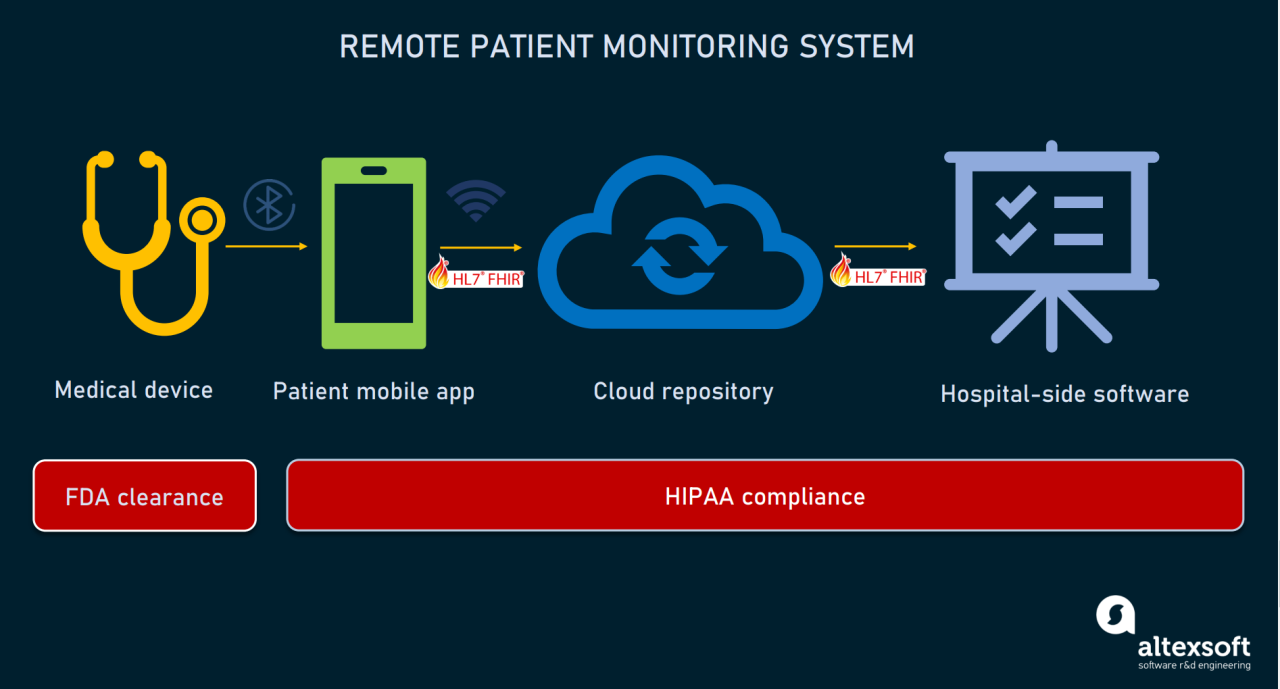
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry leverages uniform technology to ensure interoperability between different medical devices, electronic health records (EHRs), and healthcare information systems. This allows for seamless data sharing and efficient patient care across various hospitals and clinics.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions rely on uniform technology to maintain consistent security standards, data processing procedures, and regulatory compliance across different branches and departments. This ensures secure and reliable transactions, risk management, and data protection.
- Transportation: The transportation industry utilizes uniform technology for traffic management, logistics, and communication. This includes standardized traffic control systems, GPS navigation systems, and communication protocols for vehicles and infrastructure.
Benefits of Uniform Technology

Uniform technology offers a myriad of advantages for organizations, streamlining operations, enhancing productivity, and ultimately driving business success. This approach to technology adoption, characterized by the use of standardized systems and processes, brings about significant improvements across various aspects of an organization’s functioning.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
The implementation of uniform technology directly translates to increased efficiency and productivity within an organization. By adopting standardized systems and processes, organizations can eliminate redundancy, reduce errors, and streamline workflows. This leads to a more efficient use of resources, including time, manpower, and finances.
Standardization fosters a cohesive and streamlined environment, enabling employees to operate seamlessly across different departments and tasks.
For instance, a company that adopts a uniform customer relationship management (CRM) system across all its departments can ensure consistent data management, improved customer service, and enhanced sales performance.
Cost Reduction and Increased ROI
Uniform technology also plays a crucial role in cost reduction and maximizing return on investment (ROI). By consolidating systems and processes, organizations can eliminate the need for multiple, disparate solutions, leading to lower maintenance costs, reduced training requirements, and simplified licensing agreements.
Uniform technology fosters a more efficient allocation of resources, enabling organizations to achieve greater value from their investments.
Consider a manufacturing company that adopts a uniform enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. This unified system eliminates the need for multiple, standalone applications for inventory management, production planning, and financial reporting. By streamlining these processes, the company can achieve significant cost savings while improving operational efficiency and increasing its overall ROI.
Types of Uniform Technology
Uniform technology encompasses a wide range of technologies that can be categorized based on their functions and applications. These technologies are designed to enhance various aspects of uniform design, production, and usage, ultimately contributing to improved efficiency, safety, and performance.
Types of Uniform Technology
Uniform technology can be broadly classified into the following categories:
- Fabric Technologies: These technologies focus on developing innovative fabrics that offer enhanced properties such as durability, breathability, moisture-wicking, and protection from environmental elements.
- Performance Fabrics: Performance fabrics are engineered to provide specific benefits like moisture management, temperature regulation, and abrasion resistance. Examples include polyester blends for moisture-wicking, nylon for durability, and spandex for stretch.
- Protective Fabrics: These fabrics offer protection against hazards such as fire, chemicals, and biological agents. Examples include flame-retardant fabrics for firefighters, chemical-resistant fabrics for lab workers, and anti-microbial fabrics for healthcare professionals.
- Design and Manufacturing Technologies: These technologies streamline the design and production process, enabling faster turnaround times, improved accuracy, and customized solutions.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software allows designers to create virtual prototypes of uniforms, experiment with different designs, and optimize fit and functionality.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing technology can be used to create custom-fit uniforms, especially for specialized applications like sports gear or protective equipment.
- Automated Cutting and Sewing: Automated systems can cut and sew fabric with precision, reducing errors and improving efficiency in uniform production.
- Smart Uniform Technologies: These technologies integrate electronics and sensors into uniforms to provide enhanced functionality, data collection, and communication capabilities.
- Wearable Sensors: These sensors can monitor vital signs like heart rate, body temperature, and movement, providing real-time data for performance tracking, safety monitoring, and health management.
- Integrated Communication Systems: Smart uniforms can incorporate communication devices like GPS trackers, two-way radios, and Bluetooth connectivity, enabling real-time communication and location tracking.
- RFID Tags: RFID tags can be embedded in uniforms for inventory management, tracking, and authentication purposes.
Implementing Uniform Technology

Implementing uniform technology requires a strategic approach that considers the organization’s unique needs and goals. This process involves careful planning, execution, and ongoing monitoring to ensure successful integration and adoption.
Steps Involved in Implementing Uniform Technology
Implementing uniform technology involves a series of steps, each crucial for achieving a seamless transition and realizing the benefits of standardization.
- Define the Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the scope of the uniform technology implementation, identifying the specific areas, departments, or processes that will be affected. Set clear objectives, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing security, or enhancing user experience.
- Conduct a Thorough Assessment: Perform a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s current technology landscape, including hardware, software, infrastructure, and existing processes. This assessment will identify potential challenges, compatibility issues, and areas requiring optimization.
- Choose the Right Technology: Select the most appropriate uniform technology based on the organization’s specific requirements, budget, and future scalability needs. Research and evaluate different options, considering factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, and vendor support.
- Develop a Detailed Implementation Plan: Create a detailed implementation plan outlining the steps, timelines, resources, and responsibilities for each stage of the process. This plan should include clear communication strategies, training programs, and contingency plans for potential roadblocks.
- Pilot Testing and Feedback: Conduct pilot testing with a small group of users to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement before full-scale deployment. Gather feedback from pilot participants to refine the implementation strategy and address any concerns.
- Rollout and Training: Gradually roll out the uniform technology to the organization, providing comprehensive training programs to ensure users are familiar with the new system and can effectively utilize its features.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor the performance of the uniform technology, collecting data on user adoption, efficiency gains, and cost savings. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and optimize the system to maximize its effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations
Adopting uniform technology presents several challenges and considerations that organizations must address for a successful implementation.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new technology, especially if they are accustomed to their existing workflows. Effective communication, training, and demonstrating the benefits of the new system can mitigate this resistance.
- Compatibility Issues: Ensuring compatibility between the new uniform technology and existing systems and applications is crucial. This may require modifications or adjustments to existing infrastructure or applications.
- Data Migration and Security: Migrating data from existing systems to the new uniform platform requires careful planning and execution to avoid data loss or security breaches. Robust security measures should be implemented throughout the migration process.
- Cost and Budget: Implementing uniform technology can involve significant upfront costs for software, hardware, training, and ongoing maintenance. Organizations must carefully assess the costs and benefits to ensure a positive return on investment.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the uniform technology with existing systems and applications can be complex, requiring specialized skills and resources. Thorough planning and testing are essential to ensure a seamless integration process.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Organizations can significantly increase the chances of a successful implementation by following best practices.
- Strong Leadership and Communication: Strong leadership commitment and clear communication throughout the implementation process are essential for gaining buy-in from employees and ensuring a smooth transition.
- User-Centric Design: Prioritize the user experience by designing the uniform technology with user needs and preferences in mind. This includes providing intuitive interfaces, comprehensive training, and ongoing support.
- Iterative Development and Feedback: Implement the uniform technology in phases, gathering feedback from users at each stage to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed.
- Data Security and Privacy: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Regular security audits and updates are essential.
- Continuous Improvement: After implementation, monitor the performance of the uniform technology and continuously seek ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance user experience.
Case Studies of Uniform Technology
Uniform technology has proven its effectiveness in diverse industries, revolutionizing operations and achieving significant improvements. By examining real-world examples, we can gain valuable insights into the impact of uniform technology on organizations and understand the lessons learned from their successful implementations.
Case Study: Amazon’s Fulfillment Centers
Amazon, a global e-commerce giant, has extensively implemented uniform technology in its fulfillment centers to optimize logistics and enhance efficiency.
Amazon utilizes robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and sophisticated software systems to manage inventory, pick and pack orders, and transport goods within its vast warehouses. This technology has significantly reduced manual labor, minimized errors, and accelerated order fulfillment times.
“Amazon’s investment in robotics and automation has allowed us to scale our operations and meet the ever-growing demands of our customers.” – Jeff Bezos, Founder of Amazon
Impact of Uniform Technology
- Increased efficiency: Robots and AGVs have automated repetitive tasks, leading to faster order processing and increased throughput.
- Reduced errors: Automated systems minimize human error, ensuring accuracy in picking, packing, and shipping.
- Improved safety: By taking over hazardous and physically demanding tasks, uniform technology enhances worker safety.
- Cost savings: Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes waste, leading to significant cost savings.
Lessons Learned
- Scalability: Uniform technology allows organizations to scale their operations efficiently, meeting growing demands without compromising speed or accuracy.
- Employee training: Effective implementation requires proper training and upskilling of employees to work alongside and manage the technology.
- Data analytics: Uniform technology generates vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to optimize processes and identify areas for improvement.
Future Trends in Uniform Technology
Uniform technology is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and consumer preferences. These innovations are shaping the future of uniforms across various industries, leading to more comfortable, durable, and technologically advanced garments.
Emerging Trends and Advancements
The future of uniform technology is characterized by several emerging trends that are poised to revolutionize the way uniforms are designed, manufactured, and worn. These trends are driven by factors such as sustainability, personalization, and the integration of smart technologies.
- Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing Processes: The growing emphasis on sustainability is driving the adoption of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes in uniform technology. This includes the use of recycled fabrics, biodegradable materials, and low-impact dyes. For instance, companies like Patagonia are using recycled polyester and organic cotton in their uniforms, reducing their environmental footprint.
- Personalization and Customization: The demand for personalized uniforms is increasing, with employees seeking garments that fit their individual needs and preferences. This trend is fueled by advancements in 3D printing and mass customization technologies. Companies like Nike are using 3D printing to create customized athletic uniforms for athletes, allowing for a perfect fit and performance enhancement.
- Smart Fabrics and Wearable Technology: Smart fabrics are becoming increasingly prevalent in uniform technology, offering features such as temperature regulation, moisture management, and data tracking. For example, uniforms for firefighters can now incorporate sensors that monitor their vital signs and alert emergency responders if they are in danger.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: The integration of IoT devices into uniforms is opening up new possibilities for data collection and communication. Smart uniforms can be equipped with sensors that track employee movements, monitor their health, and provide real-time information about their work environment. For example, delivery drivers can use smart uniforms to track their packages, receive delivery instructions, and communicate with dispatchers.
Impact on Industries
The advancements in uniform technology are expected to have a significant impact on various industries, transforming the way employees work and interact with their surroundings.
- Healthcare: Smart uniforms can monitor vital signs, track patient data, and provide real-time feedback to healthcare professionals. This can enhance patient care and improve the efficiency of medical operations.
- Manufacturing: Smart uniforms can track worker movements, monitor their safety, and provide feedback on their performance. This can improve productivity, reduce accidents, and optimize manufacturing processes.
- Hospitality: Smart uniforms can provide guests with personalized service and information, enhancing their overall experience. For example, hotel staff can use smart uniforms to access guest profiles, provide personalized recommendations, and respond to guest requests efficiently.
- Public Safety: Smart uniforms can enhance the safety and efficiency of first responders. For example, firefighters can use smart uniforms to monitor their vital signs, track their location, and communicate with each other in hazardous environments.
Key Future Trends in Uniform Technology
The following table Artikels some of the key future trends in uniform technology, their expected impact, and their anticipated timeline:
| Trend | Expected Impact | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing Processes | Reduced environmental footprint, lower cost of production, improved brand image | Short-term (1-3 years) |
| Personalization and Customization | Improved employee comfort, increased productivity, enhanced brand loyalty | Mid-term (3-5 years) |
| Smart Fabrics and Wearable Technology | Enhanced safety, improved performance, increased efficiency | Mid-term (3-5 years) |
| Internet of Things (IoT) Integration | Real-time data collection, improved communication, enhanced operational efficiency | Long-term (5+ years) |
Summary
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, uniform technology stands as a beacon of progress. By unifying processes and leveraging shared resources, it empowers organizations to achieve greater efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately, drive success. As we look toward the future, the adoption of uniform technology will undoubtedly continue to shape industries, unlocking new possibilities and propelling businesses forward.
Uniform technology encompasses a wide range of solutions, from barcode scanners to automated sorting systems. This technology is often integrated with other industrial tools, such as scales industrial technologies , to streamline operations and improve efficiency. By leveraging these combined systems, businesses can optimize their workflows, minimize errors, and achieve greater accuracy in their operations.