Tube-Mac Piping Technologies: A Comprehensive Guide
Tube-mac piping technologies represent a vital component in various industries, offering efficient and reliable solutions for fluid transfer and system integration. This guide delves into the world of tube-mac piping, […]

Tube-mac piping technologies represent a vital component in various industries, offering efficient and reliable solutions for fluid transfer and system integration. This guide delves into the world of tube-mac piping, exploring its history, applications, and future advancements. From understanding the different types and materials to mastering fabrication and installation techniques, this comprehensive resource aims to provide a clear and concise understanding of this critical technology.
Tube-mac piping is a versatile and adaptable solution, finding applications in diverse sectors such as power generation, oil and gas, chemical processing, and more. The inherent strength and durability of tube-mac piping systems contribute to their widespread adoption in demanding environments where reliability and longevity are paramount.
Introduction to Tube-Mac Piping Technologies

Tube-Mac piping technologies represent a specialized approach to piping construction that employs the use of prefabricated components, primarily tubes and machined fittings, to create intricate and robust piping systems. This method offers several advantages over traditional piping techniques, making it highly sought-after in diverse industrial applications.
Significance of Tube-Mac Piping Technologies
The significance of Tube-Mac piping technologies lies in their ability to deliver superior performance and efficiency across various industrial sectors. This approach offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Accuracy and Precision: The use of prefabricated components minimizes the need for on-site fabrication, resulting in increased dimensional accuracy and reduced potential for errors. This precision is crucial for applications demanding tight tolerances and leak-free performance.
- Improved Durability and Reliability: The inherent strength and resilience of the components, coupled with the precise assembly process, contribute to highly durable and reliable piping systems. This is particularly important in industries handling high-pressure fluids, corrosive substances, or demanding environments.
- Faster Installation and Reduced Downtime: Prefabricated components allow for faster installation times, significantly reducing project timelines and minimizing downtime. This is a critical factor in industries where production interruptions can be costly.
- Simplified Maintenance and Repair: The modular nature of Tube-Mac piping systems facilitates easy maintenance and repair. Individual components can be readily replaced, reducing the need for extensive dismantling and minimizing downtime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial investment in Tube-Mac piping technologies may appear higher, the long-term cost savings associated with enhanced performance, reduced downtime, and simplified maintenance often make it a more cost-effective solution in the long run.
Historical Development of Tube-Mac Piping
The evolution of Tube-Mac piping technologies can be traced back to the early 20th century, driven by the increasing demand for reliable and efficient piping solutions in various industries.
- Early Developments: The initial development of Tube-Mac piping focused on utilizing seamless steel tubes and simple machined fittings for applications in the oil and gas industry. The focus was on achieving leak-proof connections and robust performance in demanding environments.
- Advancements in Materials and Techniques: As the demand for Tube-Mac piping expanded, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques played a crucial role in its evolution. The introduction of high-strength alloys, specialized coatings, and innovative joining methods further enhanced the capabilities and applications of Tube-Mac piping.
- Modern Innovations: Today, Tube-Mac piping technologies are at the forefront of innovation, incorporating advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) techniques, sophisticated materials, and innovative joining methods. These advancements have expanded the applications of Tube-Mac piping to encompass a wide range of industries, including power generation, chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food and beverage production.
Applications of Tube-Mac Piping
Tube-Mac piping technologies find widespread applications across diverse industries, driven by their ability to deliver superior performance, reliability, and efficiency.
- Oil and Gas: Tube-Mac piping is extensively used in oil and gas production, processing, and transportation due to its ability to withstand high pressures, corrosive environments, and demanding operating conditions. It is employed in applications such as pipelines, wellhead systems, and processing plants.
- Power Generation: In power generation facilities, Tube-Mac piping is crucial for handling high-pressure steam, cooling water, and other critical fluids. Its high reliability and resistance to thermal stresses make it an ideal choice for applications such as boilers, turbines, and heat exchangers.
- Chemical Processing: The chemical processing industry relies heavily on Tube-Mac piping to handle corrosive and hazardous substances. Its resistance to chemical attack and leak-free performance are essential for safe and efficient operations in chemical plants and refineries.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, Tube-Mac piping is vital for handling sterile fluids and maintaining the integrity of drug production processes. Its ability to meet stringent hygiene standards and minimize contamination risks is crucial for ensuring the safety and quality of pharmaceutical products.
- Food and Beverage Production: The food and beverage industry requires piping systems that are hygienic, corrosion-resistant, and capable of handling a variety of fluids. Tube-Mac piping meets these requirements, making it ideal for applications in food processing, beverage production, and packaging lines.
Types and Materials of Tube-Mac Piping
Tube-Mac piping, also known as “tube-in-tube” or “tube-within-tube” piping, is a specialized type of piping system that employs a unique construction technique to achieve specific performance characteristics. This type of piping system is often used in demanding applications where high pressure, temperature, or corrosive environments are present. Understanding the various types and materials used in Tube-Mac piping is crucial for selecting the right system for a given application.
Types of Tube-Mac Piping
The design and construction of Tube-Mac piping systems can vary based on the specific requirements of the application. Here are some common types:
- Single Wall Tube-Mac Piping: This is the simplest type of Tube-Mac piping, consisting of two concentric tubes. The inner tube carries the process fluid, while the outer tube acts as a protective shell. This type is often used for applications requiring high pressure and temperature resistance.
- Double Wall Tube-Mac Piping: This type features three concentric tubes. The inner tube carries the process fluid, the middle tube serves as a barrier, and the outer tube provides additional protection. This design enhances safety and reliability by providing an extra layer of containment in case of leaks or failures.
- Multi-Wall Tube-Mac Piping: This type involves more than three concentric tubes, providing even greater levels of protection and containment. It is often used in applications requiring extreme conditions or handling hazardous materials.
- Insulated Tube-Mac Piping: This type incorporates insulation between the inner and outer tubes to minimize heat loss or gain. This is particularly beneficial for applications involving high-temperature fluids or where temperature control is critical.
- Flanged Tube-Mac Piping: This type utilizes flanges at the ends of the tubes for easy connection and disassembly. This allows for flexibility in installation and maintenance.
Materials Used in Tube-Mac Piping
A wide range of materials are employed in Tube-Mac piping, each offering specific properties and advantages depending on the application. Here is a comprehensive list:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures, stainless steel is a popular choice for Tube-Mac piping systems. Various grades of stainless steel, such as 304, 316, and 316L, are used based on the specific requirements of the application.
- Nickel Alloys: These alloys, such as Inconel, Monel, and Hastelloy, exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in aggressive environments. They are commonly used in applications involving high temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and high pressures.
- Titanium: This material is highly resistant to corrosion, even in highly aggressive environments. It also has a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent heat transfer properties. Titanium is often used in applications requiring extreme resistance to chemical attack.
- Carbon Steel: This material is cost-effective and offers good strength. It is commonly used in Tube-Mac piping systems operating at lower temperatures and pressures. However, carbon steel is susceptible to corrosion, requiring proper protective coatings or linings.
- Copper Alloys: These alloys, such as copper-nickel and brass, offer good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. They are often used in applications involving seawater or other corrosive environments.
Comparing Tube-Mac Piping Materials
The selection of the right material for Tube-Mac piping is critical for the performance and longevity of the system. Here is a comparison of the characteristics of different materials:
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Temperature Resistance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent | High | High | Moderate |
| Nickel Alloys | Exceptional | High | Very High | High |
| Titanium | Very High | High | High | Very High |
| Carbon Steel | Moderate | Good | Moderate | Low |
| Copper Alloys | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Fabrication and Installation Processes
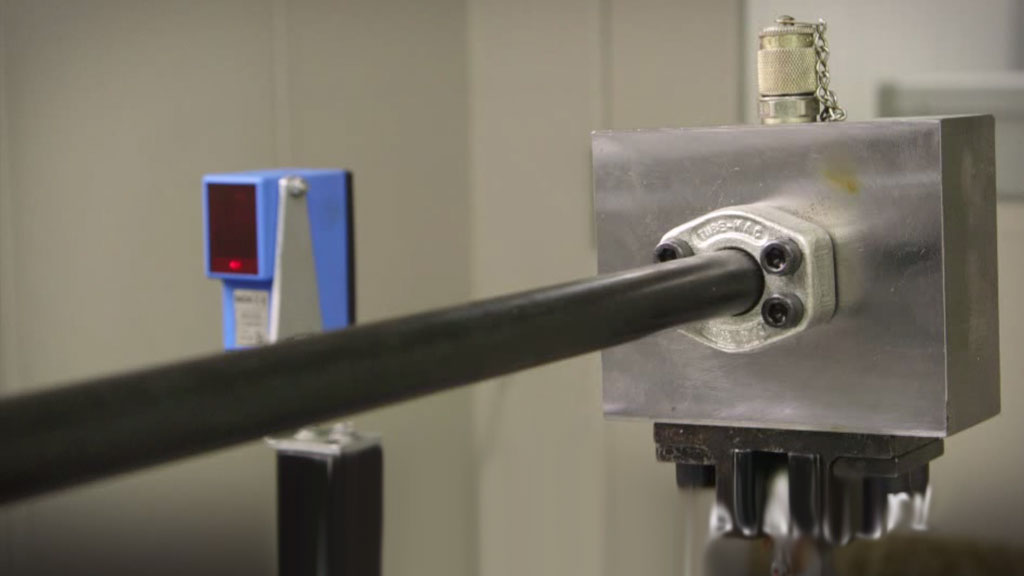
The fabrication and installation of tube-mac piping systems involve meticulous processes to ensure the integrity and functionality of the entire system. This section will delve into the detailed steps involved in fabricating tube-mac piping components and explore the techniques employed for assembling and installing these systems. It will also highlight the critical role of specialized tools and equipment in facilitating these processes.
Fabrication of Tube-Mac Piping Components
Fabrication of tube-mac piping components is a crucial step in the overall construction process. The steps involved are:
- Cutting and Beveling: The first step is cutting the tube-mac pipes to the required length using specialized cutting tools. Beveling the edges of the pipes is essential for creating a smooth and consistent weld joint.
- Cleaning and Preparation: Before welding, the cut ends of the pipes must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants, such as grease, oil, or rust. This ensures a strong and durable weld.
- Welding: The process of joining the tube-mac pipes involves specialized welding techniques, such as TIG (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) or MIG (Gas Metal Arc Welding). These techniques are chosen based on the material of the pipes and the specific requirements of the application.
- Post-Weld Inspection: Once the welding is complete, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure the weld joint meets the required standards. This may involve visual inspection, X-ray testing, or other non-destructive testing methods.
- Machining and Finishing: After welding, the tube-mac piping components may require machining to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish. This can include operations such as threading, grooving, or drilling.
Assembly and Installation of Tube-Mac Piping Systems
Assembling and installing tube-mac piping systems require careful planning and execution to ensure a leak-proof and efficient system. The steps involved are:
- Pre-Assembly: Before assembling the piping system, it is crucial to review the design drawings and ensure that all components are available and in the correct specifications.
- Assembly: The fabricated tube-mac piping components are then assembled according to the design specifications. This may involve connecting the pipes using various fittings, such as elbows, tees, and reducers.
- Installation: The assembled piping system is then installed in the designated location, typically using supports, hangers, or other structural elements. The installation process must be carried out carefully to avoid damage to the pipes or fittings.
- Pressure Testing: After installation, the tube-mac piping system is subjected to a pressure test to verify its integrity and leak-proofness. This test involves pressurizing the system with a specified pressure and monitoring for any leaks.
- Final Inspection: A final inspection is conducted to ensure that the installed system meets all design and regulatory requirements. This may involve visual inspection, dimensional checks, and leak detection tests.
Specialized Tools and Equipment
Fabrication and installation of tube-mac piping systems rely heavily on specialized tools and equipment. These tools and equipment play a critical role in ensuring the accuracy, efficiency, and safety of the processes. Some examples include:
- Cutting Tools: Specialized cutting tools, such as plasma cutters, band saws, and pipe shears, are used to cut the tube-mac pipes to the required lengths with precision.
- Welding Equipment: TIG and MIG welding machines, along with specialized welding consumables, are essential for creating strong and durable weld joints.
- Machining Equipment: Lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines are used for machining the tube-mac piping components to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
- Lifting Equipment: Cranes, hoists, and other lifting equipment are used to safely handle and position heavy tube-mac piping components during assembly and installation.
- Pressure Testing Equipment: Pressure testing equipment, such as pumps, gauges, and leak detectors, is essential for verifying the integrity and leak-proofness of the installed piping system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tube-Mac Piping
Tube-mac piping technologies offer several advantages over traditional piping methods, making them suitable for various applications. However, it’s essential to consider the potential drawbacks and limitations before choosing this method. This section will explore the key advantages and disadvantages of tube-mac piping, highlighting the trade-offs involved in its selection.
Advantages of Tube-Mac Piping
Tube-mac piping systems provide numerous advantages, making them a popular choice for various industries.
- Enhanced Strength and Durability: The seamless construction of tube-mac piping contributes to its exceptional strength and durability. The absence of welds eliminates potential weak points, making the system resistant to pressure fluctuations, temperature variations, and corrosive environments. This makes it ideal for demanding applications requiring high reliability and longevity.
- Reduced Weight and Space Requirements: Tube-mac piping systems are generally lighter than traditional welded piping systems, reducing overall weight and space requirements. This is particularly beneficial in applications where weight and space are critical considerations, such as in aerospace, marine, and transportation industries.
- Improved Flow Characteristics: The smooth interior surface of tube-mac piping minimizes friction loss, resulting in improved flow characteristics. This translates to higher flow rates, reduced energy consumption, and improved system efficiency. This is particularly advantageous in applications requiring high-volume fluid transport or where minimizing pressure drops is crucial.
- Reduced Maintenance and Repair Costs: The high quality and durability of tube-mac piping systems reduce the need for frequent maintenance and repairs. This translates to lower operating costs and increased system uptime. The absence of welds also eliminates the risk of weld failures, further contributing to reduced maintenance requirements.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Tube-mac piping systems offer flexibility in design and installation. The use of pre-fabricated components allows for easy customization and adaptation to specific project requirements. This is particularly beneficial in complex or challenging installations where traditional piping methods might be difficult or impractical.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial costs may be higher than traditional piping methods, the long-term benefits of tube-mac piping, such as reduced maintenance, increased efficiency, and extended service life, can lead to significant cost savings over the system’s lifespan. The reduced weight and space requirements can also lead to cost savings in transportation, installation, and supporting infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Tube-Mac Piping
Despite its numerous advantages, tube-mac piping also has some drawbacks that need to be considered before selecting it for a particular application.
- Higher Initial Costs: Tube-mac piping systems typically have higher initial costs compared to traditional welded piping systems. This is primarily due to the specialized manufacturing processes and materials used in their construction. The cost difference can be significant, especially for large-scale projects.
- Limited Size and Configuration Options: Tube-mac piping systems are typically limited in terms of size and configuration options compared to traditional welded piping systems. This can be a challenge in applications requiring large-diameter piping or complex configurations. The limited availability of standard components can also lead to longer lead times and increased costs.
- Potential for Leakage: While tube-mac piping is known for its high quality and durability, leakage can still occur if the system is not properly installed or maintained. Improper installation or damage to the piping can create weak points that can lead to leaks. This is particularly important in applications involving hazardous or corrosive fluids.
- Complexity of Installation: Installing tube-mac piping systems can be more complex than installing traditional welded piping systems, requiring specialized tools and techniques. This can increase installation costs and require more skilled labor. The need for precise alignment and fitting can also lead to delays in installation.
Maintenance and Repair of Tube-Mac Piping
Ensuring the longevity and reliable performance of tube-mac piping systems requires a proactive approach to maintenance and repair. Regular inspections, timely repairs, and adherence to industry best practices are crucial for minimizing downtime and maximizing the lifespan of these critical components.
Routine Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are essential for identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. A comprehensive maintenance program should include the following:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect the entire piping system for signs of corrosion, wear, leaks, misalignment, and other visible damage. Pay close attention to areas subject to high stress, vibration, or temperature fluctuations.
- Pressure Testing: Periodically test the system for leaks and pressure integrity. This involves pressurizing the system to a specified pressure and monitoring for any pressure drops or leaks. This helps identify weaknesses in the piping system.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Employ NDT methods like ultrasonic testing, radiographic inspection, and magnetic particle testing to detect internal flaws, cracks, and other hidden defects that may not be visible during visual inspections.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all inspections, maintenance activities, repairs, and any observed anomalies. This documentation provides valuable insights into the system’s history and facilitates informed decision-making regarding future maintenance and repair needs.
Common Issues and Problems, Tube-mac piping technologies
Tube-mac piping systems can encounter various issues over time, requiring timely attention to prevent catastrophic failures. Common problems include:
- Corrosion: The materials used in tube-mac piping can be susceptible to corrosion, particularly in environments with high humidity, salt content, or exposure to corrosive chemicals. This can lead to weakening of the pipe walls and potential leaks.
- Erosion: High-velocity fluids flowing through the pipes can cause erosion, particularly at bends, elbows, and other areas where the flow path changes abruptly. This can thin the pipe walls and lead to leaks or failures.
- Fatigue: Repeated stress cycles from pressure fluctuations, vibration, or thermal expansion can cause fatigue cracks in the piping. These cracks can propagate over time and eventually lead to pipe failure.
- Misalignment: Misaligned tube-mac connections can cause stress concentration, leading to premature failure. Improper installation or movement of the piping system can contribute to misalignment.
Repair and Replacement Procedures
Repairing or replacing damaged tube-mac piping components requires careful planning and execution to ensure the integrity of the system.
- Assessment: Thoroughly assess the extent of the damage and determine the most appropriate repair or replacement method. This may involve consulting with qualified engineers or specialists.
- Repair Methods: Common repair methods for tube-mac piping include welding, brazing, sleeving, and patching. The choice of method depends on the type of damage, the material of the pipe, and the operating conditions.
- Replacement: If the damage is extensive or the repair is not feasible, replacement of the damaged section is necessary. This involves cutting out the damaged portion and replacing it with a new section of pipe, ensuring proper alignment and connections.
- Post-Repair Inspection: After any repair or replacement, a thorough inspection is crucial to ensure the integrity of the system. This may involve visual inspection, pressure testing, and NDT methods to verify the effectiveness of the repair.
Industry Standards and Regulations
The design, fabrication, and installation of tube-mac piping systems are subject to strict industry standards and regulations, ensuring safety, reliability, and performance. These standards, developed by various organizations, provide a framework for the entire lifecycle of the piping system, from initial design to maintenance and repair.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in enforcing these standards and ensuring the safety and reliability of tube-mac piping systems. They conduct inspections, issue permits, and enforce regulations to ensure compliance. Some of the key regulatory bodies involved include:
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME): ASME sets standards for the design, fabrication, and inspection of pressure vessels, boilers, and piping systems, including tube-mac piping. Their codes, such as ASME B31.1 and ASME B31.3, provide comprehensive guidelines for the construction and operation of piping systems.
- American Petroleum Institute (API): API develops standards for the oil and gas industry, including specifications for materials, design, fabrication, and inspection of tube-mac piping used in refineries, pipelines, and offshore platforms. API 5L and API 5D are some of the relevant standards.
- National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors (NBBI): NBBI sets standards for the inspection, certification, and repair of pressure vessels and boilers, including tube-mac piping. Their codes ensure the safe operation of these systems.
Impact of Compliance on Performance
Compliance with industry standards is crucial for the overall performance of tube-mac piping systems. Adherence to these standards leads to:
- Enhanced Safety: Standards address potential hazards, such as pressure surges, corrosion, and fatigue, ensuring safe operation and minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Improved Reliability: Standards promote the use of high-quality materials and fabrication processes, leading to increased durability and reliability of the piping system.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Well-designed and properly installed tube-mac piping systems require less maintenance, reducing operational costs and downtime.
- Increased Longevity: Compliance with standards contributes to the longevity of the piping system, extending its service life and reducing the need for premature replacement.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of tube-mac piping technologies is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in materials science, fabrication techniques, and design concepts. These innovations are shaping the future of tube-mac piping, leading to enhanced performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The development of new materials, fabrication techniques, and design concepts is driving innovation in tube-mac piping technologies.
- Advanced Materials: The use of advanced materials such as high-strength alloys, composites, and ceramics is increasing in tube-mac piping. These materials offer improved strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance, extending the lifespan and reliability of piping systems.
- Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is revolutionizing tube-mac piping fabrication. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized designs, reducing waste and lead times.
- Smart Sensors and Monitoring: Integration of smart sensors and monitoring systems is enabling real-time condition monitoring of tube-mac piping systems. These sensors can detect leaks, corrosion, and other anomalies, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing catastrophic failures.
- Digital Twins: Digital twin technology is being used to create virtual representations of tube-mac piping systems. These digital twins allow for simulation and optimization of design, operation, and maintenance, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Impact of New Materials, Fabrication Techniques, and Design Concepts
The adoption of new materials, fabrication techniques, and design concepts is having a significant impact on the future of tube-mac piping.
- Enhanced Performance: Advanced materials and fabrication techniques are leading to increased strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, resulting in improved performance and reliability of tube-mac piping systems.
- Reduced Costs: Additive manufacturing and other innovative fabrication techniques are reducing waste and lead times, leading to lower production costs and faster deployment of tube-mac piping systems.
- Increased Sustainability: The use of sustainable materials and the reduction of waste through innovative fabrication techniques are promoting environmentally friendly practices in tube-mac piping.
- Improved Safety: Smart sensors and monitoring systems are enhancing safety by detecting potential issues early and allowing for timely interventions, reducing the risk of accidents and failures.
Key Areas of Research and Development
Research and development in tube-mac piping technologies are focused on addressing key challenges and opportunities.
- Development of High-Performance Materials: Research is ongoing to develop new materials with improved strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance for use in tube-mac piping systems.
- Advancements in Fabrication Techniques: Ongoing research is exploring the potential of additive manufacturing, robotics, and other advanced fabrication techniques for efficient and cost-effective production of tube-mac piping.
- Integration of Smart Sensors and Monitoring Systems: Research is focusing on the development and integration of advanced sensors and monitoring systems for real-time condition monitoring of tube-mac piping systems.
- Development of Digital Twin Technologies: Research is being conducted to enhance digital twin technologies for improved simulation, optimization, and maintenance of tube-mac piping systems.
Case Studies and Applications

Tube-mac piping has proven its effectiveness in various industries, addressing specific challenges and delivering significant benefits. This section explores real-world applications of tube-mac piping across different sectors, highlighting the solutions implemented and the positive outcomes achieved.
Applications Across Industries
The following table showcases successful tube-mac piping applications across various industries:
| Industry | Application | Challenges | Solutions | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Heat Exchangers in Power Plants | High temperatures, corrosive environments, and demanding operating conditions. | Tube-mac piping provides excellent heat transfer, corrosion resistance, and durability. | Increased efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and improved reliability. |
| Chemical Processing | Piping Systems for Chemical Plants | Handling corrosive and hazardous chemicals, pressure fluctuations, and temperature variations. | Tube-mac piping offers superior resistance to chemical attack, pressure containment, and temperature stability. | Enhanced safety, reduced downtime, and improved process control. |
| Oil and Gas | Pipelines for Oil and Gas Transportation | High pressures, extreme temperatures, and demanding environments. | Tube-mac piping provides excellent strength, durability, and leak-proof performance. | Reduced risk of leaks, improved safety, and increased efficiency. |
| Pharmaceutical | Piping Systems for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Sterile environments, stringent hygiene requirements, and precise fluid handling. | Tube-mac piping offers excellent cleanliness, corrosion resistance, and smooth surfaces for efficient fluid flow. | Enhanced product quality, reduced contamination risk, and improved process control. |
Case Study: Power Plant Heat Exchanger
One notable case study involves the use of tube-mac piping in a large power plant heat exchanger. The plant experienced frequent maintenance issues due to corrosion and leaks in the existing piping system. The solution involved replacing the existing piping with tube-mac piping, specifically designed for high-temperature and corrosive environments. The new piping system significantly reduced corrosion and leaks, leading to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower maintenance costs. The plant’s overall reliability increased, resulting in significant cost savings and improved operational performance.
Closing Summary: Tube-mac Piping Technologies
As tube-mac piping technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements in materials, fabrication techniques, and design concepts. The industry’s focus on sustainability and efficiency will drive innovation, leading to even more reliable and cost-effective solutions. By embracing the advancements in tube-mac piping technologies, we can ensure the seamless operation of critical infrastructure and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Tube-mac piping technologies are essential in various industries, especially those requiring high-performance and reliable fluid transfer systems. To optimize these systems, consider incorporating advanced network technology solutions like those offered by xihe network technology. By integrating network capabilities, you can monitor and control tube-mac piping systems in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and reducing downtime.