Technology Risk Manager: Safeguarding Digital Assets
Technology risk manager, a crucial role in today’s digital landscape, ensures the protection of an organization’s most valuable assets – its technology infrastructure and data. This role is not just […]

Technology risk manager, a crucial role in today’s digital landscape, ensures the protection of an organization’s most valuable assets – its technology infrastructure and data. This role is not just about mitigating potential threats but also about enabling innovation and growth while minimizing risk. A technology risk manager acts as a strategic advisor, identifying and evaluating potential threats, implementing robust security measures, and ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
By proactively assessing and managing technology risks, they play a vital role in maintaining operational efficiency, protecting sensitive information, and building trust with stakeholders. Their expertise spans a wide range of areas, including cybersecurity, data privacy, cloud computing, and emerging technologies. In essence, technology risk managers are the guardians of an organization’s digital future, safeguarding its operations and reputation in an increasingly interconnected and volatile world.
The Role of a Technology Risk Manager
In today’s digitally driven world, organizations rely heavily on technology to operate efficiently and achieve their goals. However, this reliance also introduces significant risks that can threaten their stability and success. This is where the technology risk manager plays a crucial role.
A technology risk manager is responsible for identifying, assessing, and mitigating technology-related risks that could impact an organization’s operations, reputation, and financial performance. They act as a bridge between the IT department and senior management, ensuring that technology decisions are aligned with overall business objectives and risk tolerance.
Key Responsibilities of a Technology Risk Manager
The responsibilities of a technology risk manager are multifaceted and encompass various aspects of technology risk management.
A technology risk manager must consider the entire ecosystem, from hardware to software, when assessing potential vulnerabilities. This includes evaluating the reliability of cooling systems, which are crucial for data centers and other critical infrastructure. American cooling technology is known for its innovation and efficiency, offering solutions that can help mitigate risks and ensure optimal performance.
A thorough understanding of these technologies is essential for any technology risk manager seeking to build a resilient and secure environment.
- Identify and assess technology risks: This involves understanding the organization’s technology landscape, identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, and evaluating the likelihood and impact of each risk.
- Develop and implement risk mitigation strategies: This includes designing and implementing controls, policies, and procedures to address identified risks and reduce their impact.
- Monitor and report on technology risk: This involves continuously tracking and evaluating the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies, reporting on risk status to senior management, and recommending improvements.
- Maintain and enhance technology risk management framework: This involves regularly reviewing and updating the organization’s technology risk management framework to ensure it remains relevant and effective in addressing emerging risks.
- Collaborate with other key functions: Technology risk managers work closely with IT security, compliance, legal, and other departments to ensure a holistic approach to risk management.
Aligning Technology Risk Management with Business Objectives
Technology risk management must be aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives to ensure that it is contributing to the achievement of strategic goals. This involves:
- Understanding the organization’s risk appetite: This refers to the level of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
- Prioritizing risks based on their impact on business objectives: This ensures that resources are allocated to address the risks that pose the greatest threat to the organization’s success.
- Integrating technology risk management into business processes: This ensures that technology risks are considered at all stages of decision-making, from planning and development to implementation and operation.
Relationship with Other Key Functions, Technology risk manager
Technology risk management is closely intertwined with other key functions within an organization, such as IT security, compliance, and legal.
- IT Security: Technology risk managers work closely with IT security professionals to ensure that appropriate security controls are in place to protect the organization’s data and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Compliance: Technology risk managers must ensure that the organization’s technology practices comply with relevant laws and regulations, such as data privacy laws and cybersecurity standards.
- Legal: Technology risk managers may work with legal counsel to assess the legal implications of technology risks and to develop strategies for mitigating legal liabilities.
Identifying and Assessing Technology Risks
Identifying and assessing technology risks is a crucial part of any organization’s risk management program. By understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities within their IT infrastructure, organizations can proactively mitigate risks and protect their valuable assets.
Common Technology Risks
Organizations face a wide range of technology risks that can disrupt operations, compromise data security, and damage their reputation.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data can result in financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
- Cyberattacks: Malicious actors can launch various attacks, including ransomware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks, to disrupt operations, steal data, or extort money.
- System Failures: Hardware or software failures can cause downtime, data loss, and operational disruptions.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Unpatched vulnerabilities in software or hardware can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Compliance Violations: Failing to comply with industry regulations and data privacy laws can lead to fines and penalties.
- Business Interruption: Disruptions to critical IT systems can significantly impact business operations and revenue.
- Data Loss: Accidental or intentional deletion of data can result in significant financial and operational losses.
- Cloud Security: Security risks associated with using cloud computing services, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and data loss.
- Emerging Technologies: Risks associated with adopting new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT), including security vulnerabilities, data privacy concerns, and ethical considerations.
Risk Assessment Methodologies
Various methodologies can be used to identify and assess technology risks. These methodologies help organizations understand the likelihood and impact of potential risks, enabling them to prioritize mitigation efforts.
Risk Assessments
A risk assessment is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks. It involves:
- Identifying Assets: Identifying critical IT assets, such as systems, data, applications, and networks.
- Identifying Threats: Identifying potential threats that could target these assets, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, and human errors.
- Analyzing Vulnerabilities: Assessing the weaknesses in systems and applications that could be exploited by threats.
- Determining Likelihood and Impact: Estimating the likelihood of each threat occurring and the potential impact on the organization.
- Prioritizing Risks: Ranking risks based on their likelihood and impact to determine which ones require immediate attention.
Vulnerability Scans
Vulnerability scans are automated tools that identify security weaknesses in systems and applications. They analyze systems for known vulnerabilities and provide detailed reports that highlight potential risks. These scans are crucial for identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Threat Modeling
Threat modeling is a structured approach to identifying and assessing security risks. It involves:
- Defining the System: Defining the system under analysis, including its components, data flows, and security controls.
- Identifying Threats: Identifying potential threats that could target the system, based on its functionality and design.
- Analyzing Vulnerabilities: Assessing the weaknesses in the system that could be exploited by threats.
- Developing Mitigation Strategies: Creating strategies to address identified vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of attacks.
Prioritizing Technology Risks
Organizations must prioritize technology risks based on their likelihood and impact. This prioritization helps them focus on the most critical risks and allocate resources effectively.
Risk Priority = Likelihood x Impact
For example, a risk with a high likelihood and high impact would be considered a high-priority risk, while a risk with a low likelihood and low impact would be considered a low-priority risk. Organizations can use various methods to assess likelihood and impact, including:
- Expert Opinions: Seeking input from security experts and subject matter experts.
- Historical Data: Analyzing past incidents and security breaches.
- Industry Benchmarks: Comparing risk levels to industry best practices and standards.
- Quantitative Analysis: Using statistical models and data to estimate likelihood and impact.
Developing and Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies

Once technology risks have been identified and assessed, the next crucial step is to develop and implement effective mitigation strategies. This involves creating a plan to reduce the likelihood and impact of these risks, ensuring the organization’s technological infrastructure and operations remain secure and resilient.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Effective risk mitigation strategies are tailored to the specific nature of the identified risks. These strategies aim to either reduce the probability of the risk occurring or minimize its potential impact. Here are some examples of effective risk mitigation strategies:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit significantly reduces the risk of data breaches. This involves using strong encryption algorithms and secure key management practices.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, before granting access to sensitive systems. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Patching and Updates: Regularly updating software and operating systems with security patches helps to address known vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of exploitation by malicious actors.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning: Having a comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity plan ensures that the organization can quickly recover from disruptions, such as natural disasters or cyberattacks, minimizing downtime and potential financial losses.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as strong password management, phishing awareness, and safe browsing habits, reduces the risk of human error and social engineering attacks.
Implementing Controls
To effectively implement risk mitigation strategies, organizations need to put in place appropriate controls. Controls are mechanisms that help to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks. These controls can be categorized into three main types:
- Preventive Controls: These controls aim to prevent risks from occurring in the first place. Examples include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control measures.
- Detective Controls: These controls focus on detecting risks that have already occurred. Examples include security monitoring tools, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention software.
- Corrective Controls: These controls help to recover from incidents that have already occurred. Examples include backup and recovery procedures, incident response plans, and data breach notification processes.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Risk mitigation strategies are not static. They need to be continuously monitored and evaluated to ensure their effectiveness. This involves:
- Regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments: As the technological landscape evolves, new risks emerge, and existing risks may change in nature or severity. Regular risk assessments ensure that the organization remains aware of the current risk profile.
- Monitoring control effectiveness: It’s crucial to monitor the effectiveness of implemented controls to identify any gaps or weaknesses. This can be done through periodic audits, security assessments, and vulnerability scans.
- Analyzing security incidents: Every security incident provides valuable learning opportunities. By analyzing incident reports, organizations can identify patterns, improve their risk mitigation strategies, and strengthen their defenses.
Emerging Technology Risks and Challenges
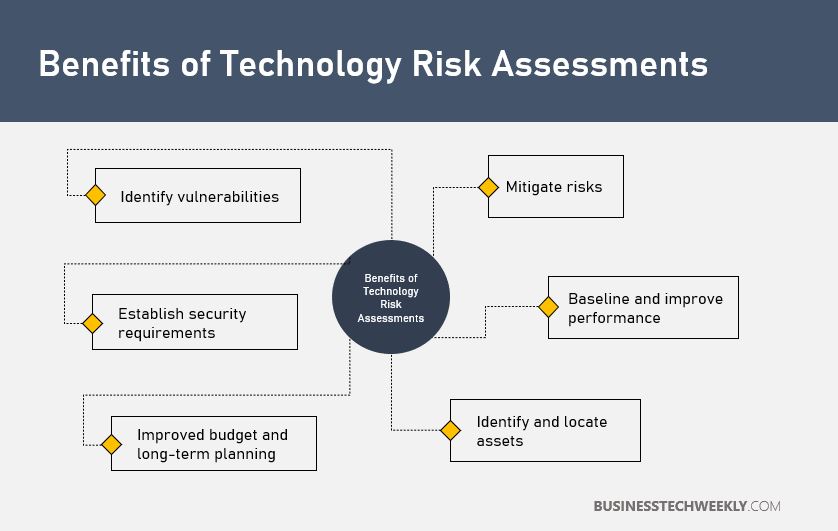
The rapid advancement of technology has ushered in a new era of innovation and opportunity, but it has also brought forth a complex landscape of emerging technology risks. This section will explore some of the most pressing risks associated with cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), and discuss the challenges of managing these risks in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Cloud Computing Risks
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. However, it also presents unique security and privacy risks that must be carefully addressed.
- Data breaches and security vulnerabilities: Cloud service providers are responsible for the security of their infrastructure, but organizations still need to implement strong security measures to protect their data. Cloud environments can be vulnerable to attacks such as denial-of-service attacks, malware infections, and unauthorized access.
- Data privacy and compliance: Organizations need to ensure that their cloud service providers comply with relevant data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). They also need to consider the implications of data sovereignty laws, which may restrict the transfer of data across borders.
- Vendor lock-in: Organizations may become dependent on a specific cloud provider, making it difficult to switch to another provider later. This can lead to higher costs and reduced flexibility.
Artificial Intelligence Risks
AI is rapidly transforming various industries, but it also raises concerns about potential risks, including:
- Algorithmic bias: AI algorithms can be biased if they are trained on data that reflects existing societal biases. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, such as unfair loan approvals or hiring decisions.
- Job displacement: AI is automating tasks previously performed by humans, potentially leading to job displacement in various sectors.
- Privacy concerns: AI systems collect and analyze vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
- Autonomous weapons systems: The development of autonomous weapons systems raises ethical concerns about the potential for unintended consequences and the loss of human control.
Internet of Things Risks
The IoT connects billions of devices to the internet, creating a vast network of interconnected systems. However, this interconnectedness also presents security and privacy risks:
- Security vulnerabilities: IoT devices are often designed with limited security features, making them vulnerable to attacks such as malware infections and unauthorized access.
- Data privacy: IoT devices collect and transmit large amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
- Interoperability issues: The lack of standardization in the IoT ecosystem can lead to interoperability issues, making it difficult for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other.
Challenges of Managing Technology Risks in a Rapidly Evolving Landscape
Managing technology risks in a rapidly evolving landscape presents unique challenges:
- Keeping up with emerging technologies: The pace of technological innovation is accelerating, making it difficult for organizations to keep up with emerging technologies and their associated risks.
- Developing and adapting risk management strategies: Risk management strategies need to be flexible and adaptable to accommodate the rapid evolution of technology.
- Building a skilled workforce: Organizations need to invest in training and development to ensure that their workforce has the skills and knowledge to manage emerging technology risks.
Best Practices for Staying Ahead of Emerging Technology Risks
To stay ahead of emerging technology risks, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
- Proactively monitor emerging technologies: Organizations should proactively monitor emerging technologies and their associated risks through research, industry events, and collaboration with experts.
- Develop a comprehensive risk management framework: A comprehensive risk management framework should identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with emerging technologies.
- Invest in cybersecurity: Organizations should invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their systems and data from attacks.
- Embrace a culture of security: A culture of security should be fostered throughout the organization, with employees trained on security best practices and encouraged to report any suspicious activity.
- Collaborate with industry partners: Organizations should collaborate with industry partners to share best practices and learn from each other’s experiences.
The Future of Technology Risk Management
The landscape of technology risk management is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing complexity of technology, the growing prevalence of cyberattacks, and the emergence of new technologies. To remain effective, technology risk managers must adapt to these changes and embrace new approaches to identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
The Role of Automation, Data Analytics, and Emerging Technologies
Automation, data analytics, and emerging technologies are transforming the way technology risk is managed.
- Automation: Automation tools can streamline repetitive tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and risk assessments, freeing up risk managers to focus on more strategic initiatives. These tools can also improve the accuracy and efficiency of risk management processes. For example, automated threat intelligence feeds can provide real-time updates on emerging threats, enabling risk managers to proactively address potential vulnerabilities.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics can be used to identify patterns and trends in risk data, enabling risk managers to make more informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies. By analyzing historical data on cyberattacks, data breaches, and other security incidents, risk managers can identify common attack vectors and develop strategies to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. For example, analyzing data on past phishing attacks can help organizations identify common phishing techniques and develop training programs to educate employees on how to identify and avoid phishing attempts.
- Emerging Technologies: Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing are presenting new challenges and opportunities for technology risk management. AI-powered security tools can help organizations detect and respond to threats more effectively, while blockchain technology can improve the security of data storage and transactions. Quantum computing, on the other hand, poses a significant threat to traditional encryption methods, requiring organizations to develop new security strategies to protect sensitive data.
The Impact of Increasing Cyberattacks and Data Breaches
The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks and data breaches are forcing organizations to re-evaluate their technology risk management strategies.
- Proactive Risk Management: Organizations are moving away from reactive approaches to risk management and embracing proactive strategies that focus on identifying and mitigating risks before they can cause harm. This includes implementing strong security controls, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and developing incident response plans. For example, organizations are investing in advanced security technologies such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to detect and prevent cyberattacks.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data security and privacy are becoming increasingly important as organizations collect and store more data. Organizations must implement strong data protection measures to comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). This includes implementing data encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions.
- Building Resilience: Organizations must build resilience into their systems and processes to withstand cyberattacks and data breaches. This includes developing business continuity and disaster recovery plans to ensure that critical business functions can continue to operate in the event of an attack. For example, organizations are implementing cloud-based solutions to ensure that data is accessible even if their on-premises systems are compromised.
Evolving Skills and Qualifications for Technology Risk Management
The future of technology risk management requires professionals with a broad range of skills and qualifications.
- Technical Skills: Technology risk managers must have a strong understanding of technology and security concepts, including networking, operating systems, databases, and cybersecurity. They must also be familiar with industry best practices and standards, such as ISO 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- Business Acumen: Technology risk managers must understand the business context in which they operate and be able to communicate effectively with stakeholders at all levels. They must also be able to translate technical concepts into business language and explain the impact of technology risks on the organization’s operations.
- Analytical Skills: Technology risk managers must be able to analyze data, identify trends, and make informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies. They must also be able to develop and implement risk management frameworks and processes.
- Communication Skills: Technology risk managers must be able to communicate effectively with both technical and non-technical audiences. They must be able to explain complex concepts in a clear and concise manner and build consensus among stakeholders. They must also be able to effectively present risk assessments and mitigation strategies to senior management.
Final Wrap-Up
The role of a technology risk manager is critical in today’s digital world, where organizations face an ever-growing range of threats. By understanding and mitigating these risks, they ensure the stability, security, and continued success of their organizations. Their ability to adapt to evolving technologies and security landscapes is crucial for navigating the complex and dynamic world of digital risk management. As organizations increasingly rely on technology, the role of a technology risk manager will become even more critical, ensuring that they can thrive in a digital world while minimizing the potential for disruption and damage.