Technology Private Equity Firms: Driving Innovation and Growth
Technology private equity firms play a crucial role in shaping the future of innovation and growth. They invest in promising technology companies, providing them with the capital and expertise needed […]

Technology private equity firms play a crucial role in shaping the future of innovation and growth. They invest in promising technology companies, providing them with the capital and expertise needed to scale their operations and disrupt industries. The technology sector has witnessed unprecedented growth in recent years, attracting significant private equity interest due to its high potential for returns and transformative impact on society.
These firms focus on various segments within the technology landscape, including software, hardware, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. Their investment strategies vary depending on their specific focus and risk appetite. Some firms prefer early-stage investments, while others focus on established companies with proven track records. The key is to identify companies with strong management teams, innovative products, and a clear path to profitability.
Introduction to Technology Private Equity
Technology private equity is a specialized area of private equity investing that focuses on acquiring and growing companies operating in the technology sector. It differs from traditional private equity by emphasizing the rapid pace of innovation, disruptive technologies, and the potential for significant growth in the technology industry.
Technology private equity firms invest in a wide range of technology companies, from early-stage startups to established businesses, across various sectors, including software, hardware, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. These firms often bring expertise in technology, operations, and finance to help their portfolio companies scale their businesses, expand into new markets, and achieve their growth objectives.
Growth of the Technology Sector and its Impact on Private Equity
The technology sector has experienced exponential growth in recent decades, driven by factors such as technological advancements, increasing internet penetration, and the rise of mobile devices. This growth has attracted significant investment from private equity firms, which see the technology sector as a lucrative opportunity to generate high returns.
The impact of the technology sector on private equity is significant:
* Increased Investment: The growth of the technology sector has led to a surge in private equity investment in technology companies.
* New Investment Strategies: Technology private equity firms have developed specialized investment strategies to capitalize on the unique characteristics of the technology sector.
* High Returns: Technology private equity investments have historically generated high returns, attracting investors seeking growth and diversification.
* Disruption of Traditional Industries: Technology companies are disrupting traditional industries, creating new opportunities for private equity investment.
Examples of Successful Technology Private Equity Investments
There have been numerous successful technology private equity investments over the years. Here are a few notable examples:
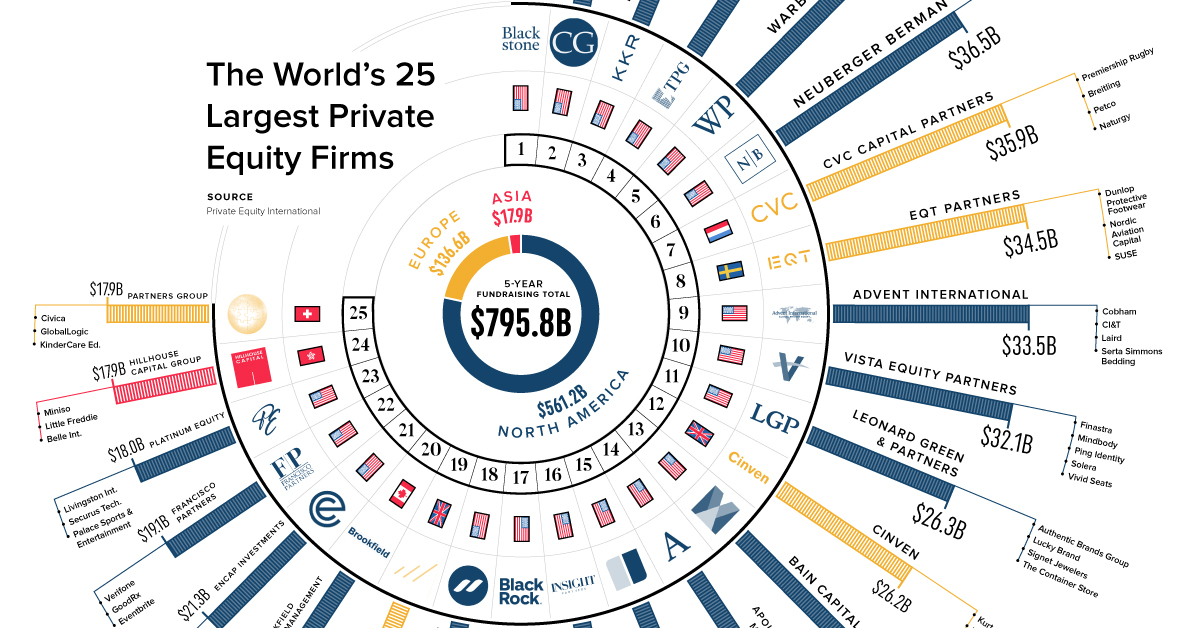
* Vista Equity Partners’ investment in Ping Identity: Vista Equity Partners acquired Ping Identity in 2016 and helped the company expand its product offerings and grow its customer base. Ping Identity went public in 2017 and has since become a leading identity and access management provider.
* Silver Lake’s investment in Dell: Silver Lake partnered with Michael Dell to take Dell private in 2013. The transaction was the largest leveraged buyout in history at the time. Dell went public again in 2018, and Silver Lake has generated significant returns on its investment.
* KKR’s investment in Cloudera: KKR invested in Cloudera in 2014 and helped the company grow its business and expand into new markets. Cloudera went public in 2017 and has since become a leading provider of data management and analytics solutions.
These examples illustrate the potential for high returns in technology private equity investments. However, it’s important to note that technology private equity investing is not without risk. The rapid pace of innovation and competition in the technology sector can make it challenging to identify and invest in companies that will succeed.
Key Players in the Technology Private Equity Landscape
The technology private equity landscape is dominated by a handful of leading firms that have consistently demonstrated expertise in identifying and nurturing high-growth technology companies. These firms are characterized by their deep industry knowledge, extensive networks, and sophisticated investment strategies.
Leading Technology Private Equity Firms
The following firms are widely recognized as leaders in the technology private equity space:
- Vista Equity Partners: Vista Equity Partners is a leading private equity firm specializing in software, data, and technology-enabled businesses. With a focus on enterprise software, financial technology, and healthcare technology, Vista Equity Partners has a proven track record of driving value creation through operational improvements and strategic acquisitions.
- Silver Lake: Silver Lake is a global private equity firm with a strong focus on technology, with significant investments in software, semiconductors, and consumer technology. The firm has a history of successful investments in companies like Dell, GoDaddy, and Alibaba.
- KKR: KKR is a global investment firm with a broad portfolio across multiple industries, including technology. KKR has a strong track record of investing in and building technology companies, with notable investments in companies like Cloudera, Pinterest, and Global Payments.
- Permira: Permira is a European private equity firm with a global reach, known for its expertise in technology investments. The firm has a history of successful investments in companies like Ancestry.com, Avaloq, and TeamViewer.
- TPG Capital: TPG Capital is a global private equity firm with a diversified portfolio, including significant investments in technology. The firm has a history of successful investments in companies like Uber, Airbnb, and Spotify.
Investment Strategies and Focus Areas
Technology private equity firms employ a range of investment strategies, tailored to the specific characteristics of the technology sector. These strategies often involve:
- Growth Equity: Investing in companies with high growth potential, often in later stages of development. These firms provide capital to support expansion, acquisitions, and product development.
- Buyout: Acquiring controlling stakes in mature companies, often with the aim of improving operations, restructuring debt, or preparing for a sale. Buyout firms typically seek to unlock value through operational improvements and strategic acquisitions.
- Venture Capital: Investing in early-stage technology companies with high growth potential. Venture capital firms provide capital to support product development, market entry, and team building.
The focus areas of these firms vary, but common themes include:
- Software: Software companies, including enterprise software, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, are a significant focus for many technology private equity firms. These firms often invest in companies with strong recurring revenue streams and a proven track record of innovation.
- E-commerce: The rapid growth of e-commerce has attracted significant investment from technology private equity firms. These firms invest in companies that are disrupting traditional retail models and leveraging technology to enhance customer experiences.
- FinTech: Financial technology companies, including payments, lending, and wealth management, are another major focus for technology private equity firms. These firms invest in companies that are using technology to innovate and improve financial services.
- Healthcare Technology: Healthcare technology companies, including telemedicine, digital health, and medical devices, are increasingly attracting investment from technology private equity firms. These firms invest in companies that are leveraging technology to improve healthcare outcomes and reduce costs.
Comparison of Investment Approaches
Technology private equity firms often differ in their investment approaches, reflecting their unique expertise and investment philosophies.
- Vista Equity Partners is known for its focus on enterprise software and its operational expertise. The firm takes a long-term approach to investing and is known for its ability to improve the operations of its portfolio companies.
- Silver Lake has a broader investment focus, including software, semiconductors, and consumer technology. The firm is known for its strong network and its ability to identify emerging trends in the technology sector.
- KKR has a diversified portfolio across multiple industries, including technology. The firm is known for its disciplined investment process and its ability to navigate complex transactions.
- Permira is a European firm with a global reach, known for its expertise in technology investments. The firm has a strong track record of investing in companies with a global footprint.
- TPG Capital has a diversified portfolio, including significant investments in technology. The firm is known for its ability to identify and invest in high-growth companies in emerging markets.
Investment Opportunities in Technology
The technology sector is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape, presenting both significant opportunities and challenges for investors. Technology private equity firms are actively seeking to capitalize on the growth potential of innovative companies across various sub-sectors.
Software
Software continues to be a dominant force in the technology sector, with significant growth driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Private equity firms are investing in a wide range of software companies, including:
- Enterprise software: Companies developing software solutions for businesses, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and data analytics.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Companies providing software applications delivered over the internet, such as cloud storage, collaboration tools, and online productivity suites.
- FinTech (Financial Technology): Companies using technology to disrupt traditional financial services, such as online payments, digital lending, and investment platforms.
- Cybersecurity: Companies developing software and services to protect businesses and individuals from cyber threats.
Hardware, Technology private equity firms
While software has dominated recent technology growth, hardware still plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Private equity firms are investing in companies developing innovative hardware products, including:
- Semiconductors: Companies designing and manufacturing semiconductors, which are essential components for computing devices, smartphones, and other electronic devices.
- Networking equipment: Companies developing networking infrastructure, such as routers, switches, and wireless access points.
- Consumer electronics: Companies developing and manufacturing consumer electronics devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices.
- Robotics and automation: Companies developing robots and automation systems for various industries, including manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a rapidly growing market, with companies increasingly relying on cloud services for storage, computing power, and software applications. Private equity firms are investing in cloud computing companies, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Companies providing cloud infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Companies providing platforms for developing and deploying applications in the cloud.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Companies providing software applications delivered over the internet, as discussed earlier.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various industries, from healthcare to finance. Private equity firms are investing in AI companies, including:
- Machine learning: Companies developing algorithms for analyzing large datasets and making predictions.
- Computer vision: Companies developing systems for interpreting images and videos.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Companies developing systems for understanding and generating human language.
- Robotics and automation: Companies developing robots and automation systems powered by AI.
Challenges and Risks
Investing in technology presents several challenges and risks, including:
- Rapid technological change: The technology sector is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging and existing ones becoming obsolete quickly. This can make it difficult to identify companies with sustainable competitive advantages.
- Competition: The technology sector is highly competitive, with many startups and established players vying for market share. This can make it difficult for companies to achieve profitability and scale.
- Valuation: Valuing technology companies can be challenging, as their revenue streams and growth prospects can be difficult to predict.
- Regulatory uncertainty: The technology sector is subject to increasing regulatory scrutiny, which can create uncertainty for investors.
Deal Structure and Investment Process: Technology Private Equity Firms
Technology private equity investments follow a structured process, starting with identifying potential opportunities and culminating in a successful exit. This process involves several key stages, including deal sourcing, due diligence, valuation, negotiation, and closing.
Deal Sourcing and Initial Screening
Technology private equity firms actively seek out investment opportunities in promising technology companies. They use various methods to identify potential targets, including:
- Networking with industry professionals and entrepreneurs
- Monitoring industry trends and emerging technologies
- Utilizing online databases and research platforms
- Engaging with investment bankers and advisors
Once a potential target is identified, the firm conducts initial screening to assess the company’s viability and potential for growth.
Due Diligence
Due diligence is a critical step in the investment process, where the firm thoroughly examines the target company’s financials, operations, management team, and market position.
- Financial Due Diligence: This involves reviewing the company’s financial statements, including revenue, profitability, cash flow, and debt levels. It also includes analyzing the company’s financial controls and accounting practices.
- Operational Due Diligence: This focuses on understanding the company’s business model, operations, technology, and customer base. It also includes assessing the company’s competitive landscape and its ability to scale.
- Legal Due Diligence: This involves reviewing the company’s legal documents, including contracts, licenses, and intellectual property rights. It also includes assessing the company’s regulatory compliance and potential legal risks.
- Management Due Diligence: This focuses on evaluating the company’s management team, including their experience, expertise, and leadership skills. It also includes assessing the team’s ability to execute the company’s growth strategy.
This process helps the firm identify potential risks and opportunities associated with the investment.
Valuation and Financial Modeling
Valuation is a crucial aspect of technology private equity investments. It involves determining the fair market value of the target company.
- Comparable Company Analysis: This method involves comparing the target company to similar publicly traded companies in the same industry. This provides a benchmark for the target company’s valuation.
- Precedent Transaction Analysis: This method involves analyzing recent transactions of similar companies to determine the typical valuation multiples used in the industry. This provides a range of potential valuations for the target company.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis: This method involves projecting the target company’s future cash flows and discounting them back to present value using a discount rate. This provides a more intrinsic valuation based on the company’s expected future performance.
Financial modeling plays a key role in valuation, allowing the firm to project the company’s future financial performance and assess the potential return on investment.
Negotiation and Closing
Once the firm has completed its due diligence and valuation, it enters into negotiations with the target company’s management and shareholders. This process involves determining the terms of the investment, including the purchase price, ownership structure, and management rights. Once the terms are agreed upon, the firm closes the transaction, which involves legal documentation, funding, and transfer of ownership.
Exit Strategies and Performance
Technology private equity firms invest in companies with the goal of generating returns for their investors. The success of these investments is ultimately measured by the ability to exit the investment at a profit. Exit strategies are the methods used to realize the value of the investment and return capital to investors.
Exit Strategies
The most common exit strategies for technology private equity investments include:
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): This involves listing the company’s shares on a public stock exchange, allowing investors to sell their shares to the public. This is often considered the most lucrative exit strategy, but it is also the most challenging, as it requires the company to meet specific regulatory requirements and investor expectations.
- Sale to a Strategic Buyer: This involves selling the company to another company that operates in the same or a related industry. This can be a good option for companies that have reached a certain size and maturity, as it allows them to gain access to new markets, resources, and expertise.
- Sale to a Financial Buyer: This involves selling the company to a private equity firm or other financial institution. This is often a less risky option than an IPO, as it does not require the company to meet the same level of public scrutiny. However, it may also result in a lower valuation.
- Management Buyout (MBO): This involves selling the company to its existing management team. This can be a good option for companies that have a strong management team and a clear vision for the future.
- Secondary Sale: This involves selling the investment to another private equity firm or institutional investor. This can be a good option for investors who need to exit their investment quickly or who want to diversify their portfolio.
Factors Influencing Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of technology private equity investments, including:
- Market Conditions: The overall economic climate and the specific sector in which the company operates can significantly impact performance. For example, during a period of economic growth, technology companies tend to perform well, while during a recession, they may struggle.
- Company Management: The quality of the company’s management team is crucial to its success. A strong management team can effectively execute the company’s strategy, manage risks, and navigate challenging market conditions.
- Competitive Landscape: The level of competition in the company’s industry can impact its ability to grow and generate profits. A highly competitive market can make it difficult for companies to gain market share and achieve profitability.
- Technology Innovation: The pace of technological innovation is rapid in the technology sector. Companies that fail to keep up with the latest trends and technologies may struggle to compete.
- Valuation: The initial valuation of the company can have a significant impact on the return on investment. A high valuation can make it more difficult to achieve a profitable exit.
Successful Exits
There have been numerous successful exits in the technology private equity sector, resulting in significant returns for investors. For example:
- The sale of Instagram to Facebook in 2012 for $1 billion: This acquisition allowed Facebook to expand its social media presence and enter the mobile photo-sharing market. It also generated a significant return for investors in Instagram, who had invested in the company just two years earlier.
- The IPO of Spotify in 2018: Spotify’s IPO was a major success, raising $1.6 billion and valuing the company at $26.5 billion. This exit provided a significant return for investors who had backed the company during its early stages.
- The sale of WhatsApp to Facebook in 2014 for $19 billion: This acquisition gave Facebook a dominant position in the mobile messaging market. It also provided a significant return for investors in WhatsApp, who had invested in the company just four years earlier.
Impact of Technology Private Equity on the Ecosystem

Technology private equity firms play a pivotal role in shaping the technological landscape by providing capital and expertise to innovative companies, driving growth and fostering innovation. Their influence extends beyond financial investments, impacting the competitive landscape, and raising ethical considerations within the broader technology ecosystem.
Impact on Innovation and Growth
Technology private equity firms contribute significantly to innovation and growth within the technology sector. They act as catalysts for the development and scaling of disruptive technologies, enabling companies to reach new heights and contribute to broader economic progress.
- Capital Infusion: By providing substantial capital, technology private equity firms empower companies to invest in research and development, expand their operations, and bring innovative products and services to market. This financial support allows companies to overcome initial hurdles and accelerate their growth trajectory.
- Strategic Guidance: Technology private equity firms offer more than just capital; they provide strategic guidance and operational expertise. Their experienced professionals offer insights into market trends, competitive dynamics, and best practices, helping companies navigate the complex world of technology and achieve their full potential.
- Network Access: Technology private equity firms possess extensive networks within the technology industry, connecting portfolio companies with potential partners, customers, and talent. This access to a broader ecosystem facilitates growth and collaboration, fostering a more dynamic and interconnected technology landscape.
Impact on the Competitive Landscape
The involvement of technology private equity firms significantly influences the competitive landscape within the technology sector. Their investments can reshape market dynamics, leading to consolidation, increased competition, and the emergence of new players.
- Consolidation: Technology private equity firms often invest in companies with the goal of consolidating market share. They may acquire multiple players within a specific niche or industry, creating larger, more powerful entities that can better compete in the market. This consolidation can lead to increased efficiency, economies of scale, and a more concentrated competitive landscape.
- Accelerated Growth: By providing capital and expertise, technology private equity firms accelerate the growth of their portfolio companies, enabling them to compete more effectively with established players. This increased competition can drive innovation and force incumbents to adapt to new market realities.
- New Entrants: Technology private equity firms also play a role in fostering the emergence of new players in the technology landscape. They invest in startups and early-stage companies with disruptive potential, providing them with the resources to challenge existing industry leaders and create new market opportunities.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Implications
While technology private equity firms contribute to innovation and growth, their investments also raise ethical considerations and societal implications. These concerns revolve around the potential impact on employment, data privacy, and the concentration of power within the technology sector.
- Job Displacement: The rapid growth and consolidation fueled by technology private equity investments can lead to job displacement in certain sectors. As companies automate processes and streamline operations, some jobs may become obsolete, raising concerns about the impact on workers and the need for reskilling initiatives.
- Data Privacy: Technology companies often collect and utilize vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and security. The role of technology private equity firms in shaping the data landscape requires careful consideration of data protection regulations and ethical practices.
- Concentration of Power: Technology private equity firms play a role in the concentration of power within the technology sector. Their investments can create dominant players with significant market influence, potentially leading to concerns about anti-competitive practices and the need for regulatory oversight.
Future Trends in Technology Private Equity
The technology private equity landscape is constantly evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology and changing investor preferences. Understanding the future trends in this dynamic sector is crucial for both investors and entrepreneurs. This section will explore the key trends shaping the future of technology private equity, including the impact of emerging technologies and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Private Equity Investments
Emerging technologies are fundamentally transforming the technology landscape and creating new investment opportunities for private equity firms. The adoption of these technologies will significantly impact deal flow, valuation, and exit strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is rapidly transforming various industries, from healthcare to finance, creating new business models and driving efficiency gains. Private equity firms are actively investing in AI companies, seeking to capitalize on the transformative potential of this technology. For example, the investment in AI-powered medical imaging company, [Insert Name of Company], demonstrates the growing interest in this sector.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize industries by creating secure and transparent systems for transactions and data management. Private equity firms are exploring investment opportunities in blockchain-based solutions, particularly in areas like supply chain management, financial services, and identity verification. [Insert Name of Company], a leading blockchain solutions provider, recently received significant funding from a private equity firm.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing has become ubiquitous, enabling businesses to access computing resources on demand. Private equity firms are actively investing in cloud-based solutions, including software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies, infrastructure providers, and data analytics platforms. [Insert Name of Company], a cloud-based data analytics platform, is a prime example of a successful investment in this sector.
- Cybersecurity: As the threat landscape evolves, the demand for cybersecurity solutions is growing rapidly. Private equity firms are investing in companies that offer advanced cybersecurity solutions, including threat intelligence, data breach prevention, and incident response services. [Insert Name of Company], a leading cybersecurity firm, received significant funding from a private equity consortium.
Challenges and Opportunities
The technology private equity sector faces a unique set of challenges and opportunities as it navigates the evolving technological landscape.
- Valuation Challenges: Valuing technology companies can be challenging due to the rapid pace of innovation and the lack of historical data. Private equity firms must develop sophisticated valuation models that account for future growth potential and the impact of emerging technologies.
- Competition: The technology private equity sector is becoming increasingly competitive, with more firms vying for the same investment opportunities. Private equity firms must differentiate themselves by developing a deep understanding of the technology landscape and building strong relationships with entrepreneurs and investors.
- Regulatory Environment: The regulatory environment for technology companies is evolving rapidly, particularly in areas such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and antitrust. Private equity firms must navigate these regulatory complexities and ensure that their portfolio companies are compliant.
- Talent Acquisition: Attracting and retaining top talent is crucial for success in the technology sector. Private equity firms must offer competitive compensation packages and create a culture that fosters innovation and growth.
Last Recap
Technology private equity firms are at the forefront of innovation, driving growth and transforming industries. Their investments not only generate significant financial returns but also contribute to the development of groundbreaking technologies that shape our future. As the technology sector continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the role of private equity firms will become even more critical in supporting and nurturing the next generation of disruptive companies.
Technology private equity firms are constantly seeking innovative companies that can disrupt industries and generate significant returns. One such company that has caught their attention is Risk Control Technologies Inc , a leading provider of risk management solutions. Their expertise in identifying and mitigating potential risks makes them an attractive investment for firms looking to capitalize on the growing demand for robust security measures in today’s interconnected world.