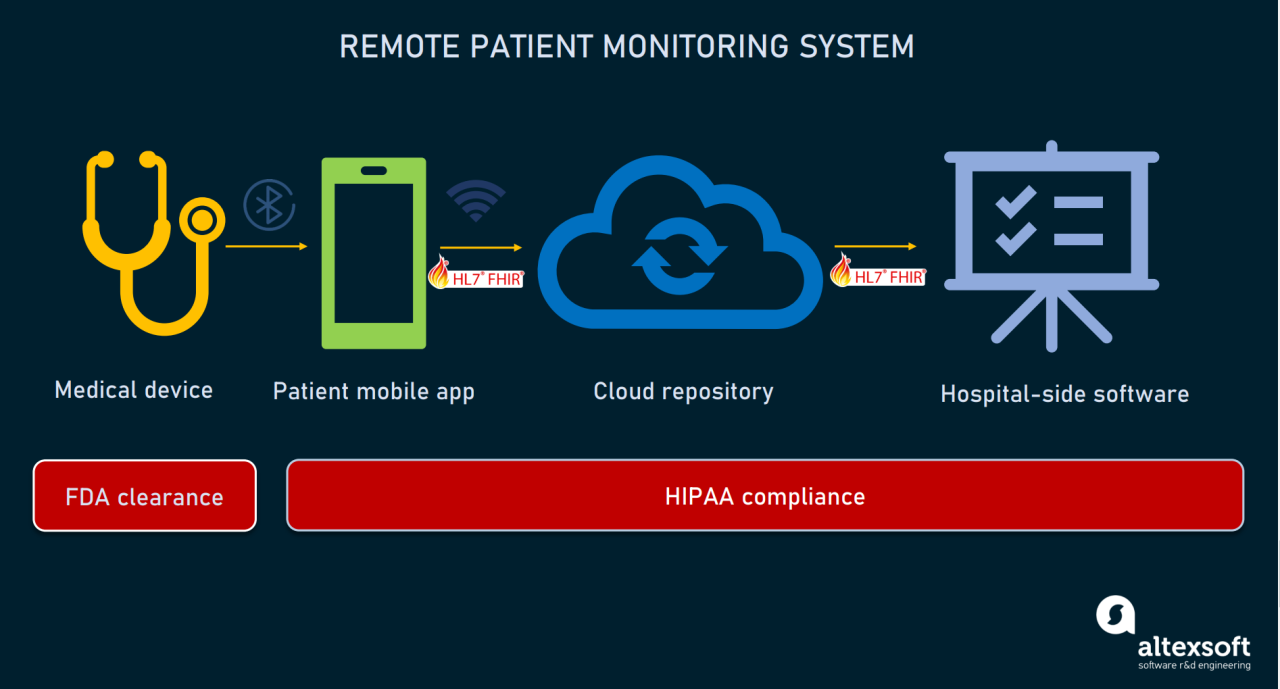
Technolog Services: Transforming Businesses
Technolog services are no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s digital age. They have revolutionized how businesses operate, interact with customers, and innovate. From software development and cloud […]

Technolog services are no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s digital age. They have revolutionized how businesses operate, interact with customers, and innovate. From software development and cloud computing to cybersecurity and data analytics, these services empower organizations to achieve greater efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth.
This exploration delves into the evolution of technolog services, highlighting key milestones and advancements. We’ll explore the various types of services available, their benefits, and how to choose the right ones for your specific needs. Finally, we’ll discuss the future of technolog services, including emerging trends and their potential impact on the industry.
The Evolution of Technology Services
Technology services have undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from rudimentary systems to sophisticated, cloud-based solutions that shape our modern world. This journey has been marked by key milestones and advancements, shaping the landscape of how businesses operate and individuals interact with technology.
The Rise of Traditional IT
The early days of technology services were characterized by on-premise infrastructure and dedicated IT departments. Businesses relied heavily on physical servers, storage devices, and software installed within their own facilities. This traditional model provided a sense of control and security, but it also came with significant challenges:
- High upfront costs: Acquiring and maintaining hardware and software required substantial investments.
- Limited scalability: Expanding capacity required additional hardware purchases and physical space.
- Complex management: Managing and maintaining on-premise systems demanded specialized expertise and resources.
The Cloud Revolution
The advent of cloud computing ushered in a paradigm shift in technology services. Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offered a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to access computing resources, storage, and software over the internet. This shift brought about significant advantages:
- Reduced costs: Cloud services eliminated the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
- Enhanced scalability: Businesses could easily scale their resources up or down based on demand.
- Increased flexibility: Cloud services provided access to a wide range of tools and applications, fostering innovation and agility.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain are further transforming the technology services industry. AI is being used to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. Blockchain, with its decentralized and secure nature, is enabling new business models and revolutionizing data management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly changing how technology services are delivered and consumed. AI-powered solutions are used in various areas, including:
- Automation: AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up IT professionals for more strategic work.
- Predictive maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze data from IT systems to predict potential issues and proactively prevent downtime.
- Cybersecurity: AI-powered security solutions can detect and respond to threats in real-time.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing data security and transparency. Its decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority, making it inherently secure and tamper-proof. Blockchain is being used in technology services for:
- Secure data storage: Blockchain can provide a tamper-proof ledger for storing sensitive data.
- Identity management: Blockchain can be used to verify user identities and streamline access control.
- Supply chain management: Blockchain can track products and materials throughout their journey, improving transparency and accountability.
Types of Technology Services
Technology services are a broad spectrum of offerings that leverage digital tools and expertise to solve business challenges and drive innovation. They encompass various disciplines, each focusing on a specific aspect of technology and its applications. Understanding the different types of technology services is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their operations, enhance their competitive edge, and achieve their strategic goals.
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing, coding, testing, and deploying software applications. It involves creating custom solutions tailored to specific business needs or adapting existing software packages to meet unique requirements. Software development services can range from building simple mobile apps to complex enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Software development encompasses a wide range of offerings, including:
- Custom Software Development: Creating bespoke applications from scratch to meet specific business needs. Examples include e-commerce platforms, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
- Software Integration: Connecting different software systems to create a seamless workflow. This involves integrating existing applications, such as CRM with accounting software, or integrating third-party APIs to enhance functionality.
- Software Maintenance and Support: Providing ongoing support for existing software applications, including bug fixes, security updates, and performance optimization. This ensures smooth operation and minimizes downtime.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet. This eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own physical infrastructure, enabling them to scale their resources up or down as needed.
Cloud computing services can be categorized into three main types:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides access to fundamental computing resources, such as virtual servers, storage, and networking. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the need for infrastructure management. Examples include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, allowing users to access and use them from any device with an internet connection. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Dropbox.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity services protect organizations from cyber threats, such as data breaches, malware attacks, and denial-of-service attacks. These services encompass a wide range of activities, including:
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing: Identifying and assessing security vulnerabilities in systems and networks, simulating real-world attacks to uncover weaknesses and improve security posture.
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response: Continuously monitoring systems and networks for suspicious activity, detecting and responding to security incidents in a timely and effective manner.
- Data Security and Privacy: Implementing measures to protect sensitive data, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations, and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Data Analytics
Data analytics services help businesses extract insights from their data to make informed decisions and improve their operations. This involves collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and visualizing data to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
Data analytics services can be applied to various areas, including:
- Business Intelligence: Analyzing business data to understand customer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscape, providing insights for strategic decision-making.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data to forecast future outcomes, such as sales projections, customer churn rates, and potential risks.
- Data Visualization: Presenting data in an easy-to-understand format, using charts, graphs, and dashboards to communicate insights effectively.
IT Consulting
IT consulting services provide expert advice and guidance on technology-related matters, helping businesses to plan, implement, and manage their IT infrastructure and systems. IT consultants offer a range of services, including:
- IT Strategy and Planning: Developing a comprehensive IT strategy aligned with business goals, defining technology roadmaps, and prioritizing IT investments.
- IT Infrastructure Management: Managing and optimizing IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, networks, and security systems, ensuring efficient operation and cost-effectiveness.
- Technology Implementation and Integration: Assisting businesses in implementing new technologies, integrating systems, and ensuring seamless transition to new platforms.
| Technology Service | Key Features | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Software Development | Custom software creation, integration, maintenance, and support. | Businesses of all sizes seeking tailored software solutions. |
| Cloud Computing | On-demand access to computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, and software. | Businesses seeking flexible and scalable IT infrastructure. |
| Cybersecurity | Vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, security monitoring, incident response, and data protection. | Organizations of all sizes seeking to protect their data and systems from cyber threats. |
| Data Analytics | Data collection, cleaning, analysis, and visualization to extract insights and make informed decisions. | Businesses seeking to improve their operations, understand customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions. |
| IT Consulting | Expert advice and guidance on technology-related matters, including strategy, planning, infrastructure management, and implementation. | Businesses seeking to optimize their IT operations, implement new technologies, and achieve their strategic goals. |
Benefits of Technology Services
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations of all sizes are increasingly relying on technology services to gain a competitive edge, enhance efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction. Technology services encompass a wide range of solutions, from cloud computing and cybersecurity to data analytics and software development, all designed to empower businesses to operate more effectively and achieve their strategic goals.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Technology services play a crucial role in streamlining business processes, automating tasks, and optimizing resource allocation. By leveraging technology, organizations can eliminate manual processes, reduce errors, and increase productivity across departments.
For instance, implementing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can automate financial management, supply chain operations, and human resource functions, leading to significant time and cost savings.
Choosing the Right Technology Services

Selecting the appropriate technology services is crucial for any organization, as it directly impacts efficiency, productivity, and overall success. A strategic approach that considers various factors is essential for making informed decisions.
Evaluating Business Needs
Understanding the specific needs of your organization is the first step in choosing the right technology services. This involves a thorough analysis of current operations, identifying pain points, and defining desired outcomes. For example, a business seeking to enhance customer engagement might prioritize services that improve online communication and data analytics.
Assessing Budget Constraints
Budget limitations play a significant role in technology service selection. Organizations must determine the financial resources available for technology investments, considering factors like initial costs, ongoing maintenance, and potential upgrades. It’s important to balance desired features with realistic financial constraints.
Determining Scalability Requirements
Scalability refers to the ability of technology services to adapt to changing business demands. Organizations should consider future growth projections and ensure that chosen services can accommodate increased workloads or user volume. For example, a startup with rapid growth plans would need services that can scale easily to handle expanding operations.
Comparing Service Providers
Evaluating different service providers is essential for finding the best fit. This involves comparing their expertise, reputation, and service offerings.
Expertise
Expertise is a crucial factor when choosing technology services. Organizations should evaluate the provider’s experience in relevant industries, their technical skills, and their understanding of the specific business needs. For example, a healthcare organization would seek a provider with experience in healthcare data security and compliance.
Reputation
A provider’s reputation is a reflection of their track record and customer satisfaction. Organizations should research online reviews, industry rankings, and testimonials to gauge the provider’s reliability, responsiveness, and overall customer experience.
Service Offerings
Service offerings should align with the organization’s specific requirements. This includes evaluating the range of services provided, such as software development, cloud computing, cybersecurity, or data analytics. Organizations should choose providers that offer a comprehensive suite of services that meet their current and future needs.
Checklist for Evaluating Technology Service Providers
A checklist can be a valuable tool for evaluating potential technology service providers and assessing their suitability for specific needs.
- Technical Expertise: Does the provider have experience in the relevant industry and possess the necessary technical skills?
- Reputation and Track Record: What is the provider’s reputation in the market? Are there any testimonials or reviews available?
- Service Offerings: Does the provider offer a comprehensive suite of services that meet the organization’s current and future needs?
- Security and Compliance: Does the provider have robust security measures in place and adhere to relevant industry standards?
- Pricing and Contracts: Are the pricing models transparent and the contract terms favorable?
- Customer Support: Does the provider offer responsive and reliable customer support?
- Scalability and Flexibility: Can the provider adapt to changing business needs and scale services as required?
- Integration with Existing Systems: Can the provider seamlessly integrate their services with the organization’s existing technology infrastructure?
The Future of Technology Services: Technolog Services

The technology services landscape is constantly evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology and changing business needs. Emerging trends like automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping the industry, leading to new service offerings, business models, and job roles. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses to stay competitive and adapt to the future of technology services.
The Impact of Emerging Trends
The convergence of automation, AI, and IoT is driving significant transformation in technology services. These trends are leading to new service offerings, such as AI-powered customer support, predictive maintenance using IoT data, and automated software development.
- Automation: Automation is transforming tasks that were previously performed manually, increasing efficiency and reducing costs. For example, robotic process automation (RPA) is being used to automate repetitive tasks in areas like finance and human resources.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is enabling intelligent automation, providing insights from data and driving decision-making. AI-powered chatbots are being used for customer support, and AI algorithms are being used to detect fraud and predict customer behavior.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is connecting devices and systems, generating vast amounts of data that can be used to improve efficiency and optimize operations. For example, IoT sensors can be used to monitor equipment health and predict maintenance needs.
New Business Models
These trends are also leading to new business models, such as subscription-based services and pay-per-use models. These models offer greater flexibility and affordability for businesses, allowing them to access technology services on demand.
- Subscription-based services: Businesses are increasingly opting for subscription-based services, which provide access to software, hardware, and support for a fixed monthly fee. This model offers greater flexibility and predictability, allowing businesses to scale their technology infrastructure as needed.
- Pay-per-use models: Pay-per-use models allow businesses to pay only for the resources they use, reducing costs and improving efficiency. This model is particularly attractive for businesses with fluctuating workloads or those that require access to specialized resources.
Evolving Job Roles
The rise of automation and AI is also changing the nature of work in the technology services industry. While some jobs are being automated, new roles are emerging in areas like AI development, data science, and cybersecurity.
- AI developers: AI developers are responsible for designing, building, and deploying AI algorithms and systems. They are in high demand as businesses seek to leverage AI to improve their operations and gain a competitive advantage.
- Data scientists: Data scientists are responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to identify trends and insights. They are crucial for businesses that are looking to make data-driven decisions.
- Cybersecurity professionals: Cybersecurity professionals are responsible for protecting businesses from cyber threats. Their role is becoming increasingly important as businesses become more reliant on technology and the threat landscape continues to evolve.
A Conceptual Framework for the Future of Technology Services, Technolog services
The future of technology services is characterized by the integration of automation, AI, and IoT, leading to a more intelligent, connected, and efficient ecosystem. This ecosystem will be characterized by:
- Hyper-automation: The use of AI and other technologies to automate end-to-end processes, enabling businesses to operate with greater efficiency and agility.
- Data-driven insights: The use of data analytics and AI to gain deeper insights into business operations, customer behavior, and market trends.
- Personalized experiences: The use of AI to personalize customer experiences, providing tailored recommendations and support.
- Predictive maintenance: The use of IoT sensors and AI to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
Epilogue

The world of technolog services is constantly evolving, driven by innovation and the increasing demand for digital solutions. By understanding the landscape, the benefits, and the future of these services, businesses can leverage their power to achieve strategic goals, stay competitive, and thrive in the digital economy. Embracing technolog services is not just about adopting technology; it’s about embracing a new era of business transformation.
Technological services are constantly evolving, offering innovative solutions to a wide range of challenges. One such innovation is found in the field of cooling, where companies like kuul evaporative technologies are pioneering sustainable and efficient cooling systems. By leveraging the power of evaporation, kuul provides a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cooling methods, demonstrating the potential of technological services to address global concerns.