Smart Packaging Technology: Revolutionizing the Supply Chain
Smart packaging technology is transforming the way products are packaged, shipped, and consumed. By integrating sensors, RFID tags, and other technologies, smart packaging can track product conditions, monitor shelf life, […]

Smart packaging technology is transforming the way products are packaged, shipped, and consumed. By integrating sensors, RFID tags, and other technologies, smart packaging can track product conditions, monitor shelf life, and even interact with consumers. This evolution from traditional packaging to intelligent systems offers a range of benefits for manufacturers, retailers, and consumers alike.
The potential of smart packaging technology extends beyond simply tracking products. It can also enhance product safety, reduce waste, and improve consumer experience. For example, smart packaging can alert consumers to potential spoilage, provide real-time product information, and even facilitate personalized interactions.
Introduction to Smart Packaging Technology
Smart packaging technology refers to packaging that incorporates sensors, electronics, and other intelligent features to enhance its functionality and provide real-time information about the product and its environment. This technology goes beyond traditional packaging by actively engaging with the product and its surroundings, offering benefits to consumers, manufacturers, and the environment.
The evolution of packaging has seen a gradual shift from simple protective containers to sophisticated systems that provide valuable insights and functionalities. Traditional packaging primarily focused on product protection and branding. However, as technology advanced, the demand for more interactive and intelligent packaging solutions emerged. This led to the development of smart packaging, which leverages advancements in microelectronics, sensors, and wireless communication to create intelligent and responsive packaging systems.
Benefits of Smart Packaging
Smart packaging offers a wide range of benefits to consumers, manufacturers, and the environment.
Benefits for Consumers
Smart packaging provides consumers with enhanced product information, improved safety, and convenience.
- Real-time product information: Smart packaging can display product details such as expiration dates, storage conditions, and nutritional information, allowing consumers to make informed decisions about their purchases.
- Enhanced product safety: Smart packaging can incorporate sensors that monitor product conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. This can help prevent spoilage, contamination, and other safety risks.
- Improved convenience: Smart packaging can provide consumers with interactive features such as interactive labels, QR codes, and NFC tags. This can enhance the user experience and provide access to additional information about the product.
Benefits for Manufacturers
Smart packaging offers manufacturers improved supply chain visibility, reduced waste, and enhanced brand engagement.
- Improved supply chain visibility: Smart packaging can track the location, temperature, and other environmental conditions of products throughout the supply chain. This provides manufacturers with real-time insights into the product’s journey, enabling them to optimize logistics and reduce delays.
- Reduced waste: Smart packaging can monitor product freshness and quality, allowing manufacturers to optimize inventory management and reduce food waste.
- Enhanced brand engagement: Smart packaging can provide consumers with interactive experiences, such as augmented reality features or personalized messages. This can help manufacturers build stronger relationships with their customers and create a more memorable brand experience.
Benefits for the Environment
Smart packaging can contribute to sustainability by reducing waste, improving resource efficiency, and promoting recycling.
- Reduced waste: Smart packaging can help extend product shelf life, reducing food waste and the environmental impact of food spoilage.
- Improved resource efficiency: Smart packaging can track product usage and provide feedback to consumers, promoting responsible consumption and reducing unnecessary packaging.
- Promoting recycling: Smart packaging can incorporate materials that are easily recyclable or compostable, contributing to a circular economy.
Types of Smart Packaging Technologies
Smart packaging technologies encompass a wide range of functionalities, from providing information about the product to enhancing its safety and shelf life. These technologies are categorized based on their primary functions, each offering unique benefits and applications.
Time-Temperature Indicators
Time-temperature indicators (TTIs) are essential for ensuring product quality and safety by monitoring the temperature history of perishable goods during transportation and storage.
- Chemical TTIs utilize chemical reactions that change color or form based on temperature exposure. For example, a common type uses a chemical solution that changes color from blue to red when exposed to temperatures above a specific threshold. These are often used on pharmaceuticals, food products, and vaccines to indicate if they have been exposed to temperatures that could compromise their efficacy or safety.
- Enzymatic TTIs use enzymes that change color or fluorescence depending on the temperature and duration of exposure. These are more sensitive than chemical TTIs and can provide more accurate data on the temperature history of a product. These are commonly used in the food industry to track the temperature of frozen foods and other temperature-sensitive products.
- Electronic TTIs employ sensors that record and store temperature data over time. These sensors can be integrated into packaging and transmit the data wirelessly to a central system, allowing for real-time monitoring and tracking of product temperature. Electronic TTIs are used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and logistics, to ensure product quality and safety.
Anti-Counterfeiting Technologies
Counterfeiting is a significant concern in many industries, particularly pharmaceuticals and luxury goods. Smart packaging technologies are employed to combat counterfeiting by providing unique identification and authentication features.
- Holographic Labels utilize lasers to create unique patterns on labels, making it difficult to replicate. These patterns can be viewed under different angles, displaying various images or colors. This technology is widely used in pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and cosmetics to deter counterfeiting.
- RFID Tags contain microchips that store unique identification information. When scanned, the tags provide information about the product’s authenticity, origin, and journey. This technology is increasingly used in pharmaceuticals, clothing, and electronics to verify product authenticity and track its movement through the supply chain.
- Digital Watermarks are embedded within the packaging material itself, invisible to the naked eye but detectable using specific software. These watermarks can contain unique identification codes or information about the product’s origin. Digital watermarks are used in pharmaceuticals, food, and other industries to verify product authenticity and track its movement through the supply chain.
Interactive Packaging
Interactive packaging technologies enhance the consumer experience by providing information, entertainment, or interactive features.
- QR Codes are two-dimensional barcodes that can be scanned using smartphones to access information about the product, such as nutritional information, ingredients, or instructions for use. QR codes are widely used on food products, beverages, and other consumer goods.
- NFC Tags are similar to RFID tags but operate at shorter distances. They can be used to provide information about the product, offer discounts or promotions, or enable interactive experiences, such as games or augmented reality applications. NFC tags are used in various industries, including food, beverages, and consumer electronics.
- Augmented Reality (AR) technology overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user experience. AR-enabled packaging can provide interactive product information, virtual product demonstrations, or engaging games and entertainment. AR technology is being increasingly used in packaging for consumer goods, toys, and games.
Sensors and Monitoring Technologies
Sensors and monitoring technologies are integrated into packaging to provide real-time information about the product’s condition, such as temperature, humidity, or pressure.
- Oxygen Sensors monitor the oxygen levels inside the packaging, indicating if the product is exposed to oxygen that could affect its quality or shelf life. Oxygen sensors are commonly used in food packaging, especially for products sensitive to oxidation, such as fruits, vegetables, and meat.
- Moisture Sensors measure the humidity levels inside the packaging, providing insights into the product’s moisture content and potential for spoilage. Moisture sensors are used in food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and other industries where humidity can affect product quality.
- Pressure Sensors monitor the internal pressure inside the packaging, indicating potential leaks or changes in the product’s condition. Pressure sensors are used in packaging for beverages, pharmaceuticals, and other products that are sensitive to pressure changes.
Other Smart Packaging Technologies
- Time-Release Packaging controls the release of ingredients or active components over time, ensuring controlled and targeted delivery. This technology is used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and other industries where controlled release is essential.
- Biodegradable Packaging is made from materials that decompose naturally over time, reducing environmental impact. This technology is gaining popularity in various industries, including food, beverages, and consumer goods.
- Reusable Packaging is designed to be used multiple times, reducing waste and promoting sustainability. Reusable packaging is being explored in various industries, including food delivery, e-commerce, and logistics.
Comparison of Smart Packaging Technologies
| Technology | Features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-Temperature Indicators (TTIs) | Monitor temperature history of products | Ensure product quality and safety, track temperature fluctuations | Limited data storage, can be affected by environmental factors |
| Anti-Counterfeiting Technologies | Provide unique identification and authentication features | Combat counterfeiting, protect brand reputation, ensure product authenticity | Can be expensive to implement, requires specialized equipment for verification |
| Interactive Packaging | Enhance consumer experience, provide information and entertainment | Increase consumer engagement, provide product information, promote brand loyalty | Requires smartphone or other devices for interaction, can be expensive to develop |
| Sensors and Monitoring Technologies | Monitor product condition in real-time | Improve product quality, extend shelf life, prevent spoilage | Can be complex to implement, require specialized equipment for data analysis |
| Other Smart Packaging Technologies | Offer various functionalities, such as controlled release, biodegradability, and reusability | Promote sustainability, enhance product performance, improve consumer experience | May require specialized materials or processes, can be more expensive than traditional packaging |
Key Technologies and Components

Smart packaging technology relies on a combination of advanced components and technologies to provide enhanced functionality and information. These technologies work together to monitor, track, and communicate data related to the product’s condition, location, and other relevant factors.
Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in smart packaging by collecting data about the product and its environment. They act as the eyes and ears of the packaging, providing real-time information that can be used to optimize product quality, safety, and supply chain efficiency.
Types of Sensors Used in Smart Packaging
Sensors used in smart packaging are diverse and tailored to specific applications. Here are some common types:
- Temperature Sensors: These sensors measure the temperature of the product and its surroundings. They are essential for ensuring the product remains within its optimal temperature range, especially for perishable goods. Examples include thermistors, thermocouples, and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs).
- Humidity Sensors: These sensors monitor the moisture content of the product and its environment. They are crucial for products that are susceptible to moisture damage, such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, and food items. Common types include capacitive humidity sensors and resistive humidity sensors.
- Pressure Sensors: These sensors measure the pressure applied to the packaging, providing information about the product’s condition. They are used in applications where product integrity is critical, such as in packaging for fragile items or medical devices. Examples include strain gauge pressure sensors and piezoelectric pressure sensors.
- Gas Sensors: These sensors detect the presence of specific gases within the packaging. They are used to monitor product freshness, detect leaks, and identify potential spoilage. Common examples include electrochemical gas sensors and semiconductor gas sensors.
- Light Sensors: These sensors detect light levels within the packaging, providing information about exposure to sunlight or other light sources. They are used to monitor product quality and ensure proper storage conditions. Examples include photodiodes and phototransistors.
Integration of Sensors into Packaging
Sensors are typically integrated into packaging materials in several ways:
- Embedded Sensors: Sensors can be directly embedded into the packaging material itself, either during the manufacturing process or through a post-processing step. This allows for seamless integration and minimal impact on the packaging’s design and functionality.
- Attached Sensors: Sensors can be attached to the packaging surface using adhesives or other methods. This approach provides flexibility in sensor placement and allows for easy replacement or upgrade. However, it can potentially affect the packaging’s aesthetics and overall design.
- Integrated Sensor Systems: More complex sensor systems can be integrated into the packaging, incorporating multiple sensors, data processing units, and communication capabilities. These systems provide a comprehensive understanding of the product’s condition and environment.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
RFID technology uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. In smart packaging, RFID tags can be embedded in the packaging material or attached to the product itself, enabling real-time tracking and monitoring throughout the supply chain.
Applications of RFID in Smart Packaging
RFID technology offers numerous benefits in smart packaging, including:
- Product Authentication: RFID tags can be used to verify the authenticity of products, preventing counterfeiting and ensuring consumer trust.
- Inventory Management: RFID tags provide real-time visibility of product inventory levels, enabling efficient stock management and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
- Supply Chain Tracking: RFID tags enable the tracking of products throughout the supply chain, providing information about their location, temperature, and other relevant factors. This enhances supply chain transparency and helps to optimize logistics operations.
- Consumer Engagement: RFID tags can be used to provide consumers with product information, such as ingredients, expiration dates, and origin, enhancing their shopping experience and increasing brand loyalty.
Near Field Communication (NFC), Smart packaging technology
NFC is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables communication between devices within a few centimeters. In smart packaging, NFC tags can be embedded in the packaging material or attached to the product, allowing consumers to interact with the product using their smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices.
Applications of NFC in Smart Packaging
NFC technology offers a range of applications in smart packaging, including:
- Product Information: NFC tags can be used to provide consumers with detailed product information, such as ingredients, nutritional facts, and instructions for use, by simply tapping their smartphones on the tag.
- Brand Engagement: NFC tags can be used to create interactive experiences for consumers, such as providing access to exclusive content, online promotions, or loyalty programs.
- Payment Solutions: NFC tags can be integrated with mobile payment systems, enabling consumers to purchase products directly from the packaging using their smartphones.
- Product Authentication: NFC tags can be used to verify the authenticity of products, ensuring that consumers are purchasing genuine items.
Other Technologies
In addition to sensors, RFID, and NFC, other technologies are also being incorporated into smart packaging to enhance its functionality and capabilities. These technologies include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT enables the connection of smart packaging to the internet, allowing for real-time data collection, analysis, and communication. This enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and other advanced applications.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing provides a platform for storing, processing, and analyzing data collected from smart packaging. This enables the development of sophisticated applications and insights into product performance and consumer behavior.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can be used to analyze data collected from smart packaging, providing insights into product quality, consumer preferences, and supply chain efficiency. This enables data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can be used to secure data collected from smart packaging, ensuring its integrity and authenticity. This is particularly important for applications involving product authentication and supply chain transparency.
Applications of Smart Packaging Technology

Smart packaging technology is transforming various industries by offering innovative solutions that enhance product safety, traceability, and the overall consumer experience. Its applications extend across diverse sectors, including food, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and logistics.
Food Industry
The food industry heavily relies on smart packaging to maintain product freshness, extend shelf life, and ensure consumer safety. Smart packaging technologies help monitor temperature, humidity, and other critical factors that impact food quality.
- Time-Temperature Indicators (TTIs): These indicators change color or appearance based on the time and temperature exposure, providing a visual cue about the product’s freshness and safety.
- Oxygen Scavengers: These packets absorb oxygen from the packaging, preventing oxidation and extending the shelf life of perishable goods.
- RFID Tags: Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags can be used to track food products throughout the supply chain, enabling real-time monitoring and ensuring product authenticity.
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry utilizes smart packaging to safeguard the integrity of medications, prevent counterfeiting, and ensure patient safety.
- Tamper-Evident Packaging: Smart packaging features tamper-evident seals that indicate any unauthorized access to the product, ensuring its authenticity and safety.
- RFID Tags: RFID tags can be used to track medications from manufacturing to dispensing, enabling secure supply chain management and preventing counterfeiting.
- Temperature Sensors: These sensors monitor the temperature of sensitive medications, ensuring they remain within the required range throughout transportation and storage.
Electronics Industry
Smart packaging plays a crucial role in protecting delicate electronics during transportation and storage.
- Shock and Vibration Sensors: These sensors detect impacts and vibrations, alerting users if the product has been mishandled or subjected to potential damage.
- Humidity Indicators: These indicators provide a visual cue about the humidity levels inside the packaging, ensuring optimal conditions for sensitive electronic components.
- RFID Tags: RFID tags can be used to track electronic devices throughout the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and facilitating inventory management.
Logistics Industry
Smart packaging technologies streamline logistics operations, enhance efficiency, and improve visibility throughout the supply chain.
- GPS Tracking: Real-time GPS tracking enables monitoring the location and movement of packages, providing valuable insights for efficient delivery and route optimization.
- RFID Tags: RFID tags can be used to track packages and containers throughout the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and improving inventory management.
- Sensors: Sensors can monitor various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and shock, providing real-time data about the condition of the goods during transportation.
Concluding Remarks
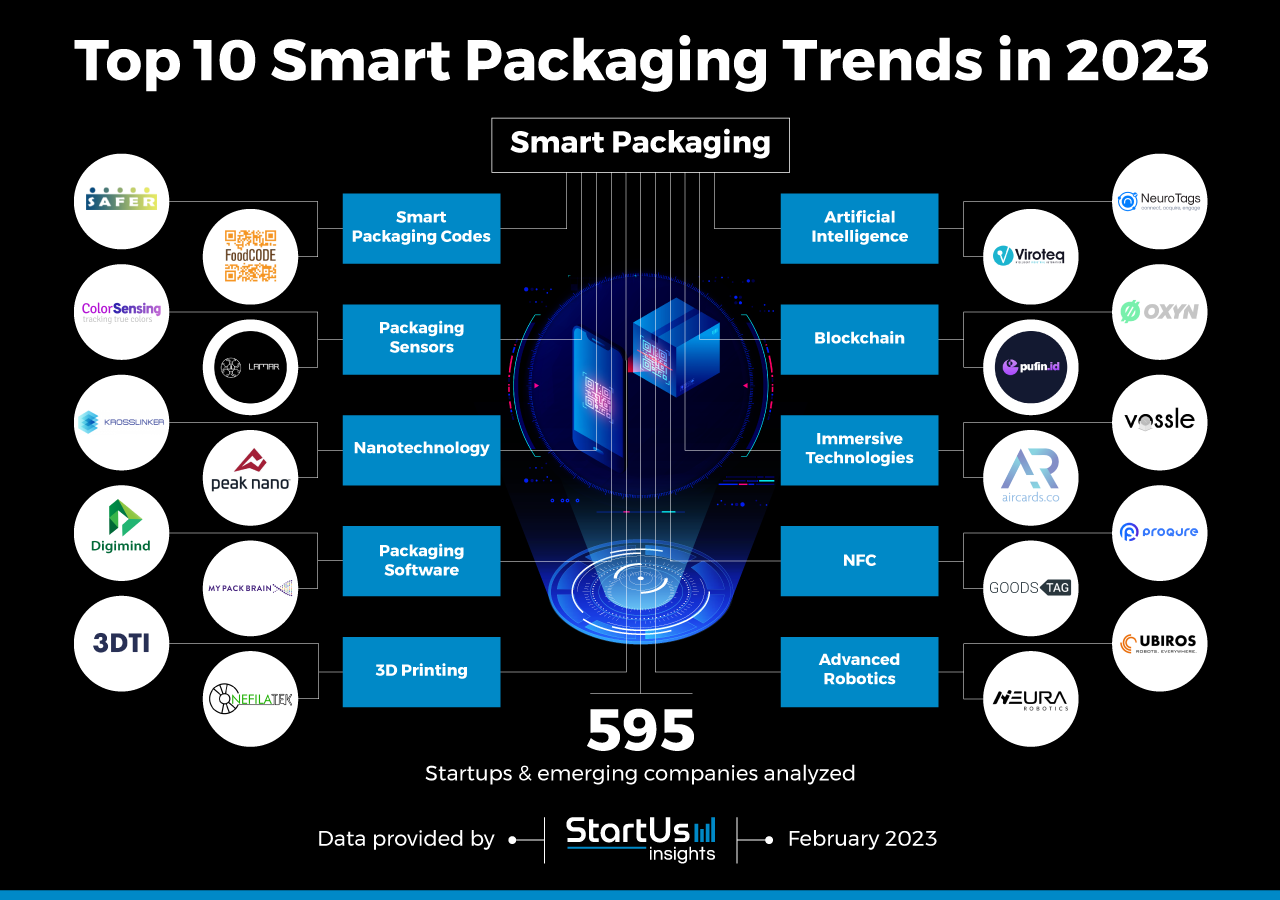
As smart packaging technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications in the future. The integration of artificial intelligence, the internet of things, and sustainable materials will further enhance the capabilities of smart packaging, leading to a more efficient, transparent, and environmentally friendly supply chain. This technology holds the key to a future where products are safer, more traceable, and better connected with consumers.
Smart packaging technology is constantly evolving, offering innovative solutions for product protection and consumer engagement. One exciting development is the integration of surenail technology , which allows for secure and tamper-proof packaging. This technology not only enhances product security but also provides valuable data insights for manufacturers, contributing to the overall efficiency and sustainability of smart packaging solutions.