RF Technologies Headset Repair: A Guide to Troubleshooting and Maintenance
RF Technologies Headset Repair: Navigating the world of wireless audio can be a delightful experience, but it comes with its own set of challenges. RF headsets, while offering a range […]

RF Technologies Headset Repair: Navigating the world of wireless audio can be a delightful experience, but it comes with its own set of challenges. RF headsets, while offering a range of benefits, can sometimes encounter issues that require repair. From understanding the fundamentals of RF technology in headsets to mastering troubleshooting techniques, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to tackle common problems and keep your wireless audio experience running smoothly.
The use of RF technology in headsets has revolutionized the way we listen to music, take calls, and engage in virtual meetings. RF headsets provide a high-quality, wireless audio experience with minimal interference, allowing for greater mobility and freedom of movement. This guide will delve into the intricacies of RF technology in headsets, providing insights into the benefits, common issues, and repair techniques that are essential for maintaining optimal performance.
Common RF Headset Problems and Their Causes

RF headsets, while generally reliable, can experience a range of issues. Understanding the common problems and their causes can help you troubleshoot and resolve them efficiently.
Faulty Antennas
Faulty antennas are a common source of RF headset problems. These issues can arise from various factors, including physical damage, wear and tear, or manufacturing defects. A damaged antenna can lead to poor signal reception, resulting in dropped calls, distorted audio, and intermittent connectivity.
- Physical damage: Bends, kinks, or breaks in the antenna can disrupt the signal flow.
- Wear and tear: Over time, antennas can become worn out or corroded, leading to decreased performance.
- Manufacturing defects: Occasionally, antennas may have defects that impair their functionality from the start.
Damaged Connectors
Connectors play a crucial role in transmitting audio signals and power to the headset. Damaged connectors can lead to intermittent or complete loss of audio, microphone malfunction, and charging issues.
- Physical damage: Bends, breaks, or corrosion in the connector can interrupt the signal flow.
- Loose connections: Loose connectors can result in intermittent audio or connectivity problems.
- Contamination: Dust, debris, or moisture can accumulate in the connector, causing signal interference.
Interference
RF signals can be susceptible to interference from other electronic devices, wireless networks, or even environmental factors. Interference can manifest as static, crackling, or distorted audio.
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI): Devices like microwaves, cordless phones, or other wireless devices can emit electromagnetic waves that interfere with RF signals.
- Radio frequency interference (RFI): Wireless networks operating on the same frequency band can interfere with RF headset signals.
- Environmental factors: Metal objects, large structures, or even weather conditions can affect signal strength and cause interference.
Battery Issues
Battery problems are another common issue in RF headsets. Battery life, charging issues, or battery failure can lead to frequent interruptions in communication.
- Battery life: Over time, battery capacity can degrade, resulting in shorter battery life.
- Charging issues: Faulty charging cables, damaged charging ports, or incorrect charging methods can prevent proper battery charging.
- Battery failure: Battery cells can eventually fail, requiring replacement.
Software Glitches
Software glitches, while less common, can also cause problems with RF headsets. These glitches can occur in the headset’s firmware or the associated software applications.
- Firmware issues: Outdated or corrupted firmware can lead to unexpected behavior or performance problems.
- Software conflicts: Conflicts between the headset software and other applications can cause communication problems.
Troubleshooting Tips
Identifying the source of the problem is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here are some tips to help pinpoint the cause:
- Check the antenna: Inspect the antenna for any physical damage or signs of wear.
- Examine the connectors: Look for bends, breaks, or corrosion in the connectors.
- Identify potential interference sources: Move away from other electronic devices or wireless networks to see if the problem persists.
- Test the battery: Check the battery level and ensure it’s properly charged.
- Update the firmware: Update the headset’s firmware to the latest version.
- Contact the manufacturer: If the problem persists, contact the headset manufacturer for support.
Repairing RF Headset Components
Repairing an RF headset often involves disassembling the device to access the components that need attention. This process can be intricate, requiring careful handling and knowledge of the headset’s internal structure.
Disassembling an RF Headset, Rf technologies headset repair
Before attempting any repairs, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the headset’s design and understand the steps involved in disassembly. This process usually involves removing screws, clips, or other fasteners that hold the headset’s various components together. It’s crucial to use the appropriate tools to avoid damaging the headset.
- Identify the screws and fasteners: Locate all screws, clips, or other fasteners that hold the headset’s casing together. Note their sizes and types to ensure you have the correct tools for removal.
- Use the right tools: Employ appropriate screwdrivers, pliers, or other tools to remove the fasteners without stripping the screws or damaging the headset.
- Remove the casing carefully: Once the fasteners are removed, gently pry open the headset’s casing. Be mindful of any delicate components or fragile connections.
- Disconnect the internal components: Disconnect any internal components, such as the battery, antenna, or charging port, by carefully detaching the connectors.
- Document the disassembly process: Take pictures or notes to document the disassembly process. This will be helpful when reassembling the headset.
Common Components Requiring Repair or Replacement
Several components within an RF headset are prone to wear and tear, malfunction, or damage. Identifying these components is crucial for effective repair.
- Antenna: The antenna transmits and receives radio signals. It can become damaged, bent, or lose its connection, leading to poor reception or transmission.
- Battery: The battery provides power to the headset. Over time, it can lose its capacity, leading to reduced talk time or standby time. Additionally, the battery terminals might corrode, affecting the headset’s power supply.
- Charging Port: The charging port allows you to recharge the headset’s battery. Excessive use or improper handling can damage the port, preventing the headset from charging properly.
- Speaker: The speaker produces sound. Damage to the speaker can result in distorted audio or no sound at all.
- Microphone: The microphone captures your voice for communication. A faulty microphone can lead to muffled or unclear audio during conversations.
- Headset Band: The headset band holds the headset in place. Over time, the band can become stretched, broken, or lose its elasticity, making the headset uncomfortable or unstable.
Repairing or Replacing Components
Once you’ve identified the faulty component, you can either repair or replace it. Repairing a component might involve cleaning, soldering, or adjusting parts. Replacement typically involves acquiring a new component and installing it in the headset.
- Antenna: If the antenna is bent, you might be able to straighten it carefully. If the connection is loose, you can try re-soldering it. However, if the antenna is damaged beyond repair, you’ll need to replace it with a new one.
- Battery: Replacing the battery is the most common solution for a failing battery. You can purchase a new battery that’s compatible with your headset model. Ensure the battery is properly installed and securely connected.
- Charging Port: If the charging port is damaged, you might be able to repair it by cleaning it with a cotton swab and rubbing alcohol. However, if the damage is extensive, you’ll need to replace the charging port. This might involve soldering a new port onto the headset’s circuit board.
- Speaker: A damaged speaker can be replaced with a new one. You’ll need to find a speaker that’s compatible with your headset model. Replacing the speaker often requires soldering skills.
- Microphone: Replacing a faulty microphone is similar to replacing a speaker. You’ll need to find a compatible microphone and solder it onto the headset’s circuit board.
- Headset Band: A stretched or broken headset band can be replaced with a new one. You can purchase a compatible band online or from a local electronics store.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Pinpointing the source of an RF headset malfunction requires a systematic approach. Effective troubleshooting involves utilizing the right tools and techniques to test different components and isolate the specific issue.
Tools and Techniques for Diagnosis
Diagnosing RF headset problems necessitates a set of specialized tools and techniques.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is essential for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. It helps identify faulty components like batteries, wires, and connectors.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope is used to visualize and analyze electronic signals, allowing technicians to assess the integrity of audio signals and identify potential signal distortions.
- Signal Generator: A signal generator emits test signals, enabling the verification of audio transmission and reception pathways within the headset.
- Frequency Counter: A frequency counter precisely measures the operating frequency of the RF transmitter and receiver, ensuring compatibility and proper signal transmission.
- Logic Analyzer: A logic analyzer captures and displays digital signals, aiding in the analysis of control circuits and data transmission within the headset.
Testing Headset Components
Testing individual components is crucial to isolate the problem.
- Battery: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. A low or dead battery can cause poor audio quality or complete failure.
- Microphone: Speak into the microphone while observing the audio output on an oscilloscope. A weak or distorted signal indicates a microphone issue.
- Speaker: Apply a test signal to the speaker using a signal generator. If the speaker is faulty, there will be no sound or distorted audio.
- Transmitter and Receiver: Measure the output power of the transmitter and the signal strength at the receiver using a frequency counter and a signal strength meter. Weak signals suggest issues with the transmitter or receiver.
- Connectors and Wires: Visually inspect connectors for damage or corrosion. Use a multimeter to check for continuity in wires and connections.
Isolating the Issue
After testing individual components, the next step is to isolate the specific issue.
- Audio Signal Path: Trace the audio signal path from the microphone to the speaker. Identify any points where the signal is weak or distorted.
- RF Transmission: Verify the strength and clarity of the RF signal between the transmitter and receiver. Check for interference or signal dropouts.
- Control Circuits: Analyze the functionality of control circuits that manage power, volume, and other headset functions. Use a logic analyzer to diagnose any malfunctions.
- Environmental Factors: Consider external factors like temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference that can affect headset performance.
Preventive Maintenance and Care
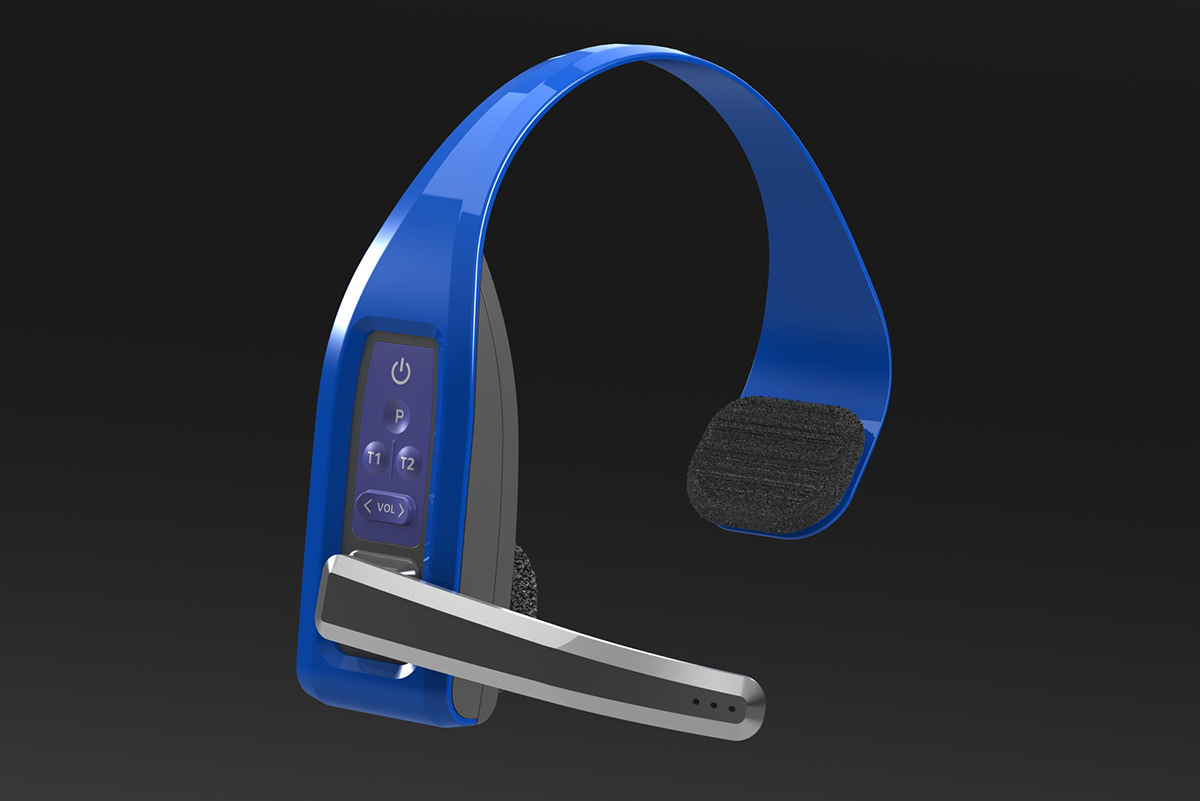
Just like any other electronic device, your RF headset requires proper care and maintenance to ensure a long and reliable lifespan. This section provides valuable tips on extending the life of your RF headset and keeping it in optimal working condition.
Proper Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling are crucial for maintaining the integrity and longevity of your RF headset. When not in use, store your headset in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture. This helps prevent damage to the delicate components and ensures the headset remains functional for a longer duration.
Here are some additional tips for proper storage and handling:
- Avoid exposing the headset to extreme temperatures, as this can affect the battery life and the performance of the electronics.
- Always handle the headset gently, avoiding dropping or subjecting it to harsh impacts. A protective case can provide additional protection during transportation.
- Keep the headset clean and free from dust and debris. Regular cleaning with a soft, dry cloth can help prevent build-up that can affect the headset’s functionality.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential for maintaining the optimal performance of your RF headset. Over time, dust, dirt, and sweat can accumulate on the headset, affecting its functionality and potentially causing damage. Regular cleaning can help prevent these issues and extend the life of your headset.
Here are some recommendations for regular cleaning and maintenance:
- Clean the earcups and microphone regularly with a soft, dry cloth. For stubborn dirt, use a slightly damp cloth with mild soap. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
- Inspect the headset for any signs of damage or wear and tear. If you notice any issues, contact the manufacturer or a qualified technician for repair.
- Keep the headset charging cable clean and free from any damage. A damaged charging cable can cause damage to the headset’s battery or other components.
- Regularly check the battery level and recharge the headset when necessary. Avoid fully draining the battery, as this can shorten its lifespan.
Importance of Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of your RF headset. Neglecting these practices can lead to several issues, including:
- Reduced audio quality: Dust and debris can accumulate in the earcups and microphone, affecting the sound quality and clarity.
- Microphone malfunction: Dirt and grime can clog the microphone, hindering its ability to pick up sound properly.
- Battery issues: Dust and dirt can affect the battery’s performance and lifespan, leading to shorter battery life and potential damage.
- Damaged components: Neglecting to clean the headset can lead to the accumulation of dirt and grime, which can damage the delicate components, affecting its functionality.
Summary: Rf Technologies Headset Repair
Repairing RF headsets can be a rewarding experience, offering a sense of accomplishment and the satisfaction of restoring a valuable device to its former glory. By understanding the underlying technology, common problems, and repair techniques, you can confidently troubleshoot and maintain your RF headsets, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable wireless audio experience.
RF technologies are essential for seamless wireless communication, making them crucial for headset functionality. While repairing a headset with RF issues can be challenging, it’s often a worthwhile endeavor, especially if you’re considering upgrading your car. The 2024 Acura MDX base vs technology package comparison can help you decide if the additional tech features, like advanced audio systems, are worth the investment.
Ultimately, a well-functioning headset, whether paired with a high-tech car or not, can enhance your listening experience and connectivity.





