Process Technology Certificate vs Degree: Which Path Is Right for You?
Process technology certificate vs degree: Choosing the right path in the world of process technology can be a tough decision. Do you go for the quick, focused training of a […]
Process technology certificate vs degree: Choosing the right path in the world of process technology can be a tough decision. Do you go for the quick, focused training of a certificate, or invest in a longer degree program for a broader skill set? This article dives into the pros and cons of each option, exploring career paths, educational requirements, and ultimately, helping you determine the best fit for your goals.
From the core differences in curriculum and learning objectives to the diverse career opportunities and salary expectations, we’ll cover everything you need to make an informed choice. We’ll also delve into the advantages and disadvantages of each option, providing a clear picture of what to expect along the way. Ultimately, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to confidently choose the path that aligns with your ambitions and career aspirations.
Understanding the Basics

Choosing between a process technology certificate and a degree depends on your career goals and the specific requirements of the industry you want to enter. Both options offer valuable knowledge and skills, but they differ in their scope, depth, and potential career paths.
Process Technology Certificate vs. Degree
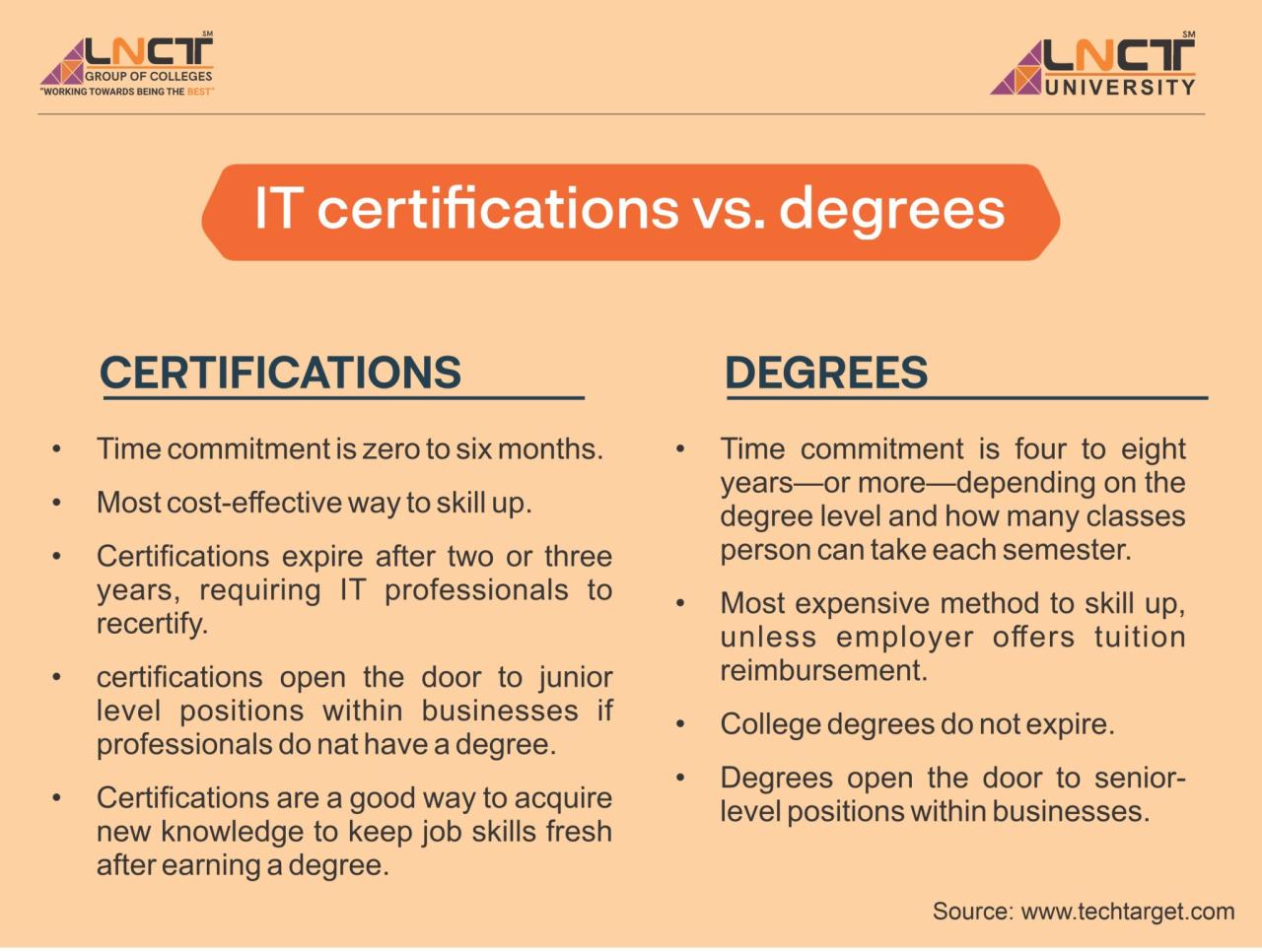
The primary difference between a process technology certificate and a degree lies in the depth and breadth of knowledge they provide. A certificate program focuses on specific skills and knowledge directly applicable to the process technology field. In contrast, a degree program offers a broader foundation in science, engineering, and process technology principles, preparing graduates for a wider range of roles and responsibilities.
Typical Coursework and Learning Objectives
- Process Technology Certificate: Coursework typically focuses on practical skills and technical knowledge, including:
- Process control and instrumentation
- Process safety and environmental regulations
- Troubleshooting and maintenance
- Basic process engineering principles
- Quality control and assurance
- Process Technology Degree: Coursework covers a broader range of topics, including:
- Chemistry and physics
- Process design and optimization
- Advanced process control systems
- Process simulation and modeling
- Project management and engineering principles
Process Technology Certifications
There are several industry-recognized process technology certifications available, such as:
- Certified Automation Professional (CAP): Offered by the International Society of Automation (ISA), this certification validates expertise in automation technologies and practices.
- Certified Control Systems Technician (CCST): This certification, also offered by ISA, recognizes knowledge and skills in control systems design, installation, and maintenance.
- Certified Process Technician (CPT): This certification, offered by the American Society for Quality (ASQ), focuses on process control, quality assurance, and troubleshooting.
Program Duration and Cost
- Process Technology Certificate: Certificate programs typically range from a few months to a year in duration. The cost can vary depending on the institution and program length, but it is generally less expensive than a degree program.
- Process Technology Degree: A process technology degree typically takes two to four years to complete. The cost of a degree program is significantly higher than a certificate program, due to the extended duration and broader scope of coursework.
Educational Requirements

The educational requirements for a process technology certificate and a process technology degree vary significantly. While both programs are designed to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to operate and maintain process equipment, the level of education and training required for each program differs.
Prerequisites
The prerequisites for each program are determined by the specific institution offering the program. However, there are some common prerequisites that are often required.
- Certificate Programs: Certificate programs typically require a high school diploma or equivalent. Some programs may require specific coursework in math, science, and technology.
- Degree Programs: Degree programs typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, and often require an associate’s degree or a minimum number of college credits. Some programs may also require specific coursework in math, science, and engineering.
Prior Education or Experience
Prior education or experience can be beneficial for both certificate and degree programs.
- Certificate Programs: Certificate programs may accept students with a variety of backgrounds, including those with experience in related fields such as manufacturing or industrial maintenance.
- Degree Programs: Degree programs often prefer applicants with some prior experience in the process industry, such as internships or work experience in a process plant. However, some programs may accept students with no prior experience, provided they have the necessary academic background.
Admission Requirements
Admission requirements for both certificate and degree programs vary depending on the institution.
- Certificate Programs: Admission requirements for certificate programs are generally less stringent than for degree programs. Applicants may need to submit an application, transcripts, and potentially a letter of recommendation.
- Degree Programs: Admission requirements for degree programs are typically more rigorous. Applicants may need to submit an application, transcripts, standardized test scores (such as the SAT or ACT), letters of recommendation, and a personal essay. Some programs may also require an interview.
Application Process
The application process for both certificate and degree programs typically involves submitting an application, transcripts, and other supporting documents.
- Certificate Programs: The application process for certificate programs is often straightforward and may be completed online.
- Degree Programs: The application process for degree programs is generally more complex and may require submitting additional documents and completing an interview.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Process Technology Certificate Vs Degree
Choosing between a process technology certificate and a degree is a crucial decision, influenced by individual goals, career aspirations, and available resources. This section explores the advantages and disadvantages of each path, providing a comprehensive understanding of the benefits and drawbacks associated with each option.
Advantages of a Process Technology Certificate
A process technology certificate provides a focused and efficient pathway to enter the process industry. It offers several advantages, including:
- Faster Completion Time: Certificates typically require less time to complete compared to a degree, allowing individuals to enter the workforce more quickly.
- Lower Cost: The cost of a certificate program is often significantly lower than a degree program, making it a more affordable option for those with budget constraints.
- Practical Skills Focus: Certificates emphasize practical skills and hands-on training, preparing individuals for immediate application in the workplace.
- Industry-Specific Training: Certificate programs are often tailored to specific industries, ensuring graduates possess the specialized knowledge and skills demanded by employers.
- Flexibility: Certificate programs offer greater flexibility in terms of scheduling and delivery, allowing individuals to study at their own pace and around their existing commitments.
Disadvantages of a Process Technology Certificate
While certificates offer numerous advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Limited Career Advancement: A certificate may not be sufficient for advancement to higher-level positions, which often require a degree.
- Lower Earning Potential: Individuals with only a certificate may earn less than those with a degree, especially in the long term.
- Limited Knowledge Base: Certificates focus on specific skills, but may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the broader process technology field.
- Less Transferable Credit: Credits earned from a certificate program may not be transferable to a degree program, potentially requiring additional coursework.
Advantages of a Process Technology Degree
A process technology degree provides a more comprehensive education and a wider range of career opportunities. The advantages include:
- Stronger Career Advancement: A degree opens doors to higher-level positions and leadership roles, providing greater opportunities for career progression.
- Higher Earning Potential: Individuals with a degree typically earn more than those with only a certificate, both in starting salaries and long-term earning potential.
- Broader Knowledge Base: A degree program provides a comprehensive understanding of process technology principles, theories, and applications, fostering a deeper understanding of the field.
- Greater Transferability: Credits earned from a degree program are more likely to be transferable to other programs, providing greater flexibility in future educational pursuits.
- Increased Job Security: A degree may enhance job security, making individuals more competitive in the job market and less vulnerable to economic downturns.
Disadvantages of a Process Technology Degree
While a degree offers numerous benefits, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Longer Completion Time: A degree program typically takes longer to complete than a certificate program, delaying entry into the workforce.
- Higher Cost: The cost of a degree program is generally higher than a certificate program, requiring a larger financial investment.
- Less Emphasis on Practical Skills: Degree programs often focus on theoretical knowledge, potentially leading to a gap between academic learning and real-world application.
- Greater Time Commitment: A degree program requires a significant time commitment, potentially impacting work-life balance and other personal responsibilities.
Choosing the Right Path
The decision between pursuing a process technology certificate or a degree is a significant one. It requires careful consideration of your career goals, financial resources, and time commitment.
Factors to Consider
This checklist can help you make an informed decision:
- Career Goals: What specific roles are you aiming for? Do you need a degree for advancement opportunities?
- Time Commitment: How much time are you willing to dedicate to your education?
- Financial Resources: Can you afford the costs associated with a degree program?
- Prior Education and Experience: Do you have any relevant prior experience or education?
- Learning Style: Do you prefer a structured learning environment or a more flexible approach?
Comparing Key Factors, Process technology certificate vs degree
This table provides a side-by-side comparison of key factors for choosing between a certificate and a degree:
| Factor | Process Technology Certificate | Process Technology Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Time Commitment | Shorter | Longer |
| Job Market Value | May be sufficient for entry-level positions | Generally preferred for higher-level roles and advancement |
| Career Advancement Potential | Limited | Greater |
A Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to navigate the decision-making process:
- Define Your Career Goals: Identify the specific process technology roles you are interested in and research the educational requirements for each.
- Assess Your Financial Resources: Determine the cost of both certificate and degree programs and consider the financial aid options available to you.
- Evaluate Your Time Commitment: Consider the time required to complete each program and factor in your work and personal commitments.
- Research Educational Institutions: Explore reputable institutions offering process technology certificates and degrees. Look for programs aligned with your career goals and learning style.
- Consult with Industry Professionals: Seek guidance from professionals in the process technology field to gain insights on industry trends and the value of certificates and degrees.
- Make an Informed Decision: Weigh the pros and cons of each option based on your individual circumstances and career aspirations.
Conclusion
The decision between a process technology certificate and degree is a personal one, influenced by individual goals, time commitments, and financial resources. While a certificate can provide a faster entry into the field, a degree often opens doors to more advanced roles and higher earning potential. By carefully considering your career aspirations, the demands of the job market, and your own learning preferences, you can make a well-informed choice that sets you on a successful path in the exciting world of process technology.
Deciding between a process technology certificate and a degree depends on your career goals and learning style. A certificate can be a great starting point for those wanting to enter the field quickly, while a degree offers a broader understanding and potential for advancement.
If you’re interested in exploring the world of process technology, you might find the resources available at https //arc.asura technologies.com/payment helpful. Ultimately, the choice between a certificate and a degree should align with your individual aspirations and professional trajectory.