Pharmaceutical Technology Transfer: Global Healthcare Impact
Pharmaceutical technology transfer stands as a critical bridge connecting scientific breakthroughs with patient care, revolutionizing the global healthcare landscape. This intricate process involves the seamless transfer of knowledge, expertise, and […]
Pharmaceutical technology transfer stands as a critical bridge connecting scientific breakthroughs with patient care, revolutionizing the global healthcare landscape. This intricate process involves the seamless transfer of knowledge, expertise, and technology for the production and distribution of life-saving medications. It encompasses a complex interplay of diverse stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, regulatory agencies, and manufacturing facilities.
The success of pharmaceutical technology transfer hinges on meticulous planning, efficient communication, and a robust understanding of regulatory frameworks. It is a multi-faceted endeavor that requires a collaborative approach to ensure the safe, effective, and timely delivery of essential medications to patients worldwide.
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Technology Transfer
Pharmaceutical technology transfer is a critical process that involves the systematic transfer of knowledge, skills, and technology from one organization to another. This transfer can occur between different departments within the same company, between different companies, or even between countries. The significance of pharmaceutical technology transfer is undeniable, as it plays a pivotal role in bringing life-saving medications to patients worldwide.
Technology transfer is essential for ensuring the successful development, manufacturing, and distribution of pharmaceuticals. It facilitates the adoption of new technologies and processes, enabling companies to optimize their operations and improve the quality of their products. Moreover, technology transfer helps to bridge the gap between research and development and commercialization, accelerating the availability of new treatments for patients.
Challenges and Opportunities
The pharmaceutical industry faces various challenges and opportunities in the context of technology transfer.
- Challenges: Technology transfer is a complex process that involves various stakeholders with different objectives and priorities. Coordinating these stakeholders and ensuring a smooth transfer of knowledge and technology can be challenging. Other challenges include intellectual property protection, regulatory compliance, and the need to maintain consistency in product quality.
- Opportunities: Technology transfer presents numerous opportunities for pharmaceutical companies. It enables them to access new technologies, expand their product portfolio, and enter new markets. Additionally, technology transfer can help companies reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance their competitive advantage.
Stakeholders in Technology Transfer
Technology transfer involves various stakeholders, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
- Technology Provider: The technology provider is the organization that possesses the knowledge, skills, and technology being transferred. This could be a research institute, a pharmaceutical company, or a university.
- Technology Recipient: The technology recipient is the organization that receives the knowledge, skills, and technology. This could be another pharmaceutical company, a manufacturing facility, or a regulatory agency.
- Regulatory Authorities: Regulatory authorities play a crucial role in ensuring that technology transfer is conducted in compliance with relevant regulations. They ensure that the transferred technology meets safety, efficacy, and quality standards.
- Consultants and Experts: Consultants and experts can provide specialized knowledge and expertise in various aspects of technology transfer, such as intellectual property, regulatory compliance, and process validation.
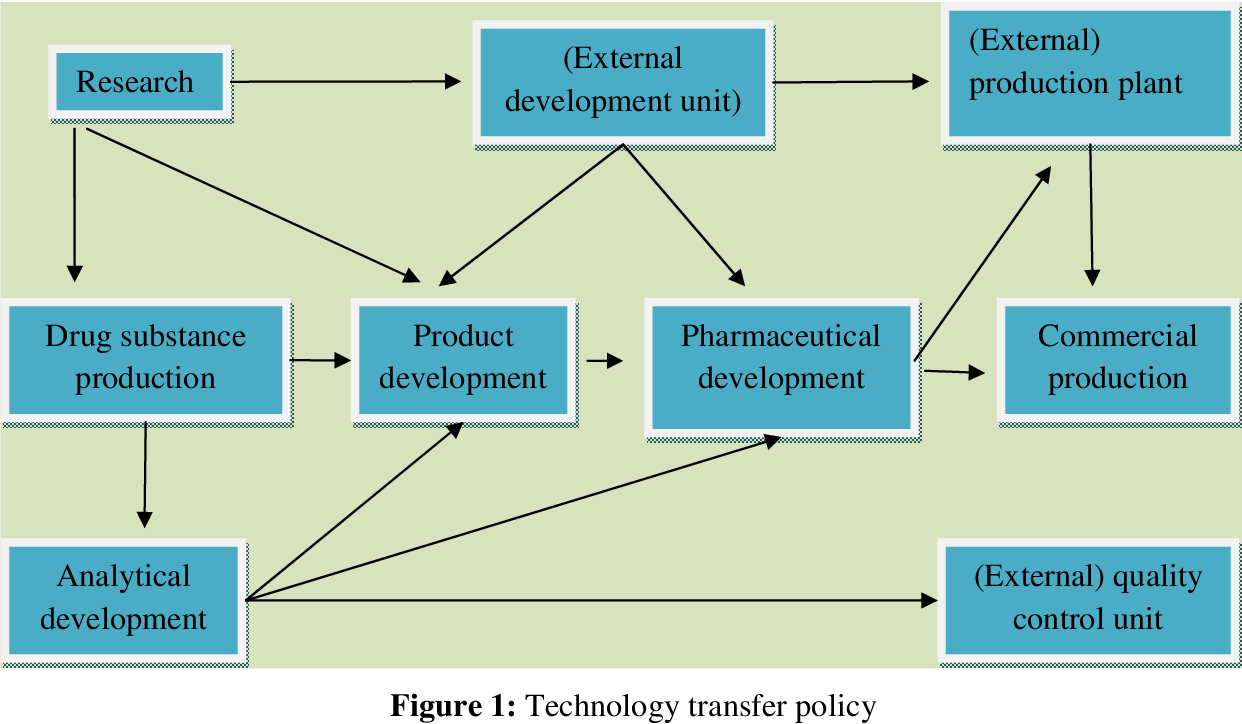
Key Components of Pharmaceutical Technology Transfer
Pharmaceutical technology transfer is a critical process that involves the transfer of knowledge, processes, and equipment from one location to another. It’s a crucial step in bringing new drugs and therapies to market, ensuring consistent quality and efficacy.
Phases of Pharmaceutical Technology Transfer
The successful implementation of pharmaceutical technology transfer depends on a well-defined and structured approach. This involves several distinct phases, each with its own set of objectives and deliverables.
- Process Development: This phase focuses on optimizing the manufacturing process to achieve the desired quality and yield. It involves extensive experimentation and data analysis to identify the most efficient and reliable production methods. Key activities include:
- Defining the target product profile and specifications.
- Developing and validating analytical methods for raw materials, intermediates, and finished products.
- Designing and optimizing the manufacturing process, including formulation, filling, and packaging.
- Conducting feasibility studies and pilot runs to assess process scalability and robustness.
- Validation: This phase ensures that the transferred process consistently meets pre-defined quality standards. It involves rigorous testing and documentation to demonstrate that the process is reliable and reproducible. Key activities include:
- Performing process validation studies to demonstrate the consistency and control of the manufacturing process.
- Establishing and documenting standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all critical process steps.
- Conducting equipment qualification and calibration to ensure their suitability for the intended use.
- Evaluating the impact of changes to the process or equipment and ensuring that any changes are properly documented and validated.
- Scale-Up: This phase involves increasing the production capacity of the manufacturing process to meet commercial demand. It requires careful consideration of the impact of scale on process parameters, equipment, and infrastructure. Key activities include:
- Designing and implementing the scale-up strategy, considering factors such as equipment capacity, process control, and material handling.
- Performing process simulations and pilot runs to assess the feasibility and performance of the scaled-up process.
- Adapting equipment and infrastructure to accommodate the increased production volume.
- Validating the scaled-up process to ensure consistent quality and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Documentation and Regulatory Requirements
Proper documentation is essential for ensuring the success and compliance of pharmaceutical technology transfer. It provides a comprehensive record of the process, supporting regulatory audits and ensuring consistent quality.
- Technology Transfer Protocol: A detailed document outlining the scope, objectives, and timelines of the technology transfer project. It defines the responsibilities of each party involved and the criteria for successful completion.
- Process Validation Documents: These documents provide evidence of the process’s ability to consistently meet predefined quality standards. They include validation protocols, reports, and summary documents.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Detailed instructions for performing critical process steps. They ensure consistency and reproducibility, minimizing the risk of errors or deviations.
- Batch Records: Detailed records of each production batch, documenting the process parameters, materials used, and any deviations or observations. They provide a complete history of the manufacturing process.
- Regulatory Submissions: Depending on the nature of the technology transfer, regulatory submissions may be required. These submissions document the process, equipment, and quality control measures, demonstrating compliance with regulatory standards.
Knowledge Management and Training
Effective knowledge management and training are crucial for successful technology transfer. They ensure that the receiving site has the necessary expertise and understanding to operate the process efficiently and consistently.
- Knowledge Transfer Documents: These documents provide a comprehensive overview of the process, equipment, and procedures. They may include process descriptions, technical specifications, SOPs, and training materials.
- On-site Training: Hands-on training at the receiving site, allowing personnel to gain practical experience with the process and equipment. It includes theoretical instruction, practical demonstrations, and supervised practice.
- Technical Support: Providing ongoing technical support to the receiving site during the implementation and operational phases. This may involve troubleshooting issues, answering questions, and providing guidance on process optimization.
- Knowledge Management Systems: Implementing a knowledge management system to capture, organize, and share critical information related to the technology transfer. This can include databases, document repositories, and online collaboration platforms.
Technology Transfer Models and Approaches
The selection of an appropriate technology transfer model is crucial for successful pharmaceutical technology transfer. Various models cater to different needs and circumstances, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models and their nuances helps stakeholders make informed decisions for their specific technology transfer projects.
Licensing
Licensing is a common technology transfer model where the technology owner (licensor) grants a license to another company (licensee) to use, manufacture, and sell the technology. This model allows the licensor to leverage its technology without significant investment in manufacturing or marketing.
- Advantages:
- Minimal capital investment for the licensor
- Access to wider markets through the licensee’s distribution network
- Potential for royalty income for the licensor
- Disadvantages:
- Limited control over the technology’s development and commercialization
- Potential for disputes over royalty payments or intellectual property rights
- Risk of losing competitive advantage if the licensee becomes a competitor
Joint Ventures
Joint ventures involve the creation of a new entity by two or more companies to develop and commercialize a technology. This model allows companies to pool resources, expertise, and market access.
- Advantages:
- Shared risks and costs
- Combined expertise and resources
- Enhanced market access through the combined network
- Disadvantages:
- Potential for conflicts of interest between partners
- Complexity in decision-making and management
- Risk of losing control over the technology if the partnership dissolves
Outsourcing
Outsourcing involves contracting out specific aspects of the technology transfer process to external companies. This can include manufacturing, testing, or regulatory support.
- Advantages:
- Cost savings by leveraging specialized expertise and resources
- Flexibility in managing the technology transfer process
- Access to specialized equipment and facilities
- Disadvantages:
- Potential for loss of control over the technology transfer process
- Risk of intellectual property infringement or confidentiality breaches
- Dependence on external partners for critical aspects of the technology transfer
Technology Transfer Facilitators and Consultants
Technology transfer facilitators and consultants play a crucial role in facilitating the technology transfer process. They provide expertise in various aspects of technology transfer, including:
- Market analysis and identification of potential partners
- Negotiation of technology transfer agreements
- Due diligence and risk assessment
- Project management and implementation support
- Regulatory compliance and intellectual property protection
Facilitators and consultants can act as intermediaries between technology owners and potential licensees, ensuring smooth and efficient technology transfer. They bring valuable insights and experience, helping to mitigate risks and maximize the chances of success.
Impact of Technology Transfer on Innovation: Pharmaceutical Technology Transfer

Technology transfer plays a pivotal role in fostering innovation and driving the development of new pharmaceuticals. It serves as a bridge between research and development, enabling the translation of scientific discoveries into tangible products that benefit patients.
Technology Transfer as a Catalyst for Innovation
Technology transfer facilitates the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and resources between academic institutions, research organizations, and pharmaceutical companies. This collaboration fosters innovation by:
- Accelerating Drug Discovery and Development: By transferring technologies and expertise, pharmaceutical companies can leverage the latest scientific advancements and accelerate the development of new drugs.
- Promoting Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Technology transfer encourages collaboration between researchers from different fields, leading to novel and innovative approaches to drug discovery and development.
- Providing Access to Specialized Equipment and Facilities: Universities and research institutions often have access to specialized equipment and facilities that may not be readily available to pharmaceutical companies. Technology transfer allows companies to leverage these resources and accelerate their research efforts.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: Technology transfer can foster entrepreneurship by providing researchers with the resources and support to commercialize their inventions and create new pharmaceutical companies.
Examples of Successful Technology Transfer Initiatives
Several successful technology transfer initiatives have led to breakthroughs in drug discovery and development. Some notable examples include:
- The development of the first monoclonal antibody, “OKT3,” by Orthoclone. This groundbreaking technology, developed at Stanford University, revolutionized the treatment of organ transplant rejection. The technology transfer from Stanford to Orthoclone allowed for the rapid development and commercialization of this life-saving drug.
- The development of the HIV drug “Combivir” by GlaxoSmithKline. This drug, developed at the University of California, San Francisco, was a major breakthrough in the fight against HIV/AIDS. The technology transfer from the university to GlaxoSmithKline enabled the rapid development and commercialization of this essential drug.
- The development of the cancer drug “Herceptin” by Genentech. This drug, developed at the University of California, San Francisco, targets a specific protein found in certain breast cancers. The technology transfer from the university to Genentech led to the development and commercialization of this highly effective treatment for breast cancer.
Impact of Technology Transfer on Access to Affordable Medicines in Developing Countries
Technology transfer plays a crucial role in ensuring access to affordable medicines in developing countries. By facilitating the transfer of knowledge, expertise, and technology, technology transfer can help:
- Promote local manufacturing: Technology transfer can enable developing countries to establish their own pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, reducing reliance on imports and lowering the cost of medicines.
- Develop affordable generic drugs: Technology transfer can support the development and production of affordable generic drugs, making essential medicines accessible to a wider population.
- Strengthen healthcare systems: By providing access to new technologies and training, technology transfer can contribute to the development of stronger healthcare systems in developing countries.
Future Trends in Pharmaceutical Technology Transfer
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by advancements in technology, evolving regulatory landscapes, and a growing focus on patient-centricity. This dynamic environment is shaping the future of pharmaceutical technology transfer, demanding innovative approaches and strategies to ensure seamless knowledge and expertise exchange between stakeholders.
Impact of Digitalization, Artificial Intelligence, and Automation
Digitalization, artificial intelligence (AI), and automation are poised to revolutionize pharmaceutical technology transfer processes, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and collaboration.
- Digital Platforms and Data Management: Secure cloud-based platforms are emerging as central hubs for managing technology transfer documentation, intellectual property, and data. These platforms facilitate real-time access, version control, and streamlined communication, enabling efficient collaboration among stakeholders. For instance, the platform developed by [insert company name] provides a centralized repository for all technology transfer documents, including protocols, reports, and data, ensuring consistency and accessibility for all involved parties.
- AI-powered Automation: AI algorithms can automate repetitive tasks such as data analysis, document review, and risk assessment, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. For example, AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential risks and suggest mitigation strategies during technology transfer, ensuring smoother transitions. The use of AI-driven tools like [insert tool name] can automate the process of identifying and analyzing potential risks associated with technology transfer, minimizing delays and ensuring a more efficient process.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: VR and AR technologies offer immersive training experiences, allowing scientists and engineers to virtually interact with equipment and processes, gaining hands-on experience without the need for physical travel. This reduces training time and costs, enabling faster technology transfer. Companies like [insert company name] are using VR simulations to train personnel on complex manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent and efficient knowledge transfer across different sites.
Role of Open Innovation and Collaborative Research
Open innovation and collaborative research are gaining traction in the pharmaceutical industry, fostering knowledge sharing and accelerating technology transfer.
- Strategic Partnerships: Pharmaceutical companies are forming strategic partnerships with academic institutions, research organizations, and other industry players to access cutting-edge technologies and expertise. These collaborations can lead to faster development and transfer of new therapies, ultimately benefiting patients. The collaboration between [insert company name] and [insert university name] resulted in the rapid development and transfer of a new cancer therapy, showcasing the benefits of open innovation.
- Crowdsourcing and Open-source Platforms: Crowdsourcing initiatives and open-source platforms allow companies to tap into a global pool of talent and expertise, accelerating innovation and knowledge sharing. For example, the open-source platform [insert platform name] allows researchers to share data and protocols, facilitating faster technology transfer and collaborative research. This platform has been instrumental in accelerating the development of new vaccines and treatments, showcasing the power of open innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Technology Transfer Hubs: Dedicated technology transfer hubs are emerging to facilitate knowledge exchange and collaboration between academia, industry, and government agencies. These hubs provide resources, expertise, and infrastructure to support the development and transfer of new technologies, fostering a thriving ecosystem for innovation. The [insert name of technology transfer hub] is a prime example of such a hub, providing resources and expertise to support the development and transfer of new technologies, fostering a thriving ecosystem for innovation.
Conclusive Thoughts
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of pharmaceutical innovation, technology transfer remains a vital catalyst for progress. By fostering collaboration, promoting knowledge sharing, and embracing technological advancements, we can ensure that groundbreaking discoveries translate into tangible benefits for patients. The future of pharmaceutical technology transfer holds immense promise for improving global health outcomes, expanding access to life-saving therapies, and shaping a healthier world for generations to come.
Pharmaceutical technology transfer plays a crucial role in bringing new therapies to market. One area seeing rapid innovation is dental implants, with exciting advancements like the new dental implant technology 2024 that promises faster healing and improved integration. This transfer of knowledge and expertise is essential to ensure these new technologies reach patients effectively and safely.





