Pallet Technology: A Foundation of Modern Supply Chains
Pallet technology, a seemingly simple yet profoundly impactful element, underpins the efficient movement of goods across the globe. From its humble beginnings as a wooden platform, pallets have evolved into […]
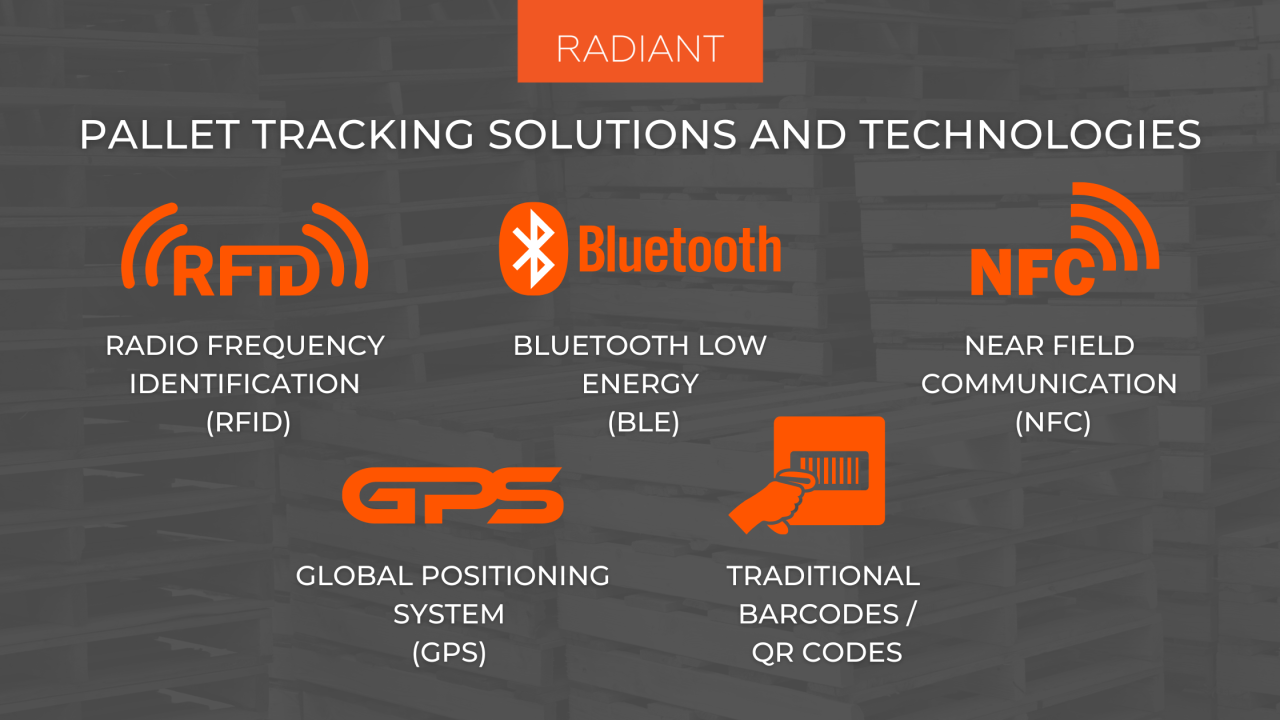
Pallet technology, a seemingly simple yet profoundly impactful element, underpins the efficient movement of goods across the globe. From its humble beginnings as a wooden platform, pallets have evolved into a cornerstone of modern supply chains, facilitating the seamless flow of products from manufacturers to consumers.
The versatility of pallets lies in their ability to standardize the handling and storage of diverse goods. They provide a stable base for stacking, allowing for efficient utilization of warehouse space and optimized loading for transportation. This standardized approach has revolutionized logistics, reducing handling time, minimizing damage, and streamlining inventory management.
Pallet Technology
![]()
Pallets are essential components in modern supply chains, facilitating the efficient movement and storage of goods. They are flat platforms made of wood, plastic, or metal, designed to support and stabilize loads for easy handling and transportation. This technology has revolutionized material handling, transforming the way goods are moved, stored, and shipped across the globe.
Historical Evolution of Pallet Technology
Pallet technology has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to changing needs and advancements in material handling practices. The earliest pallets were simple wooden platforms used for stacking and transporting goods in the early 20th century. The introduction of forklifts in the 1930s further revolutionized pallet technology, enabling faster and more efficient loading and unloading of goods. The development of standardized pallet sizes in the 1950s facilitated interoperability and streamlined logistics operations. Today, pallets are available in various materials, sizes, and configurations, catering to diverse industry requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pallet Technology
Pallets offer numerous advantages, making them indispensable in various industries.
- Improved Efficiency: Pallets streamline material handling processes, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity. Forklifts and other handling equipment can easily lift and move pallets, minimizing handling time and effort.
- Enhanced Storage Capacity: Pallets allow for efficient stacking of goods, maximizing storage space and optimizing warehouse utilization. They provide a stable base for stacking, ensuring load stability and preventing damage.
- Reduced Damage: Pallets protect goods from damage during transportation and storage. They distribute weight evenly, minimizing the risk of crushing or other damage.
- Simplified Transportation: Pallets facilitate seamless transportation of goods by truck, rail, or ship. Their standardized dimensions allow for easy loading and unloading on various transport vehicles.
However, pallets also have some disadvantages:
- Cost: Pallets can be expensive, especially when considering the costs of purchasing, maintaining, and disposing of them.
- Space Consumption: Pallets occupy space in warehouses and transportation vehicles, especially when empty.
- Environmental Concerns: Wooden pallets can contribute to deforestation, while plastic pallets can pose environmental hazards if not properly disposed of.
Different Pallet Types and Applications
The pallet industry offers a wide variety of pallet types, each designed for specific applications.
- Wood Pallets: Wooden pallets are the most common type, offering a good balance of strength, durability, and affordability. They are suitable for various applications, including general warehousing, transportation, and industrial settings.
- Plastic Pallets: Plastic pallets are becoming increasingly popular due to their durability, resistance to moisture and chemicals, and ease of cleaning. They are often used in the food and beverage industry, where hygiene is crucial.
- Metal Pallets: Metal pallets are highly durable and can withstand heavy loads. They are commonly used in industries that require high-strength pallets, such as automotive and manufacturing.
Materials and Construction
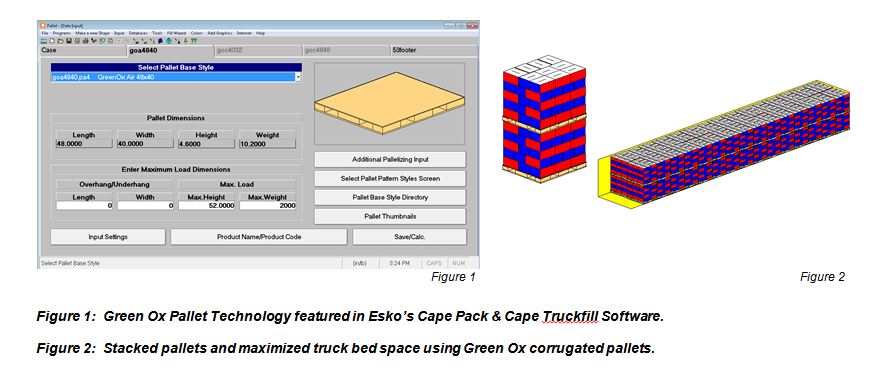
Pallet construction materials play a crucial role in determining their durability, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Understanding the properties and advantages of different materials is essential for selecting the right pallet for your needs.
Common Pallet Materials
Pallet construction materials are diverse, each with unique properties and applications. The most prevalent materials include wood, plastic, and metal.
- Wood: The most traditional and widely used material for pallet construction. Wood pallets offer several advantages, including:
- Renewable resource: Wood is a sustainable and readily available material.
- Cost-effective: Wood pallets are generally more affordable than other materials.
- Versatile: Wood can be easily modified and repaired, making it suitable for various applications.
- Plastic: Plastic pallets offer several benefits over wood, including:
- Durability: Plastic pallets are resistant to moisture, pests, and chemicals, making them suitable for demanding environments.
- Lightweight: Plastic pallets are lighter than wood, reducing transportation costs and handling effort.
- Hygienic: Plastic pallets are easy to clean and sanitize, making them ideal for food and pharmaceutical industries.
- Metal: Metal pallets are known for their exceptional strength and durability. They are often used in heavy-duty applications where weight capacity and longevity are critical.
- High strength: Metal pallets can withstand significant weight and impact loads.
- Long lifespan: Metal pallets are resistant to wear and tear, providing a long service life.
- Recyclable: Metal pallets can be recycled and reused, promoting sustainability.
Pallet Construction Methods
Pallet construction methods significantly influence their durability and cost. The most common methods include:
- Stringer construction: This method involves using horizontal stringers (beams) to support the pallet deck. The stringers are typically made of wood or metal and are connected to the deck boards using nails, screws, or other fasteners.
- Advantages: Stringer construction is a cost-effective and versatile method, suitable for various pallet sizes and configurations.
- Disadvantages: Stringer construction can be less durable than other methods, especially in high-impact environments.
- Block construction: This method uses blocks or posts to support the pallet deck. Blocks are typically made of wood or plastic and are attached to the deck boards using screws or other fasteners.
- Advantages: Block construction offers increased durability and stability compared to stringer construction.
- Disadvantages: Block construction can be more expensive than stringer construction due to the use of additional materials.
- Nested construction: This method uses a series of nested components that can be easily assembled and disassembled. Nested pallets are often made of plastic and are designed for space-saving storage and transportation.
- Advantages: Nested construction is highly efficient and allows for compact storage, reducing transportation costs.
- Disadvantages: Nested construction can be more expensive than traditional methods, and the components may not be as durable as solid construction methods.
Pallet Types and Applications
| Pallet Type | Material | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Pallet | Wood | General cargo, warehousing, distribution |
| Heavy-Duty Pallet | Wood, Metal | Industrial applications, heavy loads, construction |
| Export Pallet | Wood, Heat-Treated | International shipping, complying with ISPM 15 regulations |
| Plastic Pallet | Plastic | Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemical industries |
| Metal Pallet | Metal | Heavy-duty applications, automotive, aerospace |
Pallet Handling and Storage: Pallet Technology
Pallet handling and storage are critical aspects of warehouse and logistics operations, impacting efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. This section delves into the equipment, methods, and safety considerations involved in effectively managing pallets throughout the supply chain.
Equipment Used for Handling and Storing Pallets
Efficient pallet handling and storage require specialized equipment. The most common types include:
- Forklifts: Forklifts are versatile machines that lift and move pallets horizontally and vertically. They come in various sizes and configurations to suit different load capacities and working environments.
- Pallet Jacks: Pallet jacks are manual or powered devices used to lift and move pallets short distances. They are ideal for moving pallets within a warehouse or loading dock.
- Racking Systems: Racking systems provide organized storage for pallets, maximizing warehouse space and allowing for efficient inventory management. Common types include:
- Pallet Racking: This type of racking consists of upright frames and beams that support pallets. It offers high storage capacity and easy access to individual pallets.
- Drive-in/Drive-through Racking: This system allows for forklift access from one or both ends, enabling efficient storage of large quantities of the same product. It’s suitable for first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management.
- Push-back Racking: This system utilizes a rolling track to push pallets back as new pallets are loaded. It maximizes storage density but requires careful planning to ensure proper load distribution.
- Carousels: Carousels are automated storage systems that rotate pallets to bring the desired one to the operator. They are ideal for high-volume, fast-picking operations.
Pallet Stacking Methods
Pallet stacking methods directly impact storage efficiency and safety. Some common methods include:
- Single Stacking: This method involves stacking pallets directly on top of each other, creating a stable column. It’s suitable for low-volume storage or when access to individual pallets is frequently required.
- Double Stacking: Double stacking involves placing two pallets on top of each other, increasing storage density. It requires careful consideration of load weight and pallet stability to prevent collapse.
- Block Stacking: Block stacking involves arranging pallets in a rectangular block configuration, maximizing space utilization. This method is suitable for high-volume storage and allows for efficient access to individual pallets.
Safety Considerations for Pallet Handling and Storage
Ensuring safety during pallet handling and storage is crucial to prevent accidents and injuries. Key considerations include:
- Proper Training: Operators should be properly trained in the safe operation of handling equipment, including forklifts, pallet jacks, and other lifting devices. This training should cover safe operating procedures, emergency procedures, and load capacity limitations.
- Load Capacity: It’s essential to ensure that the load capacity of the equipment used for pallet handling is not exceeded. Exceeding load capacity can lead to equipment failure and accidents.
- Stacking Stability: Pallets should be stacked in a way that ensures stability and prevents collapse. Proper stacking methods, such as using interlock stacking or bracing, can help achieve this.
- Clear Aisles: Maintaining clear aisles and walkways around pallet storage areas is essential for safe movement of equipment and personnel.
- Proper Lighting: Adequate lighting in pallet storage areas is essential for visibility and safe operation.
- Floor Condition: The floor in pallet storage areas should be level, strong, and free of debris to prevent accidents.
Pallet Handling Methods and Their Advantages and Disadvantages, Pallet technology
| Pallet Handling Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Forklifts | Versatile, high load capacity, can lift and move pallets vertically, can operate in various environments. | High operating cost, requires skilled operators, can damage pallets if not operated correctly. |
| Pallet Jacks | Low cost, easy to operate, suitable for short-distance movement. | Limited load capacity, cannot lift pallets vertically. |
| Conveyor Systems | Highly efficient for moving pallets over long distances, can be automated. | High initial cost, limited flexibility, not suitable for all types of pallets. |
| Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Highly efficient, can operate autonomously, reduce labor costs. | High initial cost, limited flexibility, may require modifications to existing infrastructure. |
Last Point

As we move forward, pallet technology continues to evolve, embracing innovation and sustainability. The integration of automation, data analytics, and advanced materials promises to further enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and pave the way for a more sustainable future in logistics. The humble pallet, a seemingly simple invention, stands as a testament to the power of innovation in shaping the modern world.
Pallet technology has come a long way, from simple wooden platforms to automated systems that streamline warehouse operations. Much like how the VW Atlas technology package enhances driving experience with advanced features, pallet technology plays a crucial role in optimizing logistics and efficiency.
From automated guided vehicles to intelligent stacking systems, the future of pallet technology promises even greater advancements in the world of supply chain management.




