Pallet Technology: Revolutionizing Supply Chains
Pallet technology, a seemingly simple yet crucial element of modern logistics, has revolutionized the way goods are moved and stored around the world. From its humble beginnings as a wooden […]
Pallet technology, a seemingly simple yet crucial element of modern logistics, has revolutionized the way goods are moved and stored around the world. From its humble beginnings as a wooden platform, pallet technology has evolved significantly, embracing innovation and efficiency to optimize supply chains and streamline operations.
The impact of pallet technology extends far beyond the warehouse floor, influencing everything from transportation costs and inventory management to sustainability practices and the future of logistics. By understanding the principles, types, and applications of pallet technology, businesses can unlock a wealth of opportunities to enhance their operations and achieve greater success.
Types of Pallets

Pallets are essential for the efficient movement and storage of goods. They serve as a platform for stacking and transporting materials, making them a vital component of supply chains worldwide. Pallets are available in a variety of types, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
Types of Pallets
Different types of pallets are available, each suited to particular applications. These pallets are made from various materials, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Wood Pallets: Wood pallets are the most common type, known for their affordability and versatility. They are typically made from softwood or hardwood, and their construction can vary.
- Plastic Pallets: Plastic pallets are becoming increasingly popular due to their durability, hygiene, and recyclability. They are resistant to moisture, chemicals, and pests, making them ideal for food and pharmaceutical applications.
- Metal Pallets: Metal pallets, often made from steel or aluminum, offer exceptional strength and durability. They are particularly well-suited for heavy-duty applications and environments where fire hazards are a concern.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pallet Types
The choice of pallet type depends on several factors, including the nature of the goods being transported, the environment they will be stored in, and budget considerations.
Wood Pallets
- Advantages:
- Relatively inexpensive
- Widely available
- Versatile for various applications
- Can be repaired and reused
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to moisture damage
- May harbor pests
- Not as durable as other materials
- May require heat treatment for international shipping
Plastic Pallets
- Advantages:
- Durable and long-lasting
- Resistant to moisture, chemicals, and pests
- Easy to clean and sanitize
- Recyclable
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive than wood pallets
- May be susceptible to damage from extreme temperatures
- May not be compatible with all forklifts
Metal Pallets
- Advantages:
- Extremely strong and durable
- Resistant to fire and other hazards
- Long lifespan
- Disadvantages:
- Most expensive type of pallet
- Heavy and difficult to handle
- May damage floors if not handled carefully
Comparison Table, Pallet technology
The table below provides a summary of the key characteristics of different pallet types:
| Pallet Type | Material | Dimensions (Approximate) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood Pallet | Softwood or Hardwood | 48″ x 40″ | General cargo, industrial goods, construction materials |
| Plastic Pallet | Polyethylene (PE) or Polypropylene (PP) | 48″ x 40″ | Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, retail |
| Metal Pallet | Steel or Aluminum | 48″ x 40″ | Heavy-duty applications, hazardous materials, environments with fire hazards |
Pallet Manufacturing and Production
Pallet manufacturing is a complex process that involves various steps, from sourcing raw materials to quality control. Understanding these steps is essential for anyone involved in the pallet industry, from manufacturers to users. This section delves into the intricacies of pallet production, exploring different manufacturing techniques and their advantages and disadvantages.
Pallet Manufacturing Techniques
Pallet manufacturing involves various techniques, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. The choice of technique often depends on factors such as the type of pallet required, the desired production volume, and cost considerations.
- Heat Treatment: This technique involves exposing wooden pallets to high temperatures to kill any harmful pests or organisms. Heat treatment is a common method for ensuring that pallets meet international phytosanitary standards, allowing them to be exported to various countries.
- Methyl Bromide Fumigation: This method involves using methyl bromide gas to fumigate wooden pallets, eliminating pests and ensuring compliance with international regulations. However, methyl bromide is a harmful chemical, and its use is being phased out in many countries due to environmental concerns.
- Chemical Treatment: Some pallet manufacturers use chemical treatments to protect wood from decay, insects, and other threats. However, chemical treatments can be harmful to the environment and may not be suitable for all applications.
- Pressure Treatment: This method involves injecting wood with preservatives under pressure, enhancing its durability and resistance to decay. Pressure treatment is often used for pallets intended for outdoor use or in harsh environments.
- Recycling and Repurposing: The use of recycled and repurposed materials is becoming increasingly popular in pallet manufacturing. This sustainable approach involves using salvaged wood or other materials to create new pallets, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Comparison of Pallet Manufacturing Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Environmentally friendly, meets international standards | Can be expensive, requires specialized equipment |
| Methyl Bromide Fumigation | Effective pest control, meets international standards | Harmful chemical, being phased out in many countries |
| Chemical Treatment | Provides protection against decay and insects | Can be harmful to the environment, may not be suitable for all applications |
| Pressure Treatment | Increases durability and resistance to decay | Can be expensive, requires specialized equipment |
| Recycling and Repurposing | Sustainable, reduces waste and environmental impact | May not be suitable for all applications, quality can vary |
Sustainable Pallet Technology
The growing awareness of environmental concerns has led to a shift towards sustainable practices in various industries, including pallet manufacturing and use. Sustainable pallet technology focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of pallets throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal.
Environmental Considerations
Pallet production and use have a significant impact on the environment. The manufacturing process often involves the use of natural resources like wood, which can lead to deforestation. Additionally, the transportation of pallets and the disposal of old or damaged pallets contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Pallet Materials
Several sustainable materials are being used to create pallets, offering environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional wood pallets.
- Recycled Plastic: Plastic pallets made from recycled materials reduce the need for virgin plastic production and decrease landfill waste. They are durable, moisture-resistant, and can be recycled multiple times.
- Bamboo: Bamboo is a fast-growing and renewable resource that can be used to create sustainable pallets. Bamboo pallets are lightweight, strong, and biodegradable.
- Recycled Paper: Paper pallets made from recycled paper are biodegradable and compostable, offering a sustainable option for single-use applications.
Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
Several sustainable manufacturing processes are being implemented to reduce the environmental impact of pallet production.
- Efficient Wood Utilization: Manufacturers are adopting techniques that maximize the use of wood resources by using scraps and offcuts to create pallets. This minimizes waste and reduces the demand for virgin wood.
- Energy-Efficient Manufacturing: Implementing energy-efficient machinery and processes in pallet factories can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable Packaging: Using recycled or biodegradable packaging materials for pallet transport and storage can further reduce environmental impact.
Pallet Pooling
Pallet pooling is a system where pallets are shared and reused by multiple companies. This eliminates the need for individual companies to purchase and manage their own pallet inventory, leading to several sustainability benefits.
- Reduced Pallet Production: Pallet pooling reduces the demand for new pallet production, minimizing the use of natural resources and reducing waste.
- Reduced Transportation: By sharing pallets, companies can reduce the number of empty pallets transported, decreasing fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Increased Pallet Lifespan: Pallets in a pooling system are regularly maintained and repaired, extending their lifespan and reducing the need for replacements.
Future Trends in Pallet Technology
The pallet industry is constantly evolving, driven by the need for increased efficiency, sustainability, and technological advancements in the supply chain. Emerging trends in pallet technology are reshaping how pallets are designed, manufactured, handled, and tracked, leading to significant improvements in logistics and warehousing operations.
Automation and Robotics in Pallet Handling
Automation and robotics are playing an increasingly important role in pallet handling, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are autonomous robots that navigate warehouses and distribution centers without human intervention, transporting pallets to designated locations. They eliminate the need for manual handling, reducing labor costs and improving accuracy.
- Robotic Pallet Stackers and Depalletizers: Robotic systems can automatically stack and depalletize pallets, performing tasks that are often physically demanding and time-consuming for human workers. These robots increase productivity and minimize the risk of workplace injuries.
- Automated Pallet Sorting Systems: Automated sorting systems use sensors and robotics to efficiently sort pallets based on various criteria, such as destination, product type, or delivery date. This automation improves accuracy and speeds up the sorting process, leading to faster order fulfillment.
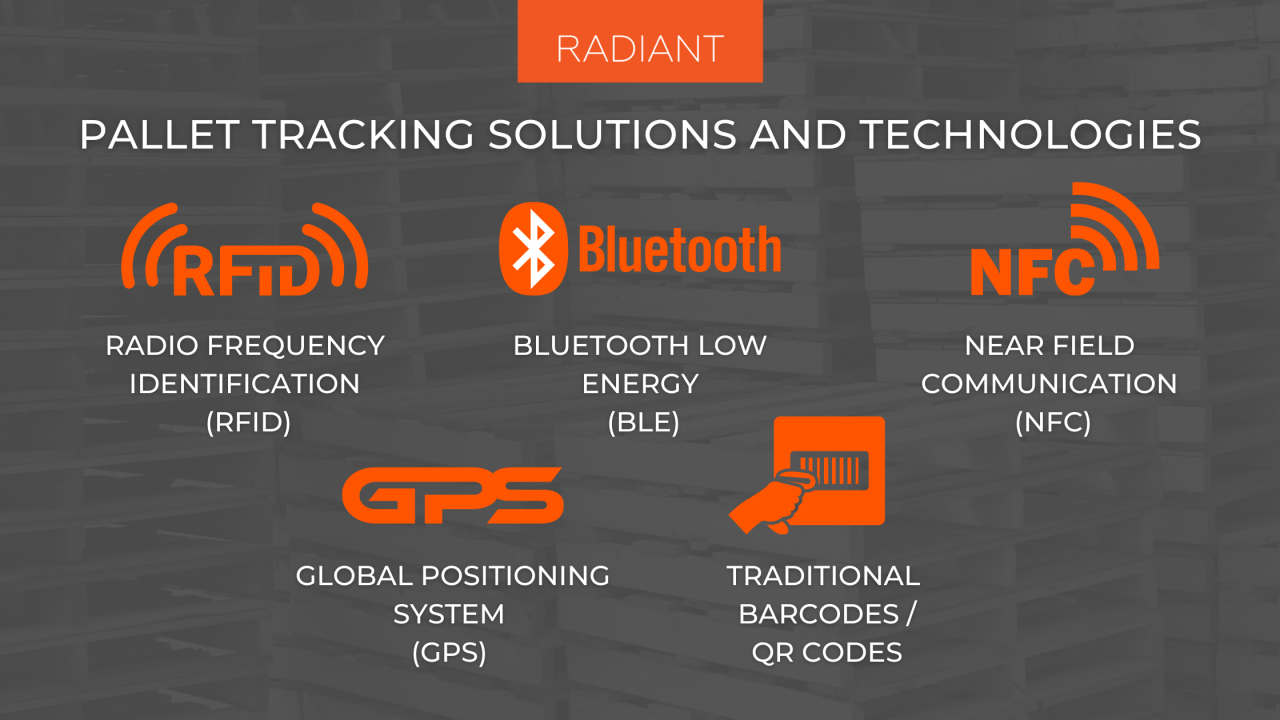
Smart Pallets and Data Analytics
Smart pallets are equipped with sensors and tracking devices that collect data on pallet location, condition, and usage. This data can be used to optimize logistics operations and enhance supply chain visibility.
- Real-Time Tracking: Smart pallets provide real-time tracking of pallet movement throughout the supply chain, enabling businesses to monitor their inventory and shipments in detail.
- Condition Monitoring: Sensors embedded in smart pallets can monitor factors such as temperature, humidity, and impact, providing insights into pallet condition and identifying potential issues early on.
- Data Analytics for Optimization: Data collected from smart pallets can be analyzed to optimize pallet utilization, reduce waste, and improve efficiency in logistics operations.
Sustainable Pallet Technology
Sustainable pallet technology focuses on minimizing environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and resource utilization.
- Recyclable and Reusable Pallets: Increasingly, companies are adopting pallets made from recycled materials or designed for multiple uses, reducing the need for new pallet production and minimizing waste.
- Lightweight Pallet Designs: Innovative pallet designs using lightweight materials, such as composites or bamboo, reduce transportation costs and carbon emissions.
- Closed-Loop Pallet Systems: Closed-loop systems involve collecting used pallets, repairing them, and reusing them within a specific supply chain, reducing the need for new pallet production and promoting circularity.
Future Advancements in Pallet Technology
| Advancement | Expected Benefits |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Pallet Optimization | AI algorithms can analyze data from smart pallets to optimize pallet design, routing, and utilization, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings. |
| 3D Printing of Pallets | 3D printing allows for the creation of customized pallets on demand, reducing lead times and enabling the production of lightweight, durable pallets with specific functionalities. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) Integration | Integrating pallets into the IoT ecosystem will enable real-time data sharing and communication between pallets, warehouse systems, and logistics platforms, further enhancing supply chain visibility and optimization. |
Summary: Pallet Technology
![]()
As we move forward, the future of pallet technology promises exciting advancements, driven by automation, robotics, and the emergence of smart pallets. These innovations will continue to reshape the landscape of supply chains, creating a more efficient, sustainable, and interconnected global marketplace. By embracing the power of pallet technology, businesses can navigate the complexities of modern logistics and unlock a future of unparalleled efficiency and growth.
Pallet technology has come a long way, with innovations like RFID tracking and automated pallet handling systems becoming increasingly commonplace. This technology is even influencing the automotive industry, as seen in the 2024 Atlas SE vs SE with technology comparison, where features like advanced driver-assist systems and infotainment screens are becoming as crucial as the engine itself.
While the focus might be on the car, the underlying logistics, including efficient pallet handling, are essential for a seamless automotive experience.




