Music Technology Class: Shaping the Soundscape
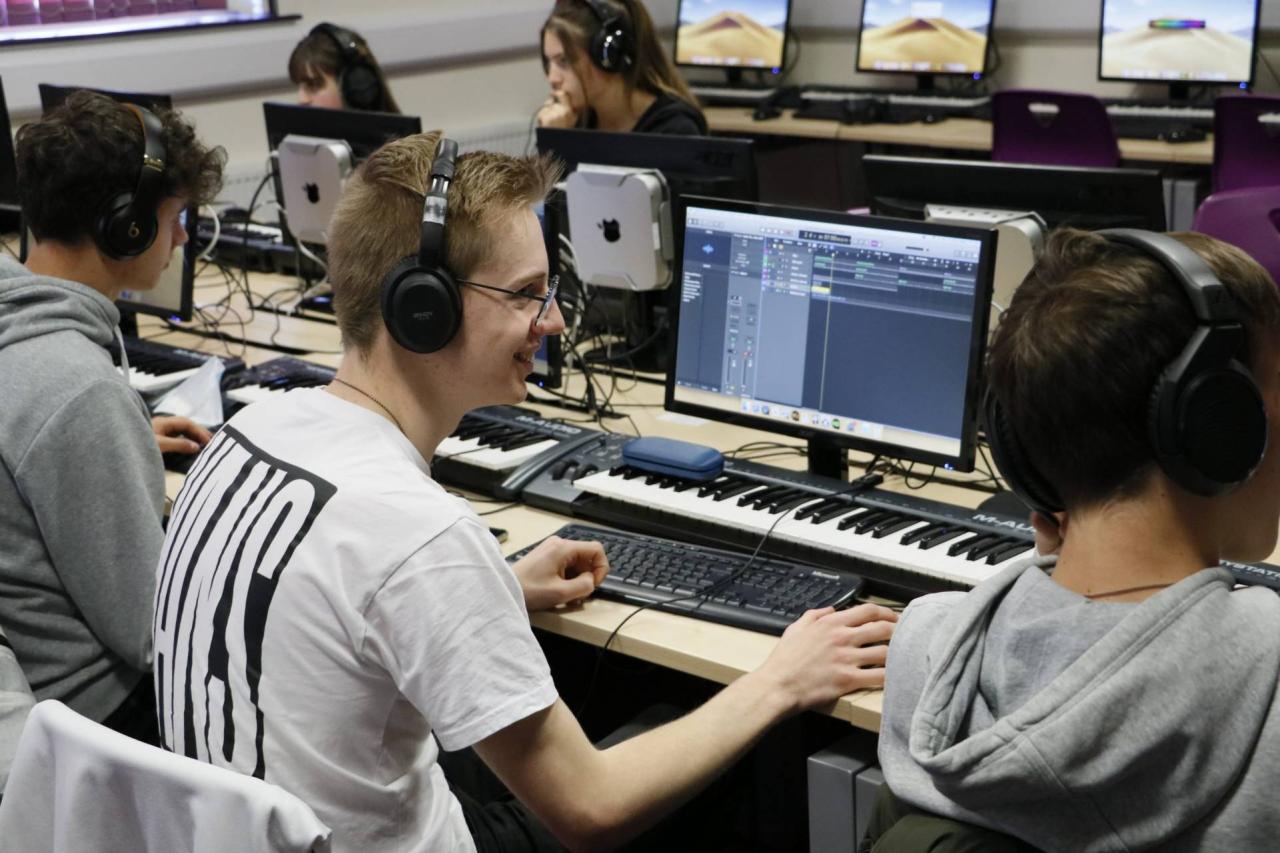
Music technology class sets the stage for an exploration of how technology has transformed the creation, performance, and consumption of music. From the evolution of recording techniques to the rise […]

Music technology class sets the stage for an exploration of how technology has transformed the creation, performance, and consumption of music. From the evolution of recording techniques to the rise of digital music production, this class delves into the fascinating world of music technology, its impact on different genres, and its influence on the modern music industry.
Through hands-on learning and theoretical discussions, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of music production software, sound design principles, audio recording techniques, and music notation software. They will explore the role of technology in live performances, the challenges and opportunities presented by digital distribution and streaming, and the ethical considerations surrounding copyright and intellectual property.
Introduction to Music Technology

Music technology encompasses the tools, techniques, and processes involved in creating, recording, manipulating, and distributing music. It has undergone a remarkable evolution, from the earliest mechanical instruments to the sophisticated digital tools of today.
The Evolution of Music Technology
Music technology has a rich history, with innovations transforming the way music is created, performed, and experienced.
- Early Mechanical Instruments: The development of instruments like the piano and the gramophone in the 19th century revolutionized music making and distribution. The piano provided a new level of expressiveness and control, while the gramophone allowed for the mass production and distribution of recorded music.
- Electronic Music: The 20th century witnessed the emergence of electronic music, with the invention of the synthesizer and other electronic instruments. This era saw the rise of genres like electronic dance music, techno, and ambient, which heavily relied on electronic sound manipulation and production techniques.
- Digital Revolution: The advent of computers and digital audio workstations (DAWs) in the late 20th and early 21st centuries ushered in a new era of music technology. DAWs provided musicians with powerful tools for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering music, allowing for unprecedented creative control and flexibility.
Impact on Music Creation
Music technology has profoundly impacted how music is created.
- Accessibility: Digital tools have made music production more accessible to individuals, regardless of their technical expertise or financial resources. Software like GarageBand and Logic Pro X have lowered the barrier to entry for aspiring musicians, allowing them to create professional-quality recordings without needing expensive studio equipment.
- Creative Exploration: Music technology provides musicians with a vast array of tools for creative exploration. Synthesizers, samplers, and other electronic instruments offer a wide range of sounds and effects, allowing musicians to experiment with new sonic possibilities.
- Collaboration: Online platforms and collaboration tools have facilitated remote music creation and collaboration. Musicians can now work together from different locations, sharing files, ideas, and feedback, fostering a global music community.
Impact on Music Performance
Music technology has also transformed live music performance.
- Virtual Instruments: The use of virtual instruments and digital audio workstations has allowed musicians to perform with a wide range of sounds and effects without needing to carry bulky equipment. This has enabled musicians to create more dynamic and immersive live performances.
- Sound Reinforcement: Advanced sound systems and audio engineering techniques have significantly improved the quality and clarity of live sound, enhancing the audience’s listening experience.
- Visuals and Special Effects: The integration of lighting, video, and other visual elements has created more immersive and engaging live music experiences, blurring the lines between performance and spectacle.
Impact on Music Consumption
Music technology has revolutionized how music is consumed.
- Streaming Services: Online music streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music have transformed how people access and listen to music. These services provide on-demand access to vast libraries of music, allowing listeners to discover new artists and genres with ease.
- Personalization: Music streaming services leverage algorithms to personalize the listening experience, recommending music based on user preferences and listening habits. This allows listeners to discover music that aligns with their tastes and interests.
- Social Media Integration: Social media platforms have become integral to music consumption, providing artists with a direct channel to connect with fans, share their music, and build a following.
Impact on Music Genres, Music technology class
Music technology has had a profound impact on various genres of music.
- Electronic Dance Music: The development of synthesizers, drum machines, and other electronic instruments has been instrumental in the rise of electronic dance music (EDM) genres like techno, house, and trance. These genres rely heavily on electronic sound manipulation and production techniques.
- Hip-Hop: Music technology has played a significant role in the evolution of hip-hop, with the use of samplers, drum machines, and turntables becoming integral to the genre’s sound.
- Pop Music: Music technology has been used extensively in pop music, with producers using digital audio workstations, synthesizers, and other tools to create polished and commercially successful tracks.
Music Production Software: Music Technology Class

Music production software, also known as Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), are essential tools for musicians, producers, and sound engineers. They provide a comprehensive platform for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering audio, allowing users to create professional-quality music productions.
Popular DAWs
DAWs offer a wide range of features and functionalities, catering to various needs and preferences. Some of the most popular DAWs include:
- Ableton Live: Known for its intuitive workflow, loop-based production capabilities, and live performance features, Ableton Live is a favorite among electronic music producers and DJs.
- Logic Pro X: A powerful and comprehensive DAW designed for macOS, Logic Pro X offers a wide array of instruments, effects, and features, making it suitable for a variety of genres.
- FL Studio: A popular choice for hip-hop and electronic music producers, FL Studio features a step sequencer, a wide selection of plugins, and a user-friendly interface.
- Pro Tools: The industry standard for professional audio production, Pro Tools offers advanced features for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering, making it a popular choice among studios and professionals.
- Cubase: A versatile DAW known for its powerful MIDI editing capabilities and extensive sound library, Cubase is suitable for a wide range of genres, including classical, jazz, and rock.
Comparing DAW Features
DAWs differ in their features and functionalities, catering to different workflows and preferences. Some key areas of comparison include:
- Recording and Editing: Features like multi-track recording, audio editing tools, and automation capabilities vary across DAWs.
- MIDI Editing: DAWs offer different features for creating and editing MIDI data, including step sequencers, piano rolls, and note editors.
- Mixing and Mastering: Features like mixing consoles, effects plugins, and mastering tools vary in their functionality and quality across DAWs.
- Instruments and Plugins: DAWs come with built-in instruments and plugins, and offer support for third-party plugins, providing a wide range of creative options.
- Workflow and User Interface: DAWs have different user interfaces and workflows, catering to different preferences and production styles.
Workflow for Creating a Music Track in Ableton Live
A typical workflow for creating a music track in Ableton Live might involve the following steps:
- Session View: Start by arranging loops and samples in the Session View, experimenting with different combinations and ideas.
- Arrangement View: Once a satisfactory arrangement is created, move to the Arrangement View and arrange the elements in a linear timeline.
- Recording and Editing: Record audio tracks, edit them, and apply effects to create the desired sound.
- Mixing: Use the mixer to balance the levels of different tracks, apply effects, and create a cohesive sound.
- Mastering: Apply final touches to the track, including EQ, compression, and limiting, to optimize the sound for different formats and platforms.
Final Wrap-Up

By understanding the history, principles, and applications of music technology, students will be equipped to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of the music industry. This class provides a foundation for aspiring musicians, producers, engineers, and anyone interested in the intersection of technology and music.
A music technology class can be a great way to learn about the technical aspects of music creation and production. You might even learn about the STEAM science technology engineering art mathematics principles that underpin the technology used in music production.
From the physics of sound waves to the digital signal processing involved in creating effects, there’s a lot to discover in a music technology class.