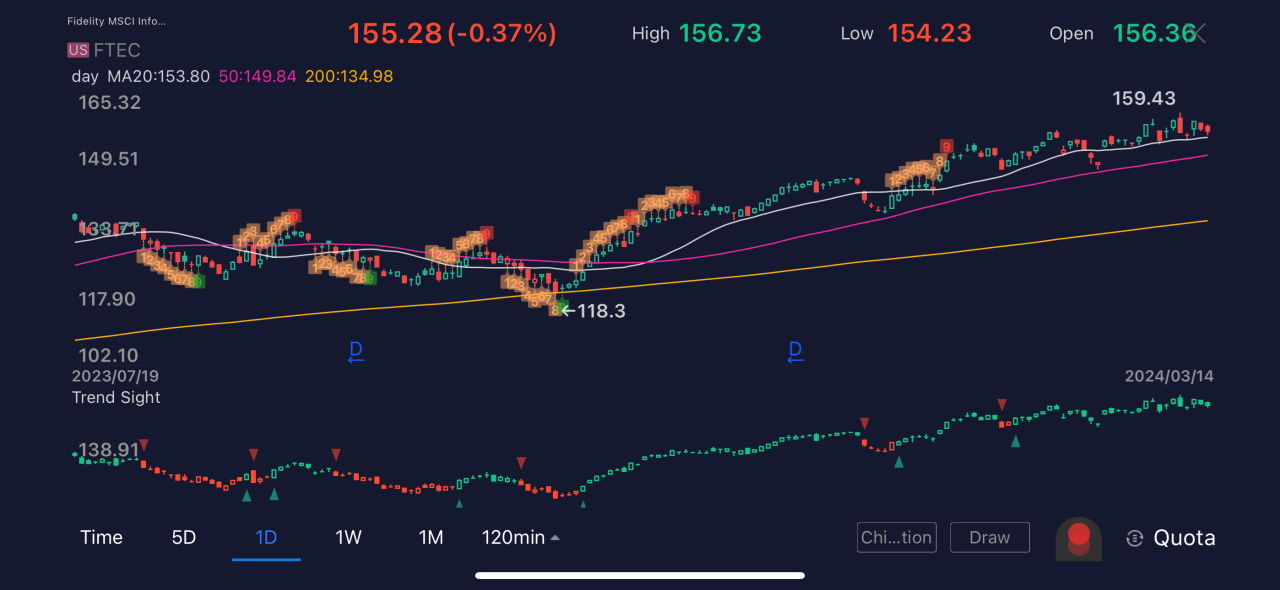
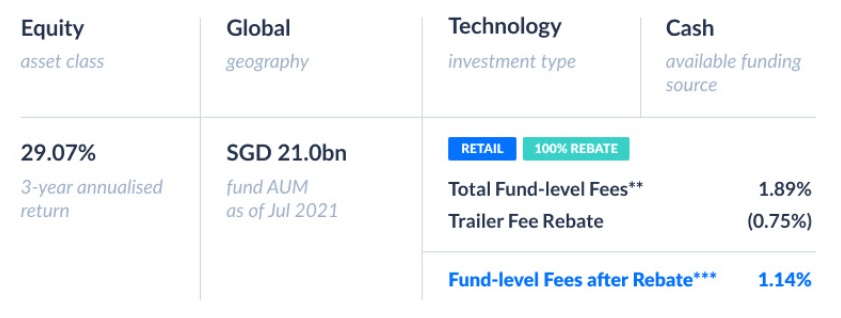
MSCI US Investable Market Index: Information Technology Sector
The MSCI US Investable Market Index/Information Technology 25/50 is a key indicator of the performance of the US technology sector. It tracks the performance of a large segment of the […]
The MSCI US Investable Market Index/Information Technology 25/50 is a key indicator of the performance of the US technology sector. It tracks the performance of a large segment of the US stock market, providing insights into the growth and innovation happening within the information technology industry. The index represents a significant portion of the broader US market, reflecting the importance of technology in the global economy.
The MSCI US Investable Market Index (IMI) is a widely recognized benchmark for the US stock market, encompassing a broad range of companies across various sectors. The Information Technology sector within the IMI is a key focus for investors, given its significant contribution to overall market performance and the potential for growth driven by technological advancements. This sector is a powerhouse, encompassing giants like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon, which are driving innovation and shaping the future of technology.
Investment Strategies for the Information Technology Sector
Investing in the Information Technology (IT) sector can be a rewarding endeavor, offering the potential for substantial growth. However, it’s crucial to employ suitable strategies to navigate the complexities of this dynamic market. Investors can choose from various approaches to gain exposure to the IT sector within the MSCI US Investable Market Index.
Passive Investing
Passive investing involves tracking a specific index, such as the MSCI US IMI Information Technology 25/50 Index, without attempting to outperform it. This strategy aims to replicate the index’s performance, providing broad exposure to the sector.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs are investment funds traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They offer a cost-effective way to invest in a diversified portfolio of IT companies, mirroring the index’s composition. Examples include the Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ) and the Vanguard Information Technology ETF (VGT). These ETFs track the performance of major technology companies, providing investors with a convenient and liquid way to gain exposure to the sector.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to buy a portfolio of securities, including IT stocks. They offer professional management and diversification, but may have higher fees compared to ETFs. Examples include the Fidelity Magellan Fund (FMAGX) and the Schwab Total Stock Market Index (SWTSX), which include a significant portion of their holdings in IT companies.
Active Management
Active management involves employing a strategy to outperform the market by selecting specific stocks within the IT sector. This approach requires expert analysis and portfolio management.
- Growth Investing: This strategy focuses on companies with high growth potential, often in emerging technologies or innovative businesses. Investors seek companies with strong earnings growth, market share expansion, and a competitive advantage in their respective industries. Examples include Amazon (AMZN), Microsoft (MSFT), and Apple (AAPL), which have consistently delivered strong growth and innovation.
- Value Investing: This strategy targets undervalued companies with strong fundamentals but currently trading at a discount to their intrinsic value. Investors aim to identify companies with a solid track record, a stable financial position, and the potential for a future price appreciation. Examples include Cisco Systems (CSCO), Intel (INTC), and IBM (IBM), which may have faced challenges in recent years but offer value to investors willing to hold for the long term.
- Sector Rotation: This strategy involves shifting investments between different sectors based on economic trends, market cycles, and industry performance. Investors may allocate a higher portion of their portfolio to the IT sector during periods of strong economic growth and technological innovation. Examples include Nvidia (NVDA), Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSM), and ASML Holding (ASML), which are leading players in the semiconductor and artificial intelligence industries.
Hypothetical Portfolio Allocation
A hypothetical portfolio allocation strategy for investors seeking exposure to the IT sector could include:
- 60% Passive Investing: This portion can be invested in a broad-market IT ETF like the Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ), providing diversified exposure to the sector.
- 20% Growth Investing: This portion can be allocated to individual stocks with high growth potential, such as Amazon (AMZN) and Microsoft (MSFT), focusing on companies with a proven track record of innovation and market leadership.
- 20% Value Investing: This portion can be invested in undervalued IT companies with strong fundamentals, such as Cisco Systems (CSCO) and Intel (INTC), aiming to capture potential upside from their future growth prospects.
Risks and Rewards
Investing in the IT sector offers potential for high returns but also comes with inherent risks:
- Volatility: The IT sector is known for its high volatility, driven by rapid technological advancements, market competition, and investor sentiment. This volatility can lead to significant price fluctuations, both upward and downward.
- Disruption: New technologies can quickly disrupt established businesses, creating winners and losers in the market. Companies failing to adapt to technological changes may face challenges in maintaining their market share and profitability.
- Competition: The IT sector is highly competitive, with numerous companies vying for market share and customer loyalty. Intense competition can pressure margins and hinder growth prospects.
- Regulation: Governments and regulators are increasingly scrutinizing the IT sector, particularly regarding data privacy, antitrust, and cybersecurity. Regulatory changes can impact company operations, profitability, and investor confidence.
Impact of Technological Trends on the Sector

The Information Technology (IT) sector is constantly evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology. These trends have a profound impact on the sector, creating both opportunities and challenges for businesses. This section delves into the key technological trends shaping the IT sector, exploring their impact, benefits, and risks.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Cloud Computing, and Cybersecurity
AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity are among the most significant technological trends shaping the IT sector. These trends are driving innovation, improving efficiency, and enhancing security, while also posing new challenges.
AI
AI is transforming various industries, including IT. Machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing are revolutionizing how businesses operate. AI-powered applications are being used for tasks such as data analysis, customer service, and fraud detection.
- Benefits: AI can automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance customer experiences. For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, while AI-driven fraud detection systems can identify suspicious transactions in real time.
- Risks: AI raises concerns about job displacement, bias in algorithms, and data privacy. It is crucial to address these concerns through ethical development and responsible use of AI.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become ubiquitous, enabling businesses to access computing resources on demand. This has led to increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Benefits: Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their operations quickly and efficiently, pay only for the resources they use, and access advanced technologies without significant upfront investments. For example, cloud-based services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure provide a wide range of computing, storage, and networking capabilities.
- Risks: Cloud computing raises concerns about data security, vendor lock-in, and compliance with regulations. It is important to choose reliable cloud providers with robust security measures and ensure compliance with relevant data protection laws.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as businesses rely more heavily on technology. Cybersecurity threats are evolving rapidly, and businesses need to stay ahead of these threats to protect their data and systems.
- Benefits: Investing in cybersecurity solutions can help businesses protect their data, systems, and reputation from cyberattacks. This can include implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption.
- Risks: Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, and businesses need to invest in ongoing training and updates to their security measures. Failure to do so can lead to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
| Trend | Impact | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI | Automates tasks, improves decision-making, and enhances customer experiences. | Increased efficiency, better decision-making, improved customer experiences. | Job displacement, bias in algorithms, data privacy concerns. |
| Cloud Computing | Provides on-demand access to computing resources, increasing flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. | Increased flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, access to advanced technologies. | Data security concerns, vendor lock-in, compliance with regulations. |
| Cybersecurity | Protects data and systems from cyberattacks, ensuring business continuity and data integrity. | Enhanced data security, reduced risk of cyberattacks, improved business continuity. | Evolving threats, need for ongoing training and updates, potential for financial losses and reputational damage. |
The Future of the Information Technology Sector
The Information Technology (IT) sector within the MSCI US Investable Market Index (IMI) is poised for continued growth and evolution, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, shifting consumer behaviors, and evolving business models. This section explores the long-term outlook for the IT sector within the IMI, analyzing the factors that could drive future growth and potential challenges. Insights from industry experts and analysts regarding the sector’s future prospects are also incorporated, focusing on key themes such as innovation, regulation, and competition.
Growth Drivers and Challenges
The IT sector is expected to experience sustained growth in the coming years, fueled by several key factors. These include:
- Continued Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of innovation in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is creating new opportunities for growth and disruption within the IT sector. For example, AI-powered applications are transforming industries from healthcare to finance, driving demand for advanced computing capabilities and software solutions.
- Increasing Digital Transformation: Businesses across all sectors are increasingly embracing digital technologies to enhance efficiency, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. This trend is driving demand for IT services, software, and hardware, contributing to the sector’s growth.
- Rising Consumer Demand for Digital Products and Services: Consumers are increasingly relying on digital devices, services, and platforms for entertainment, communication, and information. This trend is fueling the growth of companies in areas such as e-commerce, streaming services, and social media.
However, the IT sector also faces several challenges, including:
- Cybersecurity Threats: As businesses and individuals become more reliant on digital technologies, the risk of cyberattacks is also increasing. This poses a significant challenge for IT companies, as they must invest in robust security measures to protect their systems and data.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Governments around the world are increasingly scrutinizing the activities of large technology companies, particularly in areas such as data privacy, antitrust, and content moderation. This regulatory scrutiny could impact the growth and profitability of IT companies.
- Competition: The IT sector is highly competitive, with numerous established players and emerging startups vying for market share. This competition can put pressure on pricing and profitability, making it challenging for companies to maintain their market position.
Innovation: The Engine of Growth
Innovation is a key driver of growth in the IT sector. Companies that can develop and commercialize new technologies and solutions are well-positioned to capture market share and generate strong returns.
“Innovation is the lifeblood of the IT sector. Companies that can stay ahead of the curve and develop cutting-edge technologies will be the winners in the long run.” – [Industry Expert Name]
Examples of recent innovations in the IT sector include:
- 5G Networks: The rollout of 5G networks is enabling faster speeds and lower latency, opening up new possibilities for mobile devices, cloud computing, and IoT applications.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling. While still in its early stages, quantum computing is attracting significant investment and could have a major impact on the IT sector in the future.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computing power closer to users, reducing latency and improving performance for applications such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Regulation: Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
The IT sector is subject to a growing number of regulations, driven by concerns about data privacy, antitrust, and content moderation. Companies must navigate this evolving regulatory landscape to ensure compliance and avoid legal risks.
“The regulatory environment for the IT sector is becoming increasingly complex. Companies need to be proactive in understanding and complying with new regulations to avoid potential penalties.” – [Industry Analyst Name]
Examples of recent regulatory developments in the IT sector include:
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This EU regulation aims to protect personal data and give individuals more control over their information. Companies that handle personal data of EU residents must comply with GDPR requirements.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This California law gives consumers the right to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal data. Companies that operate in California must comply with CCPA requirements.
- Antitrust Investigations: Governments around the world are investigating the market dominance of large technology companies, such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook. These investigations could lead to antitrust actions, such as fines or forced divestitures.
Competition: A Dynamic and Evolving Landscape, Msci us investable market index/information technology 25/50
The IT sector is highly competitive, with numerous established players and emerging startups vying for market share. This competition can drive innovation and lower prices for consumers, but it can also make it challenging for companies to maintain their market position.
“The IT sector is a constant battleground for market share. Companies need to be agile and innovative to stay ahead of the competition.” – [Industry Expert Name]
Examples of competitive dynamics in the IT sector include:
- Cloud Computing: The cloud computing market is dominated by a few major players, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. These companies are constantly innovating and expanding their offerings to maintain their market share.
- Mobile Devices: The smartphone market is dominated by Apple and Samsung, but Chinese companies such as Huawei and Xiaomi are making significant inroads. This competition is driving innovation in areas such as hardware design, software features, and pricing.
- Artificial Intelligence: The AI market is attracting significant investment from both established companies and startups. This competition is driving the development of new AI algorithms, applications, and platforms.
Closing Summary: Msci Us Investable Market Index/information Technology 25/50

The future of the Information Technology sector within the IMI is promising, with continued growth driven by innovation, technological advancements, and evolving consumer needs. However, it’s important to consider potential challenges, such as regulation, competition, and economic uncertainty. Investors should carefully analyze the sector, its key players, and emerging trends to make informed decisions. The Information Technology sector is a dynamic landscape, and staying ahead of the curve requires a keen understanding of its evolving dynamics.
The MSCI US Investable Market Index, with its Information Technology sector holding a significant 25% to 50% weight, reflects the ever-evolving nature of the tech landscape. As companies innovate and develop cutting-edge solutions, securing intellectual property rights becomes crucial. A technology patent lawyer can guide businesses through the complex process of obtaining and protecting patents, ensuring their competitive advantage in the dynamic world of Information Technology.
This is especially relevant for companies operating within the MSCI US Investable Market Index, where technological advancements are driving significant growth and value creation.