MCS Technology: Revolutionizing Industries
MCS technology, a game-changer in various sectors, has emerged as a powerful tool for optimizing processes, enhancing efficiency, and driving innovation. From its humble beginnings, MCS technology has evolved significantly, […]

MCS technology, a game-changer in various sectors, has emerged as a powerful tool for optimizing processes, enhancing efficiency, and driving innovation. From its humble beginnings, MCS technology has evolved significantly, finding applications across diverse industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to agriculture and energy.
This technology encompasses a wide range of components, including sensors, actuators, and controllers, working in harmony to collect data, analyze information, and execute actions based on pre-defined parameters. This sophisticated system empowers businesses to make informed decisions, automate tasks, and achieve unprecedented levels of precision and control.
Introduction to MCS Technology

MCS technology, also known as “Microcontroller-based Control Systems,” is a revolutionary approach to automation and control. At its core, MCS technology utilizes microcontrollers, compact integrated circuits that combine a central processing unit (CPU) with memory and input/output (I/O) peripherals, to manage and execute control functions in various applications. This integration allows for efficient and versatile control solutions, making MCS technology a cornerstone of modern automation.
Fundamental Principles and Concepts
The foundation of MCS technology lies in the ability of microcontrollers to process data and execute instructions based on inputs received from sensors and actuators. This data processing enables the microcontroller to make decisions and adjust system parameters in real-time, leading to precise and dynamic control.
Key Components and Functionality
- Microcontroller: The brain of the system, responsible for processing data, making decisions, and controlling outputs.
- Sensors: Devices that measure physical parameters like temperature, pressure, or light and convert them into electrical signals.
- Actuators: Devices that convert electrical signals from the microcontroller into physical actions, such as controlling motors, valves, or heaters.
- Software: Programs that define the microcontroller’s behavior, including control algorithms, data processing routines, and communication protocols.
Historical Evolution of MCS Technology
MCS technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 20th century. Early microcontrollers were limited in processing power and memory capacity, leading to simpler applications. However, advancements in semiconductor technology have enabled the development of powerful and versatile microcontrollers with enhanced computational capabilities and integrated features.
Key Milestones
- Early Microcontrollers (1970s-1980s): Simple 8-bit microcontrollers with limited memory and processing power were primarily used in embedded applications like automotive systems and consumer electronics.
- Advanced Microcontrollers (1990s-Present): The development of 16-bit and 32-bit microcontrollers with increased processing power, memory capacity, and integrated peripherals paved the way for more complex and sophisticated applications in industries like industrial automation, robotics, and medical devices.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud Integration (2000s-Present): The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing has further expanded the scope of MCS technology, enabling remote monitoring, data analysis, and advanced control capabilities.
Real-World Applications of MCS Technology
MCS technology has become ubiquitous in various industries, revolutionizing automation and control processes. The versatility of microcontrollers and their ability to interact with sensors and actuators make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Industry Examples
- Automotive: Engine control units (ECUs), anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and electronic stability control (ESC) are all powered by MCS technology.
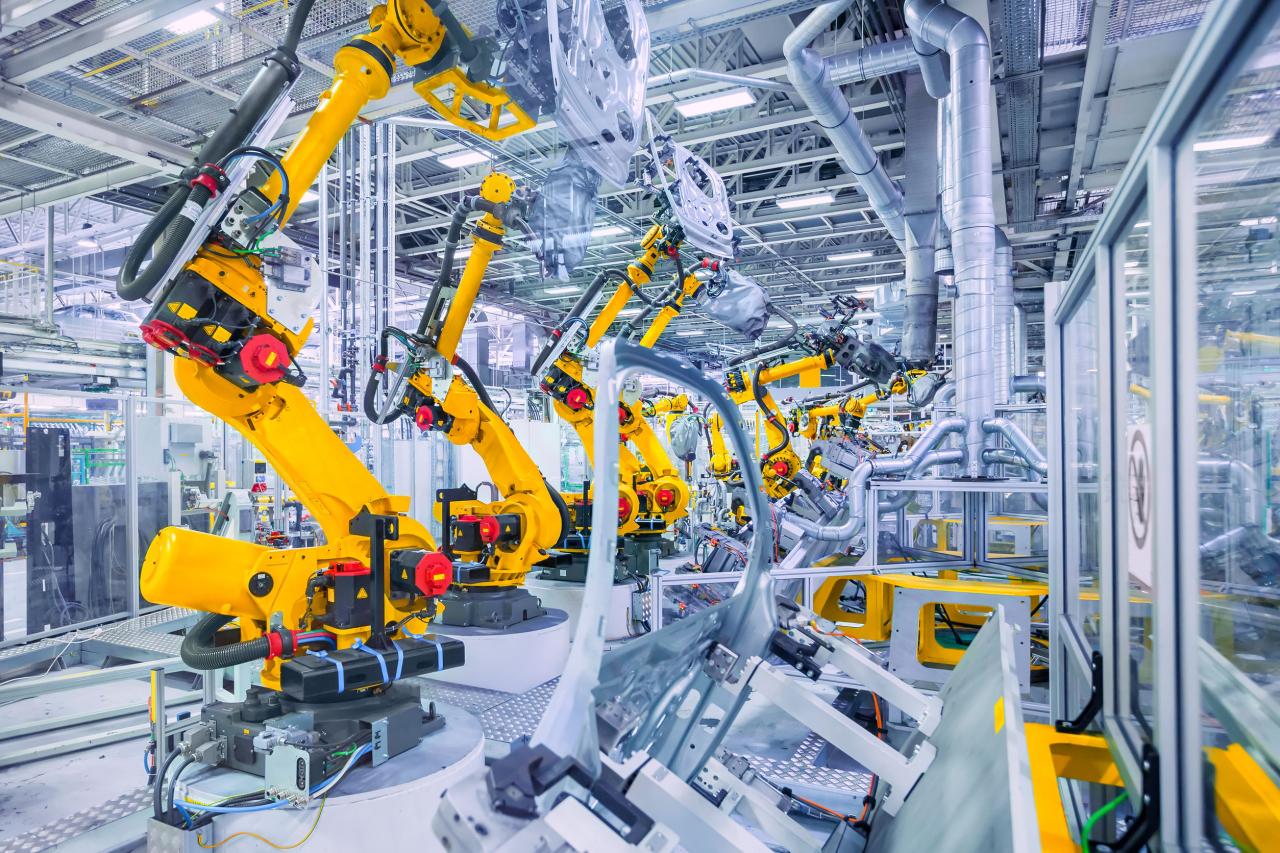
- Industrial Automation: MCS technology is used in manufacturing processes for tasks such as robotic control, machine automation, and process monitoring.
- Home Appliances: Modern appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and ovens incorporate MCS technology for efficient operation and user-friendly interfaces.
- Medical Devices: MCS technology is used in medical devices like pacemakers, insulin pumps, and drug delivery systems to monitor and control vital functions.
- Robotics: MCS technology plays a crucial role in controlling robots for tasks like assembly, welding, and logistics.
- Smart Homes and Buildings: MCS technology is used in smart home systems for lighting control, temperature regulation, security, and energy management.
Last Word

MCS technology holds immense potential for the future, promising further advancements in automation, data analytics, and intelligent decision-making. As we continue to embrace the power of interconnected systems and the rise of artificial intelligence, MCS technology is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the industries of tomorrow, paving the way for a more efficient, sustainable, and technologically advanced world.
MCS technology is revolutionizing the way we interact with machines. It’s all about making systems smarter and more intuitive. A great example of this is mei technologies inc , which specializes in developing innovative MCS solutions for various industries. These solutions help companies streamline processes, improve efficiency, and gain valuable insights from their data.