Management Technologies: Shaping the Future of Business
Management technologies are no longer just tools; they are the driving force behind modern business success. From the early days of paper-based systems to the sophisticated software solutions we see […]

Management technologies are no longer just tools; they are the driving force behind modern business success. From the early days of paper-based systems to the sophisticated software solutions we see today, management technologies have continuously evolved, adapting to the ever-changing needs of organizations. This evolution has been fueled by technological advancements, shifting business priorities, and the evolving dynamics of the workforce.
This exploration delves into the fascinating world of management technologies, uncovering their history, types, impact on organizations, and the exciting trends shaping their future. We will examine how these technologies have transformed the way businesses operate, make decisions, and interact with their customers. We will also discuss the potential challenges and opportunities that lie ahead as these technologies continue to advance.
Evolution of Management Technologies

Management technologies have undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from rudimentary paper-based systems to sophisticated software solutions that shape modern business operations. This evolution has been driven by technological advancements, changing business needs, and evolving workforce dynamics, significantly impacting organizational efficiency and decision-making.
Early Management Technologies
Early management technologies relied heavily on manual processes and paper-based systems. These systems, while simple, were often inefficient, prone to errors, and lacked the ability to analyze data effectively. For instance, businesses relied on physical ledgers for financial record-keeping, which was time-consuming and susceptible to human errors.
The Rise of Computerized Management Systems
The advent of computers in the mid-20th century marked a significant shift in management technologies. Early computerized systems focused on automating repetitive tasks, such as payroll processing and inventory management. These systems, though primitive compared to modern solutions, provided organizations with greater accuracy, efficiency, and data storage capabilities.
The Emergence of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
The 1990s saw the emergence of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, which integrated various business functions, such as finance, human resources, and supply chain management, into a single platform. ERP systems revolutionized business operations by providing real-time data visibility, streamlining processes, and improving decision-making.
The Era of Cloud Computing and Mobile Technologies
The 21st century has witnessed the rise of cloud computing and mobile technologies, further transforming management technologies. Cloud-based solutions offer organizations greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, while mobile applications provide access to critical information and management tools anytime, anywhere.
Key Drivers of Evolution
Several key drivers have fueled the continuous evolution of management technologies.
Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements has been a primary driver. Advancements in computing power, data storage, and network connectivity have enabled the development of increasingly sophisticated management tools.
Changing Business Needs
Evolving business needs have also driven the evolution of management technologies. Organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Management technologies have evolved to meet these needs, providing tools for process automation, data analytics, and customer relationship management.
Evolving Workforce Dynamics
The changing nature of the workforce, characterized by increased mobility and remote work, has also influenced the development of management technologies. Mobile-first solutions and collaboration tools have emerged to enable effective communication and collaboration among geographically dispersed teams.
Types of Management Technologies
Management technologies are tools and systems that help organizations streamline operations, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions. These technologies are categorized based on their specific functions and applications, ranging from managing projects and resources to fostering customer relationships and overseeing financial activities.
Project Management Technologies
Project management technologies are designed to assist organizations in planning, executing, and monitoring projects effectively. These tools provide a structured framework for managing tasks, resources, timelines, and budgets, enabling teams to collaborate and track progress towards project goals.
- Project Management Software: This category encompasses a wide range of software applications, such as Asana, Trello, Jira, and Microsoft Project. These platforms offer features like task management, Gantt charts, collaboration tools, and reporting dashboards, helping teams visualize project progress and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Project Management Methodologies: Methodologies like Agile, Scrum, and Kanban provide frameworks for organizing and managing projects, focusing on iterative development, continuous improvement, and flexible adaptation to changing requirements.
Resource Management Technologies
Resource management technologies focus on optimizing the allocation and utilization of resources within an organization. These tools help organizations track and manage various resources, including human capital, equipment, and financial assets, to ensure efficient deployment and maximize productivity.
- Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS): HRMS platforms streamline HR processes, including recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and payroll. They provide tools for managing employee data, tracking attendance, and automating administrative tasks.
- Asset Management Software: Asset management software helps organizations track and manage physical assets, such as equipment, vehicles, and infrastructure. These tools enable organizations to monitor asset lifecycles, schedule maintenance, and optimize asset utilization.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Technologies
CRM technologies are designed to manage and enhance customer interactions, fostering stronger relationships and driving customer loyalty. These tools provide a centralized platform for storing customer data, managing interactions, and automating marketing and sales processes.
- CRM Software: Popular CRM platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM offer features for managing customer contacts, tracking interactions, analyzing customer behavior, and automating marketing campaigns.
- Customer Service Automation: Tools like chatbots and live chat software automate customer interactions, providing instant support and resolving inquiries efficiently.
Financial Management Technologies
Financial management technologies are essential for organizations to manage their financial operations effectively. These tools provide insights into financial performance, facilitate budgeting and forecasting, and automate financial processes.
- Accounting Software: Accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage Intacct automate accounting tasks, manage financial records, generate financial reports, and streamline financial processes.
- Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A) Software: FP&A software helps organizations develop financial forecasts, analyze financial performance, and make informed financial decisions.
| Technology | Category | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Management Software | Project Management | Improved collaboration, increased efficiency, better project visibility, enhanced reporting | Implementation costs, learning curve, potential data security concerns |
| HRMS | Resource Management | Streamlined HR processes, improved employee engagement, automated tasks, reduced administrative burden | Implementation costs, data security concerns, potential for system integration challenges |
| CRM Software | Customer Relationship Management | Enhanced customer relationships, improved customer service, increased sales opportunities, data-driven insights | Implementation costs, data security concerns, potential for system integration challenges |
| Accounting Software | Financial Management | Automated financial processes, improved accuracy, enhanced financial reporting, reduced errors | Implementation costs, potential for data security concerns, need for regular updates and maintenance |
Impact of Management Technologies on Organizations
Management technologies have revolutionized the way organizations operate, impacting every aspect from efficiency and decision-making to employee engagement and overall culture. These technologies offer a plethora of benefits, but their implementation also presents unique challenges that organizations must navigate.
Positive Impacts on Organizational Performance
Management technologies have a significant positive impact on organizational performance by enhancing efficiency, improving decision-making, facilitating communication, and fostering collaboration.
- Increased Efficiency: Management technologies streamline processes, automate tasks, and eliminate redundancies, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. For example, project management software allows teams to track progress, allocate resources effectively, and identify potential bottlenecks, resulting in faster project completion and improved resource utilization.
- Improved Decision-Making: Management technologies provide access to real-time data and analytics, enabling organizations to make informed and data-driven decisions. Business intelligence tools analyze vast amounts of data, identifying trends, patterns, and insights that support strategic planning and operational improvements.
- Better Communication: Communication technologies like instant messaging, video conferencing, and collaborative platforms facilitate seamless communication within and across teams. This enhanced communication fosters transparency, reduces misunderstandings, and promotes quicker response times, leading to improved collaboration and faster problem-solving.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Management technologies enable teams to work together effectively, regardless of their physical location. Collaborative platforms provide shared workspaces for document editing, project management, and communication, fostering a sense of shared ownership and accountability, and ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Challenges of Implementing Management Technologies
While management technologies offer significant benefits, their implementation also presents challenges, including resistance to change, data security concerns, and the need for ongoing training and support.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new technologies due to concerns about job security, lack of training, or discomfort with unfamiliar tools. Effective communication, training programs, and demonstrating the benefits of the technology can help address this resistance.
- Data Security Concerns: Management technologies involve handling sensitive data, requiring robust security measures to prevent breaches and protect confidential information. Organizations must implement strong data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to ensure data integrity and compliance with regulations.
- Need for Ongoing Training and Support: Management technologies require ongoing training and support to ensure effective utilization and prevent user frustration. Organizations must provide comprehensive training programs, user manuals, and technical support to enable employees to maximize the benefits of these technologies.
Impact on Organizational Culture, Employee Engagement, and Work Environment
Management technologies can significantly influence organizational culture, employee engagement, and the overall work environment.
- Organizational Culture: Management technologies can foster a more collaborative and data-driven culture. By providing access to information and facilitating communication, these technologies promote transparency and shared decision-making, contributing to a more inclusive and agile work environment.
- Employee Engagement: Management technologies can enhance employee engagement by providing them with the tools and resources they need to perform their tasks effectively. Automated processes, personalized dashboards, and access to real-time data can empower employees, making them feel valued and contributing to their overall job satisfaction.
- Work Environment: Management technologies can create a more flexible and remote-friendly work environment. Collaboration platforms and communication tools allow employees to work from anywhere, fostering a sense of work-life balance and reducing commuting time, leading to increased employee satisfaction and productivity.
Emerging Trends in Management Technologies
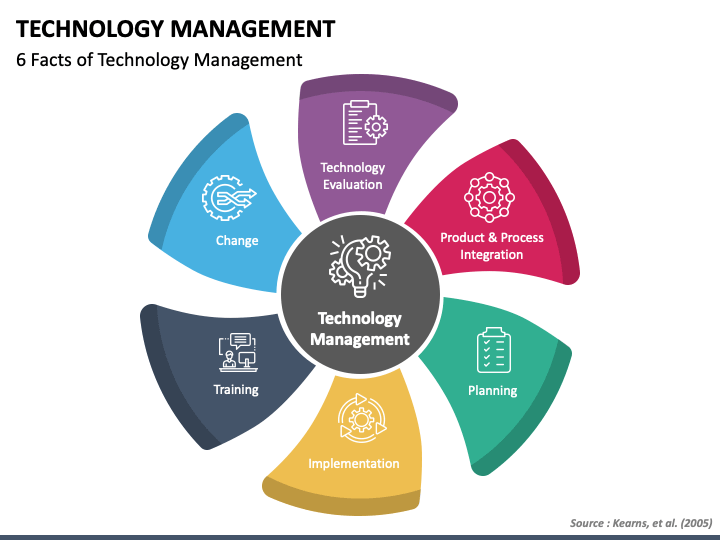
The world of management is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by the emergence of powerful technologies that are fundamentally altering how organizations operate and make decisions. From artificial intelligence to blockchain, these technologies are redefining efficiency, productivity, and the very nature of work itself.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are at the forefront of this technological revolution. AI systems are designed to mimic human intelligence, enabling them to learn from data, solve problems, and make decisions. Machine learning, a subset of AI, focuses on training computers to learn from data without explicit programming. These technologies are revolutionizing various aspects of management, including:
- Automation: AI and ML are automating repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees for more strategic and creative work. For example, AI-powered chatbots are handling customer service inquiries, while ML algorithms are automating data entry and analysis.
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future trends. This allows organizations to make more informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and mitigate risks. For example, a retail company can use AI to predict customer demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Personalized Experiences: AI and ML can personalize customer experiences by tailoring products, services, and marketing messages to individual preferences. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, online retailers use AI to recommend products based on past purchases and browsing history.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources, such as servers, storage, and software, over the internet. This technology has fundamentally changed how organizations manage their IT infrastructure, offering several benefits:
- Scalability: Cloud computing allows organizations to easily scale their resources up or down as needed, eliminating the need for expensive upfront investments in hardware. This is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or fluctuating workloads.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud computing can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises IT infrastructure, as organizations only pay for the resources they use. This can significantly reduce capital expenditures and operational costs.
- Flexibility: Cloud computing provides organizations with greater flexibility in terms of location and access. Employees can access applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that securely records transactions across a network of computers. This technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and traceability by providing a secure and immutable record of goods movement. This can help organizations improve efficiency, reduce fraud, and ensure product safety.
- Financial Services: Blockchain can streamline financial transactions, reduce costs, and improve security. For example, cryptocurrency transactions are processed on a blockchain, enabling peer-to-peer payments without the need for intermediaries.
- Data Security: Blockchain can enhance data security by providing a tamper-proof record of transactions and data changes. This can help organizations protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory requirements.
Last Word
The future of management technologies is brimming with possibilities. As AI, automation, and data analytics continue to evolve, businesses will have access to even more powerful tools to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and improve customer experiences. The challenge will be to harness these technologies responsibly and ethically, ensuring they are used to empower employees, foster innovation, and ultimately create a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Management technologies are constantly evolving, offering new ways to streamline processes and improve efficiency. One exciting area of development is the integration of face technologies into management systems. This allows for enhanced security, personalized interactions, and even automated tasks.
As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications within the realm of management.