Latest Dental Implant Technology: Revolutionizing Smiles
Latest dental implant technology has revolutionized the way we approach tooth loss, offering a durable and aesthetically pleasing solution. Gone are the days of uncomfortable dentures and bridges, as implants […]
Latest dental implant technology has revolutionized the way we approach tooth loss, offering a durable and aesthetically pleasing solution. Gone are the days of uncomfortable dentures and bridges, as implants provide a natural-looking and functional alternative. This article delves into the exciting advancements in implant materials, surgical techniques, and restoration options, showcasing how this technology is transforming the field of dentistry.
Dental implants have come a long way since their inception, evolving from rudimentary titanium screws to highly sophisticated biocompatible materials and digitally guided placement techniques. The advancements in implant technology have not only improved the success rate of implant procedures but have also enhanced patient comfort and overall treatment experience.
Introduction to Dental Implants
Dental implants are a revolutionary advancement in dentistry that provide a permanent and natural-looking solution for missing teeth. They are artificial tooth roots that are surgically implanted into the jawbone, serving as a strong and stable foundation for replacement teeth. Dental implants offer numerous benefits over traditional dentures and bridges, including enhanced stability, improved chewing ability, and a more natural appearance.
History of Dental Implants
The concept of dental implants dates back centuries, with early attempts using materials like ivory and bone. However, modern dental implant technology emerged in the 1960s with the development of titanium implants, which possess exceptional biocompatibility and osseointegration properties. Osseointegration refers to the direct bonding of living bone to the implant surface, ensuring a secure and long-lasting connection. The introduction of titanium implants revolutionized the field of dentistry, paving the way for the widespread use of dental implants today.
Types of Dental Implants
Dental implants come in various forms, each designed to address specific needs and preferences. The most common types include:
- Endosteal Implants: These are the most prevalent type, consisting of a titanium screw-shaped implant that is surgically placed into the jawbone. Endosteal implants are suitable for most patients and provide excellent stability and support for replacement teeth.
- Subperiosteal Implants: These implants are placed on top of the jawbone, beneath the gum tissue. Subperiosteal implants are typically used when there is insufficient bone height for endosteal implants. They consist of a metal frame with posts that protrude through the gums, supporting replacement teeth.
- Zygomatic Implants: These implants are designed for patients with significant bone loss in the upper jaw. Zygomatic implants are longer than traditional implants and are anchored to the cheekbone, providing strong support for dentures or bridges.
Latest Advancements in Implant Materials
Dental implant materials have come a long way, with advancements leading to better biocompatibility, strength, and aesthetics. This section will delve into the latest innovations in implant materials, exploring the advantages and disadvantages of each material.
Zirconia Implants
Zirconia, a ceramic material, has emerged as a viable alternative to titanium implants. Zirconia implants offer several advantages, including excellent biocompatibility, high strength, and a natural tooth-like appearance.
- Biocompatibility: Zirconia exhibits high biocompatibility, meaning it is well-tolerated by the body and unlikely to cause allergic reactions. This is particularly beneficial for patients with titanium allergies.
- Strength: Zirconia implants are known for their high strength and durability, comparable to titanium implants. They can withstand the forces of chewing and biting, providing long-lasting support.
- Aesthetics: Zirconia’s natural white color closely resembles the color of natural teeth, making it an excellent choice for patients concerned about aesthetics. This material can blend seamlessly with surrounding teeth, ensuring a natural and discreet appearance.
However, zirconia implants also have some disadvantages:
- Cost: Zirconia implants are generally more expensive than titanium implants due to the complex manufacturing process and higher material cost.
- Brittleness: While zirconia is strong, it is more brittle than titanium. This means that zirconia implants are more susceptible to fracture under extreme force or impact.
- Limited Implant Designs: The range of zirconia implant designs is currently more limited compared to titanium implants, which may restrict the options available to dentists and patients.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys remain the most widely used material for dental implants due to their proven track record and favorable properties. Titanium’s biocompatibility, strength, and osseointegration capabilities have made it a gold standard in implant dentistry.
- Biocompatibility: Titanium is highly biocompatible, meaning it is well-tolerated by the body and unlikely to cause allergic reactions. This makes it suitable for a wide range of patients.
- Strength: Titanium is a strong and durable material, capable of withstanding the forces of chewing and biting. This ensures the longevity and stability of the implant.
- Osseointegration: Titanium has excellent osseointegration properties, meaning it bonds directly to the surrounding bone tissue. This strong bond provides a stable foundation for the implant and prevents movement or loosening.
Titanium alloys are constantly being refined and improved, with advancements focusing on enhancing their surface properties for better osseointegration and reducing the risk of implant failure.
Biocompatible Ceramics
Biocompatible ceramics, such as hydroxyapatite and bioactive glass, are increasingly being explored for dental implant applications. These materials offer unique advantages in terms of biocompatibility and bone regeneration.
- Biocompatibility: Biocompatible ceramics are naturally compatible with bone tissue, promoting rapid bone healing and integration.
- Bone Regeneration: These materials can stimulate bone growth and regeneration, aiding in the formation of a strong bond between the implant and the jawbone.
- Antibacterial Properties: Some biocompatible ceramics exhibit antibacterial properties, reducing the risk of infection and promoting implant stability.
Research and development efforts are ongoing to further improve the properties of biocompatible ceramics, making them more durable and versatile for dental implant applications.
Research and Development Efforts
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on creating novel implant materials with enhanced properties, such as:
- Improved Biocompatibility: Researchers are exploring new materials and surface modifications to enhance biocompatibility and minimize the risk of immune rejection.
- Enhanced Osseointegration: Efforts are underway to develop materials that promote faster and stronger bone integration, leading to improved implant stability.
- Tailored Materials: Researchers are investigating the use of tailored materials, specifically designed for individual patient needs, to optimize implant performance.
- Bioactive Coatings: Developing bioactive coatings that stimulate bone growth and reduce the risk of infection is a key area of research.
These advancements in implant materials are expected to revolutionize dental implant technology, leading to more effective, durable, and aesthetically pleasing solutions for patients.
Digital Technology in Implant Dentistry

Digital technology has revolutionized implant dentistry, transforming the way implants are planned, placed, and restored. This shift towards digital workflows has led to increased accuracy, efficiency, and predictability in implant procedures, benefiting both patients and dentists.
Comparison of Traditional and Digital Implant Procedures
The integration of digital technology has significantly changed implant dentistry. Here is a table comparing traditional implant procedures with digital workflows:
| Feature | Traditional Method | Digital Workflow |
|———————|——————–|——————-|
| Planning | Based on 2D radiographs and physical models | 3D imaging, digital planning software |
| Implant Placement | Freehand surgery | Guided surgery |
| Prosthetic Design | Based on impressions and physical models | Digital impressions, CAD/CAM technology |
| Accuracy | Limited accuracy, potential for errors | High accuracy, reduced errors |
| Efficiency | Time-consuming, multiple appointments | Efficient, fewer appointments |
| Predictability | Less predictable outcomes | More predictable outcomes |
Use of 3D Imaging, CAD/CAM Technology, and Guided Surgery
- 3D Imaging: Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans provide detailed 3D images of the jawbone, allowing for precise implant planning. This technology helps identify bone density, nerve locations, and anatomical structures, enabling dentists to plan the optimal implant placement.
- CAD/CAM Technology: Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology is used to create custom implant components, such as abutments and crowns. Digital impressions are taken, and the data is used to design and fabricate the prosthetics, ensuring a perfect fit and improved aesthetics.
- Guided Surgery: Guided surgery utilizes a surgical stent created from the 3D model. The stent guides the dentist to the pre-planned implant position, ensuring accurate placement and minimizing surgical trauma. This technique reduces the need for extensive bone grafting and allows for minimally invasive procedures.
Benefits of Digital Technology for Patients and Dentists, Latest dental implant technology
- Increased Accuracy: Digital workflows, especially guided surgery, offer unparalleled accuracy in implant placement. This minimizes the risk of complications and ensures a successful outcome.
- Improved Efficiency: Digital technology streamlines the implant process, reducing the number of appointments and overall treatment time. This benefits patients by minimizing disruption to their daily lives.
- Enhanced Predictability: Digital planning and guided surgery lead to more predictable outcomes, increasing the likelihood of successful implant integration and long-term stability. This gives patients greater confidence in their treatment.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Guided surgery allows for minimally invasive procedures, reducing surgical trauma, discomfort, and recovery time for patients.
- Improved Aesthetics: CAD/CAM technology allows for the creation of highly aesthetic restorations, blending seamlessly with natural teeth. This is particularly beneficial for patients concerned about the appearance of their implants.
Minimally Invasive Implant Techniques
Minimally invasive implant surgery is a modern approach that prioritizes patient comfort and faster recovery. It aims to minimize tissue disruption and surgical trauma, resulting in less pain, faster healing, and improved aesthetics.
Flapless Surgery
Flapless surgery is a minimally invasive technique that eliminates the need for a traditional surgical flap. Instead of cutting and lifting the gum tissue, a small incision is made in the gum, allowing the dentist to access the bone and place the implant.
- Reduced Surgical Trauma: Flapless surgery involves minimal tissue manipulation, reducing post-operative pain and swelling.
- Faster Healing: The absence of a surgical flap allows for faster healing and a shorter recovery time.
- Improved Aesthetics: Flapless surgery minimizes scarring and preserves the natural gum contour, leading to a more aesthetically pleasing result.
Immediate Implant Placement
Immediate implant placement is a technique where the implant is placed immediately after tooth extraction. This eliminates the need for a separate surgical procedure and allows for faster bone integration.
- One-Step Procedure: Immediate implant placement combines tooth extraction and implant placement into a single procedure, reducing the number of surgical interventions and overall treatment time.
- Preserves Bone Volume: Immediate implant placement helps maintain the bone structure around the extraction site, reducing the risk of bone resorption and improving the long-term stability of the implant.
- Reduced Healing Time: By placing the implant immediately, the healing process is initiated sooner, leading to a faster recovery and a quicker return to function.
Advanced Implant Restorations
Once the dental implant has successfully integrated with the jawbone, the next step is to place the restoration, which is the visible part of the tooth that replaces the missing tooth structure. Implant restorations are designed to seamlessly blend with the surrounding teeth and restore both function and aesthetics.
Types of Implant Restorations
Implant restorations come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and missing teeth.
- Dental Crowns: These are caps that cover the entire visible portion of the tooth, restoring its shape, size, and color. They are commonly used for single-tooth replacements.
- Dental Bridges: These restorations replace multiple missing teeth by spanning the gap with a series of crowns connected by a bridge. They are supported by dental implants on either side of the gap.
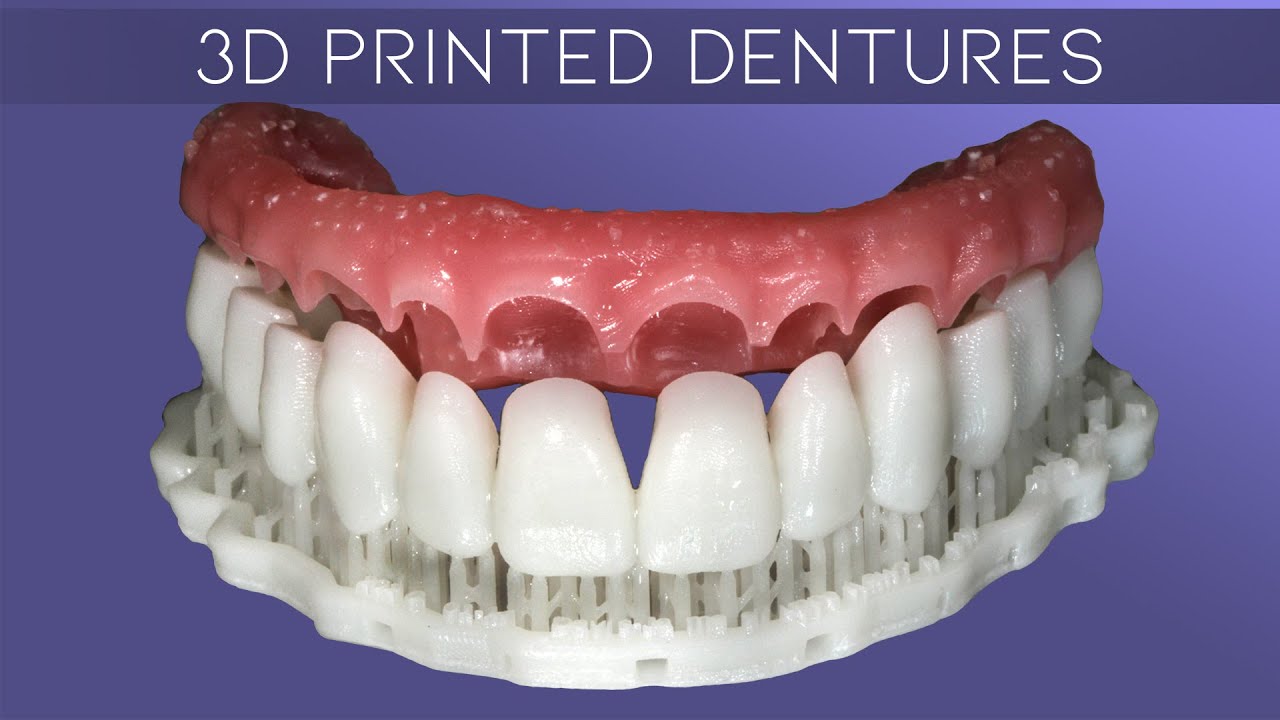
- Implant-Supported Dentures: For patients with missing teeth throughout the mouth, implant-supported dentures offer a secure and stable solution. Implants are strategically placed in the jawbone to provide support for the denture, which can be either fixed (permanently attached) or removable.
Materials and Techniques for Implant Restorations
The choice of materials and techniques for creating implant restorations plays a crucial role in their durability, aesthetics, and longevity.
- Ceramic Restorations: Ceramic materials like porcelain and zirconia are highly biocompatible, aesthetically pleasing, and resistant to staining. They are commonly used for crowns and bridges, mimicking the natural look of teeth.
- Composite Restorations: Composite materials are tooth-colored and can be used to build up missing tooth structure or create aesthetically pleasing restorations. They are often used for smaller restorations or repairs.
- CAD/CAM Technology: Computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology allows for highly precise and customized restorations. A digital scan of the patient’s mouth is used to create a 3D model, which is then used to mill the restoration from a block of ceramic or composite material.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Implant Restoration Options
The choice of implant restoration depends on factors such as the number of missing teeth, the patient’s budget, and their aesthetic goals.
| Restoration Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Dental Crowns | – Restores single missing tooth – Natural-looking – Durable |
– More expensive than traditional crowns – Requires a healthy abutment tooth |
| Dental Bridges | – Replaces multiple missing teeth – Restores chewing function – Can improve aesthetics |
– Requires healthy abutment teeth – May require more maintenance than single crowns |
| Implant-Supported Dentures | – Secure and stable – Comfortable – Improved chewing function |
– More expensive than traditional dentures – Requires surgical placement of implants |
Future Trends in Dental Implant Technology
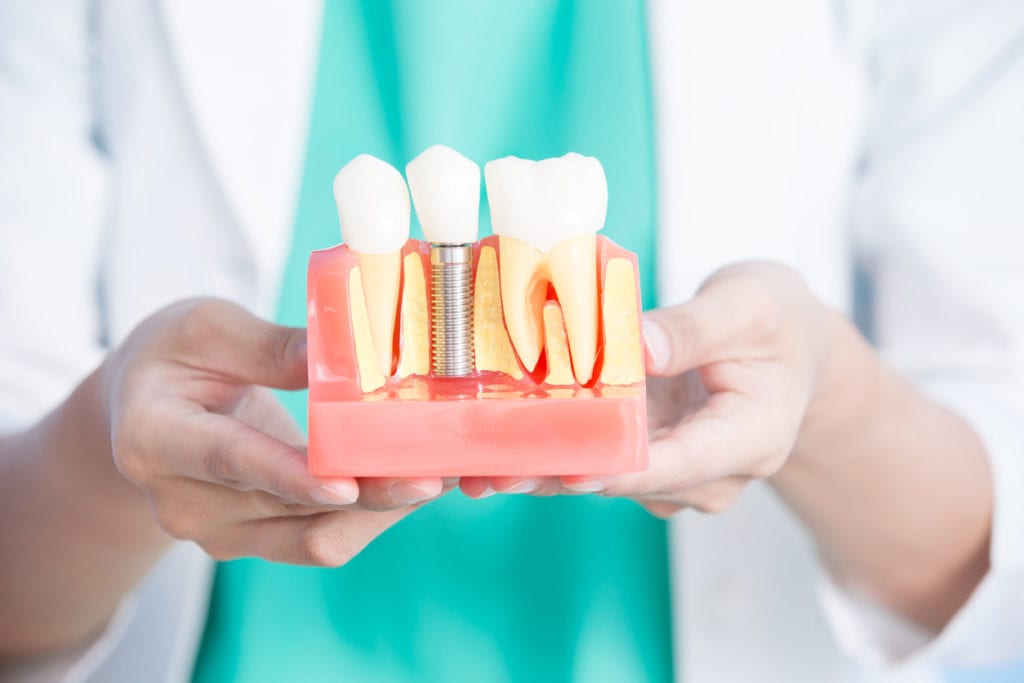
The field of dental implants is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development leading to exciting advancements that promise to revolutionize the way we treat tooth loss. These advancements are focused on improving implant materials, surgical techniques, restoration options, and integration with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and nanotechnology.
Advancements in Implant Materials
The search for biocompatible, durable, and osteointegrative materials continues to drive innovation in dental implants. Current research focuses on developing materials that are:
- Stronger and more resistant to wear and tear: Researchers are exploring new alloys, ceramics, and composites to enhance the longevity and performance of dental implants. For instance, zirconia implants, known for their exceptional strength and biocompatibility, are gaining popularity.
- More biocompatible and osteoconductive: Advancements in surface treatments and coatings are aimed at promoting faster bone integration and reducing the risk of implant rejection. For example, titanium implants with a bioactive coating have shown promising results in clinical trials, promoting enhanced bone growth around the implant.
- Customizable and personalized: The development of 3D-printed implants tailored to individual patients’ anatomy is a significant step towards personalized medicine in dental implantology. This technology allows for precise fit and improved integration, potentially leading to faster healing and reduced complications.
Minimally Invasive Implant Techniques
Minimally invasive techniques are gaining traction in implant dentistry, aiming to reduce surgical trauma, pain, and recovery time. These techniques include:
- Guided implant surgery: This technique utilizes 3D imaging and computer-aided design (CAD) to plan and execute implant placement with precision. It allows for minimally invasive procedures with reduced soft tissue trauma and predictable outcomes.
- Flapless surgery: This technique minimizes the need for incisions, reducing pain and swelling. It involves using a specialized drill to create a small opening in the gum tissue, allowing for implant placement without significant tissue disruption.
- Immediate implant placement: In certain cases, implants can be placed immediately after tooth extraction, reducing the need for a second surgical procedure and minimizing bone loss. This technique requires careful planning and patient selection to ensure optimal outcomes.
Advanced Implant Restorations
Technological advancements are transforming the way dental implants are restored, leading to improved aesthetics, function, and durability. Key advancements include:
- CAD/CAM technology: Computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems allow for the creation of highly precise and aesthetically pleasing crowns, bridges, and dentures. These restorations are custom-made to fit the individual patient’s needs and improve overall satisfaction.
- Digital impressions: Digital impressions using intraoral scanners eliminate the need for traditional impression materials, resulting in a faster, more comfortable, and accurate process. The digital data can then be used to create custom restorations with greater precision.
- Implant-supported dentures: Advancements in implant technology have led to the development of more stable and comfortable implant-supported dentures. These dentures offer improved retention, stability, and chewing function, enhancing the quality of life for patients with complete tooth loss.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Nanotechnology
Emerging technologies like AI and nanotechnology are poised to revolutionize dental implantology, leading to significant improvements in implant design, surgical techniques, and patient care.
- AI-powered implant planning: AI algorithms can analyze patient data, including 3D scans and medical history, to provide personalized implant plans with greater accuracy and efficiency. AI can also assist in identifying potential complications and optimize treatment strategies.
- Nanotechnology in implant coatings: Nanotechnology is being used to develop advanced coatings for dental implants that enhance biocompatibility, promote bone growth, and reduce bacterial adhesion. These coatings can improve the long-term success and stability of implants.
- AI-driven patient monitoring: AI can be used to analyze data from wearable sensors and smart devices to monitor patient recovery and identify potential complications after implant surgery. This allows for early intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Closing Notes: Latest Dental Implant Technology
As research and development continue at a rapid pace, the future of dental implant technology holds immense promise. From innovative implant materials that seamlessly integrate with bone to AI-powered tools for personalized treatment planning, the possibilities are endless. With these advancements, dental implants are poised to become even more accessible and effective, ensuring a brighter and healthier smile for generations to come.
The latest dental implant technology utilizes advanced materials and techniques to provide a more natural and comfortable experience. These implants are designed to seamlessly integrate with the jawbone, offering a long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing solution. Similar to the precision and innovation found in the latest dental implants, you’ll find cutting-edge design and functionality in anthro technology furniture.
Just as dental implants strive to improve oral health, Anthro furniture aims to enhance productivity and comfort in the workplace. Ultimately, both fields demonstrate a commitment to utilizing technology to improve our lives.