Knowledge Management Technologies: Empowering Modern Organizations
Knowledge management technologies are the backbone of modern organizations, enabling them to capture, organize, share, and leverage valuable insights for strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. These technologies empower organizations to […]
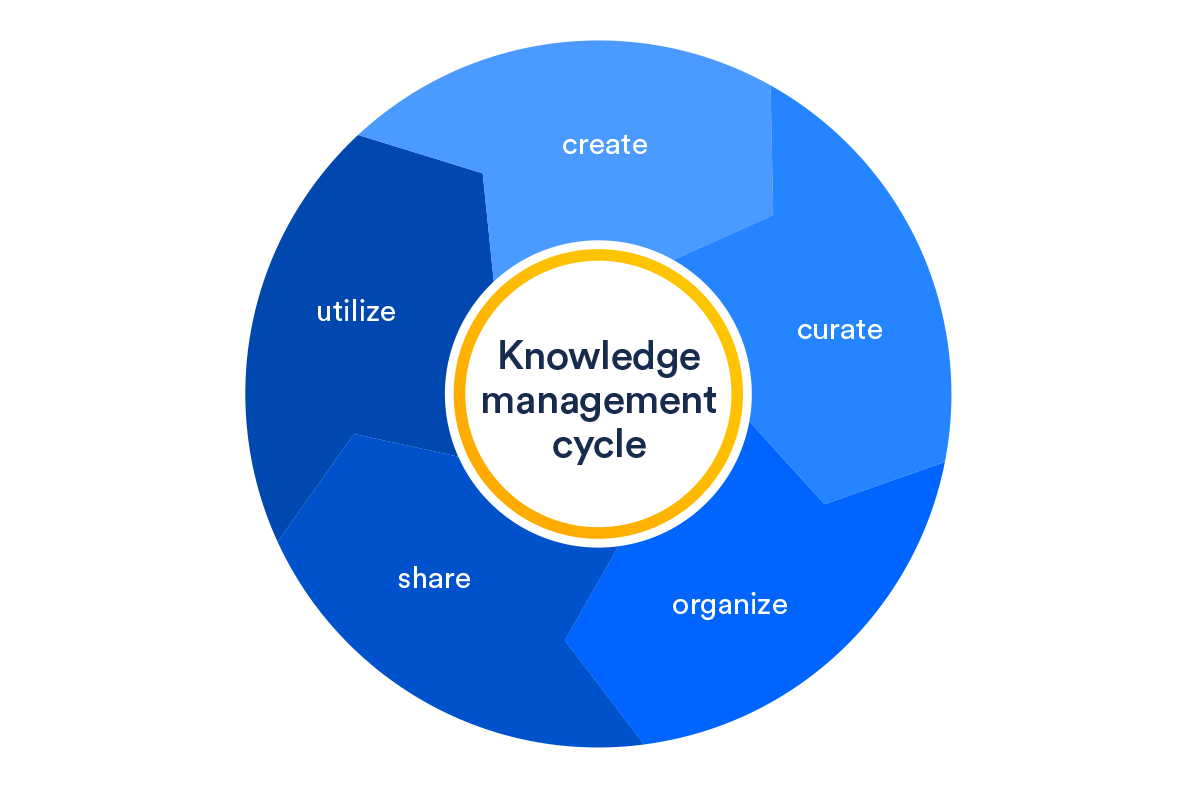
Knowledge management technologies are the backbone of modern organizations, enabling them to capture, organize, share, and leverage valuable insights for strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. These technologies empower organizations to transform raw information into actionable knowledge, fostering innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning.
From sophisticated knowledge bases and collaboration platforms to intelligent search engines and data analytics tools, knowledge management technologies offer a diverse range of solutions tailored to specific organizational needs. By effectively managing knowledge assets, organizations can streamline processes, enhance employee productivity, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Knowledge Capture and Organization

Knowledge capture and organization are fundamental aspects of knowledge management, enabling the systematic collection, structuring, and dissemination of valuable insights within an organization. Effective knowledge capture ensures that valuable information is not lost, while organization facilitates efficient retrieval and application.
Capturing Knowledge from Various Sources
Knowledge capture involves identifying, extracting, and storing knowledge from various sources. These sources can be both internal and external to the organization.
- Internal Sources: Internal sources include employee expertise, project documentation, meeting minutes, reports, training materials, and company databases.
- External Sources: External sources encompass industry publications, research papers, competitor analysis, market trends, customer feedback, and online resources.
Methods for Organizing and Structuring Captured Knowledge
Once knowledge is captured, it needs to be organized and structured for easy access and retrieval. Common methods include:
- Taxonomies and Ontologies: These hierarchical systems classify knowledge based on predefined categories and relationships. They provide a structured framework for organizing information and facilitate search and retrieval.
- Knowledge Maps: Visual representations of knowledge domains, depicting relationships between concepts and topics. They provide a holistic view of the knowledge landscape and aid in navigating complex information.
- Knowledge Graphs: Data structures that represent knowledge as a network of interconnected entities and relationships. They enable complex queries and the discovery of hidden connections within the knowledge base.
Tools and Techniques for Managing Knowledge Assets
Various tools and techniques are employed to manage knowledge assets effectively.
- Knowledge Management Systems (KMS): Software platforms designed to store, manage, and share knowledge. They offer features such as document repositories, collaboration tools, search functionalities, and reporting capabilities.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Tools for creating, editing, and managing digital content. They are commonly used for website development, but can also be adapted for knowledge management purposes.
- Social Collaboration Tools: Platforms that facilitate communication and collaboration among employees. They allow for knowledge sharing through forums, discussion groups, and knowledge bases.
Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration: Knowledge Management Technologies
Knowledge management technologies are not just about capturing and organizing information; they are also about making that knowledge accessible and usable. Effective knowledge sharing is crucial for organizations to leverage the collective intelligence of their workforce and foster innovation.
Facilitating Knowledge Sharing
Knowledge management technologies provide a platform for sharing information in various formats. These technologies can be used to create a central repository of knowledge, making it easily accessible to all employees. Some examples of how these technologies facilitate knowledge sharing include:
- Document sharing platforms: These platforms allow users to upload, store, and share documents, presentations, and other files. They often have features for version control, collaboration, and search, making it easy to find the right information.
- Knowledge bases: These platforms are designed to store and organize knowledge in a structured way. They can be used to create FAQs, tutorials, best practices, and other types of information. Knowledge bases can be integrated with search engines, making it easy to find the information you need.
- Social collaboration tools: These tools allow users to connect and collaborate in real-time. They can be used for discussions, brainstorming, and sharing ideas. Social collaboration tools can also be used to create communities of practice around specific topics, allowing users to learn from each other and share their expertise.
The Role of Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools play a vital role in knowledge dissemination by providing a platform for real-time interaction and information exchange. These tools allow employees to work together on projects, share ideas, and provide feedback. Examples of collaboration tools that facilitate knowledge sharing include:
- Project management software: This software helps teams plan, track, and manage projects. It provides a central platform for communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing.
- Instant messaging platforms: These platforms allow for quick and easy communication between team members. They can be used to share information, ask questions, and get feedback.
- Video conferencing tools: These tools allow for real-time video and audio communication. They can be used for meetings, presentations, and training sessions.
Best Practices for Effective Knowledge Sharing
Effective knowledge sharing requires a strategic approach. Here are some best practices for maximizing the benefits of knowledge management technologies:
- Encourage a culture of sharing: Organizations need to create a culture where employees feel comfortable sharing their knowledge and ideas. This can be achieved by recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions to knowledge sharing.
- Make it easy to find and access information: Knowledge management technologies should be designed to make it easy for employees to find the information they need. This includes providing clear search functionality, organizing information into relevant categories, and using tagging systems to make it easier to find information.
- Provide training and support: Employees need to be trained on how to use knowledge management technologies effectively. Organizations should also provide ongoing support to ensure that employees can access and utilize the information they need.
- Monitor and evaluate knowledge sharing activities: Organizations should track the usage of their knowledge management technologies and assess their effectiveness. This information can be used to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the technologies are meeting the needs of the organization.
Knowledge Retrieval and Search
Efficient knowledge retrieval is the cornerstone of any effective knowledge management system. It allows users to quickly and easily find the information they need, when they need it, maximizing the value of the knowledge base. This section explores the importance of efficient knowledge retrieval, examines various search functionalities and indexing techniques, and delves into how knowledge management technologies enhance knowledge accessibility.
Search Functionalities and Indexing Techniques
Search functionalities and indexing techniques are crucial for enabling efficient knowledge retrieval. They ensure that users can locate relevant information within a vast knowledge base.
- Search: This is the most basic search functionality, allowing users to enter s related to the information they are seeking. The system then returns documents containing those s.
- Boolean Search: This advanced search functionality allows users to combine s using operators such as AND, OR, and NOT to refine their search results. For example, a search for “knowledge management AND tools” would only return documents containing both terms.
- Natural Language Search: This functionality allows users to enter search queries in natural language, similar to how they would ask a question. The system then attempts to understand the intent behind the query and return relevant results.
- Faceting: This technique allows users to filter search results based on specific criteria, such as document type, author, or date.
- Semantic Search: This advanced search functionality utilizes natural language processing and machine learning to understand the meaning of search queries and return results based on semantic relationships between words and concepts.
Indexing techniques play a critical role in facilitating efficient search. They involve creating a structured representation of the knowledge base that allows the search engine to quickly locate relevant information.
- Full-text Indexing: This technique indexes every word in every document, allowing for comprehensive searches.
- Inverted Indexing: This technique creates an index that maps words to the documents containing them, enabling faster retrieval of documents containing specific s.
- Stemming and Lemmatization: These techniques reduce words to their root forms, improving search accuracy by matching variations of the same word.
- Stop Word Removal: This technique eliminates common words like “the,” “a,” and “is” from the index, improving search efficiency by focusing on more relevant words.
Knowledge Management Technologies Enhance Knowledge Accessibility
Knowledge management technologies play a vital role in enhancing knowledge accessibility by providing users with a range of tools and features for searching, retrieving, and sharing information.
- Centralized Knowledge Repositories: These repositories serve as a single source of truth for all knowledge assets, ensuring that users can access the most up-to-date information.
- Search Engines: Powerful search engines enable users to quickly and easily find the information they need, regardless of the size of the knowledge base.
- Metadata Management: Metadata, such as s, tags, and categories, helps users find relevant information by providing additional context and filtering options.
- Personalization: Knowledge management systems can personalize search results based on user preferences, roles, and past activity, making the retrieval process more efficient and relevant.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaboration tools, such as forums, wikis, and social networks, facilitate knowledge sharing and retrieval by enabling users to ask questions, share insights, and discuss topics.
Knowledge Preservation and Management
Knowledge preservation is a critical aspect of knowledge management. It ensures that valuable knowledge, accumulated over time, is not lost or forgotten. This process involves actively safeguarding and maintaining knowledge assets, making them accessible and useful for future generations.
Archiving and Managing Knowledge Assets
Effective archiving and management of knowledge assets are essential for preserving valuable knowledge. These methods help in organizing, storing, and retrieving information efficiently.
- Document Management Systems (DMS): DMS are specialized software solutions designed to store, organize, and manage electronic documents. They offer features like version control, access control, and search functionalities, making it easy to find and retrieve specific documents.
- Digital Repositories: These repositories serve as central hubs for storing and preserving digital knowledge assets, including research papers, reports, presentations, and other digital content. They ensure long-term preservation and provide secure access to information.
- Knowledge Bases: Knowledge bases are structured repositories of information that can be easily searched and accessed. They often use a question-and-answer format, making it simple to find relevant information.
Tools and Techniques for Ensuring Knowledge Continuity, Knowledge management technologies
Knowledge continuity is crucial for maintaining organizational knowledge even as employees leave or retire. It involves implementing strategies and tools to ensure that knowledge remains accessible and readily available.
- Knowledge Transfer Programs: These programs facilitate the transfer of knowledge from experienced employees to new or less experienced ones. They can involve mentoring, shadowing, or structured training programs.
- Knowledge Mapping: Knowledge mapping involves creating visual representations of the knowledge landscape within an organization. It helps identify key knowledge areas, expertise gaps, and potential knowledge loss.
- Knowledge Sharing Platforms: Online platforms, such as wikis, forums, and social media groups, provide spaces for employees to share knowledge, ask questions, and collaborate. These platforms help to create a culture of knowledge sharing and facilitate knowledge continuity.
Measuring Knowledge Management Effectiveness
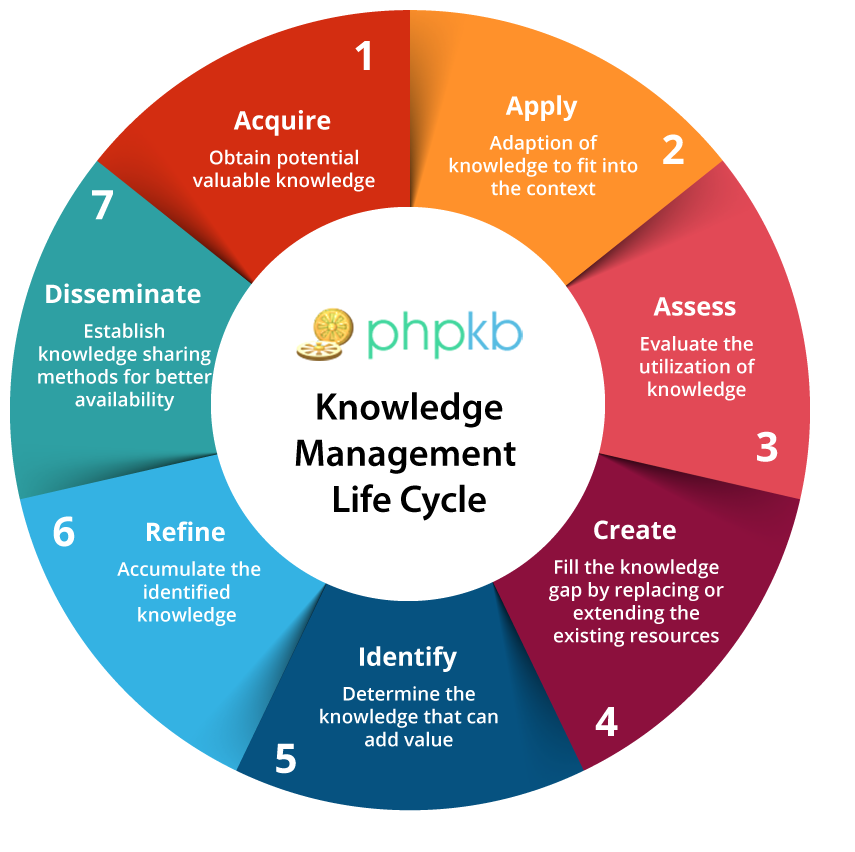
It’s crucial to measure the effectiveness of your knowledge management system to ensure it’s delivering real value to your organization. This involves identifying key metrics, tracking performance, and analyzing the results to understand what’s working and what needs improvement.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Knowledge Management Success
These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of your knowledge management system.
- Knowledge Usage: This metric measures how often knowledge assets are accessed and utilized. It can be tracked through website analytics, document downloads, or user activity logs.
- Knowledge Creation: This metric assesses the rate at which new knowledge is being created and added to the knowledge base. It can be measured by tracking the number of new documents, articles, or forum posts.
- Knowledge Sharing: This metric measures the frequency and reach of knowledge sharing activities. It can be tracked through the number of knowledge-sharing events, forum participation, or social media engagement.
- Knowledge Impact: This metric measures the positive impact of knowledge management on key organizational goals. It can be assessed through improved decision-making, increased productivity, reduced errors, or enhanced customer satisfaction.
- User Satisfaction: This metric evaluates the overall satisfaction of knowledge management system users. It can be measured through surveys, feedback forms, or user reviews.
Tracking and Analyzing Knowledge Management Performance
Tracking and analyzing knowledge management performance is essential for identifying areas for improvement and optimizing the system for maximum impact.
- Regular Reporting: Regularly generate reports on key knowledge management metrics. This allows you to track progress over time and identify trends.
- Data Visualization: Use data visualization tools to create dashboards and charts that provide clear and concise insights into knowledge management performance.
- Benchmarking: Compare your knowledge management performance against industry benchmarks or best practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the data collected to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance the effectiveness of your knowledge management system.
Examples of Successful Knowledge Management Initiatives
Many organizations have implemented successful knowledge management initiatives that have delivered tangible benefits.
- IBM’s Watson: IBM’s Watson is an AI-powered knowledge management system that uses natural language processing and machine learning to analyze vast amounts of data and provide insights. Watson has been used in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and education, to improve decision-making and enhance customer experiences.
- Google’s Knowledge Graph: Google’s Knowledge Graph is a massive database of entities and their relationships, which is used to power Google Search and other Google services. It helps users find relevant information quickly and efficiently by understanding the context of their queries.
- Wikipedia: Wikipedia is a collaborative online encyclopedia that allows users to create, edit, and share knowledge freely. It is a prime example of a successful knowledge management system that relies on community participation and open access.
Future Trends in Knowledge Management Technologies

Knowledge management is a dynamic field, constantly evolving with advancements in technology. As we enter the digital age, new technologies are emerging that are transforming the way we capture, organize, share, and retrieve knowledge. This section will explore some of these trends and their impact on the future of knowledge management.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly changing the landscape of knowledge management. AI-powered tools can automate tasks like data analysis, content tagging, and knowledge discovery, freeing up human experts to focus on more strategic initiatives. For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide instant answers to employee queries, while machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify hidden patterns and insights.
The Importance of Data Analytics
Data analytics plays a crucial role in understanding and extracting value from knowledge. By analyzing data from various sources, organizations can gain insights into employee performance, customer behavior, and market trends. This information can then be used to improve decision-making, optimize processes, and enhance customer experiences.
The Future of Knowledge Management in the Digital Age
The digital age is characterized by an explosion of data, making it more challenging than ever to manage and leverage knowledge effectively. Emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are creating new opportunities and challenges for knowledge management.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Data Security and Privacy: As organizations collect and store increasing amounts of data, ensuring data security and privacy becomes paramount. Implementing robust security measures and adhering to data privacy regulations is essential to protect sensitive information.
- Data Governance: With the proliferation of data, establishing effective data governance policies is crucial. This includes defining data ownership, access control, and data quality standards to ensure data integrity and consistency.
- Integration of Emerging Technologies: Integrating emerging technologies like AI and blockchain into existing knowledge management systems requires careful planning and execution. Organizations need to consider the potential impact of these technologies on their workflows and processes.
- Building a Knowledge-Driven Culture: To fully leverage the benefits of knowledge management, organizations need to foster a culture that values knowledge sharing, collaboration, and continuous learning. This involves encouraging employees to contribute their expertise and providing them with the tools and resources they need to succeed.
Final Review
In conclusion, knowledge management technologies play a pivotal role in transforming organizations into knowledge-driven entities. By embracing these technologies, organizations can unlock the potential of their collective intelligence, foster innovation, and achieve sustainable success in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve, the future of knowledge management holds exciting possibilities, promising even greater opportunities for organizations to leverage knowledge as a strategic asset.
Knowledge management technologies are essential for organizations to leverage their collective intelligence. These technologies help to capture, store, and share information effectively, but they also need to be protected from unauthorized access. This is where perimeter technology plays a crucial role, providing a secure boundary around sensitive data and systems.
By integrating robust perimeter technology, organizations can ensure that their knowledge management systems remain secure and accessible only to authorized users.