Information Technology Governance Best Practices: A Guide to Success
Information technology governance best practices are essential for organizations of all sizes to ensure their technology investments align with business objectives, manage risks effectively, and achieve sustainable growth. By implementing […]
Information technology governance best practices are essential for organizations of all sizes to ensure their technology investments align with business objectives, manage risks effectively, and achieve sustainable growth. By implementing a robust IT governance framework, organizations can gain control over their technology assets, improve operational efficiency, and enhance their competitive advantage.
This guide explores the key components of IT governance, best practices for implementation, and the benefits of adopting a structured approach to managing technology. We’ll delve into topics such as establishing clear policies and procedures, fostering effective communication and collaboration, and conducting regular assessments to ensure continuous improvement. By understanding and implementing these best practices, organizations can leverage technology to drive innovation, achieve strategic goals, and thrive in the digital age.
Best Practices for IT Governance
Effective IT governance ensures that an organization’s IT resources are aligned with its strategic goals and objectives. It encompasses establishing clear policies, procedures, and processes to manage IT risks, ensure compliance, and optimize IT investments.
Establishing Clear IT Policies and Procedures
Clear and concise IT policies and procedures are essential for effective IT governance. They provide a framework for decision-making, guide IT operations, and promote consistency and accountability.
- Develop comprehensive IT policies: Policies should cover key areas such as data security, access control, software usage, and acceptable use. These policies should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in technology, regulations, and business needs.
- Establish clear IT procedures: Procedures provide detailed instructions for carrying out specific IT tasks, such as password management, incident response, and data backup. They should be written in a clear and concise manner and readily accessible to all relevant personnel.
- Ensure alignment with business objectives: IT policies and procedures should be aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy and goals. This ensures that IT investments and initiatives support the organization’s strategic priorities.
- Communicate effectively: IT policies and procedures should be communicated effectively to all stakeholders, including employees, contractors, and vendors. This can be done through training programs, online resources, and regular communication channels.
- Implement monitoring and enforcement: It is crucial to monitor compliance with IT policies and procedures and to enforce them consistently. This can be done through regular audits, performance reviews, and disciplinary actions.
Importance of Effective Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are critical for successful IT governance. They facilitate information sharing, promote transparency, and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned on IT priorities and initiatives.
- Establish clear communication channels: Regular communication channels should be established between IT governance stakeholders, including senior management, IT professionals, and business users. These channels can include meetings, email, and online collaboration platforms.
- Promote transparency and accountability: Transparency is crucial in IT governance. Stakeholders should be informed about IT decisions, risks, and performance. This promotes trust and accountability.
- Encourage open dialogue and feedback: Open dialogue and feedback are essential for identifying and addressing issues related to IT governance. This can be facilitated through regular meetings, surveys, and feedback mechanisms.
- Foster a culture of collaboration: A collaborative culture is essential for effective IT governance. This involves breaking down silos between IT and business units and promoting cross-functional teamwork.
Framework for Regular IT Governance Reviews and Assessments, Information technology governance best practices
Regular reviews and assessments are crucial for ensuring that IT governance remains effective and aligned with the organization’s changing needs.
- Establish a review schedule: A regular schedule should be established for reviewing IT governance processes, policies, and procedures. This could be done annually, semi-annually, or quarterly, depending on the organization’s specific needs.
- Define review scope: The scope of the review should be clearly defined and should include all key aspects of IT governance, such as risk management, compliance, security, and performance.
- Use appropriate assessment tools: Various assessment tools can be used to evaluate IT governance effectiveness. These tools may include questionnaires, checklists, and benchmarking data.
- Document findings and recommendations: The findings of the review should be documented, along with recommendations for improvement. This documentation should be shared with relevant stakeholders.
- Implement recommendations and monitor progress: The recommendations from the review should be implemented in a timely manner. Progress should be monitored to ensure that the recommendations are having the desired impact.
IT Governance and Security

IT governance plays a crucial role in establishing and maintaining a secure IT environment. It provides the framework and oversight necessary to ensure that information security is effectively implemented and maintained.
Role of IT Governance in Information Security
IT governance provides a comprehensive approach to managing information security risks. It ensures that security policies, standards, and procedures are aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives. By establishing clear accountability and responsibility for security, IT governance fosters a culture of security awareness and promotes proactive risk management.
IT Governance and Data Privacy
IT governance contributes to data privacy by defining and enforcing policies and procedures that comply with relevant data protection regulations. For instance, IT governance ensures that data is collected, processed, and stored in accordance with privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). It also establishes mechanisms for data breach notification and incident response, minimizing the impact of data breaches.
IT Governance and Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation
IT governance is essential for mitigating cybersecurity risks. It enables organizations to identify, assess, and prioritize security risks, allowing them to allocate resources effectively to address the most critical threats. By establishing clear security controls and monitoring their effectiveness, IT governance helps to reduce the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks.
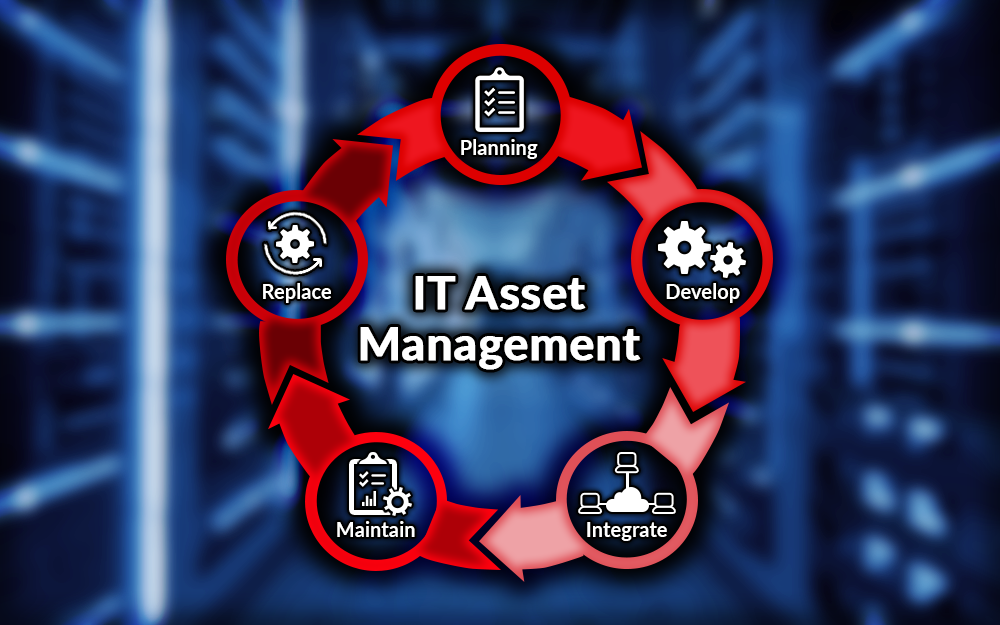
Implementing IT Governance
Implementing IT governance within an organization is a crucial step in ensuring that IT aligns with business goals and objectives. It involves establishing a framework for decision-making, accountability, and risk management related to IT.
Steps for Implementing IT Governance
The process of implementing IT governance involves a series of steps, each crucial to achieving success.
- Define IT Governance Objectives: The initial step involves clearly defining the organization’s IT governance objectives. This includes identifying the desired outcomes, such as improved IT performance, reduced risk, and enhanced alignment with business goals.
- Establish a Governance Structure: Next, establish a clear governance structure, including roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines. This structure ensures that IT decisions are made in a coordinated and accountable manner.
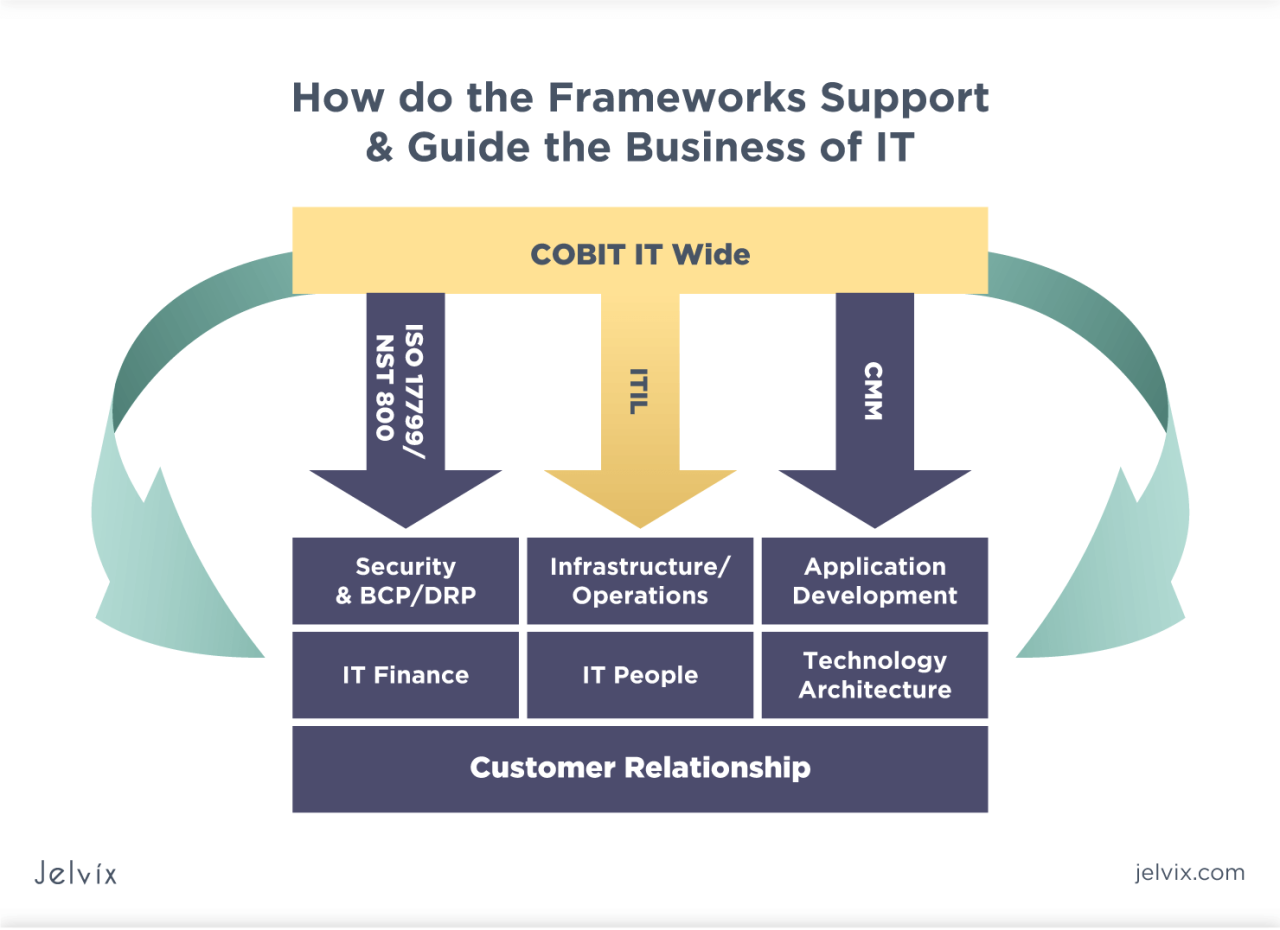
- Select an IT Governance Framework: Choosing a suitable IT governance framework provides a structured approach to implementing and managing IT governance. Frameworks like COBIT, ISO/IEC 38500, and ITIL offer guidelines, best practices, and tools for effective governance.
- Develop Policies and Procedures: Create comprehensive policies and procedures to guide IT decision-making, risk management, and resource allocation. These documents should be clear, concise, and easily accessible to all stakeholders.
- Implement Risk Management Processes: IT governance necessitates a robust risk management framework to identify, assess, and mitigate IT risks. This involves developing risk assessment processes, implementing controls, and monitoring risk levels.
- Monitor and Evaluate Performance: Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of IT governance practices. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting audits, and making adjustments as needed.
Continuous Improvement in IT Governance
IT governance is not a one-time effort but rather an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Organizations must adapt their governance practices to evolving business needs, technological advancements, and changing regulatory landscapes.
- Regularly Review and Update Governance Practices: Conduct periodic reviews of IT governance policies, procedures, and frameworks to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
- Embrace New Technologies and Trends: Stay informed about emerging technologies and trends that can impact IT governance. Adapt governance practices to address new risks and opportunities.
- Encourage Feedback and Collaboration: Foster a culture of open communication and collaboration among stakeholders. Encourage feedback on IT governance practices and use it to drive improvements.
Comparison of IT Governance Frameworks
Various IT governance frameworks offer different approaches and key features. Choosing the right framework depends on the organization’s specific needs and context.
| Framework | Key Features |
|---|---|
| COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and related Technology) | Comprehensive framework covering all aspects of IT governance, including planning, organizing, directing, and controlling IT resources. |
| ISO/IEC 38500:2015 (Governance of IT for organizations) | Provides guidance on the responsibilities of boards and senior management for the governance of IT, focusing on aligning IT with business objectives. |
| ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) | A set of best practices for managing IT services, including service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement. |
IT Governance and Business Value: Information Technology Governance Best Practices
Effective IT governance is not merely a compliance exercise; it is a strategic tool that drives business value by aligning IT investments with organizational goals and ensuring that IT resources are utilized efficiently and effectively. This section explores how IT governance contributes to business success by enhancing operational efficiency, fostering innovation, and creating a competitive advantage.
Operational Efficiency
IT governance improves operational efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing costs, and minimizing risks.
- Standardized Processes: IT governance establishes standardized processes and procedures for managing IT systems and services, reducing inconsistencies and errors, and enabling smooth operations.
- Cost Optimization: By optimizing resource allocation, IT governance helps organizations identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses, leading to cost savings. For example, by consolidating data centers and implementing cloud-based solutions, companies can reduce infrastructure costs.
- Risk Management: IT governance frameworks include robust risk management practices, such as vulnerability assessments, security audits, and incident response plans, to mitigate potential risks and ensure business continuity.
Innovation
IT governance supports innovation by fostering a culture of collaboration, promoting experimentation, and enabling the adoption of new technologies.
- Agile Development: IT governance encourages the adoption of agile development methodologies, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing market demands and introduce new products or services efficiently.
- Technology Adoption: IT governance provides a framework for evaluating and adopting new technologies, ensuring that investments align with strategic goals and organizational needs.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By establishing data governance policies and procedures, IT governance promotes data quality and integrity, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable data.
Competitive Advantage
IT governance plays a crucial role in achieving a competitive advantage by enabling organizations to leverage technology to differentiate themselves from competitors and deliver superior customer experiences.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: IT governance ensures that IT systems and services meet customer expectations, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Market Agility: By enabling organizations to respond quickly to market changes, IT governance contributes to market agility and competitiveness.
- Strategic Alignment: IT governance aligns IT investments with business strategy, ensuring that technology supports the achievement of organizational goals and objectives.
Epilogue

By embracing information technology governance best practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of the digital landscape with confidence. From aligning IT strategy with business objectives to mitigating cybersecurity risks and fostering innovation, a well-defined governance framework empowers organizations to unlock the full potential of technology and achieve lasting success.
Information technology governance best practices ensure alignment between technology investments and business goals. A crucial element in this alignment is effective communication, which is where a skilled technology copywriter comes in. They can translate complex technical concepts into clear, compelling language that resonates with stakeholders, fostering understanding and buy-in for IT initiatives.