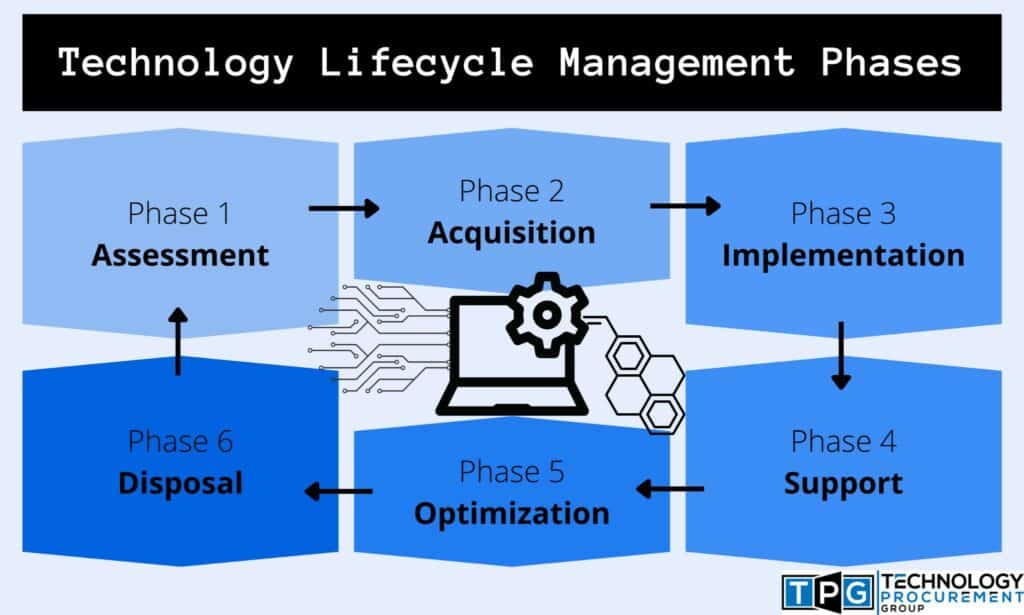
Information Technology Governance Best Practices: A Guide for Organizations
Information technology governance best practices set the stage for a smooth and efficient operation of any organization, ensuring that IT resources are aligned with strategic goals and risk management is […]

Information technology governance best practices set the stage for a smooth and efficient operation of any organization, ensuring that IT resources are aligned with strategic goals and risk management is robust. This framework serves as a compass, guiding organizations through the complex landscape of data management, infrastructure, application development, and security, all while navigating the ever-evolving digital landscape.
By establishing a comprehensive governance framework, organizations can foster a culture of accountability, transparency, and control, leading to better decision-making, improved risk mitigation, and enhanced overall performance. This approach ensures that IT investments are strategic, aligned with business needs, and contribute to organizational success.
Understanding Information Technology Governance: Information Technology Governance Best Practices

Information technology governance (IT governance) is the framework that ensures an organization’s IT investments align with its strategic goals. It provides the structure for making decisions about IT resources, aligning them with business needs, and managing risks effectively.
Defining IT Governance
IT governance is a crucial aspect of an organization’s overall strategy. It provides a framework for managing IT risks, ensuring IT investments are aligned with business goals, and maximizing the value of IT resources. It involves establishing clear responsibilities, processes, and controls for IT activities, ensuring that IT decisions are made in a consistent and transparent manner.
Key Principles of IT Governance
The principles of IT governance guide organizations in establishing a framework that aligns IT with business objectives. These principles include:
- Strategic Alignment: IT investments should be aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and priorities. This ensures that IT resources are used to support business growth and achieve desired outcomes.
- Risk Management: IT governance addresses potential risks associated with IT systems and data. It ensures that appropriate controls are in place to mitigate risks and protect the organization’s assets.
- Value Delivery: IT governance focuses on maximizing the value of IT investments. This includes measuring the effectiveness of IT initiatives and ensuring that IT resources are used efficiently.
- Resource Management: IT governance establishes processes for managing IT resources effectively. This includes budgeting, resource allocation, and performance management.
- Performance Measurement: IT governance requires regular monitoring and evaluation of IT performance. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and identifying areas for improvement.
Benefits of a Strong IT Governance Framework
Establishing a robust IT governance framework provides numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved Business Alignment: IT governance ensures that IT investments and initiatives are aligned with business objectives, leading to greater efficiency and effectiveness.
- Enhanced Risk Management: A well-defined IT governance framework helps organizations identify and mitigate potential risks associated with IT systems and data, protecting valuable assets.
- Increased Efficiency: IT governance promotes standardized processes and controls, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
- Improved Compliance: IT governance helps organizations comply with relevant regulations and industry standards, minimizing the risk of legal and financial penalties.
- Enhanced Decision Making: A clear governance framework provides a structured approach to decision-making, ensuring that IT decisions are made in a consistent and transparent manner.
Key Governance Areas
Effective information technology (IT) governance requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various critical areas. These areas are interconnected and work together to ensure the alignment of IT with business objectives, while also addressing security, risk, and compliance considerations.
Data Management
Data management is a crucial aspect of IT governance, as it involves protecting sensitive information, ensuring data integrity, and complying with relevant regulations. Data governance encompasses policies, processes, and tools to manage the entire data lifecycle, from creation to deletion.
- Data Security: Robust data security measures are essential to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Best practices for data security include:
- Implementing strong access controls and authentication mechanisms.
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- Regularly conducting security assessments and vulnerability scans.
- Maintaining a comprehensive security awareness program for employees.
- Data Privacy: Protecting personal information is paramount, and data governance plays a critical role in ensuring compliance with privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Best practices for data privacy include:
- Obtaining explicit consent for data collection and use.
- Implementing data minimization principles, only collecting necessary data.
- Providing individuals with access to their data and the right to erasure.
- Ensuring data breaches are promptly reported and investigated.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining data integrity ensures that information is accurate, complete, and consistent. Best practices for data integrity include:
- Establishing data validation rules and implementing data quality checks.
- Regularly backing up and recovering data to prevent loss.
- Implementing data governance policies to ensure data consistency across systems.
Data retention policies define the duration for which data should be stored and the procedures for managing data throughout its lifecycle. Establishing data retention policies helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements, reduce storage costs, and minimize security risks.
- Data retention policies should be based on legal requirements, business needs, and industry best practices.
- Clear procedures for data retention, deletion, and archiving should be documented and communicated to all stakeholders.
- Organizations should regularly review and update their data retention policies to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Data governance frameworks and tools provide a structured approach to managing data effectively. Examples of data governance frameworks include:
- COBIT 5: A comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, including data governance principles and practices.
- DAMA-DMBOK: A widely recognized body of knowledge for data management, providing guidance on data governance, data quality, and data architecture.
- ISO 27001: An international standard for information security management systems, encompassing data security and privacy controls.
Tools for data governance can assist in automating data management tasks, tracking data lineage, and enforcing data policies. Examples of data governance tools include:
- Data Catalogs: Centralized repositories for metadata about data assets, providing a comprehensive view of data across the organization.
- Data Quality Management Tools: Tools that help organizations assess, monitor, and improve data quality.
- Data Masking and Anonymization Tools: Tools for protecting sensitive data by replacing it with non-sensitive substitutes.
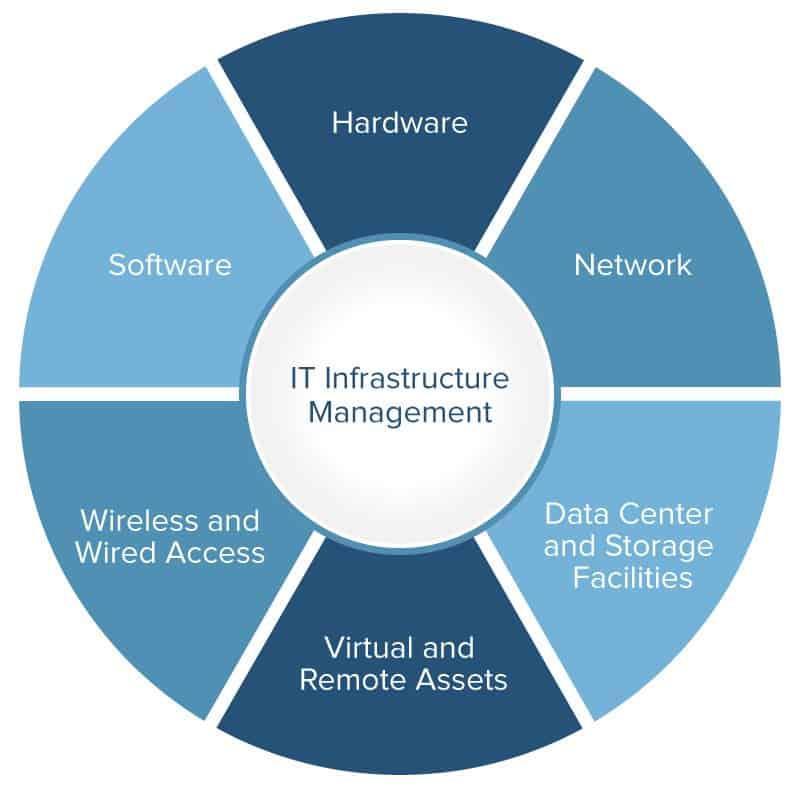
IT Infrastructure, Information technology governance best practices
IT infrastructure forms the backbone of an organization’s technology operations. Effective IT infrastructure governance ensures that the infrastructure is reliable, secure, and cost-effective.
- Capacity Planning: Capacity planning involves assessing current and future infrastructure needs to ensure sufficient resources are available to meet business demands. Best practices for capacity planning include:
- Regularly monitoring infrastructure performance and utilization.
- Forecasting future infrastructure requirements based on business growth and technology trends.
- Developing capacity plans that align with business objectives and budget constraints.
- Disaster Recovery: Disaster recovery plans are essential for mitigating the impact of unexpected events, such as natural disasters, system failures, or cyberattacks. Best practices for disaster recovery include:
- Identifying critical business functions and data.
- Developing recovery strategies and procedures for restoring critical systems and data.
- Regularly testing disaster recovery plans to ensure effectiveness.
- Business Continuity: Business continuity plans ensure that an organization can continue operating during and after disruptions. Best practices for business continuity include:
- Identifying critical business processes and dependencies.
- Developing alternative operational procedures and communication plans.
- Regularly testing business continuity plans to ensure effectiveness.
Managing IT infrastructure costs and optimizing performance are key considerations for IT governance. Best practices for managing IT infrastructure costs include:
- Cloud Optimization: Leveraging cloud computing services can help organizations reduce infrastructure costs and improve scalability.
- Hardware and Software Standardization: Standardizing hardware and software can simplify management, reduce costs, and improve compatibility.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient infrastructure solutions can reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
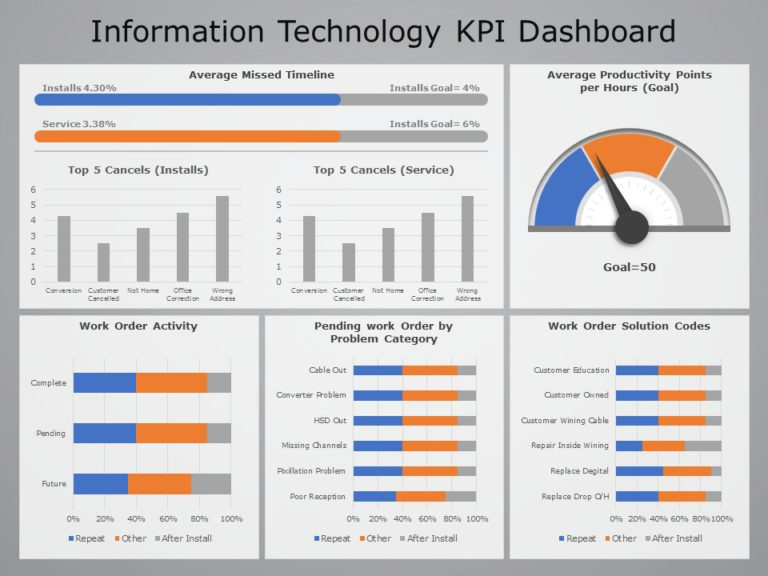
Optimizing IT infrastructure performance can enhance business agility and user experience. Best practices for optimizing performance include:
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly monitoring infrastructure performance to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Capacity Management: Proactively managing infrastructure capacity to avoid performance degradation.
- Infrastructure Optimization: Implementing performance tuning techniques and optimizing resource allocation.
Examples of infrastructure governance best practices include:
- Establishing clear infrastructure policies and procedures: Defining standards for hardware, software, and network configurations.
- Implementing a robust change management process: Controlling changes to infrastructure to minimize disruptions and ensure stability.
- Regularly reviewing and updating infrastructure governance policies: Ensuring that policies remain relevant and effective in a constantly evolving technology landscape.
Application Development and Management
Application development and management are critical aspects of IT governance, ensuring that applications meet business needs, are secure, and comply with relevant regulations.
- Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) Management: SDLC management encompasses the entire software development process, from requirements gathering to deployment and maintenance. Best practices for SDLC management include:
- Adopting a structured SDLC methodology, such as Agile or Waterfall.
- Implementing quality assurance processes throughout the SDLC.
- Ensuring proper documentation and version control.
- Application Security: Application security focuses on protecting applications from vulnerabilities and attacks. Best practices for application security include:
- Implementing secure coding practices and using security frameworks.
- Conducting regular security testing and vulnerability assessments.
- Using security tools and technologies to detect and prevent threats.
- Application Compliance: Ensuring that applications comply with relevant regulations and industry standards is crucial for maintaining data integrity and protecting sensitive information. Best practices for application compliance include:
- Conducting regular compliance audits and assessments.
- Implementing controls to meet regulatory requirements.
- Maintaining documentation to demonstrate compliance.
Examples of application governance best practices include:
- Establishing clear application development and management policies: Defining standards for coding practices, security, and compliance.
- Implementing a robust application lifecycle management (ALM) system: Providing a centralized platform for managing the entire application lifecycle, from development to retirement.
- Regularly reviewing and updating application governance policies: Ensuring that policies remain relevant and effective in a constantly evolving technology landscape.
IT Security
IT security is a fundamental aspect of IT governance, ensuring that information assets are protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Risk Assessment: Risk assessment involves identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing security risks to determine the likelihood and impact of potential threats. Best practices for risk assessment include:
- Conducting regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
- Analyzing potential threats and their impact on business operations.
- Developing risk mitigation strategies to address identified vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Management: Vulnerability management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating security vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Best practices for vulnerability management include:
- Regularly scanning systems for vulnerabilities using automated tools.
- Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on severity and impact.
- Implementing patches and updates to address identified vulnerabilities.
- Security Controls: Security controls are mechanisms that help protect information assets from threats. Best practices for implementing security controls include:
- Implementing access controls to restrict unauthorized access to systems and data.
- Using firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized network access.
- Implementing data encryption to protect sensitive information.
- Security Policies: Security policies define the organization’s security standards and procedures. Best practices for developing security policies include:
- Clearly defining security objectives and responsibilities.
- Establishing rules and procedures for managing security risks.
- Communicating security policies to all employees and stakeholders.
Examples of IT security governance best practices include:
- Establishing a security governance framework: Defining roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing IT security.
- Implementing a security awareness program: Educating employees about security risks and best practices.
- Regularly reviewing and updating security policies and procedures: Ensuring that policies remain relevant and effective in a constantly evolving threat landscape.
Final Review

As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, it is crucial for organizations to remain agile and adaptable. Implementing information technology governance best practices empowers organizations to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the digital age, ensuring that IT resources are used effectively and strategically to achieve business objectives.
Information technology governance best practices are crucial for any organization seeking to optimize its technology infrastructure. A key aspect of this governance involves making informed decisions about technology acquisitions, and that’s where technology brokers can play a valuable role. These brokers act as intermediaries, connecting organizations with the most suitable technology solutions based on their specific needs.
By leveraging the expertise of technology brokers, organizations can enhance their decision-making process and ultimately improve their overall IT governance.