Information Technology Audit Checklist: A Guide to Ensuring Security and Compliance
The Information Technology Audit Checklist is an essential tool for organizations seeking to safeguard their data, systems, and operations. This comprehensive checklist serves as a roadmap, guiding auditors through a […]
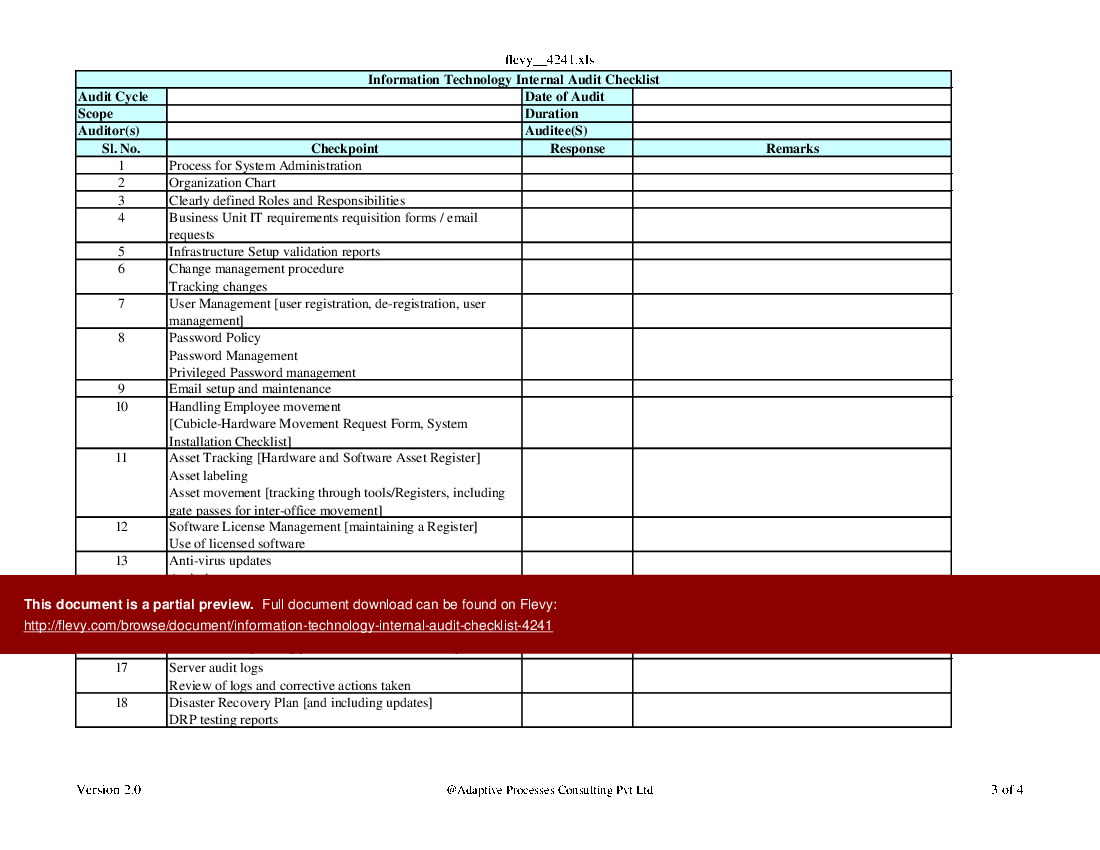
The Information Technology Audit Checklist is an essential tool for organizations seeking to safeguard their data, systems, and operations. This comprehensive checklist serves as a roadmap, guiding auditors through a meticulous evaluation of an organization’s IT infrastructure, security practices, and compliance posture. From network security and system vulnerabilities to data privacy and disaster recovery, the checklist encompasses all critical aspects of modern IT environments.
By meticulously examining each area, auditors can identify potential weaknesses, risks, and areas for improvement. The checklist provides a structured framework for assessing compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards, ensuring that organizations are meeting their legal and ethical obligations. Ultimately, the Information Technology Audit Checklist empowers organizations to build a robust and secure IT environment, fostering trust, efficiency, and resilience.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Audit

Business continuity and disaster recovery plans are crucial components of any IT audit. These plans ensure that an organization can maintain critical business operations during disruptions caused by natural disasters, cyberattacks, or other unforeseen events. By evaluating the effectiveness of these plans, auditors can assess an organization’s preparedness for potential disruptions and identify areas for improvement.
Disaster Recovery Procedures
Disaster recovery procedures are a critical aspect of business continuity planning. These procedures Artikel the steps an organization will take to restore its IT infrastructure and operations in the event of a disaster. During an audit, it is important to assess the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of these procedures. This involves evaluating the following:
- Identification of Critical Systems: The disaster recovery plan should clearly identify the critical systems that are essential for business operations. This includes applications, databases, servers, and networks. The audit should confirm that these systems have been accurately identified and prioritized.
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs): RTOs define the maximum acceptable downtime for each critical system. The audit should verify that RTOs are realistic and aligned with the organization’s business needs. It is also important to assess whether the organization has the necessary resources and procedures to meet these RTOs.
- Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs): RPOs specify the maximum acceptable data loss that can occur during a disaster. The audit should examine the organization’s backup and recovery processes to ensure they meet the defined RPOs. This includes evaluating the frequency of backups, the storage locations, and the recovery procedures.
- Disaster Recovery Site: The organization should have a designated disaster recovery site that can be used to restore operations in the event of a disaster. The audit should verify the availability and functionality of this site, including the physical infrastructure, network connectivity, and data storage capabilities.
- Testing and Maintenance: Disaster recovery procedures should be regularly tested to ensure their effectiveness. The audit should assess the frequency and scope of these tests, as well as the documentation of test results. It is also important to evaluate the maintenance procedures for the disaster recovery plan to ensure it remains current and relevant.
Backup and Recovery Processes
Backup and recovery processes are essential for protecting data and ensuring business continuity. These processes involve regularly backing up critical data and systems and restoring them in the event of a data loss. An audit should assess the following aspects of backup and recovery processes:
- Backup Strategy: The organization should have a comprehensive backup strategy that defines the types of data to be backed up, the frequency of backups, the backup methods, and the storage locations. The audit should review the backup strategy and confirm its alignment with the organization’s data protection requirements.
- Backup Procedures: The audit should evaluate the organization’s backup procedures to ensure they are well-defined, documented, and followed consistently. This includes reviewing the steps involved in creating backups, verifying backup integrity, and storing backups securely.
- Recovery Procedures: The audit should assess the organization’s recovery procedures to ensure they are effective and can be executed quickly in the event of a data loss. This involves reviewing the steps involved in restoring data from backups, verifying data integrity, and restarting critical systems.
- Backup Storage: The audit should examine the storage locations for backups to ensure they are secure and protected from potential threats. This includes evaluating the physical security of the storage facility, the use of encryption, and the availability of offsite backups.
- Backup Testing: Regular testing of backup and recovery procedures is essential to ensure their effectiveness. The audit should assess the frequency and scope of these tests, as well as the documentation of test results.
Data Replication Strategies
Data replication is a critical component of disaster recovery planning. It involves creating copies of data and storing them in different locations, ensuring that data is available even if one location is affected by a disaster. The audit should evaluate the following aspects of data replication strategies:
- Replication Methods: The organization should use appropriate data replication methods, such as synchronous or asynchronous replication, to ensure data consistency and availability. The audit should assess the suitability of the chosen replication methods based on the organization’s requirements for data integrity and recovery time.
- Replication Frequency: The frequency of data replication should be aligned with the organization’s RPOs. The audit should verify that data is replicated frequently enough to minimize potential data loss in the event of a disaster.
- Replication Destination: The audit should examine the location of the replicated data to ensure it is physically separate from the primary data center. This ensures that data is available even if the primary location is affected by a disaster.
- Replication Testing: Regular testing of data replication processes is essential to ensure their effectiveness. The audit should assess the frequency and scope of these tests, as well as the documentation of test results.
IT Governance and Risk Management Audit
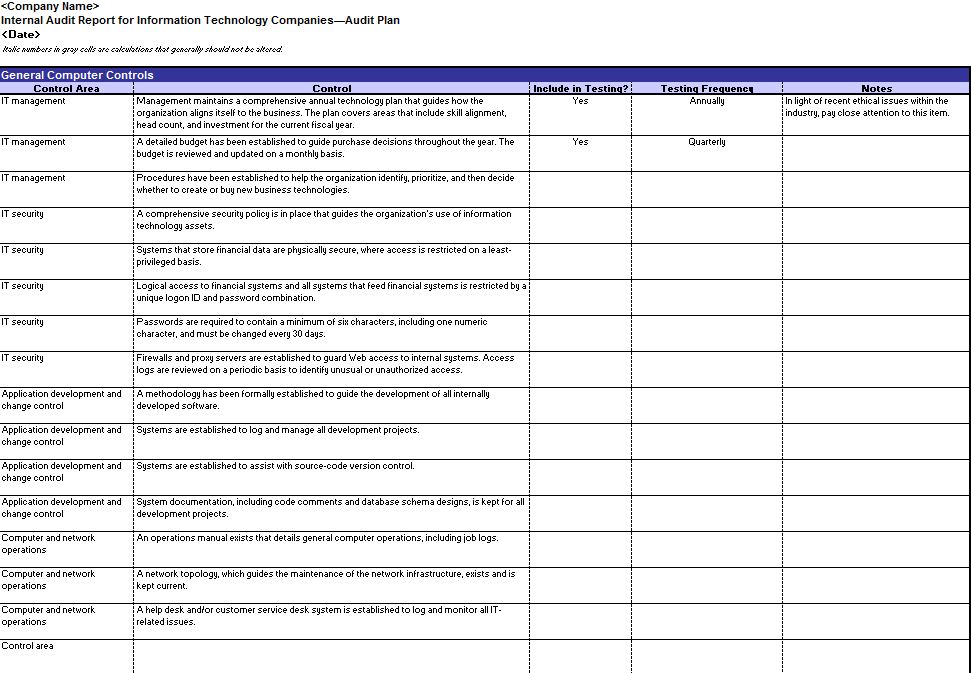
IT governance and risk management are crucial for any organization, especially those heavily reliant on technology. They ensure alignment between business objectives and IT strategies, enabling organizations to effectively manage risks, protect their assets, and achieve their goals.
Key Areas to Assess
This section Artikels the key areas to be assessed during an IT governance and risk management audit, including IT policies and procedures, risk assessments, and change management processes.
- IT Policies and Procedures: These policies and procedures provide the framework for managing IT resources and processes, including data security, access control, and system maintenance.
- Risk Assessments: Organizations must regularly assess and identify potential risks to their IT infrastructure and systems. This involves analyzing the likelihood and impact of various threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and system failures.
- Change Management Processes: Change management processes ensure that changes to IT systems are implemented in a controlled and documented manner, minimizing disruptions and ensuring the integrity of the IT environment.
Audit Procedures
An IT governance and risk management audit evaluates the effectiveness of these frameworks. This section provides a checklist of audit procedures to evaluate the effectiveness of IT governance and risk management frameworks.
- Review of IT Policies and Procedures: Assess the comprehensiveness and relevance of IT policies and procedures, including those related to data security, access control, and system maintenance. Evaluate the effectiveness of their implementation and adherence by IT staff and users.
- Evaluation of Risk Assessments: Examine the organization’s risk assessment process, including the identification and prioritization of risks. Evaluate the accuracy and completeness of risk assessments, the adequacy of risk mitigation strategies, and the effectiveness of their implementation.
- Assessment of Change Management Processes: Assess the organization’s change management process, including the identification, approval, implementation, and documentation of changes. Evaluate the effectiveness of the process in minimizing disruptions and ensuring the integrity of the IT environment.
- Review of IT Security Controls: Evaluate the effectiveness of IT security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control mechanisms. Assess the adequacy of security awareness training for employees and the organization’s response to security incidents.
- Assessment of IT Infrastructure and Systems: Evaluate the reliability and performance of the organization’s IT infrastructure and systems, including hardware, software, and networks. Assess the organization’s disaster recovery and business continuity plans, and their effectiveness in mitigating the impact of disruptions.
- Review of IT Governance Structure: Evaluate the organization’s IT governance structure, including the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, such as the IT department, the board of directors, and senior management. Assess the effectiveness of the governance structure in ensuring alignment between IT strategies and business objectives.
- Assessment of IT Service Delivery: Evaluate the quality and effectiveness of IT service delivery, including the availability, reliability, and performance of IT services. Assess the organization’s customer satisfaction with IT services and the effectiveness of its service level agreements (SLAs).
- Review of IT Vendor Management: Evaluate the organization’s process for managing IT vendors, including the selection, contracting, and monitoring of vendors. Assess the effectiveness of the vendor management process in ensuring the security and reliability of IT services provided by external vendors.
- Assessment of IT Compliance: Evaluate the organization’s compliance with relevant IT laws and regulations, including data privacy laws, cybersecurity regulations, and industry standards. Assess the organization’s ability to demonstrate compliance and its response to any regulatory inquiries.
IT Infrastructure and Operations Audit
Auditing IT infrastructure and operations is essential for ensuring the reliability, security, and efficiency of an organization’s technology systems. A comprehensive audit helps identify potential vulnerabilities, risks, and areas for improvement in the management and operation of IT infrastructure.
Hardware and Software Infrastructure Assessment
A thorough assessment of hardware and software infrastructure is crucial for understanding the overall health and performance of the IT environment. This includes:
- Hardware Inventory and Configuration: Verifying the accuracy and completeness of hardware inventory records, including servers, workstations, networking devices, and peripherals. Assessing the configuration of hardware components, including memory, storage, and processing power, to ensure they meet current and future needs.
- Software Inventory and Licensing: Ensuring that all software applications are properly licensed and compliant with relevant agreements. Assessing the security posture of software, including the presence of vulnerabilities and outdated versions.
- Hardware and Software Maintenance: Reviewing maintenance contracts and schedules for hardware and software, ensuring that systems are regularly updated and patched.
Network Performance and Security
Network performance and security are critical aspects of IT infrastructure, and a thorough audit should assess these areas:
- Network Performance Monitoring: Evaluating the effectiveness of network performance monitoring tools and procedures. Assessing network latency, bandwidth utilization, and packet loss to identify potential bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Network Security Measures: Reviewing network security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control policies. Assessing the effectiveness of these measures in preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Network Segmentation: Evaluating the implementation of network segmentation, which isolates sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access.
- Wireless Network Security: Assessing the security of wireless networks, including the use of encryption protocols, access control, and intrusion detection systems.
System Availability and Disaster Recovery
Ensuring the availability and resilience of IT systems is paramount for business continuity. The audit should assess:
- System Availability Monitoring: Reviewing system availability monitoring tools and procedures, ensuring that critical systems are monitored for uptime and performance.
- Disaster Recovery Plans: Evaluating the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of disaster recovery plans. Assessing the ability to restore critical systems and data in the event of a disaster.
- Backup and Recovery Procedures: Reviewing backup and recovery procedures, ensuring that data is regularly backed up and can be restored effectively. Assessing the security and integrity of backup data.
IT Service Management Audit
An IT service management audit is a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s IT service management processes to assess their effectiveness, efficiency, and compliance with industry best practices. This audit helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that IT services meet the needs of the business.
Key Areas to Assess
The key areas to assess during an IT service management audit include:
- Incident Management: The effectiveness of incident management processes in resolving IT issues promptly and efficiently.
- Problem Management: The effectiveness of problem management processes in identifying and resolving root causes of recurring incidents.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): The alignment of IT service delivery with agreed-upon service levels and the effectiveness of monitoring and reporting on SLA performance.
- Change Management: The effectiveness of change management processes in managing and controlling changes to IT infrastructure and services.
- Configuration Management: The accuracy and completeness of IT asset and configuration information and the effectiveness of configuration management processes.
- Service Request Management: The effectiveness of service request management processes in handling and resolving user requests for IT services.
- Capacity Management: The effectiveness of capacity management processes in ensuring that IT infrastructure has sufficient capacity to meet current and future demands.
- Availability Management: The effectiveness of availability management processes in ensuring that IT services are available when needed.
- IT Security Management: The effectiveness of IT security management processes in protecting IT infrastructure and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- IT Service Continuity Management: The effectiveness of IT service continuity management processes in ensuring that IT services can continue to operate in the event of a disaster or other disruption.
Audit Procedures
To evaluate the effectiveness of IT service management processes, auditors can use a variety of audit procedures, including:
- Review of documentation: This includes reviewing IT service management policies, procedures, and standards, as well as service level agreements and other relevant documentation.
- Interviews with IT staff: This helps to understand how IT service management processes are implemented in practice.
- Observation of IT operations: This provides direct insight into the effectiveness of IT service management processes.
- Testing of IT service management processes: This includes testing the effectiveness of incident management, problem management, change management, and other processes.
- Review of IT service performance metrics: This helps to assess the effectiveness of IT service management processes in meeting agreed-upon service levels.
- Comparison of IT service management practices to industry best practices: This helps to identify areas for improvement.
Reporting and Recommendations: Information Technology Audit Checklist
A comprehensive audit report is the culmination of an IT audit process. It provides a detailed overview of the findings, recommendations, and action plans to address any identified vulnerabilities or areas for improvement.
Types of Audit Reports
Audit reports are tailored to the specific objectives of the audit and the audience they are intended for. Different types of audit reports exist, each serving a distinct purpose:
- Management Letter: This report provides a high-level overview of the audit findings, focusing on significant issues and recommendations for improvement. It is typically addressed to management and is used to inform decision-making.
- Technical Report: This report delves into the technical details of the audit, providing in-depth analysis of specific vulnerabilities, risks, and control deficiencies. It is often used by technical teams to implement corrective actions.
- Public Report: This report is intended for a broader audience, such as stakeholders, investors, or the public. It typically summarizes the audit findings and highlights key areas of concern.
Key Elements of an IT Audit Report
An effective IT audit report includes several key elements:
- Executive Summary: This concise section provides a high-level overview of the audit’s scope, objectives, findings, and recommendations.
- Audit Scope and Objectives: This section clearly defines the specific areas covered by the audit and the goals that were sought to be achieved.
- Methodology: This section describes the audit procedures used, including data collection methods, sampling techniques, and review processes.
- Findings: This section presents the results of the audit, outlining any vulnerabilities, risks, or control deficiencies identified. It includes specific examples and evidence to support the findings.
- Recommendations: This section proposes actionable steps to address the identified issues. Recommendations should be clear, specific, and achievable.
- Action Plan: This section Artikels the steps that will be taken to implement the recommendations, including timelines, responsibilities, and expected outcomes.
Importance of Comprehensive Audit Reports, Information technology audit checklist
Comprehensive audit reports are essential for several reasons:
- Identify and Mitigate Risks: By identifying vulnerabilities and control weaknesses, audit reports help organizations proactively address potential risks and prevent future incidents.
- Improve IT Governance: Audit reports provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of IT governance practices and highlight areas for improvement in aligning IT with business objectives.
- Enhance Compliance: Audit reports can help organizations demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards, reducing the risk of penalties or legal issues.
- Improve Efficiency and Effectiveness: By identifying areas for optimization and streamlining processes, audit reports can contribute to increased efficiency and effectiveness in IT operations.
- Support Decision-Making: Audit reports provide management with the information they need to make informed decisions about IT investments, risk mitigation strategies, and overall IT strategy.
Last Recap
The Information Technology Audit Checklist serves as a critical cornerstone for organizations striving to maintain the integrity and security of their IT systems. By implementing the checklist’s recommendations, organizations can strengthen their security posture, mitigate risks, and achieve greater operational efficiency. Regular audits ensure ongoing vigilance, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving threats and maintain a high level of data protection and compliance.
An information technology audit checklist should include a review of security measures for all systems, including those that manage transactions. This is especially important for businesses like those using USA Technologies vending machines , which rely heavily on secure payment processing and data storage.
By ensuring that these systems are adequately protected, you can mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive customer information.