Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology: A Revolutionary Approach
Extracorporeal pulse activation technology (EPAT) sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the […]

Extracorporeal pulse activation technology (EPAT) sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. EPAT is a non-invasive treatment modality that utilizes focused sound waves to stimulate healing and regeneration within the body. This technology has emerged as a promising therapeutic option for a range of medical conditions, with its applications spanning musculoskeletal disorders, wound healing, and even nerve regeneration.
The principles behind EPAT are rooted in the understanding of how sound waves interact with biological tissues. When focused sound waves are applied to the body, they generate mechanical vibrations that stimulate cellular activity, promote blood flow, and enhance tissue repair. This process ultimately leads to pain reduction, improved mobility, and accelerated healing.
Introduction to Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT)

Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is a non-invasive treatment modality that uses radial pressure waves to stimulate tissue regeneration and healing. It has gained increasing popularity in recent years as a potential alternative or adjunct to traditional treatments for various musculoskeletal conditions.
Historical Development and Evolution of EPAT
EPAT’s roots can be traced back to the 1980s when researchers began exploring the use of shock waves for lithotripsy, the non-invasive breakdown of kidney stones. Early shock wave devices were large and bulky, requiring specialized equipment and expertise. However, advancements in technology led to the development of more compact and user-friendly devices, making EPAT more accessible for clinical applications.
Basic Principles and Mechanisms of Action of EPAT
EPAT devices generate radial pressure waves that travel through the body and reach the targeted tissues. These pressure waves, characterized by their rapid rise and fall in pressure, create cavitation bubbles within the tissues. The collapse of these bubbles produces mechanical stress and microtrauma, triggering a cascade of biological responses that promote healing.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Use of EPAT
Numerous studies have investigated the efficacy of EPAT for various musculoskeletal conditions. While the exact mechanisms by which EPAT exerts its therapeutic effects are still being explored, research suggests that it can:
- Reduce pain and inflammation
- Promote tissue regeneration and repair
- Improve blood flow and oxygenation
- Stimulate the release of growth factors
Applications of EPAT in Medicine: Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology

Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is a non-invasive treatment modality that utilizes radial pressure waves to stimulate tissue regeneration and healing. EPAT has gained significant traction in the medical field, finding applications in various conditions. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals seeking to provide patients with effective and minimally invasive treatment options.
Conditions Treated with EPAT
EPAT has proven effective in treating a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions. Here are some examples:
| Condition | Mechanism of Action | Benefits | Clinical Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Tendinopathies (e.g., Achilles tendinitis, tennis elbow, plantar fasciitis) | EPAT waves stimulate the production of growth factors and other beneficial molecules, promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. | Pain reduction, improved range of motion, faster healing, and reduced need for surgery. | Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of EPAT for chronic tendinopathies, with significant improvements in pain and function reported. For example, a study published in the journal “The American Journal of Sports Medicine” found that EPAT treatment was significantly more effective than placebo in reducing pain and improving function in patients with chronic Achilles tendinitis. |
| Muscle Injuries (e.g., muscle strains, tears) | EPAT promotes blood flow to the injured area, accelerating healing and reducing inflammation. | Faster recovery, reduced pain, and improved muscle function. | Studies have shown that EPAT can be beneficial for muscle injuries, particularly in cases of chronic muscle pain and stiffness. A study published in the journal “Physical Therapy” found that EPAT treatment resulted in significant improvements in pain and function in patients with chronic muscle strains. |
| Osteoarthritis | EPAT stimulates chondrocyte (cartilage cell) activity, promoting cartilage regeneration and reducing inflammation. | Pain relief, improved joint function, and delayed progression of osteoarthritis. | Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of EPAT in treating osteoarthritis, particularly in the knee and hip. A study published in the journal “Osteoarthritis and Cartilage” found that EPAT treatment resulted in significant improvements in pain and function in patients with knee osteoarthritis. |
| Plantar Fasciitis | EPAT stimulates blood flow to the plantar fascia, promoting healing and reducing inflammation. | Pain relief, improved walking ability, and reduced need for surgery. | Multiple studies have shown the efficacy of EPAT for plantar fasciitis, with patients experiencing significant pain reduction and functional improvement. A study published in the journal “The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery” found that EPAT treatment was more effective than placebo in reducing pain and improving function in patients with plantar fasciitis. |
EPAT Delivery Systems and Techniques
EPAT delivery systems and techniques are crucial for effective treatment outcomes. Understanding the different systems, their technical specifications, and the techniques used to administer EPAT is essential for healthcare professionals.
EPAT Delivery Systems
Various EPAT delivery systems are available, each with unique technical specifications and advantages.
- Radial Wave Devices: These devices utilize a radial wave generator that produces a focused shockwave. The shockwave is then transmitted through a coupling medium, typically gel, to the target area. These devices are widely used for musculoskeletal conditions and are known for their versatility and ease of use.
- Linear Wave Devices: Linear wave devices employ a linear wave generator that generates a focused shockwave. The shockwave is delivered through a handheld applicator to the target area. These devices are particularly effective for treating conditions involving tendons, ligaments, and bones.
- Focused Wave Devices: Focused wave devices use a focused wave generator that produces a high-intensity shockwave. The shockwave is precisely directed to the target area, making it suitable for treating deep-seated conditions. These devices are often used for conditions such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinitis, and calcific tendinitis.
EPAT Administration Techniques
EPAT can be administered using different techniques, each with its own advantages and limitations. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the condition being treated, the location of the target area, and the patient’s individual characteristics.
- Direct Application: In this technique, the EPAT applicator is directly applied to the target area. It is a commonly used technique for treating superficial conditions, such as plantar fasciitis and tennis elbow.
- Indirect Application: In indirect application, the EPAT applicator is placed at a distance from the target area. This technique is used for treating deep-seated conditions, such as rotator cuff tears and hip pain.
- Water Immersion: This technique involves immersing the target area in water and applying EPAT through the water. It is used for treating conditions that are difficult to access, such as Achilles tendinitis.
EPAT Delivery Systems and Techniques: Summary
| Delivery System | Technique | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radial Wave Devices | Direct Application | Versatile, easy to use, suitable for superficial conditions | May not be effective for deep-seated conditions |
| Linear Wave Devices | Indirect Application | Effective for treating tendons, ligaments, and bones | May require more experience to use |
| Focused Wave Devices | Water Immersion | Precisely targets deep-seated conditions | May be more expensive than other systems |
Safety and Side Effects of EPAT
EPAT is generally considered a safe treatment modality, with a favorable safety profile compared to other treatment options. However, like any medical procedure, it can be associated with potential risks and side effects. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions about EPAT treatment.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
The most common side effects of EPAT are typically mild and temporary, including:
- Pain or tenderness at the treatment site
- Bruising or redness
- Swelling
- Muscle soreness
- Numbness or tingling
These side effects usually resolve within a few days after treatment.
In rare cases, more serious complications can occur, such as:
- Nerve damage
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Fracture
The risk of these complications is low, but it is important to be aware of them.
Safety Protocols and Precautions, Extracorporeal pulse activation technology
To minimize the risk of complications, healthcare professionals should follow strict safety protocols during EPAT administration:
- A thorough medical history and physical examination should be conducted before treatment to identify any contraindications.
- The treatment area should be carefully prepared and disinfected.
- The appropriate EPAT device and settings should be used for the specific condition being treated.
- Patients should be monitored closely during and after treatment for any adverse reactions.
Patients should also be advised to avoid strenuous activity and contact sports for a few days after treatment.
Safety Profile Comparison with Other Treatment Modalities
EPAT is often considered a safer alternative to other treatment modalities, such as surgery or steroid injections, for certain conditions. For example, EPAT has been shown to be effective in treating plantar fasciitis, with a lower risk of complications compared to surgery.
Future Directions and Research in EPAT
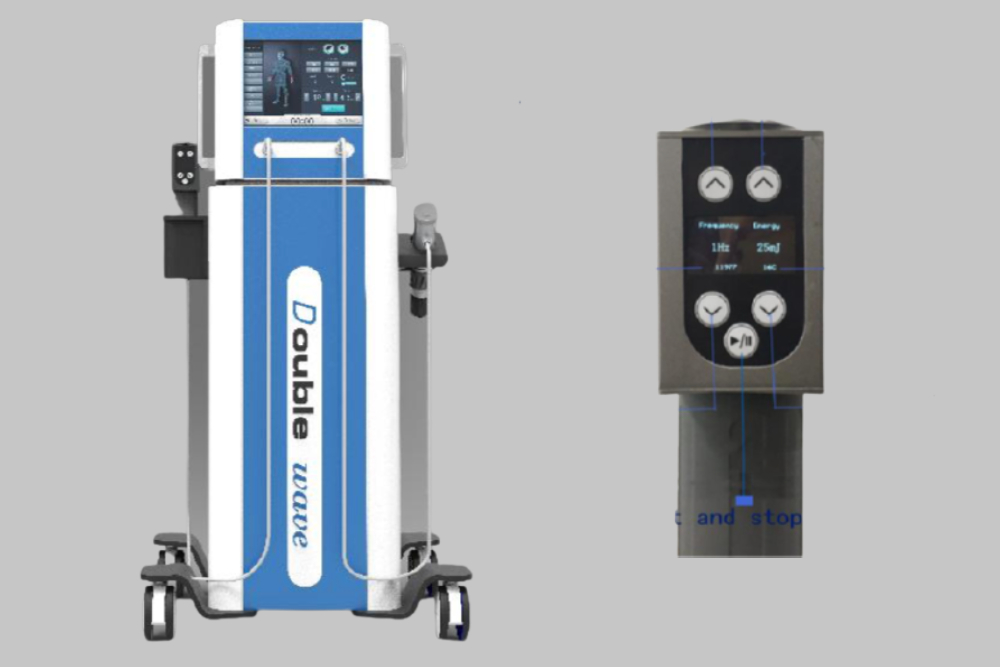

EPAT technology is a rapidly evolving field with significant potential for further development and clinical applications. Researchers are actively exploring new avenues to enhance the effectiveness, safety, and accessibility of EPAT therapy.
Emerging Areas of Research and Development
Ongoing research in EPAT focuses on refining existing techniques and exploring novel applications. Here are some key areas of research:
- Optimizing EPAT Delivery Systems: Researchers are investigating ways to improve the precision and efficiency of EPAT delivery. This includes developing new EPAT devices with advanced targeting capabilities and exploring different wave forms and frequencies to enhance therapeutic effects.
- Combining EPAT with Other Therapies: The potential of EPAT as an adjunctive therapy is being explored. For instance, combining EPAT with physical therapy, medication, or other non-invasive treatments may lead to synergistic effects and improved outcomes.
- Personalized EPAT: Tailoring EPAT treatments to individual patients based on their specific condition and response to therapy is a growing area of research. This involves using advanced imaging techniques and biofeedback to personalize treatment parameters and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
- Exploring New Applications: The therapeutic potential of EPAT is being investigated in a wide range of medical conditions beyond musculoskeletal disorders. Research is underway to explore the use of EPAT in treating neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer.
Potential Applications of EPAT in New Medical Fields
The versatility of EPAT technology extends beyond its current applications in musculoskeletal medicine. Emerging research suggests potential applications in various medical fields:
- Neurological Disorders: Studies are exploring the use of EPAT for treating conditions like stroke, traumatic brain injury, and Alzheimer’s disease. EPAT may promote neurogenesis, enhance nerve regeneration, and improve blood flow to the brain.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Research is investigating the potential of EPAT for treating heart failure, peripheral artery disease, and hypertension. EPAT may promote angiogenesis, improve blood vessel function, and reduce inflammation.
- Wound Healing: EPAT is being investigated as a potential treatment for chronic wounds, diabetic ulcers, and pressure sores. It may accelerate wound healing by stimulating cell proliferation and angiogenesis.
- Cancer Treatment: Some studies suggest that EPAT may enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiation therapy in cancer treatment. EPAT may promote tumor cell death and reduce tumor growth.
Future Directions of EPAT Therapy
The future of EPAT therapy holds significant promise for improving patient care. Research is paving the way for:
- Increased Accessibility: The development of more affordable and portable EPAT devices will make this therapy more accessible to a wider population.
- Enhanced Effectiveness: Continued research into optimizing EPAT parameters and delivery systems will lead to more effective and targeted treatments.
- Wider Clinical Applications: As research expands into new medical fields, EPAT therapy may become a valuable tool for treating a broader range of conditions.
Closure
The journey into the world of extracorporeal pulse activation technology has revealed a powerful tool with the potential to revolutionize healthcare. From its humble beginnings to its current applications, EPAT has consistently demonstrated its efficacy in addressing a variety of medical conditions. The future of EPAT is bright, with ongoing research exploring new applications and refinements of this innovative technology. As we continue to unravel the intricacies of EPAT, we can anticipate a future where this treatment modality plays a central role in improving patient outcomes and enhancing overall well-being.
Extracorporeal pulse activation technology is a fascinating area of research with the potential to revolutionize healthcare. One company actively involved in this field is nexlogic technologies inc , a leading innovator in medical device development. Nexlogic’s expertise in this domain is contributing to the advancement of extracorporeal pulse activation technology, paving the way for groundbreaking treatments and improved patient outcomes.