Enablement Technology: Empowering Individuals and Organizations
Enablement technology is the driving force behind progress, empowering individuals and organizations to achieve unprecedented heights. From automating tedious tasks to fostering seamless collaboration, enablement technology revolutionizes how we work, […]
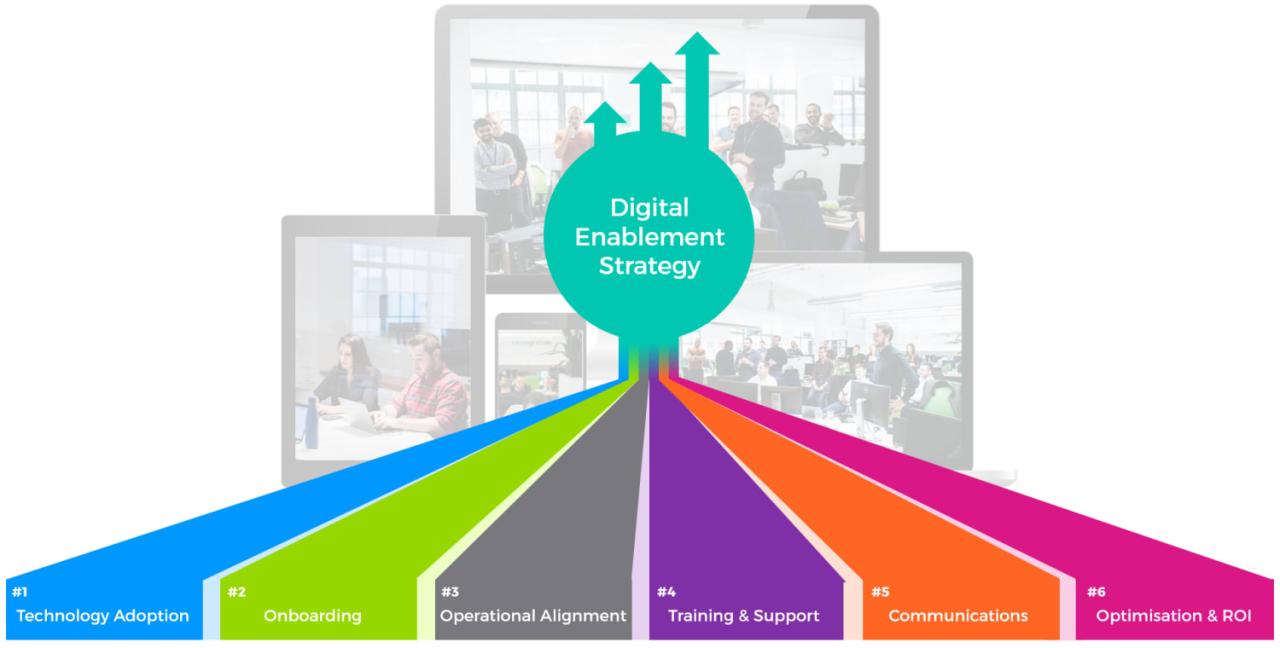
Enablement technology is the driving force behind progress, empowering individuals and organizations to achieve unprecedented heights. From automating tedious tasks to fostering seamless collaboration, enablement technology revolutionizes how we work, learn, and interact with the world around us. This transformative technology encompasses a wide range of tools and strategies, each designed to enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
By leveraging automation, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and other cutting-edge technologies, enablement technology streamlines processes, unlocks hidden insights, and empowers individuals to make data-driven decisions. It fosters a culture of collaboration, breaking down barriers and enabling teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of location or time zone.
Defining Enablement Technology

Enablement technology is a powerful force driving innovation and progress across various sectors. It’s not just about creating new tools; it’s about empowering individuals and organizations to achieve more.
Examples of Enablement Technology
Enablement technology plays a crucial role in empowering individuals and organizations to achieve their goals. Here are some examples:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM systems empower sales teams to manage customer interactions, track leads, and personalize communication, leading to improved customer satisfaction and sales growth.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): LMS platforms provide a centralized hub for training and development, enabling employees to access online courses, track progress, and acquire new skills, fostering a culture of continuous learning and professional growth.
- Project Management Software: Project management tools help teams collaborate effectively, track progress, manage tasks, and optimize workflows, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Collaboration Platforms: Collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams facilitate seamless communication and teamwork, breaking down silos and fostering a more connected and productive work environment.
Key Characteristics of Enablement Technology
Enablement technology distinguishes itself from other types of technology through its focus on empowering individuals and organizations to achieve their goals. Here are some key characteristics:
- User-Centric Design: Enablement technology prioritizes user experience, ensuring intuitive interfaces and ease of use, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Enablement technology adapts to the evolving needs of organizations, scaling to accommodate growth and adapting to changing business requirements.
- Data-Driven Insights: Enablement technology leverages data analytics to provide valuable insights, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and optimize performance.
- Integration and Interoperability: Enablement technology seamlessly integrates with existing systems and platforms, creating a cohesive and interconnected ecosystem that enhances productivity and efficiency.
Types of Enablement Technology
Enablement technology encompasses a wide range of tools and solutions designed to empower individuals and organizations to achieve their goals. These technologies enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation across various industries and functions. Understanding the different types of enablement technology is crucial for organizations seeking to leverage their potential for strategic advantage.
Automation
Automation technologies automate repetitive tasks and processes, freeing up human resources for more strategic initiatives. They streamline workflows, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. Examples of automation technologies include:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Software robots that mimic human actions to automate tasks like data entry, form filling, and system integration. For example, RPA can automate the process of invoice processing, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy.
- Business Process Management (BPM): A systematic approach to managing and optimizing business processes. BPM tools provide visualization, analysis, and automation capabilities, enabling organizations to streamline workflows and improve efficiency. For example, BPM can be used to automate customer onboarding processes, reducing processing time and improving customer satisfaction.
Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools facilitate communication, information sharing, and teamwork among individuals and teams. They enable seamless collaboration, regardless of location or time zone. Examples of collaboration tools include:
- Project Management Software: Tools like Asana, Trello, and Jira help teams plan, track, and manage projects effectively. They provide features for task assignment, progress tracking, and communication, facilitating collaboration and efficient project delivery.
- Instant Messaging Platforms: Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Chat enable real-time communication and collaboration among team members. They provide features for instant messaging, file sharing, and video conferencing, facilitating quick and efficient communication.
Data Analytics
Data analytics technologies collect, analyze, and interpret data to gain insights and make informed decisions. They provide valuable information about customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency. Examples of data analytics technologies include:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense provide interactive dashboards and reports for visualizing and analyzing data. They enable organizations to identify patterns, trends, and insights from their data, informing strategic decision-making.
- Predictive Analytics: Techniques that use historical data to predict future outcomes. Predictive analytics can be used to forecast sales, identify potential risks, and optimize marketing campaigns. For example, retailers can use predictive analytics to forecast demand for specific products, optimizing inventory management and reducing stockouts.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI technologies enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. They are transforming various industries by automating complex processes, improving customer experiences, and driving innovation. Examples of AI technologies include:
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms that enable computers to learn from data without explicit programming. ML can be used for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and fraud detection. For example, ML algorithms can be used to identify fraudulent transactions in real-time, protecting businesses from financial losses.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks to process complex data. DL is particularly effective for tasks like image and speech recognition, and is driving innovation in fields like healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles.
Enablement Technology in Action

Enablement technology isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s actively transforming how businesses operate across various sectors. From streamlining workflows to enhancing customer experiences, enablement technology empowers organizations to achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness.
Real-World Applications of Enablement Technology
The impact of enablement technology is evident in various industries, driving innovation and optimizing processes.
- Sales Enablement: Sales teams leverage enablement technology to access product information, training materials, and customer insights, resulting in improved sales performance. For example, a pharmaceutical company might use a knowledge management platform to provide sales representatives with up-to-date information on new drugs, clinical trials, and competitor analysis, enabling them to have more informed and effective conversations with healthcare professionals.
- Customer Success: Customer success teams rely on enablement technology to track customer usage, identify potential issues, and provide proactive support. This ensures customer satisfaction and retention. For instance, a software company might use a customer relationship management (CRM) system to analyze customer data, identify early warning signs of churn, and proactively reach out to customers with personalized support and guidance, minimizing customer churn and fostering long-term relationships.
- Marketing Automation: Marketing teams utilize enablement technology to automate repetitive tasks, personalize marketing campaigns, and analyze campaign performance. This leads to increased efficiency and improved marketing ROI. A marketing team might use marketing automation software to segment their audience, personalize email campaigns, and track website traffic, allowing them to deliver targeted messages and optimize their marketing efforts for better results.
- Human Resources: Enablement technology plays a crucial role in HR, automating onboarding processes, providing training resources, and managing employee performance. A company might use a learning management system (LMS) to deliver online training courses to new employees, ensuring they are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed in their roles. This streamlines onboarding, reduces training costs, and improves employee engagement.
The Future of Enablement Technology
Enablement technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. The future holds exciting possibilities for how enablement technology will transform various industries and aspects of our lives.
Emerging Trends and Advancements
The future of enablement technology will be shaped by several key trends and advancements.
- Hyper-personalization: Enablement technology will become increasingly sophisticated in tailoring experiences to individual needs and preferences. This will involve leveraging data analytics to understand user behavior, preferences, and context, enabling personalized recommendations, content, and services. For example, in the e-commerce industry, AI-powered recommendation engines will provide highly personalized product suggestions based on individual browsing history, purchase patterns, and demographic data. This level of personalization will enhance customer satisfaction and drive sales.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: AR and VR technologies will play a significant role in enabling immersive and interactive experiences. In the field of education, AR and VR can create realistic simulations and virtual environments for learning, making education more engaging and effective. For instance, students can explore historical sites in virtual reality or practice surgical procedures in a simulated environment.
- AI-Powered Automation: AI will continue to automate tasks and processes, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative endeavors. In the manufacturing industry, AI-powered robots will perform repetitive tasks with greater accuracy and efficiency, allowing human workers to focus on tasks requiring human skills and judgment.
- Edge Computing: The rise of edge computing will enable faster processing and data analysis closer to the source of data generation. This will be crucial for real-time decision-making and personalized experiences, particularly in applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Ethical Considerations and Risks
The widespread adoption of enablement technology also raises ethical concerns and potential risks.
- Privacy and Data Security: The collection and use of personal data by enablement technologies raise concerns about privacy and data security. It is essential to ensure that data is collected and used ethically and responsibly, with appropriate safeguards to protect user privacy.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks and processes by AI could lead to job displacement in certain sectors. It is important to address the potential impact on the workforce and develop strategies for retraining and reskilling employees.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI algorithms can perpetuate existing biases and discrimination if trained on biased data. It is crucial to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly, with mechanisms to mitigate bias and promote fairness.
Impact on the Healthcare Industry
Imagine a future where enablement technology revolutionizes the healthcare industry. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images and patient data to identify potential health risks early on. Virtual reality can be used to train surgeons and provide immersive experiences for patients undergoing rehabilitation. Smart devices can monitor patients’ health in real-time, providing personalized health recommendations and alerts. This scenario highlights the transformative potential of enablement technology in improving healthcare outcomes and enhancing patient experiences.
Final Thoughts: Enablement Technology
The future of enablement technology is bright, promising a world where individuals and organizations are empowered to achieve their full potential. As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions emerge, transforming industries and shaping the future of work. From personalized learning experiences to predictive maintenance, the possibilities are endless, and the impact of enablement technology on our lives will only continue to grow.
Enablement technology plays a crucial role in empowering businesses to achieve their goals. This technology often requires the expertise of a deputy chief technology officer , who can bridge the gap between technical capabilities and business strategy. Their role is vital in ensuring that enablement technology is effectively implemented and optimized, ultimately driving innovation and efficiency within the organization.








