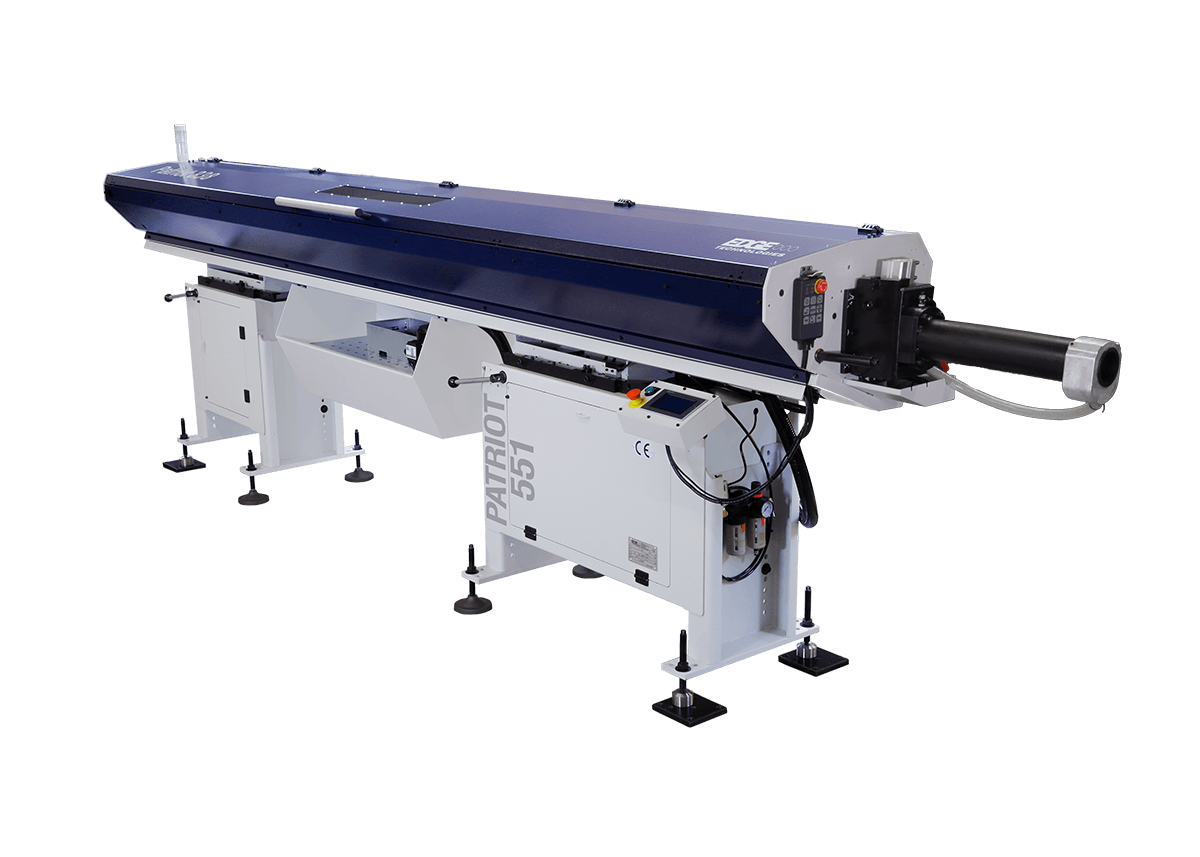
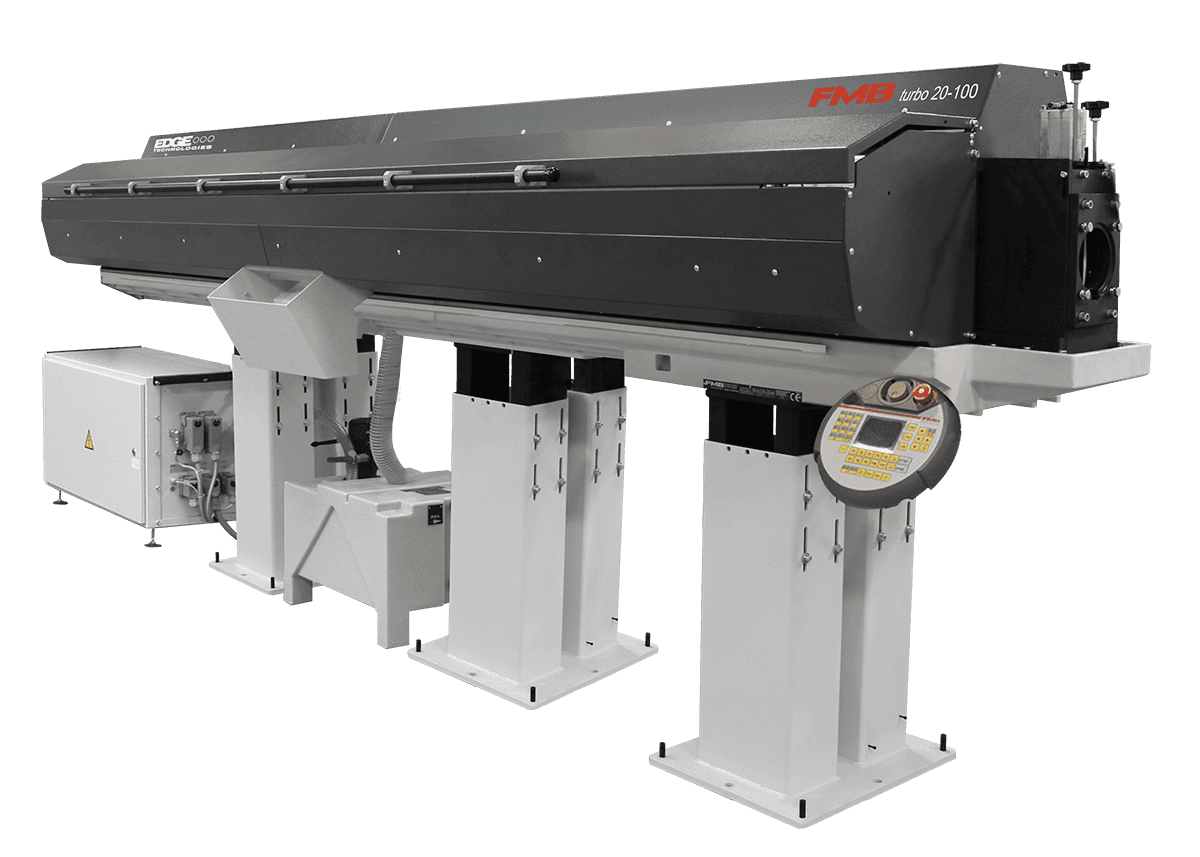
Edge Technologies Bar Feeders: Revolutionizing Manufacturing
Edge technologies bar feeders set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. […]

Edge technologies bar feeders set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Imagine a manufacturing environment where machines communicate seamlessly, anticipate maintenance needs, and optimize production processes in real-time. This vision is becoming reality with the integration of edge technologies, particularly in the realm of bar feeders. These intelligent devices, crucial for automated machining processes, are now equipped with the power of edge computing, enabling them to analyze data locally, make informed decisions, and enhance overall manufacturing efficiency.
Introduction to Edge Technologies: Edge Technologies Bar Feeders
Edge technologies are revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by bringing computing power and data analysis closer to the source of information. This shift from centralized cloud computing to distributed edge computing empowers manufacturers with real-time insights and the ability to optimize processes in a way that was previously impossible.
Edge Computing in Manufacturing
Edge computing refers to processing data closer to where it is generated, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. In manufacturing, this means deploying computing resources directly on the factory floor, alongside machines and sensors. This proximity enables real-time data analysis, reducing latency and improving responsiveness to dynamic conditions.
Benefits of Edge Technologies in Manufacturing, Edge technologies bar feeders
Edge technologies offer numerous advantages for manufacturers, including:
- Real-time data analysis: Edge computing allows for immediate processing of data from sensors, machines, and other devices, providing insights that can be used to optimize operations in real-time. This enables manufacturers to identify and address issues proactively, preventing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Improved efficiency: By analyzing data at the edge, manufacturers can gain a deeper understanding of their processes, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. This leads to increased productivity, reduced waste, and lower operating costs.
- Reduced downtime: Edge technologies enable predictive maintenance by analyzing sensor data to identify potential equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures uninterrupted production.
- Enhanced security: Edge computing can improve data security by processing sensitive information locally, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Examples of Edge Technologies in Manufacturing
Edge technologies are being implemented across various aspects of manufacturing, including:
- Machine monitoring and control: Edge devices can collect data from sensors on machines, monitor their performance, and provide real-time feedback to optimize operations.
- Quality control: Edge technologies can be used to analyze images from cameras on the production line to identify defects and ensure product quality.
- Inventory management: Edge devices can track inventory levels, predict demand, and optimize supply chain logistics.
- Robotics and automation: Edge computing enables robots to process data from sensors and make decisions autonomously, leading to greater flexibility and efficiency in automation tasks.
Bar Feeders
Bar feeders are essential components in automated machining processes, playing a crucial role in feeding raw material to CNC machines. They are devices designed to automatically load and advance bar stock into the machine’s cutting area, eliminating the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency.
Types of Bar Feeders
Bar feeders are categorized based on their feeding mechanisms and are classified into various types, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages.
- Linear Bar Feeders: These feeders utilize a linear motion mechanism to move the bar stock forward. They are commonly used for applications involving straight bar stock and offer simplicity in operation and maintenance. Their linear design allows for straightforward installation and integration with CNC machines.
- Rotary Bar Feeders: Rotary feeders employ a rotating mechanism to advance the bar stock. They are suitable for handling both straight and curved bar stock, offering flexibility in material handling. Rotary feeders are known for their compact design and ability to handle multiple bar stock lengths.
- Articulated Bar Feeders: Articulated feeders combine both linear and rotary motions, providing increased flexibility and reach. They are ideal for applications involving complex part geometries or where space is limited. Their articulated design allows them to navigate obstacles and access difficult-to-reach areas.
Working Principles of Bar Feeders
Bar feeders operate by utilizing a combination of mechanical and electrical components to ensure smooth and accurate material feeding. The process typically involves:
- Bar Loading: The bar stock is loaded into the feeder’s holding mechanism, which securely grips the material.
- Bar Advancement: The feeder’s mechanism, either linear or rotary, advances the bar stock towards the CNC machine’s cutting tool.
- Bar Cutting: Once the bar stock reaches the cutting area, the CNC machine’s tool engages and performs the machining operation.
- Bar Re-positioning: After the machining cycle is complete, the feeder retracts the bar stock, repositioning it for the next cutting operation.
Interaction with CNC Machines
Bar feeders are integrated with CNC machines to ensure seamless material handling and automated machining operations. This integration involves:
- Signal Communication: The CNC machine sends signals to the bar feeder to initiate and control material feeding.
- Synchronized Operations: The bar feeder operates in synchronization with the CNC machine, ensuring precise material advancement and cutting.
- Data Exchange: The bar feeder may exchange data with the CNC machine, such as bar stock length and remaining material quantity.
Integrating Edge Technologies with Bar Feeders
Edge technologies, like IoT sensors, machine learning, and cloud computing, are revolutionizing manufacturing by offering real-time data insights and automation capabilities. Integrating these technologies with bar feeders can unlock a wealth of opportunities to optimize production processes, enhance equipment performance, and improve overall manufacturing efficiency.
Real-Time Data Analysis and Optimization
Real-time data collected from bar feeders can provide valuable insights into various aspects of production, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions and optimize processes. This data can be used to monitor equipment health, track material consumption, analyze production cycles, and identify potential bottlenecks.
For example, sensors integrated into bar feeders can monitor parameters like bar length, feed rate, and cutting tool wear. This data can be used to predict potential tool failures, optimize material utilization, and minimize downtime.
Predictive Maintenance
Edge technologies can empower predictive maintenance strategies for bar feeders, reducing downtime and ensuring smooth production flow. By analyzing data from sensors and machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can anticipate potential equipment failures before they occur.
For instance, a system can detect abnormal vibrations in the bar feeder, indicating a potential bearing failure. This early warning allows for timely maintenance, preventing catastrophic failures and costly production disruptions.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Edge technologies enable remote monitoring and control of bar feeders, providing manufacturers with real-time visibility into equipment performance and allowing them to intervene remotely. This capability is particularly valuable for large-scale manufacturing operations with multiple bar feeders spread across different locations.
With remote monitoring, operators can track the status of bar feeders, identify potential issues, and remotely adjust parameters like feed rate and bar length. This reduces the need for on-site personnel and allows for faster troubleshooting and resolution of issues.
Automated Material Loading
Edge technologies can automate material loading for bar feeders, streamlining production and reducing manual labor. This automation can be achieved using robotics, vision systems, and machine learning algorithms.
For example, an automated system can identify and load the correct bar stock based on pre-programmed specifications. This eliminates manual intervention and ensures consistent material handling, minimizing the risk of errors and improving production efficiency.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Edge technologies, when combined with bar feeders, offer a compelling blend of automation and data-driven optimization. These solutions are transforming manufacturing processes, delivering tangible benefits in various industries.
Manufacturing Optimization in Automotive Industry
The automotive industry, known for its high-volume production and demanding quality standards, is a prime example of the transformative power of edge technologies and bar feeders. A leading automotive manufacturer implemented a system that combined real-time data from bar feeders with predictive analytics to optimize production flow and reduce downtime.
The system tracked bar feeder performance, material usage, and machine status, enabling proactive maintenance and timely material replenishment. This resulted in:
- A 15% reduction in downtime due to material shortages or machine failures.
- Improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 10%.
- Reduced scrap rates by 5% due to optimized material handling and machine settings.
The implementation involved integrating sensors and data acquisition systems with bar feeders, followed by developing algorithms for data analysis and predictive maintenance. The challenge lay in integrating legacy equipment with new technologies and ensuring data security. The solution involved a phased approach, starting with pilot projects to validate the technology and gradually expanding it across the production line.
Future Trends and Innovations
The convergence of edge computing, advanced manufacturing technologies, and the rise of Industry 4.0 are shaping the future of bar feeders. This section delves into emerging trends in edge technologies and their impact on bar feeder design and functionality. We’ll explore the role of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in optimizing bar feeder operations, and envision the future of edge-enabled bar feeders and their potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Optimizing Bar Feeder Operations
AI and ML are transforming the way bar feeders operate, enabling them to become more intelligent, efficient, and responsive. AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors and other sources to identify patterns and anomalies, predict potential issues, and optimize bar feeder performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors to detect early signs of wear and tear, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This can significantly improve machine uptime and reduce maintenance costs.
- Process Optimization: AI can analyze real-time data from bar feeders to identify bottlenecks and optimize feeding speeds, bar length, and other parameters. This can lead to increased productivity and reduced waste.
- Quality Control: AI-powered vision systems can inspect bars for defects and ensure quality control. This can eliminate the need for manual inspection and improve product quality.
Final Review

The integration of edge technologies with bar feeders represents a significant leap forward in manufacturing automation. By leveraging real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring capabilities, these systems are poised to revolutionize industrial processes, leading to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and improved material handling efficiency. As edge computing continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications of edge technologies in bar feeders, further enhancing their capabilities and driving advancements in the manufacturing landscape.
Edge technologies bar feeders are becoming increasingly popular in manufacturing due to their ability to improve efficiency and reduce waste. These systems are often integrated with advanced automation technologies, such as those developed by scion technologies , to further enhance productivity.
By leveraging these cutting-edge solutions, manufacturers can streamline their operations and gain a competitive advantage in today’s demanding marketplace.