Cold Chain Technologies Locations: Mapping the Path to Freshness
Cold chain technologies locations are the backbone of our food system, ensuring that fresh produce, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive goods reach consumers safely and efficiently. From sprawling warehouses to bustling […]

Cold chain technologies locations are the backbone of our food system, ensuring that fresh produce, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive goods reach consumers safely and efficiently. From sprawling warehouses to bustling distribution centers, these locations play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and integrity of perishable products.
The intricate network of cold chain locations involves a carefully orchestrated dance of refrigeration, transportation, and storage, all working in harmony to prevent spoilage and ensure product viability. These locations are strategically designed to meet the unique needs of different products, utilizing advanced technologies and stringent protocols to maintain optimal temperature control and minimize the risk of contamination.
Importance of Cold Chain Technologies
The cold chain, a complex network encompassing the storage, transportation, and handling of temperature-sensitive products, plays a crucial role in ensuring product quality, safety, and minimizing waste. From pharmaceuticals to fresh produce, these technologies are essential for maintaining the integrity of perishable goods throughout their journey from origin to consumer.
Maintaining Product Quality and Safety
Maintaining the desired temperature range is paramount in cold chain management, as it directly impacts product quality and safety. Cold chain technologies effectively prevent spoilage, microbial growth, and degradation, preserving the nutritional value, flavor, and texture of perishable goods. For instance, vaccines, blood products, and other pharmaceuticals require strict temperature control to maintain their efficacy and prevent contamination. Similarly, fresh produce, meat, and dairy products must be kept at specific temperatures to minimize bacterial growth and extend their shelf life.
Minimizing Food Waste and Spoilage
Food waste is a global concern, with significant economic and environmental consequences. Inefficient cold chain systems contribute significantly to food spoilage and loss, leading to substantial financial losses and resource depletion. Implementing effective cold chain technologies can significantly reduce food waste by minimizing spoilage during transportation, storage, and distribution. This includes utilizing refrigerated trucks, cold storage facilities, and temperature monitoring systems to maintain optimal conditions throughout the supply chain. For example, a study by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) estimated that approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally, highlighting the importance of cold chain solutions in reducing this waste.
Economic Benefits of Efficient Cold Chain Systems
Efficient cold chain systems offer significant economic benefits by minimizing product loss, reducing operational costs, and enhancing market access. Reduced spoilage and waste translate into lower costs for businesses, while improved product quality and safety enhance brand reputation and consumer confidence. Moreover, efficient cold chain systems facilitate the transportation of perishable goods over longer distances, expanding market access and boosting economic growth. For instance, the development of cold chain infrastructure in developing countries has enabled the export of fresh produce, contributing to economic diversification and poverty reduction.
Key Components of Cold Chain Technologies

A cold chain system is a complex network of interconnected components that work together to maintain the desired temperature and quality of perishable goods throughout their journey from origin to consumption. This intricate system encompasses various elements, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of temperature-sensitive products.
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is the cornerstone of cold chain technology, as it is responsible for maintaining the required temperature conditions throughout the entire process. Refrigeration systems utilize various methods to extract heat from the environment, thereby lowering the temperature of the storage or transportation space. Different types of refrigeration systems are employed in cold chains, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
Types of Refrigeration Systems
- Vapor-Compression Refrigeration: This is the most common type of refrigeration system used in cold chains. It operates by circulating a refrigerant through a closed loop, where it absorbs heat from the refrigerated space and releases it to the surrounding environment. This process involves compressing the refrigerant vapor, condensing it, and then expanding it to absorb heat again.
- Absorption Refrigeration: This system uses a solution of water and lithium bromide to absorb heat from the refrigerated space. The solution is then heated, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and absorb heat from the surrounding environment. This system is particularly suitable for applications where electricity is scarce or expensive.
- Air Refrigeration: This system uses air as the refrigerant, circulating it through a closed loop and using a compressor to cool it down. This method is commonly used in large cold storage facilities and is known for its energy efficiency.
Transportation
Transportation is a critical element of the cold chain, as it ensures the safe and timely delivery of perishable goods from one point to another. This process requires specialized vehicles and equipment designed to maintain the desired temperature throughout the journey.
Types of Cold Chain Transportation
- Refrigerated Trucks: These trucks are equipped with refrigeration units that maintain the temperature of the cargo during transportation. They are widely used for transporting perishable goods over short and long distances.
- Refrigerated Rail Cars: These rail cars are designed to transport large volumes of perishable goods over long distances. They are typically used for transporting fruits, vegetables, and other agricultural products.
- Refrigerated Shipping Containers: These containers are used for transporting perishable goods by sea or air. They are equipped with refrigeration units that maintain the desired temperature throughout the journey.
Storage
Storage is an essential component of the cold chain, as it provides a controlled environment for preserving the quality and safety of perishable goods. Cold storage facilities come in various sizes and configurations, catering to different storage needs.
Types of Cold Storage Facilities
- Cold Rooms: These are enclosed spaces with controlled temperature and humidity levels. They are commonly used for storing perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, and meat.
- Freezers: These facilities are designed to maintain extremely low temperatures, typically below 0°C. They are used for storing frozen foods, seafood, and other products that require deep freezing.
- Distribution Centers: These facilities are designed for receiving, storing, and distributing perishable goods to various destinations. They often incorporate advanced technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) to optimize efficiency and minimize handling.
Innovative Technologies
The cold chain industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability. These innovations are playing a crucial role in transforming the way perishable goods are managed.
Examples of Innovative Technologies
- Sensors: Sensors are used to monitor various parameters within the cold chain, such as temperature, humidity, and location. These sensors provide real-time data that can be used to identify potential issues and ensure the quality of the goods.
- Data Logging Systems: Data logging systems record and store data from sensors, providing a comprehensive history of the conditions experienced by the goods throughout the cold chain. This information can be used for quality control, traceability, and regulatory compliance.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is enabling the integration of sensors, data logging systems, and other devices into a single network. This allows for real-time monitoring and control of the cold chain, enabling proactive decision-making and optimizing efficiency.
Cold Chain Locations and Infrastructure
The cold chain relies on a network of strategically located facilities to ensure the uninterrupted flow of temperature-sensitive goods. These locations, ranging from large warehouses to smaller retail outlets, play crucial roles in maintaining the integrity of the cold chain.
Cold Chain Locations and Their Infrastructure
The cold chain ecosystem comprises various locations, each designed to serve a specific purpose. Here’s a breakdown of these locations and their key infrastructure requirements:
| Location Type | Purpose | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warehouses | Large-scale storage of temperature-sensitive goods, often acting as central hubs for distribution. |
|
|
| Distribution Centers | Facilitate the efficient movement of goods from warehouses to retail outlets or other destinations. |
|
|
| Retail Outlets | Final destination for consumers, where temperature-sensitive goods are displayed and sold. |
|
|
Challenges and Opportunities in Cold Chain Technologies: Cold Chain Technologies Locations
The cold chain, while crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of perishable goods, faces numerous challenges. These challenges arise from the delicate nature of the products being transported and the complexities of maintaining optimal conditions throughout the entire journey. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and improvement, leading to a more efficient and sustainable cold chain ecosystem.
Maintaining Cold Chain Integrity
Maintaining cold chain integrity is essential for preserving the quality and safety of perishable products. Temperature fluctuations, transportation disruptions, and improper handling can compromise the integrity of the cold chain, leading to spoilage, product loss, and financial losses.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Maintaining consistent temperatures is critical for preventing spoilage and ensuring product safety. Temperature fluctuations can occur during loading, unloading, transportation, and storage, impacting the quality of perishable goods. For example, a delay in transportation due to traffic congestion can lead to temperature deviations, potentially compromising the quality of temperature-sensitive products like vaccines and fresh produce.
- Transportation Disruptions: Disruptions in transportation can occur due to unforeseen circumstances like weather events, accidents, or political instability. These disruptions can cause delays, leading to temperature fluctuations and potential spoilage. For instance, a natural disaster like a hurricane can disrupt transportation routes, impacting the delivery of perishable goods and causing significant financial losses.
- Improper Handling: Improper handling during loading, unloading, and storage can also compromise the integrity of the cold chain. For example, mishandling of refrigerated containers during loading or unloading can lead to temperature fluctuations, impacting the quality of the goods.
Opportunities for Innovation and Improvement
The challenges faced by the cold chain present opportunities for innovation and improvement. Advancements in packaging, logistics, and monitoring systems can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of cold chain operations.
- Packaging Innovations: Advancements in packaging materials and technologies can improve temperature control and product protection. For example, the use of insulated packaging with phase change materials can help maintain consistent temperatures during transportation, even in extreme conditions. Additionally, active packaging systems, which incorporate temperature sensors and active cooling mechanisms, can further enhance temperature control and product safety.
- Logistics Optimization: Optimizing logistics routes and transportation methods can reduce transportation time and minimize temperature fluctuations. For example, using real-time tracking systems can help monitor the location and temperature of goods in transit, enabling efficient route planning and reducing delays. Additionally, the use of cold chain logistics providers with expertise in temperature-controlled transportation can ensure that products are handled properly and maintained at the required temperatures.
- Monitoring Systems: Real-time monitoring systems, equipped with sensors and data analytics, can provide continuous tracking of temperature, humidity, and other critical parameters. This data can be used to identify potential issues, alert stakeholders, and take corrective actions to prevent spoilage and ensure product safety. For instance, a remote monitoring system can detect a temperature deviation in a refrigerated truck, allowing for immediate intervention to prevent product damage.
Sustainable Practices and Energy Efficiency
Sustainable practices and energy efficiency are crucial for optimizing cold chain operations and reducing environmental impact. By implementing sustainable solutions, the cold chain can become more environmentally friendly and economically viable.
- Energy-Efficient Refrigeration Systems: Using energy-efficient refrigeration systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. For example, adopting advanced refrigeration technologies like variable-speed compressors and natural refrigerants can lead to significant energy savings.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into cold chain operations can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon footprint. For instance, installing solar panels on refrigerated warehouses can provide a sustainable source of energy for refrigeration systems.
- Optimized Logistics and Transportation: Optimizing logistics routes and transportation methods can reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. For example, using efficient transportation modes, such as rail or water transport, can minimize energy usage and environmental impact.
Future Trends in Cold Chain Technologies
The cold chain industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. Emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and automation are revolutionizing how cold chain operations are managed, leading to increased efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to track products throughout the cold chain, providing real-time visibility into their journey from origin to destination.
- Each product is assigned a unique identifier that is recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable record of its history.
- This enables stakeholders to access information about the product’s origin, temperature history, and handling events, enhancing accountability and trust.
For example, the pharmaceutical industry is leveraging blockchain to ensure the integrity and authenticity of medicines, preventing counterfeiting and ensuring that drugs are stored and transported under optimal conditions.
Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Maintenance and Optimization, Cold chain technologies locations
AI-powered systems are transforming cold chain operations by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential issues.
- These insights enable proactive maintenance and optimize resource allocation, reducing downtime and minimizing waste.
- AI algorithms can also optimize routes, optimize inventory levels, and predict demand, leading to significant cost savings.
For instance, companies are using AI to monitor refrigeration units in real-time, predicting potential breakdowns and scheduling maintenance before they occur, preventing costly disruptions in the cold chain.
Automation for Increased Efficiency and Safety
Automation is playing a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and safety in cold chain operations.
- Robotic systems are being deployed for tasks like loading and unloading trucks, picking and packing products, and managing inventory.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are being used to transport goods within warehouses and distribution centers, reducing manual labor and minimizing errors.
For example, automated warehouse systems are being implemented to optimize storage and retrieval processes, ensuring that products are stored at the correct temperature and retrieved efficiently.
Sustainable Cold Chain Solutions
As the cold chain industry grows, sustainability is becoming increasingly important.
- Companies are exploring innovative solutions to reduce their environmental footprint, such as using renewable energy sources for refrigeration and implementing energy-efficient technologies.
- There is a growing focus on developing sustainable packaging materials and reducing food waste throughout the cold chain.
For instance, some companies are using bio-based refrigerants that have a lower global warming potential than traditional refrigerants, while others are developing packaging materials that are made from recycled or renewable resources.
Final Wrap-Up
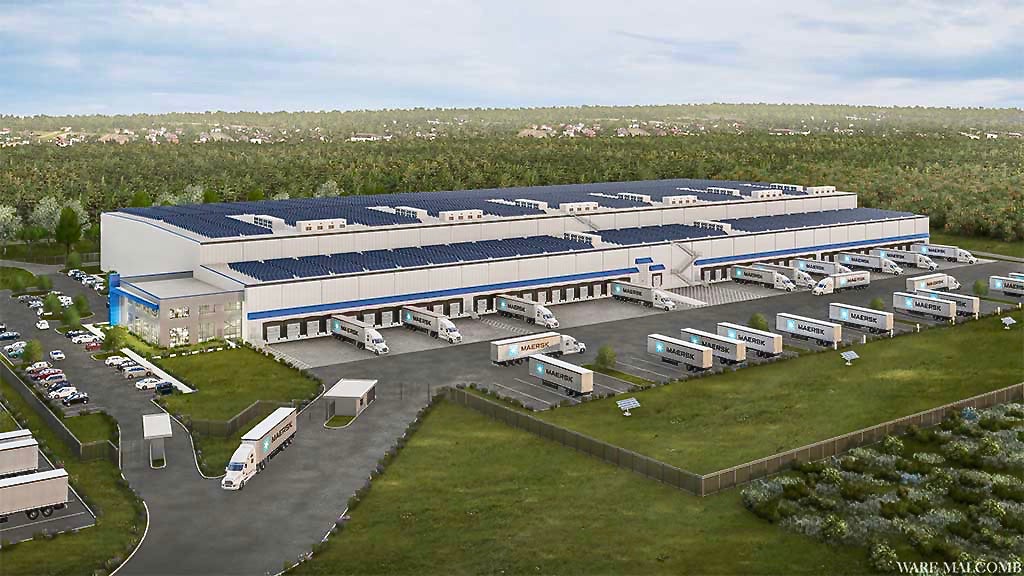

As the world’s population continues to grow and demand for fresh and safe food increases, the importance of robust and efficient cold chain technologies locations will only become more critical. Innovation and advancements in areas such as automation, blockchain, and artificial intelligence will play a key role in shaping the future of cold chain management, ensuring that we can continue to enjoy the benefits of a reliable and sustainable food supply chain.
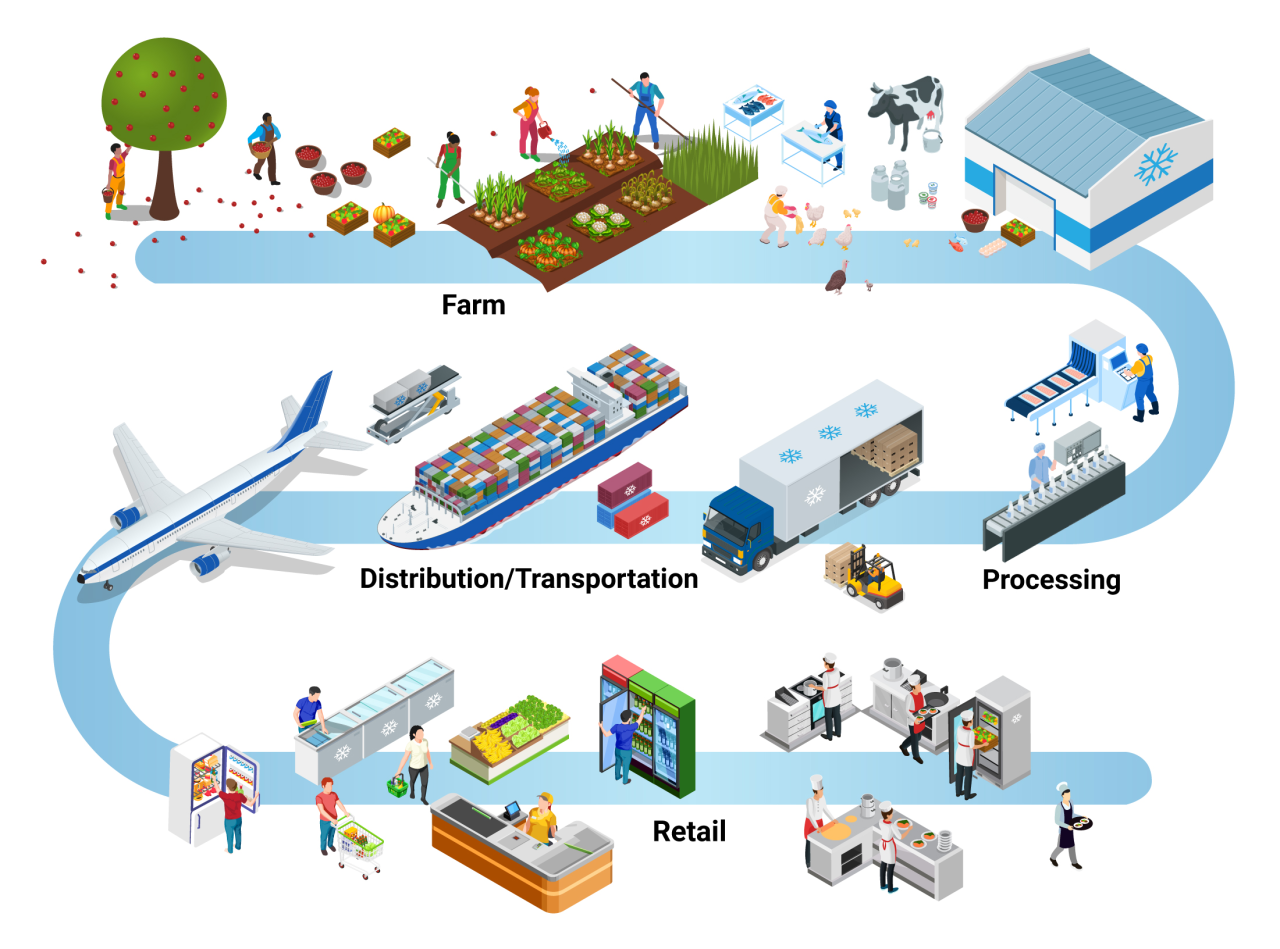
Cold chain technologies are crucial for maintaining the quality of perishable goods throughout their journey. From farms and processing facilities to distribution centers and retail outlets, these technologies play a vital role in ensuring that products arrive fresh and safe.
One innovative solution that can optimize cold chain logistics is cobwebs technology , which uses sensors and data analytics to track and monitor shipments in real-time. By leveraging this technology, companies can optimize their cold chain operations, reduce waste, and ensure the integrity of their products.




