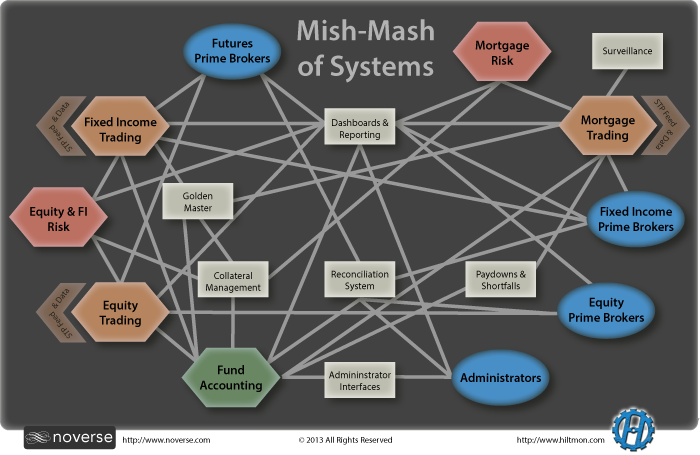
CFO Technology: Transforming Finance in the Digital Age
CFO technology has become a driving force in the evolution of finance departments, ushering in a new era of data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency. As businesses navigate the complexities of […]

CFO technology has become a driving force in the evolution of finance departments, ushering in a new era of data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency. As businesses navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, CFOs are embracing cutting-edge tools and strategies to enhance financial performance and gain a competitive edge.
This exploration delves into the dynamic landscape of CFO technology, examining the transformative technologies shaping the modern finance function. We will explore the key trends, benefits, and challenges associated with the adoption of these technologies, highlighting their impact on financial operations, decision-making, and the overall business landscape.
The Evolving Role of the CFO

The role of the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) has undergone a significant transformation in the digital age, moving beyond traditional financial management to encompass a broader strategic vision. The rapid pace of technological advancements, coupled with the increasing complexity of business operations, has demanded a new breed of CFOs who can navigate the intricate landscape of data, technology, and innovation.
Key Skills and Responsibilities of the Modern CFO, Cfo technology
The traditional CFO role, primarily focused on accounting, financial reporting, and budgeting, has evolved to include a wider range of responsibilities, driven by the need to leverage technology for strategic decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Data Analytics and Insights: Modern CFOs are expected to harness the power of data analytics to extract meaningful insights from financial and operational data. This involves using advanced analytics tools to identify trends, forecast future performance, and inform strategic decisions.
- Technology Expertise: With the increasing reliance on technology in business operations, CFOs need to possess a strong understanding of emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain. This knowledge allows them to effectively evaluate and implement technology solutions that enhance financial processes and drive innovation.
- Strategic Planning and Risk Management: CFOs are now expected to play a more active role in strategic planning, working closely with the CEO and other executives to develop long-term growth strategies. They also need to assess and mitigate financial risks, including cyber security threats and regulatory compliance issues.
- Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration skills are essential for CFOs to effectively communicate financial information to stakeholders, including investors, board members, and employees. They need to be able to present complex financial data in a clear and concise manner, fostering trust and transparency.
- Innovation and Transformation: Modern CFOs are expected to be change agents, driving innovation and transformation within their organizations. This involves embracing new technologies, streamlining financial processes, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Challenges and Opportunities for Modern CFOs
The digital age presents both challenges and opportunities for CFOs, requiring them to adapt their skills and perspectives to thrive in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
- Cybersecurity Threats: The increasing reliance on technology exposes businesses to a greater risk of cyberattacks, which can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and damage reputation. CFOs need to prioritize cybersecurity measures, investing in robust security systems and training employees to mitigate these threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, with new rules and regulations emerging to address the complexities of digital business models. CFOs need to stay abreast of these changes, ensuring compliance and managing potential legal risks.
- Data Management and Privacy: As businesses collect and analyze vast amounts of data, CFOs face the challenge of managing data effectively while adhering to privacy regulations. This involves implementing data governance policies, ensuring data integrity, and protecting sensitive customer information.
- Digital Transformation: Embracing digital transformation requires CFOs to navigate the challenges of implementing new technologies, integrating them with existing systems, and managing the associated costs. However, this also presents an opportunity to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
- Talent Acquisition and Development: Attracting and retaining skilled financial professionals with the necessary technical and analytical expertise is crucial for CFOs to build high-performing finance teams. They need to create a culture of learning and development, investing in training programs to equip their teams with the skills required to navigate the digital age.
Technology Adoption in Finance Departments

Finance departments are increasingly embracing technology to improve efficiency, accuracy, and insights. This shift is driven by the need to handle growing data volumes, comply with regulatory requirements, and gain a competitive edge.
Financial Planning and Analysis
Financial planning and analysis (FP&A) is a core function of finance departments. Technology plays a crucial role in automating tasks, improving forecasting accuracy, and providing real-time insights.
- Planning and Budgeting Software: These tools streamline the budgeting process, allowing for scenario planning, collaboration, and real-time monitoring of budget performance. Examples include Anaplan, Oracle Hyperion Planning, and IBM Cognos TM1.
- Data Visualization and Analytics Tools: These tools enable FP&A professionals to analyze large datasets, identify trends, and create insightful dashboards and reports. Popular options include Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools can automate forecasting, identify anomalies, and provide predictive insights, improving the accuracy and speed of FP&A processes.
Accounting and Reporting
Technology has revolutionized accounting and reporting, enabling automation, improved accuracy, and real-time visibility.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems integrate various business processes, including accounting, finance, and supply chain management, providing a centralized platform for data management and reporting. Leading ERP systems include SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
- Cloud-Based Accounting Software: Cloud-based solutions like Xero, QuickBooks Online, and NetSuite offer accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for accounting and reporting. They provide real-time data, automate tasks, and facilitate collaboration.
- Automated Invoice Processing: AI-powered invoice processing tools automate the capture, validation, and processing of invoices, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Regulatory Compliance Software: Software solutions specifically designed for regulatory compliance help finance departments meet evolving reporting requirements and ensure data accuracy.
Risk Management
Technology empowers finance departments to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks.
- Risk Management Software: These tools help organizations manage risk across various categories, including operational, financial, and regulatory risks. They provide a centralized platform for risk identification, assessment, and mitigation planning.
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Advanced analytics and machine learning techniques can identify potential risks early, enabling proactive risk management strategies. For example, fraud detection systems use AI to identify unusual patterns and transactions that might indicate fraudulent activity.
- Cybersecurity Solutions: Protecting sensitive financial data is crucial. Cybersecurity solutions like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption help mitigate cyber threats and ensure data security.
Treasury Management
Technology streamlines treasury operations, improves cash flow management, and enhances investment decision-making.
- Treasury Management Systems (TMS): TMS platforms centralize treasury operations, providing tools for cash forecasting, bank account management, payment processing, and investment management.
- Real-Time Payment Solutions: Real-time payment systems enable faster and more efficient payments, improving cash flow and reducing payment delays. Examples include Zelle and Faster Payments.
- Investment Management Platforms: These platforms provide tools for portfolio analysis, risk management, and performance reporting, supporting investment decision-making.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on CFO Functions
The integration of AI into finance departments is transforming the CFO’s role, creating new opportunities to enhance decision-making, optimize operations, and drive value. AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate insights at unprecedented speeds is revolutionizing how CFOs manage risk, optimize financial performance, and navigate an increasingly complex business landscape.
Applications of AI in Finance
AI’s potential in finance extends across various areas, offering significant value to CFOs.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can analyze transaction data in real-time, identifying anomalies and patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity. This allows for proactive fraud prevention and early detection, minimizing financial losses and improving risk management. For instance, AI-powered fraud detection systems can analyze transaction history, identify unusual spending patterns, and flag suspicious activities, helping CFOs prevent fraudulent transactions and protect their organization’s assets.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can leverage historical data and external factors to forecast financial performance, predict future trends, and inform strategic decision-making. CFOs can use AI-powered predictive models to forecast revenue, expenses, and cash flow, allowing for more accurate budgeting, financial planning, and resource allocation.
- Automated Reporting: AI can automate routine financial reporting tasks, freeing up CFOs and their teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. AI-powered systems can collect data from various sources, generate reports, and analyze key performance indicators, providing CFOs with real-time insights into the financial health of the organization.
Examples of AI in Leading Companies
Several companies are leading the way in leveraging AI to enhance CFO decision-making and optimize financial operations.
- JP Morgan Chase utilizes AI to automate tasks such as trade reconciliation and regulatory reporting, freeing up financial professionals for more strategic work. The bank’s AI-powered systems also help analyze large datasets to identify potential risks and opportunities.
- General Electric has implemented AI-driven systems to optimize its supply chain, predict equipment failures, and improve operational efficiency. These AI applications have helped GE reduce costs and improve profitability.
- Amazon uses AI to analyze customer data, optimize pricing strategies, and personalize customer experiences. This AI-driven approach has contributed to Amazon’s success in e-commerce and cloud computing.
Hypothetical Scenario: AI in a CFO’s Decision-Making Process
Imagine a scenario where a CFO is considering a significant investment in a new technology. AI can play a crucial role in this decision-making process by:
- Analyzing market trends and competitor strategies: AI can gather and analyze data from various sources, including industry reports, news articles, and social media, to provide insights into market dynamics and competitor actions. This information can help the CFO understand the potential risks and opportunities associated with the investment.
- Evaluating financial feasibility: AI can analyze historical financial data and project future cash flows to assess the financial viability of the investment. This includes considering factors such as return on investment, payback period, and potential risks.
- Simulating different scenarios: AI can simulate different investment scenarios, allowing the CFO to evaluate the potential outcomes under various market conditions. This can help the CFO identify potential risks and develop contingency plans.
AI can provide valuable insights and recommendations, but ultimately, the CFO remains responsible for making the final decision. It’s crucial to remember that AI is a tool, and its output should be carefully considered and validated before making any significant decisions.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence for CFOs

In today’s data-driven world, CFOs are increasingly leveraging data analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools to gain a deeper understanding of their company’s financial performance and market trends. These tools enable CFOs to move beyond traditional financial reporting and unlock valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making.
Data Sources and Insights
Data analytics and BI tools empower CFOs by providing access to a wealth of data sources, each offering unique insights into the business.
Here is a table summarizing some key data sources and the corresponding insights they provide:
| Data Source | Insights |
|—|—|
| Financial Statements | – Profitability trends
– Cash flow patterns
– Efficiency ratios |
| Sales Data | – Customer segmentation
– Product performance
– Sales cycle analysis |
| Operations Data | – Production efficiency
– Supply chain performance
– Inventory management |
| Market Data | – Competitive landscape
– Industry trends
– Economic indicators |
| Customer Data | – Customer behavior
– Customer satisfaction
– Customer churn |
Data-Driven Decision Making
By analyzing data from these various sources, CFOs can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. This enables them to make more informed decisions regarding:
– Investment allocation: Identifying profitable growth opportunities and allocating resources effectively.
– Cost optimization: Identifying areas for cost reduction and improving operational efficiency.
– Risk management: Proactively identifying and mitigating potential financial risks.
– Strategic planning: Developing data-driven forecasts and projections for future financial performance.
For example, a CFO analyzing sales data might discover a declining trend in a specific product line. By investigating further, they might find that this decline is due to increased competition. This insight could then lead to strategic decisions such as product development, marketing campaigns, or pricing adjustments to regain market share.
Cloud Computing and Cybersecurity for CFOs: Cfo Technology
The shift towards cloud-based solutions in finance departments is undeniable. Cloud computing offers several advantages for CFOs, such as cost savings, scalability, and enhanced collaboration. However, it also introduces new cybersecurity challenges that require careful consideration. This section explores the advantages and disadvantages of cloud-based solutions, identifies key cybersecurity considerations, and provides a checklist of best practices for CFOs to safeguard their financial data in the cloud.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud computing presents both opportunities and challenges for financial management.
- Advantages:
- Cost Savings: Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for expensive hardware and software investments, leading to significant cost reductions in infrastructure and maintenance. For example, a company can save millions of dollars by migrating its on-premise data center to a cloud platform, freeing up capital for strategic initiatives.
- Scalability: Cloud services provide the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand, allowing CFOs to adjust their IT infrastructure as needed without the need for large upfront investments. This scalability is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in workload.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based solutions facilitate real-time collaboration among finance teams, regardless of location. This enables faster decision-making and improved efficiency, as team members can access and share data securely from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Increased Agility: Cloud services offer greater agility and flexibility compared to traditional on-premise solutions. CFOs can quickly deploy new applications and functionalities, adapt to changing business needs, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
- Disadvantages:
- Security Concerns: Cloud computing introduces new cybersecurity risks, as sensitive financial data is stored and processed in a third-party environment. CFOs must carefully evaluate the security measures implemented by cloud providers and ensure they meet their organization’s specific requirements.
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating to a cloud platform can lead to vendor lock-in, making it difficult or costly to switch providers in the future. CFOs should carefully assess the long-term implications of choosing a particular cloud provider.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Cloud providers must comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, to protect sensitive financial information. CFOs need to ensure their chosen cloud provider has robust data privacy and compliance measures in place.
- Internet Dependency: Cloud-based solutions rely on a stable internet connection. Disruptions or outages can impact financial operations and lead to delays in data access and processing.
Key Cybersecurity Considerations for CFOs in a Cloud-Based Environment
CFOs must prioritize cybersecurity in a cloud-based environment to protect sensitive financial data.
- Data Encryption: Ensure that all financial data stored and transmitted in the cloud is encrypted using strong encryption algorithms. This safeguards data from unauthorized access, even if the cloud provider’s systems are compromised.
- Access Control: Implement robust access control measures to restrict access to financial data based on user roles and permissions. This helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive information.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all user accounts accessing cloud-based financial systems. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits of cloud-based systems to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards. This includes internal audits and third-party assessments.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to address cybersecurity incidents promptly and effectively. This plan should Artikel steps for identifying, containing, and mitigating security breaches.
- Employee Training: Provide employees with regular cybersecurity training to educate them about best practices for protecting financial data in the cloud. This includes awareness of phishing scams, malware threats, and other common cybersecurity risks.
Best Practices for Ensuring Security and Integrity of Financial Data in the Cloud
CFOs can adopt several best practices to enhance the security and integrity of their financial data in the cloud.
- Choose a Reputable Cloud Provider: Select a cloud provider with a proven track record of security and compliance. Research their security certifications, data center locations, and customer support services.
- Negotiate a Strong Service Level Agreement (SLA): Ensure the SLA includes specific security guarantees, such as uptime, data backup, and incident response times. This provides legal recourse if the cloud provider fails to meet its security obligations.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures: Utilize DLP tools to monitor and prevent unauthorized data transfers, ensuring sensitive financial data remains within the secure cloud environment.
- Regularly Review and Update Security Policies: Regularly review and update security policies to reflect evolving cybersecurity threats and industry best practices. This ensures your organization remains proactive in safeguarding financial data.
- Utilize Cloud Security Monitoring Tools: Implement cloud security monitoring tools to continuously track security events, identify potential threats, and provide real-time insights into the security posture of your cloud environment.
The Future of CFO Technology
The role of the CFO is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements that are transforming the way financial operations are conducted. Emerging technologies are poised to further revolutionize the CFO’s role, impacting financial operations, decision-making, and the overall business landscape.
Emerging Technologies and their Impact
The adoption of emerging technologies is crucial for CFOs to remain competitive and agile in the face of rapidly changing business environments. These technologies offer new opportunities to optimize processes, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is rapidly transforming financial operations by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and providing real-time insights. AI-powered tools can analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling CFOs to make more informed decisions and mitigate risks. For example, AI-driven fraud detection systems can identify suspicious transactions and prevent financial losses.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology is revolutionizing financial transactions by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient platform for recording and verifying data. Blockchain can be used to track financial transactions, manage supply chains, and improve auditing processes. For instance, blockchain-based platforms can automate payments and reduce transaction costs, streamlining financial operations.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting physical assets to the internet, generating vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to improve financial performance. CFOs can use IoT data to optimize inventory management, track asset utilization, and gain real-time insights into operational efficiency. For example, IoT sensors can track equipment performance and predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime and costs.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize financial modeling and analysis by solving complex problems that are intractable for classical computers. Quantum computers can perform calculations at unprecedented speeds, enabling CFOs to develop more sophisticated financial models and make more accurate predictions. For example, quantum computers can be used to optimize investment portfolios, analyze risk, and assess financial market volatility.
Closing Notes
The future of CFO technology holds immense potential for further innovation and disruption. As emerging technologies continue to evolve, CFOs will play a pivotal role in harnessing their power to drive financial success and navigate the ever-changing business environment. By embracing the latest advancements, CFOs can unlock new opportunities for growth, enhance risk management, and optimize financial performance, ultimately positioning their organizations for long-term prosperity.
CFO technology is rapidly evolving, with new tools and solutions emerging to streamline financial processes. One area where innovation is particularly exciting is in the realm of data security. Advanced encryption and authentication techniques are crucial for protecting sensitive financial information.
This is where sealant technology can play a role, providing an extra layer of protection against data breaches. As CFOs continue to embrace technology, solutions like sealant technology will be essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring the safety of critical financial information.