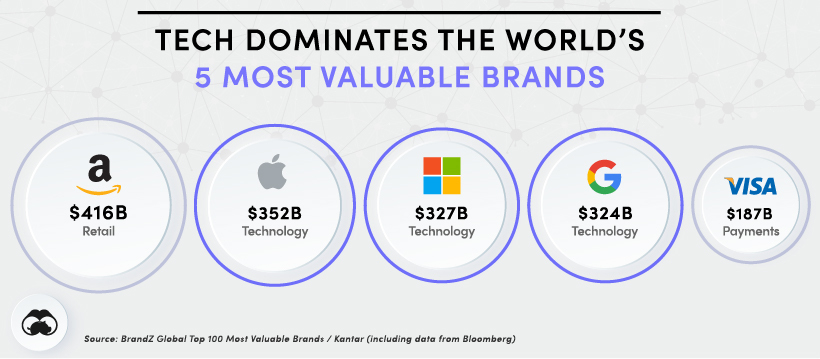
American Aerospace Technologies: A Journey of Innovation
American aerospace technologies have propelled humanity beyond the boundaries of Earth, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and revolutionizing transportation. From the Wright brothers’ pioneering flights to the moon landing […]

American aerospace technologies have propelled humanity beyond the boundaries of Earth, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and revolutionizing transportation. From the Wright brothers’ pioneering flights to the moon landing and the dawn of commercial space travel, the United States has been at the forefront of this transformative field. This journey of innovation has been fueled by the relentless pursuit of scientific knowledge, technological advancements, and the unwavering spirit of exploration.
This exploration delves into the history, current state, key players, challenges, opportunities, and future directions of American aerospace technologies. It highlights the key milestones, innovations, and influential figures that have shaped this industry, examining the role of government agencies, universities, and private companies in driving progress. We’ll explore the latest trends in aircraft design, space exploration, aerospace materials, and unmanned aerial vehicles, while also considering the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Historical Overview of American Aerospace Technologies

The history of American aerospace technologies is a captivating tale of innovation, ambition, and the relentless pursuit of pushing the boundaries of human exploration. From the pioneering days of aviation to the awe-inspiring achievements of the space race, American ingenuity has left an indelible mark on the world.
Early Aviation Pioneers and Innovations
The early 20th century witnessed the birth of aviation in the United States. A confluence of factors, including the burgeoning industrial revolution and the growing interest in flight, paved the way for remarkable advancements.
- The Wright Brothers: In 1903, Wilbur and Orville Wright made history by achieving the first successful sustained, controlled flight in a heavier-than-air machine at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. This groundbreaking achievement marked the dawn of a new era in transportation and forever changed the course of human history.
- Glenn Curtiss: A contemporary of the Wright brothers, Glenn Curtiss was another prominent figure in early aviation. Curtiss made significant contributions to the development of seaplanes, engines, and aircraft design, pushing the boundaries of flight performance. He also played a pivotal role in the establishment of the United States Navy’s first air arm.
- The Birth of the Airplane Industry: The early years of aviation were marked by rapid advancements in aircraft design and construction. Pioneers like the Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss laid the foundation for a thriving airplane industry, which would eventually become a cornerstone of the American economy.
Government Agencies and the Rise of Aerospace, American aerospace technologies
The early development of aviation in the United States was significantly influenced by the role of government agencies.
- The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA): Established in 1915, NACA played a crucial role in advancing aerospace research and development. Through its extensive research programs and collaborations with universities and private companies, NACA made significant contributions to the field, including the development of wind tunnels, aircraft design principles, and jet propulsion technology.
- The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF): During World War II, the USAAF emerged as a major force in military aviation. The war’s demands for advanced aircraft spurred technological innovation, leading to the development of powerful fighter planes, bombers, and transport aircraft. The USAAF’s experiences in World War II laid the groundwork for the future of American aerospace technology.
The Space Race and the Birth of NASA
The 1950s and 1960s witnessed a period of intense competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, known as the Space Race. This rivalry propelled the advancement of space exploration technologies, pushing the boundaries of human ingenuity and scientific understanding.
- The Formation of NASA: In 1958, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) was established to consolidate the nation’s space exploration efforts. NASA brought together scientists, engineers, and technicians from across the country, fostering a collaborative environment for research and development.
- Project Mercury: NASA’s Project Mercury, launched in 1961, focused on sending the first American into space. On May 5, 1961, Alan Shepard became the first American to achieve this feat, marking a significant milestone in the Space Race.
- Project Gemini: Following Project Mercury, NASA launched Project Gemini in 1965, which aimed to develop the technology and skills needed for longer space missions, including spacewalks and rendezvous maneuvers. Gemini missions provided valuable experience for future lunar missions.
- Project Apollo: NASA’s Project Apollo, launched in 1961, aimed to land a man on the moon before the end of the decade. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the moon, a historic achievement that captured the world’s imagination and solidified America’s dominance in space exploration.
Private Companies and the Commercialization of Aerospace
While government agencies played a dominant role in the early development of aerospace technology, the rise of private companies has significantly transformed the industry in recent decades.
- SpaceX: Founded in 2002 by Elon Musk, SpaceX has emerged as a leading player in the commercial space industry. SpaceX has developed reusable rockets and spacecraft, revolutionizing space launch capabilities and opening up new possibilities for commercial space exploration.
- Blue Origin: Founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin is another prominent player in the commercial space sector. Blue Origin has developed reusable launch vehicles and is working on technologies for space tourism and orbital space stations.
- Virgin Galactic: Founded in 2004 by Richard Branson, Virgin Galactic is focused on developing suborbital space tourism. Virgin Galactic has successfully completed test flights and is preparing for commercial operations, offering passengers the opportunity to experience space travel.
Current State of American Aerospace Technologies

The American aerospace industry is at the forefront of technological innovation, constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible in aviation and space exploration. This dynamic landscape is characterized by a confluence of factors, including advancements in materials science, computational power, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and affordability.
Key Areas of Focus in American Aerospace Research and Development
American aerospace research and development is driven by a multifaceted set of priorities, including:
- National Security: The development of advanced military aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and hypersonic weapons systems remains a critical focus for the US government.
- Space Exploration: The pursuit of human and robotic missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond continues to be a major driver of innovation in areas such as propulsion systems, life support technologies, and robotic exploration.
- Commercial Spaceflight: The emergence of private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic has significantly accelerated the development of reusable launch vehicles, space tourism, and satellite constellations.
- Sustainability and Efficiency: Increasing concerns about climate change and environmental impact have led to a growing emphasis on developing more fuel-efficient aircraft, sustainable aviation fuels, and electric aircraft technologies.
Technological Trends and Advancements in American Aerospace
The American aerospace industry is witnessing a surge in technological advancements across various areas, leading to significant progress in aircraft design, space exploration, materials science, and propulsion systems.
| Area of Focus | Key Trends | Recent Advancements | Prominent Players |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Design and Manufacturing |
|
|
|
| Space Exploration and Commercialization |
|
|
|
| Aerospace Materials and Propulsion Systems |
|
|
|
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and Drones |
|
|
|
| Hypersonic Flight and Advanced Aerospace Concepts |
|
|
|
Challenges and Opportunities in American Aerospace Technologies
The American aerospace industry, a pioneer in technological innovation, faces a dynamic landscape marked by both challenges and opportunities. While the industry has historically been at the forefront of technological advancement, it must navigate a complex web of global competition, economic pressures, and environmental concerns.
Technological Advancements in Other Countries
The emergence of strong aerospace industries in other countries, particularly in Asia and Europe, poses a significant challenge to American dominance. These competitors are investing heavily in research and development, producing innovative technologies, and capturing a growing share of the global market.
- Increased Competition: Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are rapidly developing their own aerospace capabilities, producing advanced aircraft, satellites, and space launch vehicles.
- Technological Parity: The gap in technological capabilities between the United States and its competitors is narrowing, making it increasingly difficult to maintain a competitive edge.
- Market Share Erosion: The growing competitiveness of international players is leading to a decrease in the market share of American aerospace companies.
Economic and Geopolitical Factors
The aerospace industry is heavily influenced by economic and geopolitical factors, including global trade agreements, government funding, and international relations.
- Economic Downturns: Recessions and economic instability can lead to decreased demand for aerospace products and services, impacting investment and employment in the industry.
- Government Funding: The level of government funding for aerospace research and development plays a critical role in driving innovation and maintaining competitiveness. Fluctuations in government funding can impact the industry’s ability to invest in cutting-edge technologies.
- Geopolitical Tensions: International conflicts and trade disputes can disrupt supply chains, impact export markets, and hinder collaboration between countries in the aerospace sector.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
The aerospace industry’s environmental impact is a growing concern, prompting a shift towards more sustainable practices and technologies.
- Emissions Reduction: The aviation industry is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing emissions through fuel efficiency improvements, alternative fuels, and sustainable aircraft design is crucial for environmental responsibility.
- Noise Pollution: Aircraft noise pollution is a major concern, particularly near airports. Developing quieter aircraft designs and implementing noise mitigation measures is essential for reducing community impact.
- Resource Conservation: The aerospace industry relies on a wide range of resources, including metals, composites, and fuels. Developing sustainable manufacturing processes and promoting resource conservation is crucial for long-term environmental sustainability.
Emerging Markets for Aerospace Products and Services
Despite the challenges, the global demand for aerospace products and services is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing air travel, rising demand for commercial and military aircraft, and the expansion of space exploration activities.
- Rapidly Growing Economies: Developing countries, particularly in Asia and Africa, are experiencing rapid economic growth, leading to increased demand for air travel and related infrastructure.
- Expanding Middle Class: A growing middle class in many parts of the world is fueling demand for air travel, creating new markets for airlines and aircraft manufacturers.
- Space Exploration and Commercialization: The increasing focus on space exploration, including commercial space tourism and satellite-based services, is creating new opportunities for the aerospace industry.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Automation
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and automation is transforming the aerospace industry, leading to increased efficiency, safety, and innovation.
- Autonomous Systems: AI-powered autonomous systems are being developed for tasks such as aircraft navigation, traffic management, and maintenance, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Robotics in Manufacturing: Robotics and automation are being used in manufacturing processes, improving production speed, accuracy, and quality while reducing labor costs.
- Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance: AI-driven data analytics is enabling predictive maintenance, identifying potential issues before they occur, reducing downtime, and improving safety.
Integration of Aerospace Technologies with Other Industries
Aerospace technologies are increasingly finding applications in other industries, creating opportunities for collaboration and innovation.
- Advanced Materials: Lightweight and high-strength materials developed for aerospace applications are being adopted in other sectors, such as automotive, energy, and construction.
- Sensors and Navigation: Aerospace-derived sensors and navigation systems are being used in autonomous vehicles, drones, and other industries that require precise positioning and environmental monitoring.
- Communication Technologies: Satellite communication technologies developed for aerospace applications are being used in telecommunications, broadcasting, and remote sensing.
“The future of American aerospace will be shaped by its ability to adapt to these challenges and capitalize on these opportunities. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing sustainability, the industry can continue to lead the world in technological advancement and economic growth.”
Future Directions for American Aerospace Technologies
The future of American aerospace technologies holds immense potential for innovation and advancement, shaping not only space exploration but also revolutionizing transportation, healthcare, and everyday life. From ambitious endeavors like space colonization to the integration of aerospace technologies with other industries, the United States is poised to lead the way in pushing the boundaries of human ingenuity.
Advancements in Space Exploration and Colonization
The exploration and colonization of space are key drivers of future advancements in American aerospace technologies.
- The development of reusable spacecraft, such as SpaceX’s Starship, will enable more frequent and cost-effective missions to the Moon and Mars, facilitating scientific research and the establishment of permanent outposts.
- Advanced life support systems, including closed-loop ecological systems, will be crucial for sustaining human life in the harsh environments of space, paving the way for long-duration missions and the creation of self-sustaining habitats.
- The extraction and utilization of resources found on celestial bodies, such as water ice on the Moon and Mars, will provide crucial materials and fuel for space exploration and colonization efforts.
Development of New Propulsion Systems and Space Vehicles
The development of new propulsion systems and space vehicles is essential for expanding human reach beyond Earth’s orbit.
- Advanced propulsion systems, such as ion propulsion, nuclear fusion propulsion, and antimatter propulsion, will enable faster and more efficient travel to distant destinations, enabling exploration of the outer solar system and beyond.
- The development of hypersonic aircraft, capable of traveling at speeds exceeding Mach 5, will revolutionize air travel, reducing travel times and enabling new possibilities for high-speed transportation.
- The development of reusable launch vehicles, such as SpaceX’s Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy, will make space travel more accessible and affordable, paving the way for commercial space exploration and tourism.
Integration of Aerospace Technologies with Other Industries
The integration of aerospace technologies with other industries will lead to significant advancements in various sectors.
- The application of aerospace materials and manufacturing techniques in healthcare will lead to the development of lighter, stronger, and more durable medical devices and implants, improving patient outcomes.
- The development of advanced navigation and communication systems, originally developed for space exploration, will enhance transportation safety and efficiency, leading to the creation of autonomous vehicles and smart traffic management systems.
- The use of aerospace data analysis and modeling techniques in other fields, such as finance and agriculture, will provide valuable insights and predictions, enabling better decision-making and optimizing resource allocation.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Aerospace Design and Operations
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a transformative role in aerospace design, operations, and maintenance.
- AI-powered design tools will accelerate the development of new aircraft and spacecraft, optimizing performance and reducing costs.
- ML algorithms will enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of aerospace systems, enhancing safety and reducing downtime.
- AI-powered mission control systems will optimize spacecraft operations, enabling more efficient and effective space exploration and resource utilization.
Futuristic Illustration
The illustration depicts a bustling space city orbiting Earth, a testament to the advancements in American aerospace technologies.
- A network of sleek, futuristic spacecraft, powered by advanced propulsion systems, effortlessly traverse the cosmos, connecting Earth to the city and other celestial destinations.
- The city itself is a marvel of engineering, featuring towering structures made of lightweight, durable materials developed for space exploration. These structures house residential areas, research facilities, and commercial spaces, creating a vibrant and thriving community.
- Beneath the city, vast solar arrays capture energy from the sun, providing clean and sustainable power for the entire metropolis. Advanced energy storage systems ensure a constant supply of power, even during periods of darkness.
- The city’s inhabitants move freely in zero-gravity environments, utilizing advanced personal transportation devices and innovative mobility solutions. These technologies, derived from aerospace innovations, enhance accessibility and create a seamless flow of movement throughout the city.
- The illustration highlights the seamless integration of aerospace technologies with everyday life, showcasing the transformative impact on society. From advanced communication systems that enable instant communication across vast distances to personalized healthcare services delivered through space-based platforms, the city embodies a future where technology enhances human well-being and expands the boundaries of human potential.
Final Summary
American aerospace technologies continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, with exciting advancements in space exploration, hypersonic flight, and the integration of aerospace innovations into other industries. The future holds immense promise, with the potential for revolutionary advancements in transportation, communication, and even healthcare. As we look towards the stars, American aerospace technologies stand poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of humanity and our place in the universe.
American aerospace technologies have always pushed the boundaries of innovation, from the first moon landing to the development of reusable rockets. This drive for progress has also led to advancements in other fields, like enviro technologies , where NASA’s research on lightweight materials and energy-efficient systems has found applications in sustainable solutions for our planet.
As we continue to explore the cosmos, we can expect even more breakthroughs that benefit both space exploration and our home on Earth.