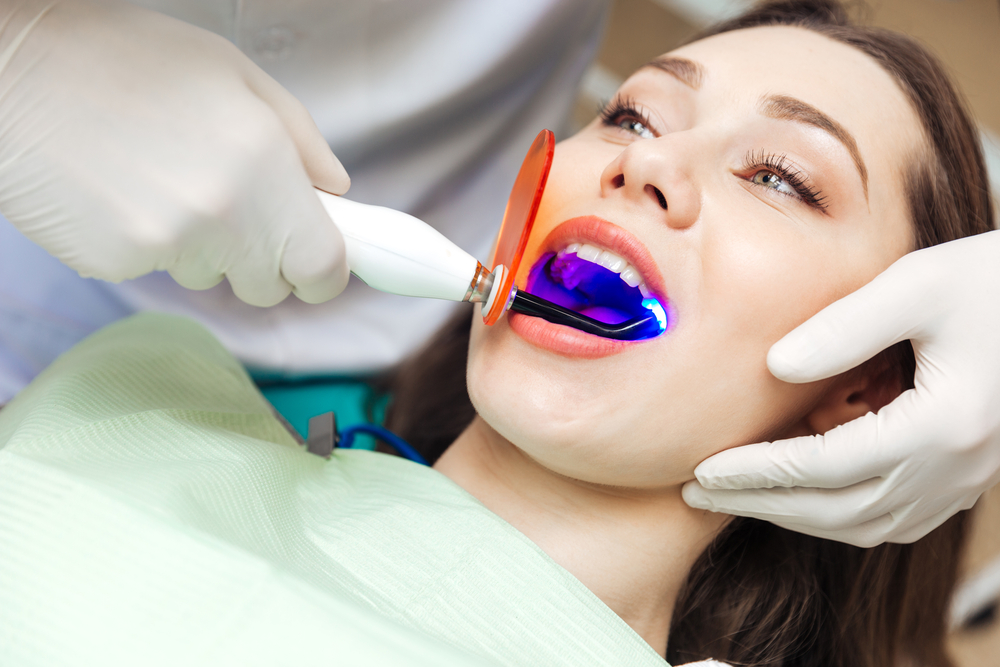
Advanced Technology and Laser Dentistry: A Modern Approach to Oral Care
Advanced technology and laser dentistry have revolutionized the field of oral care, offering patients a range of innovative treatments that are minimally invasive, highly effective, and often more comfortable than […]
Advanced technology and laser dentistry have revolutionized the field of oral care, offering patients a range of innovative treatments that are minimally invasive, highly effective, and often more comfortable than traditional methods. Laser dentistry utilizes concentrated beams of light to perform a variety of dental procedures, from cavity preparation to gum surgery, with precision and accuracy that surpasses traditional techniques. This advanced technology has significantly improved patient outcomes and redefined the dental experience.
The use of lasers in dentistry has a rich history, dating back to the early 1990s. Since then, laser technology has undergone significant advancements, leading to the development of various laser types with specific wavelengths and applications. This progress has paved the way for a wide array of dental procedures to be performed using lasers, offering patients a less invasive and more comfortable experience.
Introduction to Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry is a revolutionary approach to dental care that utilizes focused beams of light to perform various dental procedures. This advanced technology has significantly impacted the field of dentistry, offering a wide range of benefits over traditional methods.
Historical Overview of Laser Dentistry
The evolution of laser dentistry has been a journey of innovation and refinement, starting with the initial exploration of lasers in the 1960s. The first laser used in dentistry was the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser, which found applications in soft tissue procedures. Over the years, advancements in laser technology have led to the development of various lasers specifically designed for dental applications, including the erbium:YAG laser, diode laser, and Nd:YAG laser.
Advantages of Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry offers numerous advantages over traditional methods, making it a preferred choice for many patients.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Lasers allow for precise and controlled tissue removal, reducing the need for extensive cutting and resulting in less pain and discomfort.
- Reduced Bleeding: The laser’s focused beam cauterizes tissue as it cuts, minimizing bleeding during procedures. This is particularly beneficial for patients with clotting disorders or those who are apprehensive about bleeding.
- Faster Healing: The precise nature of laser surgery and the reduced trauma to surrounding tissues promote faster healing and recovery times.
- Enhanced Comfort: Laser dentistry often eliminates the need for anesthesia, reducing the risk of complications and providing a more comfortable experience for patients.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: The sterile nature of laser procedures reduces the risk of infection, making it a safer option for patients with compromised immune systems.
Types of Lasers Used in Dentistry
Lasers have become increasingly popular in dentistry due to their precision, minimally invasive nature, and ability to target specific tissues. Different types of lasers are used for various dental procedures, each with unique properties and applications. This section explores the different types of lasers commonly used in dentistry, their working principles, and specific applications.
Types of Lasers Used in Dentistry
A table outlining the types of lasers used in dentistry, their wavelengths, applications, and advantages is provided below:
| Laser Type | Wavelength (nm) | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Laser | 10,600 | Soft tissue procedures (e.g., gingivectomy, frenectomy, soft tissue ablation) | Precise tissue ablation, minimal bleeding, good hemostasis |
| Erbium:Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser | 2,940 | Hard tissue procedures (e.g., cavity preparation, enamel ablation, root canal treatment) | High absorption by water, minimal heat damage to surrounding tissues, precise ablation |
| Diode Laser | 810-1064 | Soft tissue procedures (e.g., gingivectomy, frenectomy, teeth whitening) | Less expensive than other lasers, portable, good for soft tissue procedures |
| Nd:YAG Laser | 1,064 | Soft tissue procedures (e.g., gingivectomy, frenectomy, teeth whitening), hard tissue procedures (e.g., bone surgery, implant placement) | Versatile, can be used for both soft and hard tissues, good for deep tissue penetration |
Working Principles of Dental Lasers
Dental lasers emit light energy that interacts with the target tissue based on the wavelength of the laser. The interaction can result in various effects, including:
* Photothermal Effect: The laser energy is absorbed by the tissue, causing it to heat up and evaporate. This is the primary mechanism for soft tissue ablation and coagulation.
* Photochemical Effect: The laser energy breaks down the molecular bonds in the tissue, leading to tissue breakdown. This is particularly relevant for hard tissue procedures, where the laser energy can be used to ablate enamel and dentin.
* Photoacoustic Effect: The laser energy creates a shock wave that disrupts the tissue. This effect is used for specific procedures, such as bone cutting.
Unique Properties of Each Laser Type
Each laser type has unique properties based on its wavelength and how it interacts with tissue. For example:
* CO2 Laser: This laser has a high absorption rate by water, making it ideal for soft tissue procedures. The high energy output allows for precise ablation and minimal bleeding.
* Er:YAG Laser: This laser has a shorter wavelength that is highly absorbed by water, resulting in precise ablation of hard tissues with minimal heat damage to surrounding tissues.
* Diode Laser: This laser is less expensive than other lasers and is portable, making it suitable for various soft tissue procedures.
* Nd:YAG Laser: This laser has a longer wavelength that can penetrate deeper into tissues, making it suitable for both soft and hard tissue procedures.
Applications of Lasers in Dental Procedures
Lasers are used in a wide range of dental procedures, offering advantages over traditional methods. Some common applications include:
* Soft Tissue Procedures:
* Gingivectomy: Removing excess gum tissue to improve gum health and aesthetics.
* Frenectomy: Removing a frenulum (a small fold of tissue) that restricts tongue movement or lip mobility.
* Soft Tissue Ablation: Removing soft tissue lesions or growths.
* Biopsy: Obtaining a sample of tissue for diagnosis.
* Hard Tissue Procedures:
* Cavity Preparation: Removing decayed tooth structure to prepare for a filling.
* Enamel Ablation: Removing enamel to prepare for bonding or other procedures.
* Root Canal Treatment: Cleaning and shaping the root canal system.
* Other Applications:
* Teeth Whitening: Using lasers to activate the whitening agent and accelerate the process.
* Implant Placement: Using lasers to prepare the bone for implant placement.
* Bone Surgery: Using lasers to cut and shape bone.
Applications of Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry has revolutionized dental care, offering a wide range of applications that enhance treatment effectiveness, minimize discomfort, and improve patient outcomes. Lasers are used in various procedures, providing precise and minimally invasive solutions.
Cavity Preparation
Lasers are used to remove decayed tooth structure during cavity preparation. This method offers several advantages over traditional drills, including:
- Reduced pain and discomfort: Laser energy seals nerve endings as it removes tooth structure, minimizing pain and the need for anesthesia.
- Improved precision: Lasers can precisely target decayed areas, preserving healthy tooth structure and minimizing the need for extensive drilling.
- Reduced risk of infection: Lasers sterilize the treatment area as they remove decay, minimizing the risk of infection.
Laser cavity preparation is particularly beneficial for patients with sensitive teeth, as it reduces discomfort and promotes faster healing.
Gum Surgery
Lasers are used in various gum surgeries, including:
- Gingivectomy: Laser energy precisely removes excess gum tissue, improving aesthetics and reducing the risk of gum disease.
- Gingivoplasty: Lasers reshape gum tissue, correcting gum contour irregularities and improving smile aesthetics.
- Frenectomy: Lasers are used to remove frenulums (tissue connecting the lip or tongue to the gum), improving speech and facilitating orthodontic treatment.
Laser gum surgery offers advantages such as:
- Reduced bleeding: Lasers cauterize blood vessels as they cut, minimizing bleeding and promoting faster healing.
- Minimally invasive: Lasers are less invasive than traditional surgical instruments, resulting in less pain and discomfort.
- Improved healing: Laser energy stimulates tissue regeneration, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of complications.
Tooth Whitening
Laser tooth whitening utilizes a low-level laser to accelerate the bleaching process. The laser energy activates the whitening gel, enhancing its effectiveness and producing brighter results.
- Faster whitening: Laser whitening is significantly faster than traditional methods, typically requiring one session for noticeable results.
- Long-lasting results: The laser activation process enhances the whitening gel’s penetration, resulting in longer-lasting results.
- Reduced sensitivity: Laser whitening is often less sensitive than traditional methods, minimizing discomfort during and after treatment.
Root Canal Treatment
Lasers can be used in root canal treatment to:
- Sterilize the root canal: Laser energy effectively kills bacteria within the root canal, reducing the risk of infection.
- Remove infected tissue: Lasers can precisely remove infected pulp tissue, promoting faster healing and reducing the need for extensive cleaning.
- Seal the root canal: Lasers can be used to seal the root canal after cleaning and filling, reducing the risk of reinfection.
Laser root canal treatment offers advantages such as:
- Reduced pain and discomfort: Lasers minimize pain and discomfort during treatment, promoting a more comfortable experience.
- Improved healing: Laser energy stimulates tissue regeneration, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of complications.
- Enhanced sterilization: Lasers effectively sterilize the root canal, minimizing the risk of infection and ensuring a successful outcome.
Biopsy
Lasers are used in dental biopsies to:
- Precisely remove tissue: Lasers allow for precise tissue removal, minimizing damage to surrounding structures.
- Minimize bleeding: Lasers cauterize blood vessels as they cut, minimizing bleeding and promoting faster healing.
- Sterilize the biopsy site: Laser energy sterilizes the biopsy site, reducing the risk of infection.
Laser biopsies are often less invasive and more comfortable than traditional methods, resulting in faster healing and reduced discomfort.
Benefits of Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry offers numerous advantages over traditional dental procedures, resulting in a more comfortable and efficient experience for patients. This innovative approach utilizes highly focused beams of light to perform various dental procedures, minimizing pain and discomfort while promoting faster healing.
Reduced Pain and Discomfort
Laser dentistry significantly reduces pain and discomfort associated with dental procedures. The precise nature of the laser beam allows for targeted treatment, minimizing tissue damage and reducing the need for anesthesia. The laser’s heat also seals nerve endings, reducing post-procedure sensitivity.
Faster Healing Time
Laser dentistry promotes faster healing due to its ability to sterilize the treatment area and stimulate tissue regeneration. The precise nature of the laser beam minimizes tissue trauma, allowing for quicker recovery. Studies have shown that laser-assisted procedures often result in shorter healing times compared to traditional methods.
Minimal Bleeding and Swelling
The laser’s ability to seal blood vessels during procedures minimizes bleeding and swelling. This is particularly beneficial for procedures involving gum tissue, as it reduces discomfort and promotes a faster recovery.
Improved Precision and Accuracy
Laser dentistry offers exceptional precision and accuracy. The laser beam’s ability to target specific areas allows for more controlled and precise treatment, minimizing the risk of damaging surrounding tissues. This enhanced precision contributes to more predictable outcomes and improved aesthetics.
Less Invasive Procedures
Laser dentistry often requires less invasive procedures compared to traditional methods. The laser’s ability to cut and shape tissue with minimal trauma allows for smaller incisions and less tissue removal. This translates to a more comfortable experience and a faster recovery time.
Safety and Precautions in Laser Dentistry: Advanced Technology And Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry, while offering numerous advantages, also carries certain potential risks and complications. Understanding these risks and adhering to strict safety protocols is crucial for both the dentist and the patient to ensure a safe and effective treatment experience.
Potential Risks and Complications
Potential risks and complications associated with laser dentistry are relatively rare when performed by a qualified and experienced dentist. However, it is essential to be aware of these possibilities.
- Tissue damage: The laser’s concentrated energy can potentially cause damage to surrounding tissues if not used carefully. This could result in burns, scarring, or pain.
- Eye injury: The laser beam can cause serious eye damage if not properly protected. This risk is particularly high for both the dentist and the patient during the procedure.
- Infection: Like any dental procedure, laser dentistry can carry a risk of infection, particularly if proper sterilization and hygiene practices are not followed.
- Pigmentation changes: Some lasers can cause changes in skin pigmentation, leading to discoloration or hyperpigmentation in certain individuals.
- Pain and discomfort: While laser dentistry is generally less painful than traditional methods, some patients may experience pain or discomfort during or after the procedure.
Safety Protocols and Precautions
To minimize these risks, dentists adhere to strict safety protocols during laser procedures.
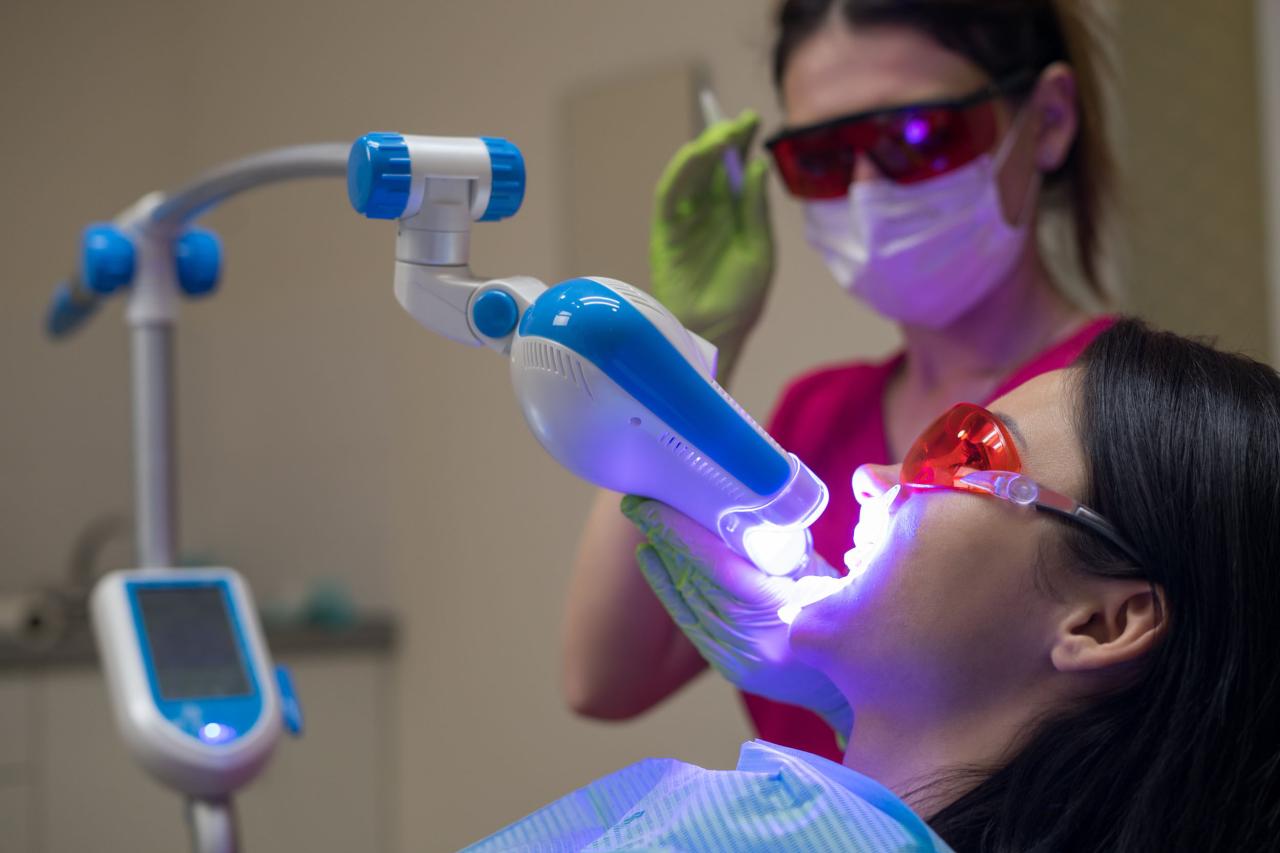
- Protective eyewear: Both the dentist and the patient must wear specialized protective eyewear that filters out the laser beam’s harmful wavelengths.
- Proper laser settings: The dentist must select the appropriate laser settings, including wavelength, power, and duration, based on the specific procedure and patient’s needs.
- Cooling techniques: Cooling techniques, such as water spray or air cooling, are often used to minimize tissue damage and discomfort.
- Sterilization: All instruments and equipment used in laser dentistry must be thoroughly sterilized to prevent infection.
- Patient education: The dentist should thoroughly explain the procedure, potential risks, and safety precautions to the patient before the treatment.
Role of the Dentist and Patient
Both the dentist and the patient play crucial roles in ensuring a safe and effective laser dentistry experience.
- Dentist’s responsibility: The dentist is responsible for:
- Selecting the appropriate laser for the procedure.
- Setting the laser parameters correctly.
- Using proper safety protocols and techniques.
- Monitoring the patient’s response throughout the procedure.
- Patient’s responsibility: The patient is responsible for:
- Providing accurate medical history to the dentist.
- Following the dentist’s instructions before, during, and after the procedure.
- Wearing protective eyewear as instructed.
- Reporting any unusual symptoms or concerns to the dentist.
Future of Laser Dentistry
The field of laser dentistry is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research and development leading to advancements in laser technology and its applications. This progress promises a future where laser dentistry plays an even more significant role in dental care, enhancing treatment outcomes and improving patient experiences.
Emerging Trends and Advancements, Advanced technology and laser dentistry
The future of laser dentistry is characterized by continuous advancements in laser technology, leading to more precise, efficient, and minimally invasive procedures. Some key trends shaping this future include:
- Enhanced Precision and Control: Laser technology is constantly being refined to provide greater precision and control during procedures. This includes advancements in laser beam delivery systems, allowing for more targeted and accurate application of laser energy. For example, the development of lasers with smaller wavelengths and higher frequencies enables dentists to perform procedures with greater accuracy, minimizing collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Laser dentistry is already known for its minimally invasive approach, but future advancements will further minimize tissue trauma and promote faster healing. This includes the development of lasers that can cut, coagulate, and sterilize tissues simultaneously, reducing the need for multiple instruments and steps.
- Integration with Digital Dentistry: Laser dentistry is increasingly being integrated with digital dentistry technologies, such as 3D imaging and computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM). This integration allows for more precise treatment planning and execution, as well as personalized solutions tailored to individual patient needs.
Potential Applications of Lasers in Future Dental Procedures
The potential applications of lasers in future dental procedures are vast and exciting. Lasers are expected to play a crucial role in a wide range of procedures, including:
- Improved Tooth Preparation: Lasers are expected to revolutionize tooth preparation for fillings, crowns, and other restorations. They can remove tooth structure with greater precision and control, minimizing the need for anesthesia and reducing post-operative sensitivity.
- Enhanced Periodontal Treatment: Lasers are already used in periodontal treatment, but future advancements will allow for more effective management of gum disease. Lasers can be used to remove infected tissue, stimulate tissue regeneration, and promote healing, leading to better outcomes for patients with periodontal problems.
- Advanced Implant Procedures: Lasers are expected to play a crucial role in implant dentistry, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of implant placement and bone grafting. Laser-assisted implant surgery can minimize trauma, reduce bleeding, and promote faster healing, leading to a more comfortable and successful implant experience.
- Oral Cancer Detection and Treatment: Laser technology is being explored for early detection and treatment of oral cancer. Lasers can be used to identify precancerous lesions and remove them with minimal damage to surrounding tissues, improving the chances of early intervention and successful treatment.
Impact of Laser Dentistry on the Dental Profession and Patient Care
The increasing adoption of laser dentistry is transforming the dental profession and improving patient care. Here’s how:
- Enhanced Skills and Training: The use of lasers in dentistry requires specialized training and skills. Dentists who incorporate lasers into their practice need to undergo rigorous training to ensure safe and effective use. This leads to a more skilled and knowledgeable dental workforce.
- Improved Patient Experience: Laser dentistry offers numerous benefits for patients, including reduced pain and discomfort, faster healing times, and improved cosmetic outcomes. This leads to a more positive and satisfying dental experience for patients.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Laser technology can streamline dental procedures, making them more efficient and productive. This allows dentists to treat more patients in a given time frame, improving access to dental care.
- Expansion of Treatment Options: Laser dentistry expands the range of treatment options available to dentists, allowing them to address a wider range of dental conditions with greater precision and effectiveness.
Closing Notes

The integration of advanced technology and laser dentistry into modern dental practice has ushered in a new era of oral care. This transformative approach has significantly enhanced patient comfort, minimized recovery time, and improved the overall dental experience. As laser technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications in the future, further revolutionizing the field of dentistry and providing patients with the most advanced and effective oral care possible.
Advanced technology in dentistry has brought us incredible innovations like laser dentistry, offering precise and minimally invasive treatments. This focus on precision extends beyond the dental chair, as we see similar advancements in other fields like directory services, where platforms like green pages technology are revolutionizing the way we find businesses and information.
These innovations, both in dentistry and beyond, highlight the ongoing evolution of technology to improve our lives in countless ways.