Accounting Technology Technician & Bookkeeping: A Modern Guide
Accounting technology technician and bookkeeping are intertwined fields, playing a crucial role in the modern business landscape. Accounting technology technicians utilize specialized software and tools to manage financial data, while […]

Accounting technology technician and bookkeeping are intertwined fields, playing a crucial role in the modern business landscape. Accounting technology technicians utilize specialized software and tools to manage financial data, while bookkeepers ensure accurate record-keeping and financial reporting. This dynamic duo ensures the smooth operation of any organization, from small startups to large corporations.
This guide delves into the intricacies of both roles, exploring their responsibilities, essential skills, and the impact of technology on their daily tasks. We’ll discuss the accounting cycle, analyze popular software solutions, and examine the future of these professions in the age of artificial intelligence and blockchain.
The Role of Accounting Technology Technicians: Accounting Technology Technician And Bookkeeping

Accounting technology technicians play a crucial role in the modern business world, ensuring the smooth operation of accounting systems and the accuracy of financial data. They bridge the gap between accounting principles and technology, enabling businesses to manage their finances effectively.
Primary Responsibilities
Accounting technology technicians are responsible for a wide range of tasks related to the implementation, maintenance, and support of accounting software and systems. Their responsibilities include:
- Installing, configuring, and customizing accounting software for new users.
- Troubleshooting software issues and providing technical support to users.
- Performing data entry and maintaining accurate financial records.
- Generating reports and analyzing financial data to identify trends and patterns.
- Developing and implementing procedures to ensure data security and integrity.
- Staying up-to-date on the latest accounting software and technology advancements.
Key Skills and Knowledge
To excel in this role, accounting technology technicians need a combination of technical and accounting skills.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in using various accounting software packages, including QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage, is essential. Strong computer skills, including data entry, spreadsheet software, and database management, are also vital.
- Accounting Knowledge: A solid understanding of accounting principles, financial reporting standards, and tax regulations is crucial for accurate data processing and financial analysis.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to diagnose and resolve technical issues efficiently is critical for maintaining smooth system operations.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication skills are essential for interacting with users, explaining technical concepts, and providing clear and concise information.
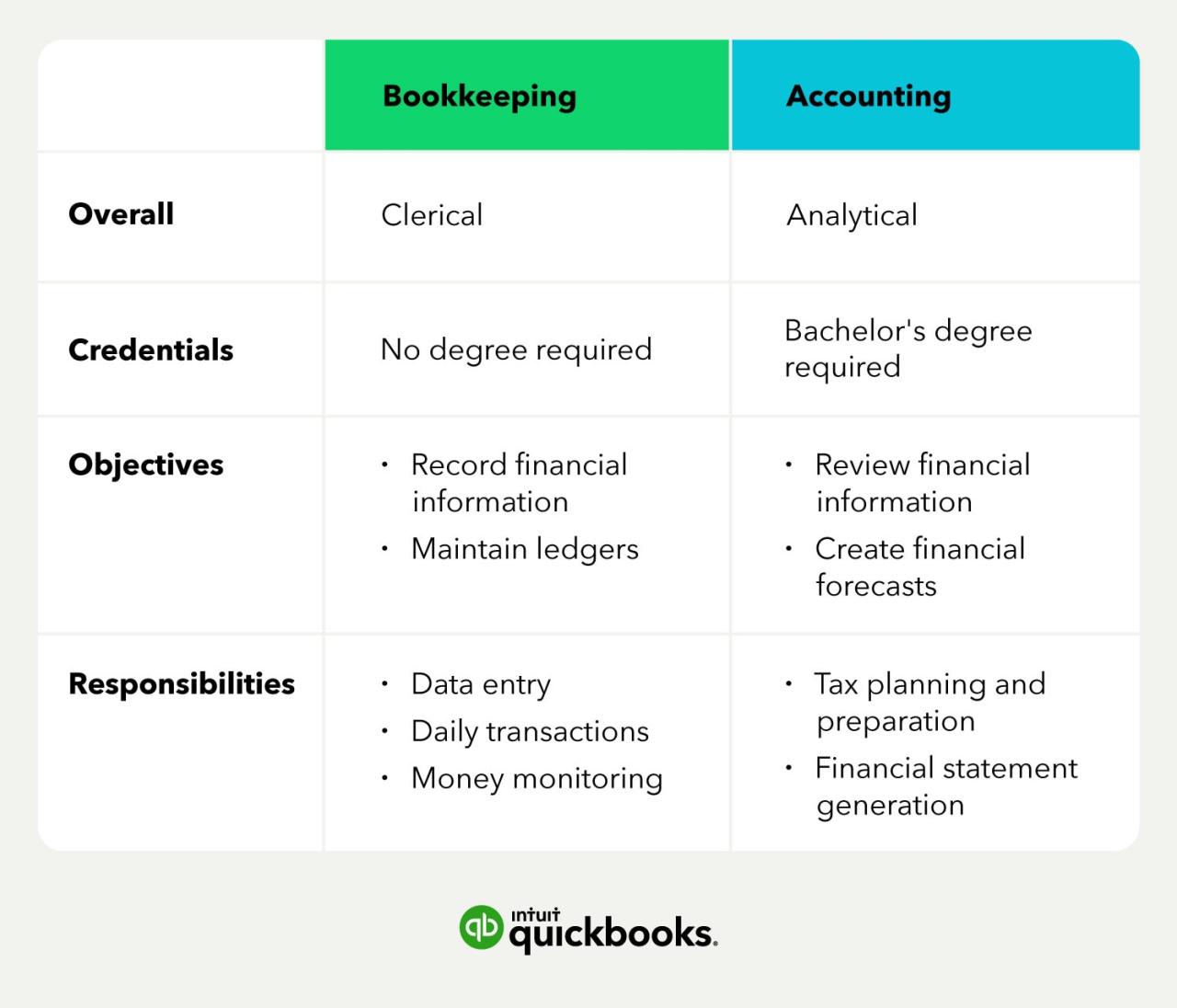
Comparison with Bookkeepers
While both accounting technology technicians and bookkeepers are involved in financial record-keeping, their roles differ significantly.
- Bookkeepers focus primarily on manual data entry, maintaining financial records, and preparing basic financial statements. They often work with paper-based systems and may use accounting software to a limited extent.
- Accounting technology technicians, on the other hand, are more technology-focused, responsible for implementing, maintaining, and supporting complex accounting software systems. They are also involved in data analysis and reporting, which requires a deeper understanding of accounting principles and financial reporting standards.
Software and Tools
Accounting technology technicians utilize a wide range of software and tools in their daily work. Some of the most commonly used software packages include:
- QuickBooks: A popular accounting software for small and medium-sized businesses, offering features such as invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting.
- Xero: A cloud-based accounting software known for its user-friendly interface and mobile accessibility, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Sage: A comprehensive accounting software suite offering a range of modules for accounting, payroll, and CRM, catering to larger businesses.
- Microsoft Excel: A versatile spreadsheet software widely used for data analysis, reporting, and financial modeling.
- Database Management Systems: Tools like Microsoft Access and MySQL are used to manage and analyze large datasets, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in financial reporting.
Bookkeeping Fundamentals
Bookkeeping is the process of recording and organizing financial transactions for a business. It is a fundamental aspect of accounting, providing a detailed record of a company’s financial activities. Effective bookkeeping ensures accurate financial reporting, facilitates informed decision-making, and helps businesses comply with tax regulations.
The Accounting Cycle
The accounting cycle is a systematic process that transforms raw financial data into meaningful financial statements. It involves a series of steps, each building upon the previous one, to ensure accurate and timely financial reporting.
- Transaction Analysis: The process begins with identifying and analyzing each financial transaction, determining its impact on the business’s accounts. This involves classifying transactions based on their nature and their impact on assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Journalizing: Transactions are recorded in a journal, which serves as a chronological record of all financial activities. Each journal entry includes the date of the transaction, the accounts affected, and the amounts involved.
- Posting: After journalizing, the information from the journal is transferred to the ledger, a collection of accounts that provides a detailed summary of each account’s balance. Posting ensures that all transactions are properly reflected in the appropriate accounts.
- Trial Balance: A trial balance is a list of all accounts and their balances at a specific point in time. It is used to ensure that the total debits equal the total credits, indicating that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) is balanced.
- Adjusting Entries: At the end of an accounting period, adjusting entries are made to ensure that revenues and expenses are recognized in the correct period. This includes adjusting for accruals, deferrals, and depreciation.
- Preparation of Financial Statements: The final step involves preparing the financial statements, including the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows. These statements summarize the financial performance and position of the business over a specific period.
Common Bookkeeping Tasks
Bookkeepers perform a variety of tasks to ensure accurate and up-to-date financial records. Some common tasks include:
- Recording Transactions: Bookkeepers meticulously record all financial transactions, including sales, purchases, payments, and receipts, in the appropriate journals. This involves using accounting software or spreadsheets to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Reconciling Bank Statements: Bookkeepers reconcile bank statements with the company’s records to ensure that all deposits, withdrawals, and other transactions are accounted for. This helps identify discrepancies and ensure that the bank balance matches the company’s records.
- Preparing Financial Reports: Bookkeepers prepare various financial reports, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports provide insights into the company’s financial performance and position, helping managers make informed decisions.
- Managing Accounts Payable and Receivable: Bookkeepers track accounts payable, which represents the company’s outstanding obligations to suppliers, and accounts receivable, which represents the money owed to the company by its customers. This involves issuing invoices, tracking payments, and managing overdue balances.
- Payroll Processing: Bookkeepers often handle payroll processing, calculating employee wages, withholding taxes, and preparing payroll reports. This involves ensuring compliance with tax regulations and ensuring that employees are paid accurately and on time.
Bookkeeping Workflow
The bookkeeping workflow can be represented by a flowchart:
Flowchart:
Step 1: Transaction Occurs
Step 2: Transaction Analysis and Documentation
Step 3: Journal Entry
Step 4: Posting to Ledger
Step 5: Trial Balance
Step 6: Adjusting Entries
Step 7: Preparation of Financial Statements
Accounting Technology in Practice
The integration of technology into accounting and bookkeeping has revolutionized the industry, transforming traditional practices into streamlined and efficient processes. Accounting technology plays a crucial role in automating tasks, improving accuracy, and enhancing efficiency, enabling businesses to make informed financial decisions.
Impact of Technology on Accounting and Bookkeeping, Accounting technology technician and bookkeeping
The advent of accounting software, cloud-based platforms, and other technological tools has significantly impacted the way accounting and bookkeeping are performed. Traditional manual methods, such as paper-based record keeping and spreadsheet calculations, have been largely replaced by automated systems that offer increased accuracy, speed, and accessibility.
Benefits of Using Accounting Software
Accounting software provides a wide range of benefits to businesses, including:
- Automation of Tasks: Accounting software automates repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice generation, and bank reconciliation, freeing up time for accountants to focus on more strategic activities.
- Improved Accuracy: By eliminating manual data entry and calculations, accounting software significantly reduces the risk of human error, leading to more accurate financial reporting.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Accounting software streamlines processes, making it easier to track financial transactions, generate reports, and analyze financial performance.
- Real-Time Insights: Accounting software provides real-time access to financial data, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
- Increased Security: Accounting software typically includes robust security features to protect sensitive financial data from unauthorized access.
Challenges of Using Accounting Software
While accounting software offers numerous benefits, there are also some challenges associated with its implementation and use:
- Initial Setup and Training: Setting up accounting software and training staff can be time-consuming and require technical expertise.
- Cost: Accounting software can be expensive, particularly for larger businesses with complex needs.
- Data Migration: Migrating data from existing systems to new accounting software can be challenging and require careful planning.
- Integration with Other Systems: Integrating accounting software with other business systems, such as CRM or inventory management, can be complex.
Examples of Accounting Technology Automation
Accounting technology can automate a wide range of tasks, including:
- Invoice Processing: Accounting software can automatically capture invoice data, process payments, and track outstanding invoices.
- Bank Reconciliation: Accounting software can automatically reconcile bank statements with accounting records, reducing the risk of errors and freeing up time for accountants.
- Financial Reporting: Accounting software can generate various financial reports, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, with just a few clicks.
- Tax Preparation: Some accounting software integrates with tax preparation software, simplifying the tax filing process.
Comparison of Accounting Software Solutions
| Software | Features | Pricing | Target User Base |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xero | Cloud-based accounting software with a wide range of features, including invoicing, bank reconciliation, and reporting. | Starts at $25 per month. | Small to medium-sized businesses. |
| QuickBooks Online | Another popular cloud-based accounting software offering similar features to Xero. | Starts at $25 per month. | Small to medium-sized businesses. |
| FreshBooks | Designed specifically for freelancers and small businesses, FreshBooks offers features such as invoicing, expense tracking, and time tracking. | Starts at $15 per month. | Freelancers and small businesses. |
| Zoho Books | A comprehensive accounting software solution that includes features for invoicing, expense tracking, inventory management, and reporting. | Starts at $19 per month. | Small to medium-sized businesses. |
The Future of Accounting Technology
The field of accounting technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations emerging all the time. These advancements are transforming the way businesses manage their finances, and they are also creating new opportunities for accounting technology technicians and bookkeepers. This section will explore some of the most exciting trends in accounting technology and discuss their potential impact on the future of the profession.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Accounting
AI is rapidly changing the accounting landscape. AI-powered tools can automate many tasks that were previously done manually, such as data entry, invoice processing, and financial reporting. These tools can also analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns and trends, providing insights that can help businesses make better decisions.
- AI-powered chatbots can provide customer service, answer questions, and resolve issues related to billing and payments.
- AI-driven fraud detection systems can analyze financial transactions and identify suspicious activity, helping to prevent fraud and protect businesses from financial losses.
- AI-based forecasting tools can analyze historical data and current market conditions to predict future financial performance, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions about investment and budgeting.
Blockchain Technology in Accounting
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that can transform the way businesses track and manage financial transactions. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent way. This makes it ideal for applications like:
- Auditing: Blockchain can streamline the auditing process by providing a secure and immutable record of transactions. This can help auditors to identify errors and fraud more quickly and efficiently.
- Supply chain management: Blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods and materials throughout the supply chain, improving transparency and accountability.
- Payment processing: Blockchain can facilitate faster and more secure payment processing, reducing the need for intermediaries and lowering transaction fees.
Innovative Accounting Technologies
Many innovative accounting technologies are already being used by businesses to streamline their operations and improve their financial performance. Here are some examples:
- Cloud accounting software: Cloud accounting software allows businesses to access their financial data from anywhere with an internet connection. This can help businesses to improve collaboration, streamline workflows, and reduce costs.
- Automated expense reporting: Automated expense reporting tools can capture and categorize receipts, making it easier for employees to track their expenses and for businesses to manage their expenses.
- Financial data visualization tools: These tools can help businesses to visualize their financial data in a way that is easy to understand, making it easier to identify trends and make informed decisions.
Timeline of Accounting Technology Evolution
| Year | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| 1970s | The first electronic spreadsheets were introduced, allowing for more efficient data analysis and calculation. |
| 1980s | Personal computers became more affordable and accessible, leading to the development of accounting software for small businesses. |
| 1990s | The internet emerged, paving the way for online accounting software and cloud-based solutions. |
| 2000s | The development of cloud computing and mobile devices led to increased accessibility and mobility for accounting software. |
| 2010s | The rise of big data and analytics, along with the emergence of AI and blockchain technologies, transformed the accounting industry. |
Last Recap

The synergy between accounting technology and bookkeeping is undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, these roles will become even more critical in ensuring financial transparency and efficiency. By understanding the fundamentals and embracing technological advancements, professionals in these fields can navigate the ever-changing landscape of accounting and contribute to the success of their organizations.
Accounting technology technicians and bookkeepers play a crucial role in managing financial records, ensuring accuracy and compliance. This often involves navigating complex systems and regulations, including understanding the intricacies of technology insurance company workers comp policies, which can be a significant factor in a company’s financial health.
By staying informed about these regulations and leveraging technology, accounting professionals can effectively manage risks and contribute to a company’s financial stability.





