Face Technologies: Shaping the Future
Face technologies are revolutionizing the way we interact with the world, from unlocking our smartphones to identifying criminals. These technologies, encompassing facial recognition, expression analysis, animation, and tracking, are rapidly […]

Face technologies are revolutionizing the way we interact with the world, from unlocking our smartphones to identifying criminals. These technologies, encompassing facial recognition, expression analysis, animation, and tracking, are rapidly advancing, driven by powerful algorithms and the increasing availability of data.
This exploration delves into the intricate workings of face technologies, examining their diverse applications across various industries. We’ll uncover the ethical considerations surrounding their use, explore the exciting possibilities they offer, and contemplate their potential impact on society.
Facial Recognition Technology: Face Technologies
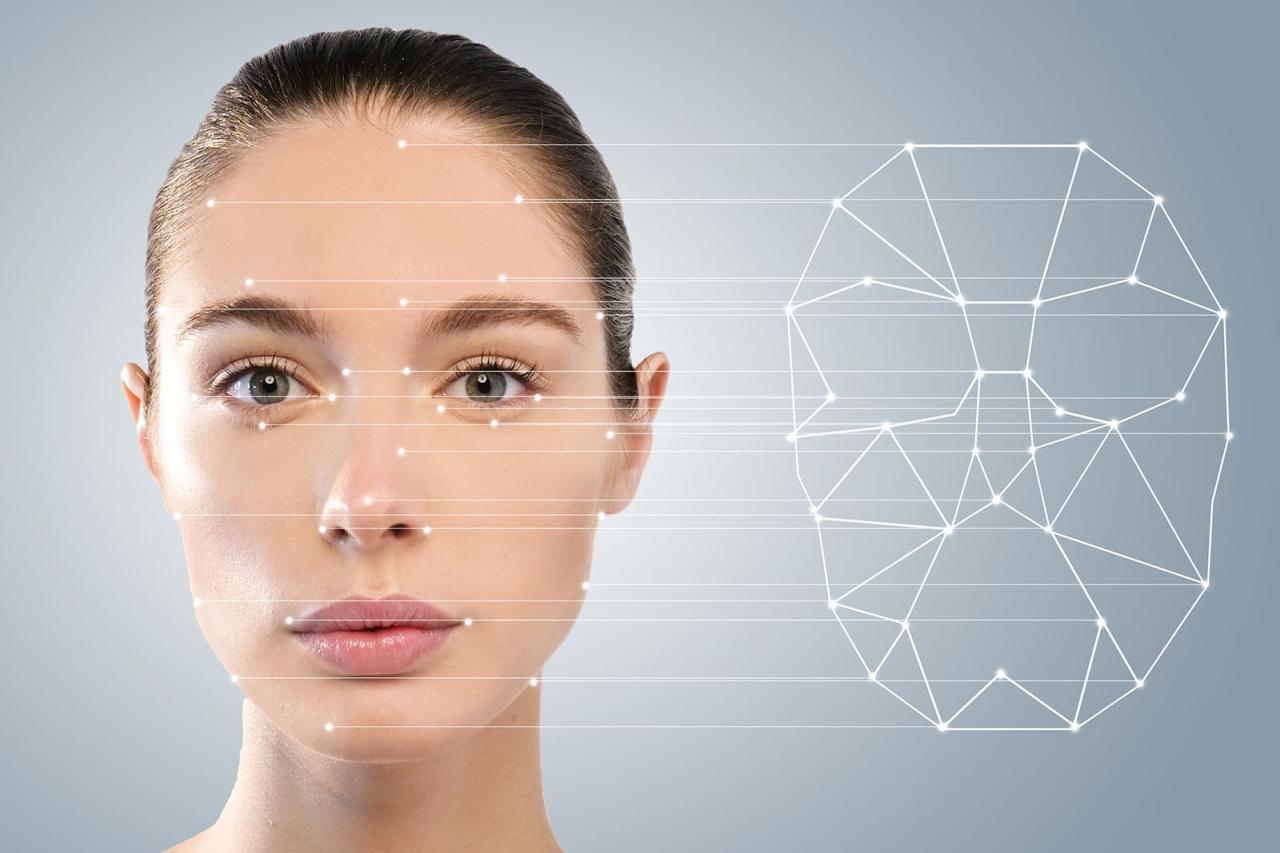
Facial recognition technology is a powerful tool that allows computers to identify and verify individuals based on their facial features. It has become increasingly prevalent in various sectors, from security and law enforcement to commercial applications. This technology leverages sophisticated algorithms to analyze facial patterns and compare them against a database of known faces.
Core Principles of Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology relies on the concept of biometrics, which involves using unique biological traits to identify individuals. In the case of facial recognition, the system captures a digital image of a person’s face and extracts key features, such as the distance between eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contour of the jawline. These features are then converted into a mathematical representation, known as a facial template. The template is then compared to a database of known faces, and if a match is found, the individual is identified.
Methods Employed for Facial Recognition
There are various methods employed for facial recognition, each with its own strengths and limitations:
- Feature-Based Methods: These methods rely on identifying and comparing specific facial features, such as the distance between eyes, the width of the nose, and the shape of the chin. These features are then used to create a unique representation of the face, which is then compared to a database of known faces.
- Template-Based Methods: These methods involve creating a template of the entire face, which is then compared to a database of known templates. The template is typically a mathematical representation of the face, which captures the overall structure and shape of the facial features.
- Deep Learning Approaches: These methods leverage artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns from large datasets of facial images. Deep learning models can identify and extract subtle features from facial images, making them highly accurate in recognizing individuals.
Applications of Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology has found applications in various sectors, including:
- Security: Facial recognition systems are deployed at airports, stadiums, and other high-security locations to identify individuals and prevent unauthorized access. They can also be used to monitor crowds and identify potential threats.
- Law Enforcement: Law enforcement agencies use facial recognition to identify suspects, locate missing persons, and track criminals. This technology can be used to analyze surveillance footage, compare faces against databases of known offenders, and assist in investigations.
- Commercial Applications: Facial recognition is increasingly being used in commercial settings, such as retail stores, banks, and hotels. It can be used for customer authentication, access control, and personalized marketing.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Facial Recognition
While facial recognition technology offers significant benefits, it also raises ethical concerns, including:
- Privacy: Facial recognition systems collect and store biometric data, which can be used to track individuals’ movements and activities. This raises concerns about privacy violations and the potential for misuse of this data.
- Bias: Facial recognition algorithms have been shown to be biased against certain demographics, such as people of color and women. This bias can lead to unfair and discriminatory outcomes, such as wrongful arrests or denied access to services.
- Misuse: Facial recognition technology can be misused for surveillance, harassment, and control. It can be used to track individuals without their consent, target specific groups, and suppress dissent.
Face Detection and Tracking

Face detection and tracking are essential components of many computer vision applications, enabling computers to understand and interact with the world in a more human-like way. These technologies work by identifying and locating faces in images or videos, and then tracking their movements over time.
Techniques for Face Detection and Tracking
Face detection and tracking rely on a combination of computer vision techniques, including:
- Feature-based methods: These methods identify distinctive features of faces, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth, and use them to locate and track faces. Common features include Haar-like features, SIFT, and HOG features.
- Appearance-based methods: These methods learn a model of the face based on its overall appearance and use this model to detect and track faces. Common approaches include template matching and neural networks.
- Deep learning methods: These methods utilize convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to learn complex patterns in images and videos, enabling highly accurate face detection and tracking.
Applications of Face Detection and Tracking
Face detection and tracking have a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Surveillance: Face detection and tracking are used in security systems to identify individuals and monitor their movements. They can be deployed in public spaces, such as airports, train stations, and shopping malls, to enhance security and prevent crime.
- Video conferencing: Face detection and tracking are essential for video conferencing applications, enabling features such as automatic framing, virtual backgrounds, and facial expressions analysis.
- Image editing: Face detection and tracking are used in image editing software to identify faces and apply filters, effects, or retouching techniques selectively.
- User experience enhancement: Face detection and tracking can enhance user experience in various applications. For example, they can be used to unlock smartphones, personalize user interfaces, and provide targeted advertising.
- Interactive applications: Face detection and tracking are used to enable interactive applications, such as games, virtual reality experiences, and augmented reality applications.
Examples of Face Detection and Tracking Applications
Here are some real-world examples of how face detection and tracking are used to enhance user experiences, improve security, and enable new interactive applications:
- Facial recognition for access control: Airports and other secure locations use facial recognition systems to verify the identity of passengers and employees. This technology helps to streamline security processes and prevent unauthorized access.
- Smart home automation: Smart home devices can use face detection to personalize user experiences. For example, a smart TV can automatically switch profiles based on the detected user or a smart lighting system can adjust brightness based on the user’s presence.
- Virtual reality experiences: Face tracking is used in VR headsets to capture facial expressions and translate them into virtual avatars, creating a more immersive and interactive experience.
- Augmented reality applications: Face detection and tracking are used in AR applications to overlay digital content onto real-world images and videos. For example, AR filters can be used to apply makeup, change hairstyles, or add virtual accessories to images.
Challenges and Limitations of Face Detection and Tracking
While face detection and tracking have advanced significantly, they still face challenges and limitations, including:
- Occlusion: When faces are partially hidden by objects or other people, it can be difficult for algorithms to detect and track them accurately.
- Lighting variations: Changes in lighting conditions can affect the performance of face detection and tracking algorithms. For example, strong backlighting can make it difficult to detect faces.
- Motion blur: When faces are moving quickly, they can become blurry, making it difficult for algorithms to detect and track them accurately.
- Privacy concerns: The use of face detection and tracking raises concerns about privacy, as it can be used to collect and analyze personal information without consent.
Future Trends in Face Technologies
Face technologies are rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in deep learning, 3D facial modeling, and biometrics. These innovations are transforming various industries and aspects of our lives, opening up new possibilities for personalized experiences and enhanced interactions.
Advancements in Deep Learning
Deep learning algorithms are playing a pivotal role in enhancing face technologies. These algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, enabling more accurate and sophisticated facial recognition, detection, and tracking. For example, deep learning models can learn to identify subtle variations in facial expressions, making them ideal for applications requiring nuanced emotion recognition.
3D Facial Modeling
3D facial modeling is revolutionizing how we interact with digital environments. By creating realistic digital representations of human faces, 3D modeling enables immersive experiences in augmented reality and virtual reality applications. This technology is also being used to develop personalized avatars for virtual worlds and online platforms.
Biometrics, Face technologies
Biometrics is another rapidly developing area of face technologies. Biometric systems use unique biological characteristics, such as facial features, to identify individuals. Advancements in biometrics are leading to more secure and reliable authentication systems for various applications, including access control, financial transactions, and law enforcement.
Applications in Personalized Healthcare
Face technologies are transforming the healthcare industry by enabling personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring. Facial analysis can be used to detect early signs of disease, monitor patient progress, and personalize treatment plans. For example, facial recognition software can analyze subtle changes in facial expressions to identify potential health issues.
Applications in Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world. Face technologies are playing a key role in enhancing AR experiences by enabling realistic facial tracking and animation. This allows for more immersive and interactive AR applications, such as virtual try-on tools for e-commerce platforms and personalized AR filters for social media.
Applications in Human-Robot Interaction
Face technologies are crucial for developing more natural and intuitive interactions between humans and robots. By recognizing facial expressions and gestures, robots can better understand human emotions and intentions. This is paving the way for more sophisticated and engaging human-robot interactions in various settings, including healthcare, education, and customer service.
Vision for the Future of Face Technologies
The future of face technologies is bright, with the potential to further revolutionize our lives. We can expect to see more accurate and efficient facial recognition systems, personalized experiences in AR and VR, and more natural interactions with robots. These advancements will have a significant impact on various industries, improving efficiency, security, and our overall quality of life.
Potential Applications in Different Industries
| Industry | Face Technology | Potential Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Facial recognition, 3D facial modeling, biometrics | Disease detection, patient monitoring, personalized treatment |
| Retail | Facial recognition, 3D facial modeling | Personalized shopping experiences, customer analytics, fraud detection |
| Security | Facial recognition, biometrics | Access control, identity verification, surveillance |
| Entertainment | 3D facial modeling, augmented reality | Immersive gaming experiences, personalized entertainment, virtual try-on tools |
| Education | Facial recognition, 3D facial modeling, augmented reality | Personalized learning experiences, interactive educational tools, student engagement |
Closure
The future of face technologies is bright, promising a world where our interactions with technology are more intuitive, personalized, and seamless. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is crucial to engage in open discussions about their ethical implications, ensuring their development and deployment benefit all of humanity.
Face technologies are rapidly evolving, with applications ranging from security to entertainment. When it comes to automotive advancements, the Volkswagen Atlas SE with Technology trim offers a glimpse into the future of driving. To see how this trim compares to the SEL trim, and to explore the features that enhance your driving experience, check out vw atlas se with technology vs sel.
These technologies are paving the way for a more connected and intuitive driving experience, making the road ahead both safer and more enjoyable.