Assistive Technology Grant: Funding Accessibility
Assistive technology grants open doors to a world of possibilities for individuals with disabilities. These grants provide financial support for a wide range of devices and services, empowering people to […]

Assistive technology grants open doors to a world of possibilities for individuals with disabilities. These grants provide financial support for a wide range of devices and services, empowering people to overcome barriers and achieve their full potential. From specialized software to adaptive equipment, assistive technology plays a crucial role in promoting independence and inclusion.
This guide delves into the world of assistive technology grants, exploring the various funding sources, application processes, and the impact these grants have on the lives of individuals and communities. We’ll also discuss the importance of conducting needs assessments and the ongoing evaluation of assistive technology interventions.
Assistive Technology Grant Overview
Assistive technology grants are designed to help individuals with disabilities access and participate in all aspects of life. These grants provide financial support for acquiring assistive technology devices and services that can improve their independence, communication, mobility, and overall quality of life.
Assistive technology grants are designed to empower individuals with disabilities to lead fulfilling lives. These grants help individuals overcome barriers and achieve their full potential by providing access to essential tools and support.
Types of Assistive Technology Funded
Assistive technology grants can fund a wide range of devices and services. These include:
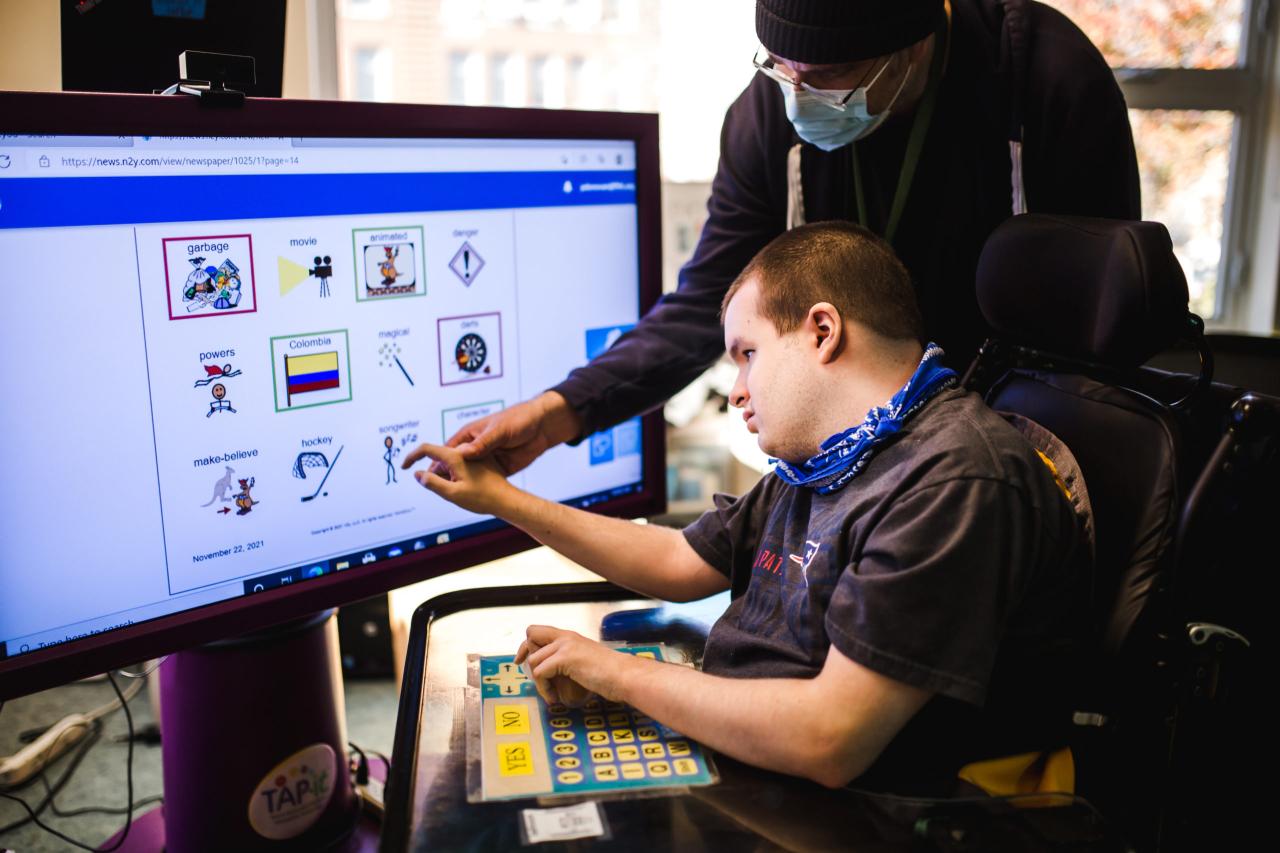
- Communication aids: Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, such as speech-generating devices, communication boards, and software programs. These tools help individuals with speech impairments communicate effectively.
- Mobility devices: Wheelchairs, scooters, walkers, and other adaptive equipment that enhance mobility and independence. These devices enable individuals with physical disabilities to navigate their environment with ease.
- Assistive listening devices: Hearing aids, cochlear implants, and assistive listening systems that improve hearing and communication for individuals with hearing loss.
- Adaptive computer equipment: Software programs, screen readers, voice recognition software, and specialized hardware that make computers accessible to individuals with disabilities.
- Sensory aids: Braille displays, tactile maps, and other sensory devices that enhance the senses and provide information to individuals with visual or auditory impairments.
Eligibility for Assistive Technology Grants
Assistive technology grants are typically available to:
- Individuals with disabilities: Individuals of all ages with a wide range of disabilities, including physical, cognitive, sensory, and developmental disabilities.
- Families of individuals with disabilities: Families may be eligible to receive grants to support their child’s assistive technology needs.
- Schools and educational institutions: Schools and educational institutions can apply for grants to purchase assistive technology for students with disabilities.
- Nonprofit organizations: Nonprofit organizations that provide assistive technology services or support to individuals with disabilities are eligible for grants.
Funding Sources for Assistive Technology Grants
There are various funding sources for assistive technology grants, including:
- Government agencies: Federal, state, and local government agencies often offer assistive technology grants through programs such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and the Rehabilitation Act.
- Private foundations: Many private foundations provide grants for assistive technology, supporting individuals and organizations working in the field.
- Corporate grants: Some corporations offer grants to support assistive technology initiatives, contributing to accessibility and inclusion.
Grant Funding Sources

Securing funding for assistive technology initiatives is crucial for improving accessibility and inclusion for individuals with disabilities. Fortunately, a range of government agencies and private organizations offer grants specifically designed to support the acquisition and implementation of assistive technology. Understanding the various funding sources, eligibility criteria, and application procedures is essential for maximizing the chances of securing funding for your project.
Government Agencies
Government agencies play a significant role in supporting assistive technology initiatives. The following agencies offer grant programs targeted at individuals, organizations, and communities:
- The National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR): This agency, part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, funds research, training, and demonstration projects related to assistive technology.
- Eligibility: NIDILRR grants are typically open to researchers, universities, rehabilitation centers, and non-profit organizations.
- Application Process: Grants are awarded through a competitive application process, requiring detailed proposals outlining the project’s goals, methodology, and budget.
- Funding Amounts: Funding amounts vary depending on the project’s scope and duration, with grants ranging from a few thousand dollars to several million dollars.
- Grant Cycles: NIDILRR grants have various funding cycles, with deadlines typically announced throughout the year.
- The Rehabilitation Services Administration (RSA): RSA, also part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, provides funding for state vocational rehabilitation agencies to support individuals with disabilities in obtaining employment.
- Eligibility: Individuals with disabilities who are eligible for vocational rehabilitation services can access assistive technology through RSA-funded programs.
- Application Process: Individuals typically apply through their state vocational rehabilitation agency, which determines eligibility and assists with obtaining assistive technology.
- Funding Amounts: Funding amounts vary based on individual needs and the type of assistive technology required.
- Grant Cycles: RSA funding is ongoing, with state agencies administering the programs and providing assistive technology as needed.
- The U.S. Department of Education: The Department of Education offers grants through various programs, including the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and the Special Education and Rehabilitative Services (SERS) program.
- Eligibility: IDEA grants are available to schools and educational institutions, while SERS grants support state and local agencies providing services to individuals with disabilities.
- Application Process: Applications for IDEA and SERS grants are submitted through the Department of Education’s online grant portal.
- Funding Amounts: Funding amounts vary depending on the program and project scope.
- Grant Cycles: Grant cycles vary by program, with deadlines announced throughout the year.
Private Organizations
Private organizations also contribute significantly to assistive technology initiatives. The following organizations offer grants to individuals, organizations, and communities:
- The Assistive Technology Industry Association (ATIA): The ATIA is a non-profit organization that promotes the advancement of assistive technology.
- Eligibility: ATIA grants are typically open to individuals, organizations, and businesses involved in assistive technology development, research, or implementation.
- Application Process: Applications for ATIA grants are submitted through their website, with specific guidelines provided for each grant program.
- Funding Amounts: Funding amounts vary depending on the grant program and project scope.
- Grant Cycles: ATIA grants have various funding cycles, with deadlines announced throughout the year.
- The American Foundation for the Blind (AFB): The AFB is a non-profit organization dedicated to empowering individuals with vision loss.
- Eligibility: AFB grants are available to individuals, organizations, and businesses working to improve the lives of individuals with vision loss.
- Application Process: Applications for AFB grants are submitted through their website, with specific guidelines provided for each grant program.
- Funding Amounts: Funding amounts vary depending on the grant program and project scope.
- Grant Cycles: AFB grants have various funding cycles, with deadlines announced throughout the year.
- The National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS): The NMSS is a non-profit organization that supports individuals with multiple sclerosis and their families.
- Eligibility: NMSS grants are available to individuals, organizations, and businesses working to improve the lives of individuals with multiple sclerosis.
- Application Process: Applications for NMSS grants are submitted through their website, with specific guidelines provided for each grant program.
- Funding Amounts: Funding amounts vary depending on the grant program and project scope.
- Grant Cycles: NMSS grants have various funding cycles, with deadlines announced throughout the year.
Assistive Technology Grant Application Process
Securing funding for assistive technology can significantly improve the lives of individuals with disabilities. Understanding the application process for assistive technology grants is crucial to increasing your chances of receiving funding.
Grant Application Process, Assistive technology grant
The application process for assistive technology grants typically involves several steps, each with specific requirements and expectations.
- Identify Eligible Grants: The first step is to identify grant opportunities that align with your needs and goals. Research different grant-making organizations and government agencies that offer assistive technology grants. Consider factors such as eligibility criteria, funding amounts, and application deadlines.
- Review Grant Guidelines: Once you’ve identified potential grants, carefully review the grant guidelines. These guidelines Artikel the specific requirements, application procedures, and evaluation criteria for each grant. Ensure you understand the application process and all necessary documentation.
- Develop a Strong Proposal: A compelling grant proposal is essential for securing funding. Your proposal should clearly articulate your project’s goals, objectives, and impact. It should also demonstrate a thorough understanding of the target population’s needs and how the assistive technology will address them.
- Gather Required Documentation: Grant applications typically require supporting documentation, such as letters of support, budget breakdowns, and project timelines. Prepare these materials in advance to ensure your application is complete and well-organized.
- Submit Application: Once your proposal and supporting documentation are finalized, submit your application according to the grant guidelines. Pay close attention to deadlines and submission instructions to avoid any delays or disqualifications.
Required Documentation and Supporting Materials
A well-prepared grant application should include comprehensive documentation that provides a detailed overview of your project and its potential impact.
- Project Narrative: This section should Artikel the project’s goals, objectives, and methodology. It should clearly explain how the assistive technology will be used and its expected impact on the target population.
- Budget Breakdown: A detailed budget breakdown is essential for demonstrating the financial feasibility of your project. Include all expenses, such as equipment costs, personnel salaries, and travel expenses.
- Project Timeline: A clear project timeline Artikels the key milestones and deliverables for your project. It helps grant reviewers understand the project’s scope and expected duration.
- Letters of Support: Letters of support from relevant stakeholders, such as community partners, professionals, or individuals who will benefit from the assistive technology, can strengthen your application.
- Evaluation Plan: Include a plan for evaluating the effectiveness of the assistive technology and its impact on the target population. This demonstrates your commitment to measuring and reporting on the project’s outcomes.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Compelling Grant Proposal
A well-written grant proposal is crucial for securing funding. Consider these tips and strategies to enhance your proposal’s persuasiveness:
- Focus on Impact: Emphasize the potential impact of your project on the target population. Use clear and compelling language to describe the benefits of the assistive technology and how it will improve lives.
- Demonstrate Need: Clearly articulate the need for assistive technology and the challenges faced by the target population. Provide evidence and data to support your claims.
- Highlight Sustainability: Demonstrate the sustainability of your project beyond the grant funding period. Explain how the assistive technology will be maintained and used long-term.
- Tailor Your Proposal: Customize your proposal to each grant opportunity. Carefully review the grant guidelines and address the specific criteria and priorities Artikeld by the funding organization.
- Proofread Carefully: Before submitting your proposal, proofread it thoroughly for any errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation. A polished and error-free proposal reflects professionalism and attention to detail.
Assistive Technology Needs Assessment
Conducting a needs assessment is a crucial step before applying for an assistive technology grant. This process helps you identify the specific needs of your target population and provides valuable information to strengthen your grant application.
Identifying Assistive Technology Needs
A comprehensive needs assessment should involve a thorough evaluation of the assistive technology requirements of individuals with disabilities. This assessment should be tailored to the specific needs of the target population and consider factors such as age, disability type, and individual preferences.
- Individual Interviews: One-on-one interviews with individuals with disabilities can provide valuable insights into their specific needs, challenges, and preferences. These interviews can help identify the assistive technologies that would be most beneficial for them.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups can be conducted with groups of individuals with disabilities to gather feedback on existing assistive technologies, identify gaps in services, and explore potential solutions.
- Surveys: Surveys can be used to gather information from a larger sample of individuals with disabilities. This can help identify common needs and trends in assistive technology usage.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing existing data, such as medical records, school records, or disability statistics, can provide valuable insights into the prevalence of disabilities and the need for assistive technology.
Developing a Needs Assessment Checklist
A needs assessment checklist can help ensure that all essential areas are covered during the assessment process. The checklist should be tailored to the specific needs of the target population and can be adapted based on the chosen assessment methods.
- Communication: This section should address needs related to communication, such as assistive listening devices, speech-to-text software, or communication aids for individuals with speech impairments.
- Mobility: This section should focus on needs related to mobility, such as wheelchairs, walkers, or adaptive equipment for individuals with physical disabilities.
- Vision: This section should address needs related to vision, such as screen readers, magnifiers, or braille displays for individuals with visual impairments.
- Hearing: This section should address needs related to hearing, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, or captioned phones for individuals with hearing impairments.
- Cognitive: This section should address needs related to cognitive abilities, such as memory aids, organizational tools, or adaptive software for individuals with cognitive disabilities.
Using Needs Assessment Results in Grant Applications
The results of a needs assessment can provide strong evidence to support your grant application. By demonstrating the specific needs of the target population and the potential impact of the proposed assistive technology, you can increase the likelihood of your grant application being approved.
- Quantify the Need: Use data from your needs assessment to quantify the need for assistive technology. For example, you could report the number of individuals in your target population who require specific types of assistive technology.
- Highlight the Impact: Explain how the proposed assistive technology will address the identified needs and improve the lives of individuals with disabilities. For example, you could describe how assistive technology will enable individuals to participate in education, employment, or community activities.
- Provide Testimonials: Include testimonials from individuals with disabilities who have benefited from assistive technology. These personal stories can add a human touch to your grant application and highlight the importance of your project.
Assistive Technology Implementation and Evaluation

The successful implementation of assistive technology requires a well-defined plan that encompasses the acquisition, integration, and evaluation of the technology. This section Artikels the essential steps involved in the implementation and evaluation process, ensuring that the assistive technology effectively meets the needs of the individuals it is intended to serve.
Implementation Process
The implementation process of assistive technology involves a series of steps designed to ensure a smooth transition and successful integration of the technology into the user’s environment.
- Needs Assessment: Before implementing assistive technology, it is crucial to conduct a thorough needs assessment to identify the specific needs of the individual. This assessment should consider the individual’s functional limitations, their goals, and the environment in which the technology will be used.
- Technology Selection: Based on the needs assessment, select assistive technology that is appropriate for the individual’s needs, abilities, and environment. Consider factors such as cost, availability, ease of use, and compatibility with existing technology.
- Training and Support: Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support is essential for successful assistive technology implementation. This includes training the individual on how to use the technology, as well as training staff who will be supporting the individual. Training should be tailored to the individual’s learning style and needs.
- Integration and Adaptation: Integrate the assistive technology into the individual’s daily routine and environment. This may involve making adjustments to the physical environment, such as modifying furniture or installing ramps, or adapting existing technology to work with the assistive device.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the assistive technology and make adjustments as needed. This may involve gathering feedback from the individual, observing their use of the technology, and assessing their progress towards their goals.
Training Strategies
Effective training is crucial for successful assistive technology implementation. It empowers individuals to use the technology independently and confidently, maximizing its benefits.
- Individualized Training: Training should be tailored to the individual’s learning style, needs, and preferences. Consider their prior experience with technology, their cognitive abilities, and their communication style.
- Hands-on Practice: Encourage hands-on practice and provide opportunities for the individual to use the assistive technology in real-life situations. This helps them develop proficiency and confidence.
- Multiple Training Methods: Utilize a variety of training methods, such as one-on-one instruction, group workshops, online tutorials, and demonstration videos. This caters to different learning styles and preferences.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support after the initial training. This can include answering questions, troubleshooting problems, and providing additional training as needed. Establish a clear system for accessing support, such as dedicated contact information or a support website.
- Peer Support: Encourage peer support by connecting individuals with others who use similar assistive technology. This fosters a sense of community and provides valuable insights and tips from experienced users.
Evaluation Methods
Evaluating the effectiveness of assistive technology interventions is essential for ensuring that the technology is meeting its intended goals and making a positive impact on the individual’s life.
- Functional Outcomes: Assess the impact of the assistive technology on the individual’s functional abilities, such as their ability to communicate, perform daily living activities, or participate in work or school.
- Quality of Life: Evaluate the impact of the assistive technology on the individual’s overall quality of life, including their well-being, independence, and social participation.
- User Satisfaction: Gather feedback from the individual about their satisfaction with the assistive technology, including its ease of use, effectiveness, and overall impact on their life.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the assistive technology by considering its cost compared to its benefits and the potential savings it may generate, such as reduced healthcare costs or increased productivity.
- Data Collection Methods: Use a variety of data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, and performance assessments, to gather comprehensive data on the effectiveness of the assistive technology.
Resources and Support for Assistive Technology: Assistive Technology Grant
Navigating the world of assistive technology can be a challenging task, but numerous resources and support systems are available to help individuals and organizations access and utilize these technologies effectively. This section will explore some of the key resources and support systems that can provide guidance, training, and advocacy in the realm of assistive technology.
Assistive Technology Organizations and Resources
A plethora of organizations and resources exist to support individuals and organizations in their quest for assistive technology. These organizations provide a wide range of services, including information, training, funding opportunities, and advocacy. Here are some examples of such organizations:
- The Assistive Technology Industry Association (ATIA): The ATIA is a leading organization that promotes the advancement and accessibility of assistive technology. They offer resources, training programs, and networking opportunities for professionals in the field.
- The National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR): This federal agency funds research and development of assistive technology and provides resources and information to individuals with disabilities.
- The American Occupational Therapy Association (AOTA): AOTA is a professional organization for occupational therapists, who play a vital role in the assessment, prescription, and training of assistive technology. They provide resources and support for occupational therapists working in the field of assistive technology.
- The National Center on Disability and Access to Education (NCDAE): The NCDAE provides information and resources on assistive technology for students with disabilities, including training programs for educators and families.
Assistive Technology Training Programs and Certification
Assistive technology training programs are crucial for equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to utilize these technologies effectively. Training programs can range from introductory workshops to comprehensive certifications, catering to various levels of expertise and needs. Here are some key aspects of assistive technology training programs and certification:
- Training for Users: Training programs for users focus on providing hands-on experience with specific assistive technologies, teaching users how to operate and troubleshoot the devices, and helping them adapt to the technology.
- Training for Professionals: Professionals involved in the assessment, prescription, and implementation of assistive technology can benefit from specialized training programs. These programs cover topics such as assessment techniques, assistive technology selection, and ethical considerations.
- Certification: Some organizations offer certification programs for professionals working in the field of assistive technology. These certifications demonstrate a professional’s knowledge and expertise in the field, enhancing their credibility and professional standing.
Assistive Technology Advocacy Groups
Advocacy groups play a vital role in promoting accessibility and ensuring that individuals with disabilities have access to the assistive technology they need. These groups advocate for policies, legislation, and funding that support the use of assistive technology. Here are some key functions of assistive technology advocacy groups:
- Raising Awareness: Advocacy groups raise awareness about the benefits of assistive technology and the challenges faced by individuals with disabilities in accessing these technologies.
- Policy Advocacy: These groups advocate for policies that promote the use of assistive technology, such as funding for assistive technology devices and services, and legislation that ensures accessibility in public spaces and workplaces.
- Supporting Individuals: Advocacy groups provide support and resources to individuals with disabilities who are seeking assistive technology. This support may include information about available resources, assistance with navigating the application process for funding, and advocacy on behalf of individuals facing barriers to accessing assistive technology.
End of Discussion

Assistive technology grants represent a vital investment in the well-being and empowerment of individuals with disabilities. By understanding the grant landscape, navigating the application process, and utilizing resources effectively, individuals and organizations can unlock the transformative power of assistive technology. Together, we can create a more accessible and inclusive world for all.
An assistive technology grant can be a valuable resource for individuals seeking to improve their independence and quality of life. Companies like berk technology specialize in providing innovative assistive technology solutions that can empower individuals with disabilities. These grants can help fund the acquisition of assistive technology devices, software, and services, making a real difference in the lives of those who need it most.