Assistive Technology for ELL Students: Bridging the Gap
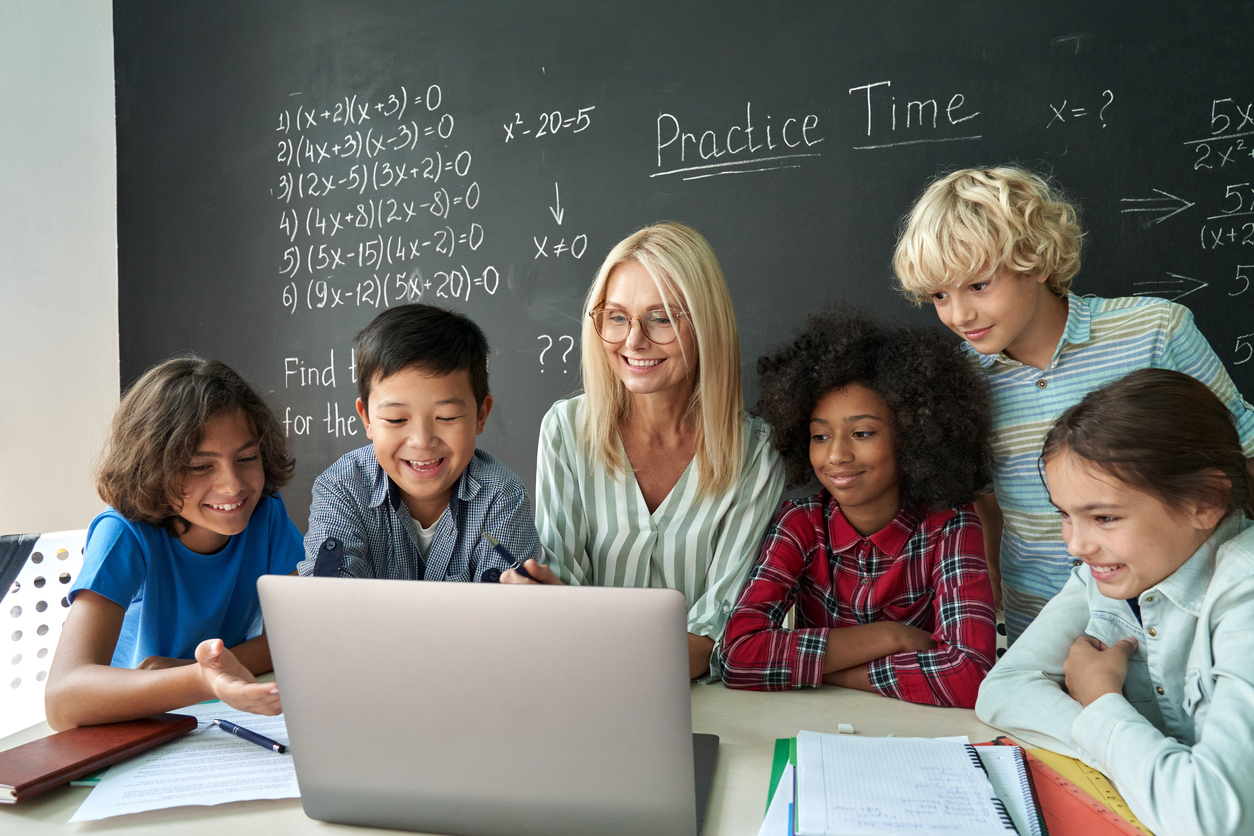
Assistive technology for ELL students takes center stage, offering a transformative approach to education. This technology empowers English Language Learners to navigate the complexities of a new language and culture, […]
Assistive technology for ELL students takes center stage, offering a transformative approach to education. This technology empowers English Language Learners to navigate the complexities of a new language and culture, unlocking their potential and fostering academic success.
By providing tailored support, assistive technology addresses the unique challenges faced by ELLs, such as language barriers, cultural differences, and varying levels of literacy. From speech-to-text software that facilitates reading comprehension to translation tools that bridge communication gaps, these technologies offer a range of solutions designed to enhance learning experiences and promote inclusivity in the classroom.
Introduction to Assistive Technology for ELL Students
Assistive technology (AT) refers to tools and resources designed to help individuals with disabilities overcome barriers to learning, communication, and participation in daily life. In the context of education, AT plays a crucial role in empowering students with diverse needs, including English Language Learners (ELLs), to achieve their full potential.
ELL students face unique challenges in accessing and utilizing technology due to their limited proficiency in English. These challenges can range from difficulty understanding instructions to navigating complex software interfaces. However, assistive technology can bridge this gap and provide ELLs with the support they need to thrive in a technology-rich learning environment.
Assistive Technology Tools for ELL Students
Assistive technology can be categorized into various types, each addressing specific needs and learning styles. These tools can help ELL students overcome language barriers, improve communication skills, and enhance their understanding of academic content.
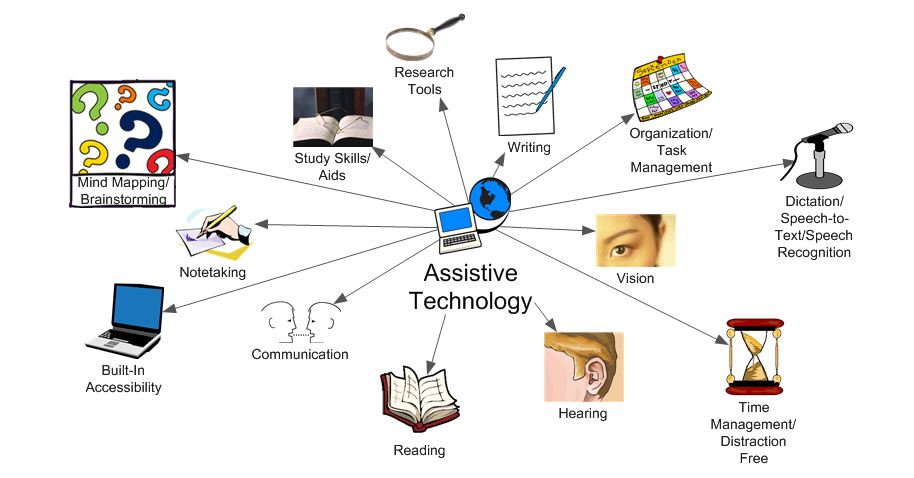
- Language Translation Tools: Online translators, dictionary apps, and language learning software can help ELLs understand and communicate in English. These tools can be used to translate text, audio, and video content, making it easier for students to access information and participate in classroom discussions.
- Speech-to-Text Software: Programs like Dragon NaturallySpeaking and VoiceNote can convert spoken words into written text, allowing ELL students to dictate their thoughts and ideas without having to rely on their writing skills. This is particularly helpful for students who are still developing their English writing abilities.
- Text-to-Speech Software: Tools like Read Aloud and NaturalReader can read text aloud, making it easier for ELL students to understand complex concepts and follow along with lectures or reading assignments. This can also help students who have difficulty reading or have learning disabilities.
- Visual Aids: Images, videos, and interactive simulations can be used to explain concepts and vocabulary in a more accessible way. These visual aids can help ELL students develop their understanding of abstract concepts and make connections between different ideas.
- Graphic Organizers: Tools like mind maps, concept maps, and flowcharts can help ELL students organize their thoughts and ideas, making it easier for them to process and understand information. This can be especially beneficial for students who are learning a new language and may struggle with complex sentence structures.
Types of Assistive Technology for ELL Students

Assistive technology (AT) plays a crucial role in supporting English Language Learners (ELLs) by providing tools that bridge language gaps and enhance their learning experience. By leveraging technology, educators can create a more inclusive and accessible learning environment for ELL students, allowing them to participate fully and achieve their academic goals.
Types of Assistive Technology for ELL Students
Assistive technology for ELL students encompasses a wide range of tools designed to address various learning needs. Here’s a breakdown of some key categories, along with examples, benefits, and implementation considerations:
| Category | Examples | Benefits for ELLs | Implementation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speech-to-Text | Dragon NaturallySpeaking | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
| Text-to-Speech | Read&Write for Google Chrome | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
| Visual Aids | Prezi | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
| Communication Tools | Boardmaker | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
| Language Learning Software | Duolingo | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
| Digital Dictionaries | WordReference | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
| Translation Tools | Google Translate | Improved reading comprehension, Increased vocabulary acquisition, Enhanced communication skills, Support for language production | Accessibility, Training for educators and students, Integration with existing curriculum, Data privacy and security |
Impact of Assistive Technology on ELL Students’ Learning Outcomes
Assistive technology (AT) has the potential to significantly enhance the learning outcomes of English Language Learners (ELLs) by providing them with the tools and support they need to overcome language barriers and access the curriculum effectively. By addressing specific learning challenges, AT can help ELLs improve their reading fluency, writing skills, and overall academic performance, fostering inclusivity and promoting equitable access to education.
Examples of AT Use to Improve ELLs’ Learning Outcomes
AT has been effectively implemented to improve reading fluency, writing skills, and overall academic performance of ELLs. Examples include:
- Text-to-speech software can help ELLs improve their reading fluency by reading aloud text passages, allowing them to hear the correct pronunciation and intonation. This can be particularly beneficial for students who are still developing their reading skills or who struggle with decoding unfamiliar words.
- Speech-to-text software can assist ELLs in writing by converting spoken words into text, allowing them to express their ideas without the need for extensive typing skills. This can be especially helpful for students who are still developing their writing skills or who have difficulty with traditional keyboard input.
- Digital dictionaries and translation tools can provide ELLs with immediate access to definitions and translations of unfamiliar words, enabling them to understand the content they are reading or writing. This can be particularly useful for students who are learning new vocabulary or who need to understand complex concepts in English.
- Interactive whiteboards and multimedia software can provide ELLs with engaging and interactive learning experiences, allowing them to visualize concepts, practice language skills, and collaborate with peers. This can be especially beneficial for students who learn best through visual or auditory means.
Research Findings on the Effectiveness of AT for ELLs
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of AT in supporting ELLs’ academic success. Research findings suggest that:
- Text-to-speech software has been shown to improve reading comprehension, fluency, and vocabulary development among ELLs.
- Speech-to-text software has been found to enhance writing skills, reduce writing anxiety, and increase writing productivity among ELLs.
- Digital dictionaries and translation tools have been proven to facilitate vocabulary acquisition, improve reading comprehension, and enhance writing accuracy among ELLs.
- Interactive whiteboards and multimedia software have been shown to increase engagement, motivation, and academic performance among ELLs.
Role of AT in Fostering Inclusivity and Equitable Access to Education for ELLs
AT plays a crucial role in fostering inclusivity and promoting equitable access to education for ELLs. By providing them with the necessary tools and support, AT helps to:
- Level the playing field for ELLs by addressing their unique learning needs and providing them with the same opportunities as their native English-speaking peers.
- Reduce language barriers and enable ELLs to participate fully in the learning process, regardless of their English proficiency level.
- Promote student independence and empower ELLs to take control of their learning, build confidence, and achieve their academic goals.
- Create a more inclusive and supportive learning environment where all students feel valued, respected, and empowered to succeed.
Considerations for Selecting and Implementing Assistive Technology
Choosing and implementing assistive technology (AT) for English Language Learners (ELL) students requires careful planning and consideration. The goal is to identify tools that effectively address individual needs and support their language development and academic success.
Identifying Individual Needs
Identifying the specific needs of each ELL student is crucial for selecting appropriate assistive technology. This process involves a collaborative effort between educators, specialists, and the student themselves.
- Conducting comprehensive assessments: Teachers and specialists should conduct thorough assessments to identify students’ strengths, weaknesses, and learning styles. This may involve using standardized tests, observations, and interviews.
- Analyzing student data: Data from assessments, classroom observations, and student work can provide insights into specific areas where AT could be beneficial. For example, if a student struggles with reading comprehension, AT tools like text-to-speech software could be considered.
- Seeking student input: Involving students in the process is essential. They can share their preferences, challenges, and what they find helpful or hindering in their learning. This fosters a sense of ownership and increases the likelihood of successful AT implementation.
Guidelines for Choosing Appropriate AT Tools
Selecting the right AT tools for ELL students requires a careful consideration of their individual needs, learning goals, and available resources.
- Match AT to specific needs: The chosen AT should directly address the student’s identified learning challenges. For example, if a student struggles with writing, a word prediction tool could be beneficial.
- Consider learning goals: AT tools should support the student’s overall academic goals. For instance, if the goal is to improve reading fluency, a text-to-speech program with adjustable reading speed could be a valuable tool.
- Assess accessibility and usability: The chosen AT should be accessible and user-friendly for the student. Consider factors such as the interface, language support, and ease of use.
- Evaluate available resources: The availability of resources, such as funding, technical support, and training, should be considered. Choose tools that are feasible within the school’s budget and have adequate support systems.
Strategies for Integrating AT into the Classroom
Successful integration of AT requires a thoughtful approach that ensures its effective use and maximizes student engagement.
- Provide comprehensive training: Teachers and students should receive adequate training on how to use the chosen AT tools. This includes hands-on practice and opportunities for troubleshooting.
- Foster collaboration: Encourage collaboration between teachers, specialists, and students to ensure that the AT is used appropriately and effectively. Regular communication and feedback are essential.
- Create a supportive environment: Establish a classroom environment where students feel comfortable using AT without fear of judgment. Promote a culture of acceptance and understanding.
- Monitor progress and make adjustments: Regularly monitor the impact of AT on student learning and make adjustments as needed. This may involve adjusting settings, exploring alternative tools, or providing additional support.
Teacher Training and Professional Development: Assistive Technology For Ell Students

Empowering educators to effectively utilize assistive technology (AT) for English Language Learners (ELLs) requires comprehensive training and ongoing professional development. A well-designed program equips teachers with the knowledge, skills, and resources to integrate AT seamlessly into their teaching practices, fostering inclusive and accessible learning environments for all students.
AT Terminology and Concepts
Understanding the terminology and concepts associated with assistive technology is crucial for educators to effectively implement and utilize AT tools. This section will delve into key definitions, classifications, and functionalities of various AT tools, providing teachers with a solid foundation for selecting and implementing appropriate technologies for their ELL students.
- Assistive Technology (AT): Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially off the shelf, modified, or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): An educational framework that promotes the creation of learning environments that are accessible and effective for all learners, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
- Adaptive Technology: Specifically designed for individuals with disabilities to address their unique needs, such as screen readers for visually impaired learners or speech-to-text software for students with writing difficulties.
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC): A broad range of methods and tools that support individuals with communication impairments to express themselves, including speech-generating devices, communication boards, and sign language.
AT Tool Selection and Implementation
Selecting and implementing appropriate AT tools for ELLs requires a systematic approach that considers individual student needs, learning goals, and available resources. This section will guide educators through the process of identifying suitable AT tools, exploring implementation strategies, and addressing potential challenges.
- Needs Assessment: Conducting a thorough needs assessment is the first step in identifying the specific AT needs of ELL students. This involves gathering information about their learning strengths, weaknesses, and areas where AT can provide support.
- Tool Selection: Based on the needs assessment, educators can select appropriate AT tools that align with the student’s learning goals and address their specific challenges. This may involve considering factors such as accessibility, ease of use, cost, and compatibility with existing classroom technology.
- Implementation Strategies: Successful AT implementation requires careful planning and collaboration. Educators should develop clear strategies for introducing AT tools to students, providing adequate training and support, and integrating them seamlessly into classroom activities.
- Student Support: Ongoing support is essential for students to effectively utilize AT tools. This may involve providing individual instruction, troubleshooting technical issues, and adapting activities to accommodate the use of AT.
Student Support and Collaboration
Providing ongoing support and collaboration is essential for ensuring the successful use of AT by ELL students. This section will highlight strategies for supporting students in utilizing AT effectively, promoting collaboration among teachers, families, and other professionals, and fostering a positive and inclusive learning environment.
- Individualized Support: Providing individualized support to ELL students using AT is crucial. This may involve offering one-on-one instruction, small group activities, or peer tutoring to ensure students are comfortable and confident using the tools.
- Collaboration with Families: Engaging families in the AT process is essential. This may involve sharing information about the selected AT tools, providing guidance on how to support their child at home, and fostering communication between teachers and families.
- Collaboration with Professionals: Collaboration with specialists such as assistive technology specialists, speech-language pathologists, and special education teachers can provide valuable insights and support in implementing AT effectively for ELL students.
Ongoing Professional Development
The field of assistive technology is constantly evolving, with new tools and technologies emerging regularly. Ongoing professional development is essential for educators to stay abreast of the latest advancements and best practices in utilizing AT for ELLs. This section will discuss the importance of ongoing training and explore various avenues for professional development in AT.
- Stay Updated: Educators should engage in ongoing learning to stay informed about the latest developments in assistive technology, including new tools, research findings, and best practices.
- Professional Development Opportunities: Numerous opportunities exist for educators to enhance their knowledge and skills in AT. This may include attending workshops, conferences, online courses, and professional development programs specifically focused on assistive technology for ELLs.
- Collaboration with Colleagues: Sharing knowledge and experiences with colleagues who are also using AT can be a valuable source of professional development. Educators can participate in peer mentoring programs, share best practices, and collaborate on projects related to assistive technology.
Future Directions in Assistive Technology for ELL Students
The field of assistive technology (AT) for English language learners (ELLs) is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and a growing understanding of the unique needs of this diverse student population. As we look to the future, several exciting trends hold the potential to transform how AT is used to support ELLs in their academic journey.
Emerging Trends in AT Development, Assistive technology for ell students
The development of innovative AT tools specifically designed for ELLs is crucial to address their specific learning challenges. Emerging trends in AT development offer promising avenues for improving the accessibility and effectiveness of AT for ELLs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered Language Learning Tools: AI-powered tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their ability to personalize language learning experiences. These tools can adapt to individual learners’ needs and provide real-time feedback, making language learning more engaging and effective. For example, AI-powered translation tools can assist ELLs in understanding complex concepts by providing instant translations and explanations.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) for Immersive Language Learning: AR/VR technologies offer immersive learning experiences that can help ELLs develop language skills in a more engaging and interactive way. For example, AR/VR simulations can create realistic scenarios where ELLs can practice communication skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: Adaptive learning platforms use AI algorithms to tailor instruction to each student’s learning pace and style. These platforms can identify areas where ELLs need extra support and provide personalized learning resources.
Research on Effectiveness and Accessibility
Continued research is vital to ensure that AT for ELLs is effective and accessible to all learners.
- Evaluating the Impact of AT on ELLs’ Learning Outcomes: Research is needed to systematically evaluate the impact of different AT tools on ELLs’ academic performance, language proficiency, and overall learning experience. This research should consider factors such as the type of AT, the specific learning needs of the ELLs, and the context in which the AT is used.
- Addressing Accessibility Barriers for Diverse Learners: Research should focus on identifying and addressing accessibility barriers for ELLs with diverse learning needs, such as students with disabilities, students from different cultural backgrounds, and students with limited English proficiency. This research should consider factors such as language, culture, and technology access.
Collaboration for Advancement
The advancement of AT for ELLs requires a collaborative effort among educators, researchers, and technology developers.
- Shared Knowledge and Resources: Collaboration can facilitate the sharing of knowledge and resources among stakeholders, leading to the development of more effective and accessible AT solutions.
- Joint Research Initiatives: Collaborative research initiatives can provide valuable insights into the needs and challenges of ELLs and inform the development of effective AT interventions.
- Professional Development Opportunities: Collaboration can support the development of professional development opportunities for educators on how to effectively use AT to support ELLs.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, assistive technology plays a vital role in empowering ELL students and creating an equitable learning environment. By providing personalized support and bridging communication gaps, these tools enhance language acquisition, foster academic success, and promote inclusivity. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for assistive technology to transform ELL education is boundless. By embracing these innovative tools, educators can empower ELL students to reach their full potential and thrive in a globalized world.
Assistive technology can play a crucial role in helping English Language Learners (ELL) students access and succeed in their education. A key step in this process is conducting a thorough assistive technology assessment to identify the student’s specific needs and determine the most appropriate tools to support their learning.
By providing ELL students with the right assistive technology, educators can create a more inclusive and equitable learning environment that empowers them to reach their full potential.