Technology Transfer: Shaping the Pharmaceutical Industry
Technology transfer pharmaceutical industry – Technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry plays a crucial role in driving innovation and bringing life-saving treatments to patients. It involves the transfer of knowledge, […]
Technology transfer pharmaceutical industry – Technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry plays a crucial role in driving innovation and bringing life-saving treatments to patients. It involves the transfer of knowledge, expertise, and technology from one entity to another, enabling the development, manufacturing, and commercialization of new drugs and therapies.
This intricate process encompasses various aspects, including licensing agreements, joint ventures, and research collaborations. It involves the transfer of intellectual property, manufacturing processes, and regulatory know-how, all while navigating complex legal and ethical considerations.
The Pharmaceutical Industry and Technology Transfer
Technology transfer plays a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry, enabling the development and commercialization of new drugs and therapies. It facilitates the movement of knowledge, expertise, and resources between different entities, ultimately accelerating the pace of innovation and bringing life-saving treatments to patients.
Types of Technology Transfer in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry encompasses a wide range of activities. These activities can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its unique characteristics and objectives:
- Licensing: This involves granting a company the right to use a specific technology, such as a patent or know-how, in exchange for royalties or other forms of compensation. It is a common approach for transferring intellectual property to companies that lack the necessary expertise or resources to develop a product themselves.
- Joint Ventures: These collaborations involve two or more companies pooling their resources and expertise to develop and commercialize a product. This can be particularly beneficial for transferring complex technologies that require a multidisciplinary approach.
- Spin-offs: This involves the creation of a new company based on technology developed by a larger organization. This can be a way to commercialize promising technologies that do not align with the core business of the parent company.
- Out-licensing: This involves transferring technology to another company for development and commercialization. This can be a strategic move for companies seeking to focus on their core competencies or expand their reach into new markets.
- Contract Manufacturing: This involves outsourcing the manufacturing of a product to a third-party company. This can be a cost-effective way to access specialized manufacturing capabilities or to scale up production.
Examples of Successful Technology Transfer Initiatives
Several successful technology transfer initiatives have revolutionized the pharmaceutical industry, leading to the development of groundbreaking drugs and therapies:
- The development of the first successful mRNA vaccine for COVID-19: This groundbreaking technology, developed by Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, was the result of years of research and development. It involved transferring expertise and know-how from academic institutions to pharmaceutical companies, ultimately leading to the rapid development and deployment of life-saving vaccines.
- The development of CAR T-cell therapy: This innovative cancer treatment involves genetically modifying a patient’s immune cells to target and destroy cancer cells. The technology was developed by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and was subsequently licensed to Novartis, which commercialized the therapy under the brand name Kymriah.
- The development of monoclonal antibody therapies for autoimmune diseases: These therapies target specific proteins involved in the immune response, effectively reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms. The technology was developed by researchers at Genentech and was subsequently licensed to Roche, which commercialized the therapy under the brand name Rituxan.
Key Drivers of Technology Transfer in Pharmaceuticals: Technology Transfer Pharmaceutical Industry

Technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry is a complex process involving the transfer of knowledge, expertise, and technology from one entity to another. It is crucial for driving innovation, improving efficiency, and bringing new therapies to market faster. The pharmaceutical industry is witnessing a rapid evolution, with several key drivers shaping the landscape of technology transfer.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes play a pivotal role in driving technology transfer. The evolving regulatory landscape demands that pharmaceutical companies adapt their processes and technologies to meet new requirements. For example, the increasing emphasis on quality by design (QbD) principles has led to a shift towards more robust and standardized technology transfer practices. QbD promotes a proactive approach to drug development, focusing on designing quality into the product and process from the outset. This shift necessitates the transfer of knowledge and expertise related to QbD principles, analytical methods, and process validation.
Increasing Competition, Technology transfer pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry is highly competitive, with companies constantly striving to gain an edge over their rivals. This intense competition drives technology transfer as companies seek to leverage the latest technologies and innovations to enhance their efficiency, reduce costs, and accelerate product development. For instance, the adoption of continuous manufacturing technologies allows for faster production cycles and improved product quality. Companies are increasingly looking to transfer these technologies to their manufacturing facilities to gain a competitive advantage.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing the pharmaceutical industry, impacting technology transfer in profound ways. AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling companies to optimize their drug discovery, development, and manufacturing processes. For example, AI-powered drug discovery platforms can accelerate the identification and development of new drug candidates, while ML algorithms can optimize process parameters for enhanced efficiency and product quality. The transfer of these AI and ML technologies requires specialized expertise and infrastructure, creating new opportunities for technology transfer.
Best Practices for Effective Technology Transfer
Successful technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry is crucial for the development and commercialization of new drugs and therapies. It involves a seamless transition of knowledge, processes, and technology from the research and development stage to manufacturing and commercialization. Effective technology transfer ensures that the product meets quality standards, regulatory requirements, and market demands.
Key Steps in Technology Transfer
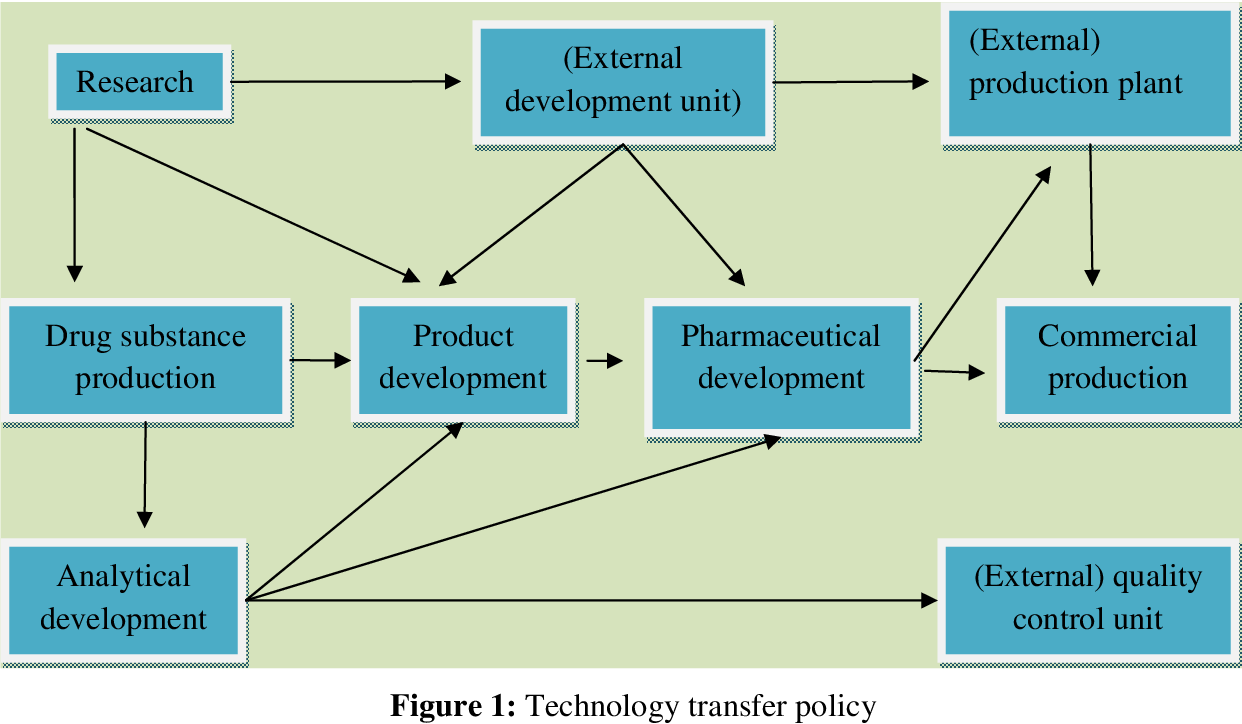
The technology transfer process involves several key steps, each requiring careful planning and execution. These steps ensure a smooth transition and minimize potential risks.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Planning and Scoping | Defining the scope of the technology transfer, identifying key deliverables, and establishing clear objectives. |
| 2. Technology Documentation | Compiling and documenting all relevant information, including protocols, specifications, and training materials. |
| 3. Training and Knowledge Transfer | Providing comprehensive training to the receiving team, ensuring they have the necessary skills and understanding. |
| 4. Process Validation and Qualification | Verifying that the transferred process meets predefined quality standards and regulatory requirements. |
| 5. Technology Implementation and Scale-up | Implementing the transferred technology at the new site, ensuring seamless integration and successful scale-up. |
| 6. Monitoring and Evaluation | Continuously monitoring the transferred technology, identifying potential issues, and making necessary adjustments. |
The Importance of Clear Communication and Documentation
Clear communication and comprehensive documentation are crucial for successful technology transfer.
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Clear Communication | Ensures all parties involved have a shared understanding of the technology, process, and expectations. |
| Comprehensive Documentation | Provides a detailed record of the technology, process, and any relevant information, ensuring consistency and reproducibility. |
| Effective Training Materials | Supports knowledge transfer and ensures that the receiving team has the necessary skills and understanding. |
| Regular Communication and Feedback | Facilitates problem-solving, promotes collaboration, and ensures that the technology transfer is on track. |
Impact of Technology Transfer on Pharmaceutical Innovation
Technology transfer plays a crucial role in driving innovation within the pharmaceutical industry. It facilitates the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources, ultimately accelerating the development of new drugs and therapies. This process allows for the transfer of cutting-edge technologies, research findings, and manufacturing capabilities between academic institutions, research organizations, and pharmaceutical companies.
Impact of Technology Transfer on Drug Development
Technology transfer significantly impacts the development of new drugs and therapies. It enables the efficient translation of research discoveries into commercially viable products, ultimately benefiting patients. The process involves various stages, from preclinical research to clinical trials and finally, commercialization.
- Preclinical Research: Technology transfer allows pharmaceutical companies to access innovative technologies and research findings from academic institutions or research organizations. This access enables them to conduct preclinical studies, assess the safety and efficacy of potential drug candidates, and identify promising targets for further development.
- Clinical Trials: Technology transfer facilitates the transfer of clinical trial protocols, data management systems, and expertise in conducting clinical trials. This ensures that trials are conducted efficiently and effectively, ultimately leading to faster and more successful drug development.
- Commercialization: Technology transfer plays a crucial role in the commercialization of new drugs. It enables pharmaceutical companies to access manufacturing technologies, regulatory expertise, and marketing strategies, allowing them to bring new drugs to market more quickly and efficiently.
Technology Transfer Accelerates Pharmaceutical Innovation
Technology transfer plays a vital role in accelerating the pace of pharmaceutical innovation. It fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing between different stakeholders, leading to faster progress in research and development.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Technology transfer promotes collaboration between academic institutions, research organizations, and pharmaceutical companies. This collaboration allows for the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources, ultimately leading to faster progress in drug development.
- Access to New Technologies: Technology transfer enables pharmaceutical companies to access cutting-edge technologies and research findings. This access allows them to develop new drugs and therapies more efficiently and effectively.
- Faster Time to Market: Technology transfer can help reduce the time it takes to bring new drugs to market. By streamlining the development process and providing access to essential resources, technology transfer allows for faster progress and more efficient commercialization.
Examples of Technology Transfer in Pharmaceutical Innovation
Technology transfer has been instrumental in numerous breakthroughs in pharmaceutical research and development.
- Development of mRNA Vaccines: The development of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 is a prime example of technology transfer in action. The technology behind these vaccines was developed in academic labs and then transferred to pharmaceutical companies for further development and commercialization. This transfer of knowledge and expertise allowed for the rapid development and deployment of these life-saving vaccines.
- Targeted Therapies for Cancer: Technology transfer has been instrumental in the development of targeted therapies for cancer. These therapies target specific proteins or pathways involved in cancer growth and development, leading to more effective treatment options with fewer side effects. The transfer of research findings and technologies from academic institutions to pharmaceutical companies has been crucial in this area.
- Development of Biologics: The development of biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies, has been heavily reliant on technology transfer. These therapies are complex and require specialized technologies for their production and purification. The transfer of knowledge and expertise from research organizations to pharmaceutical companies has enabled the successful development and commercialization of these innovative therapies.
Ending Remarks
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, technology transfer will remain a critical driver of progress. By fostering collaboration, leveraging emerging technologies, and addressing the challenges associated with this complex process, stakeholders can unlock the full potential of innovation and bring groundbreaking therapies to those who need them most.
Technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry is a complex process, involving the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and resources. This transfer can be facilitated by organizations like aeronix technologies group , which specialize in providing solutions for various aspects of pharmaceutical development.
Aeronix’s expertise can be invaluable for companies seeking to optimize their technology transfer processes, ensuring a seamless transition from research to commercialization.