Technology Sourcing: Strategies for Modern Businesses
Technology sourcing, a critical aspect of modern business operations, involves strategically acquiring and managing the technology resources an organization needs to achieve its goals. This multifaceted approach encompasses various models, […]
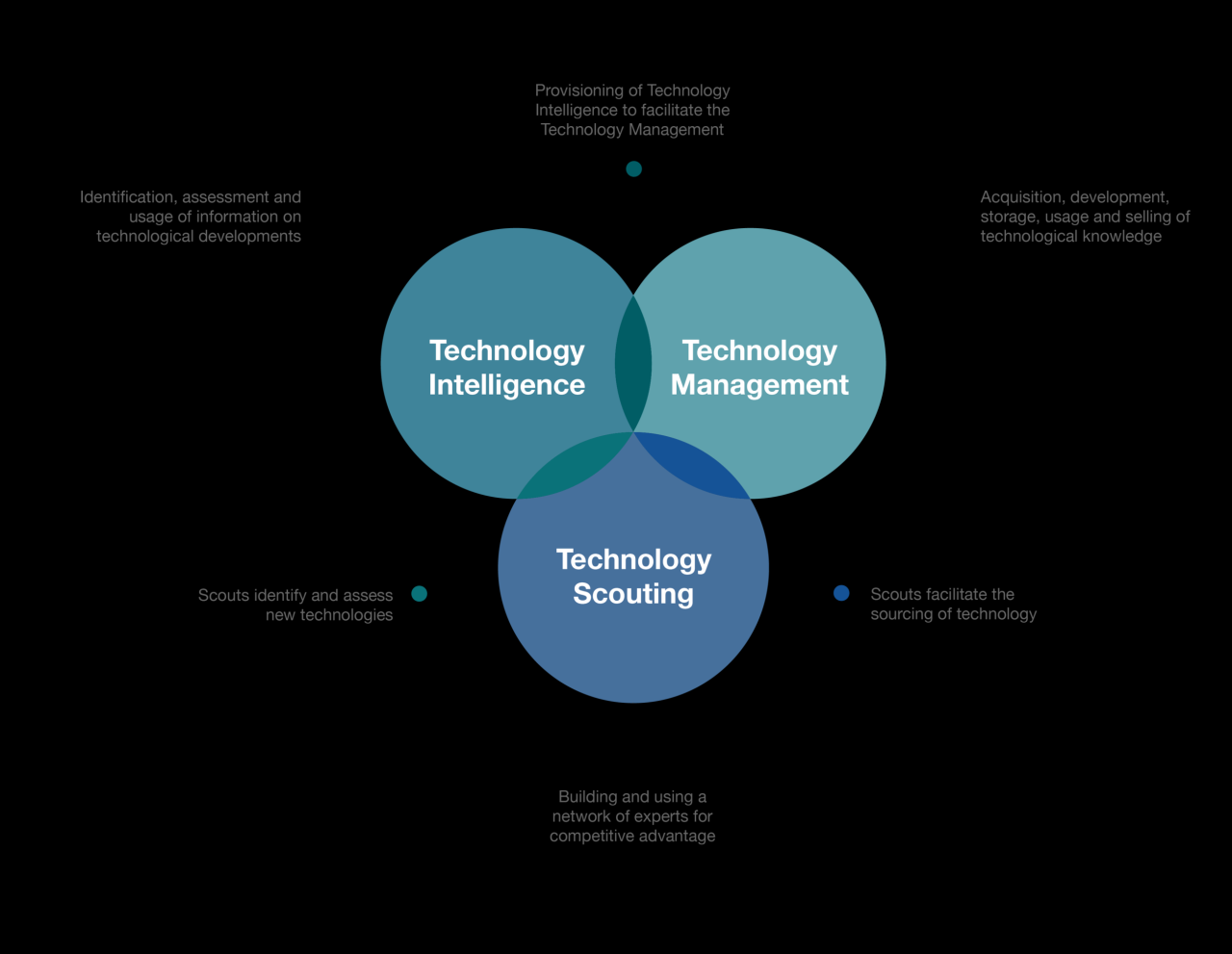
Technology sourcing, a critical aspect of modern business operations, involves strategically acquiring and managing the technology resources an organization needs to achieve its goals. This multifaceted approach encompasses various models, including outsourcing, insourcing, and co-sourcing, each tailored to address specific business requirements.
Understanding the intricacies of technology sourcing is paramount for businesses seeking to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. By carefully evaluating factors such as cost, risk, and strategic alignment, organizations can make informed decisions regarding their technology sourcing strategies, ensuring they leverage the best resources available to achieve their objectives.
Benefits and Challenges of Technology Sourcing
Technology sourcing, the process of acquiring technology resources from external providers, has become increasingly prevalent in today’s dynamic business landscape. This approach offers numerous advantages, enabling organizations to leverage specialized expertise, streamline operations, and enhance agility. However, it also presents challenges that require careful consideration and strategic planning.
Benefits of Technology Sourcing
Technology sourcing offers a range of benefits that can significantly impact an organization’s success. By outsourcing technology functions, companies can gain access to specialized expertise, reduce costs, and enhance agility.
- Cost Reduction: Technology sourcing can help organizations reduce costs associated with technology infrastructure, development, and maintenance. By leveraging the economies of scale offered by external providers, companies can minimize capital expenditures and operational expenses. For example, a small business might find it more cost-effective to outsource its IT infrastructure to a cloud provider rather than investing in expensive hardware and personnel.
- Access to Expertise: Technology sourcing provides access to a vast pool of specialized expertise that may not be readily available within an organization. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that require specialized skills in areas such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, or data analytics. By partnering with experienced technology providers, companies can tap into a wealth of knowledge and experience, ensuring that their technology solutions are robust and aligned with industry best practices.
- Increased Agility: Technology sourcing can enhance an organization’s agility by allowing it to quickly scale its technology resources up or down as needed. This flexibility is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving business environment, where companies need to adapt quickly to changing market demands and technological advancements. For instance, a company launching a new product or service might need to rapidly scale its IT infrastructure to handle increased demand. Technology sourcing allows them to access the necessary resources without significant upfront investments or long-term commitments.
Challenges of Technology Sourcing
While technology sourcing offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges that require careful consideration and management. These challenges can include vendor management, security risks, and loss of control over technology operations.
- Vendor Management: Managing multiple technology vendors can be complex and time-consuming. Organizations need to establish clear contracts, monitor vendor performance, and ensure that their technology solutions are integrated seamlessly. A lack of effective vendor management can lead to delays, cost overruns, and security vulnerabilities. For example, a company might encounter difficulties managing multiple cloud providers, ensuring data consistency and security across different platforms.
- Security Risks: Technology sourcing can introduce security risks if proper safeguards are not in place. Organizations need to carefully vet their technology vendors and ensure that they have robust security protocols in place to protect sensitive data. Data breaches and security incidents can have significant financial and reputational consequences. For instance, a company outsourcing its customer data management might face risks if the vendor’s security measures are inadequate.
- Loss of Control: Outsourcing technology functions can lead to a loss of control over technology operations. This can be particularly challenging if an organization relies heavily on external providers for critical technology functions. It is essential to establish clear service level agreements (SLAs) and monitoring mechanisms to ensure that vendors meet performance expectations and that the organization retains sufficient control over its technology environment.
Technology Sourcing Models
Different technology sourcing models offer varying levels of benefits and challenges. The following table Artikels the advantages and disadvantages of several common models:
| Technology Sourcing Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| On-Premise | High level of control, security, and customization. | High upfront costs, ongoing maintenance expenses, limited scalability. |
| Cloud Computing | Scalability, cost-effectiveness, flexibility. | Security concerns, vendor lock-in, potential data privacy issues. |
| Managed Services | Access to specialized expertise, reduced operational costs. | Potential loss of control, vendor dependence, limited customization. |
| Outsourcing | Cost savings, access to a wider talent pool, focus on core competencies. | Potential loss of control, security risks, cultural differences. |
Best Practices for Effective Technology Sourcing

Technology sourcing is a critical process for organizations seeking to leverage technology effectively. It involves identifying, evaluating, and selecting technology solutions and vendors that align with business objectives. Effective technology sourcing requires a well-defined strategy, meticulous planning, and a comprehensive understanding of the market landscape.
Establishing Clear Sourcing Objectives
Clearly defined sourcing objectives are essential for guiding the technology sourcing process. They provide a framework for evaluating potential vendors and solutions, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- Identify Business Needs: The first step is to define the specific business needs that the technology solution should address. This includes identifying pain points, desired outcomes, and the scope of the project.
- Define Requirements: Once business needs are understood, translate them into detailed technical requirements. This includes specifications for functionalities, performance, security, and integration capabilities.
- Set Budget and Timeline: Establish a realistic budget and timeline for the sourcing process. This helps in narrowing down potential vendors and solutions that align with financial constraints and project deadlines.
- Prioritize Success Criteria: Define success criteria that will be used to evaluate potential vendors and solutions. This may include factors like vendor experience, industry expertise, solution features, and pricing.
Selecting Appropriate Vendors, Technology sourcing
Selecting the right vendor is crucial for successful technology sourcing. A thorough evaluation process is essential to identify vendors that meet the organization’s needs and expectations.
- Vendor Research: Conduct comprehensive research to identify potential vendors. Explore industry publications, online directories, and vendor websites to gather information about their offerings, expertise, and track record.
- Request for Information (RFI): Send an RFI to shortlisted vendors to gather preliminary information about their capabilities and solutions. This helps in narrowing down the list to vendors that best align with the organization’s requirements.
- Request for Proposal (RFP): Issue an RFP to the selected vendors, outlining the detailed requirements, specifications, and evaluation criteria. This provides vendors with a clear understanding of the project scope and allows them to submit comprehensive proposals.
- Vendor Evaluation: Establish a robust evaluation process to assess vendor proposals based on the defined criteria. This may involve technical evaluations, financial assessments, and reference checks.
Managing Vendor Relationships
Building and managing strong vendor relationships is crucial for long-term success in technology sourcing. This involves establishing clear communication channels, fostering trust, and ensuring ongoing collaboration.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of both the organization and the vendor. This ensures that everyone understands their obligations and expectations.
- Establish Communication Channels: Set up clear communication channels for regular updates, feedback, and issue resolution. This may include meetings, email correspondence, and project management tools.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the vendor’s performance against agreed-upon service level agreements (SLAs). This helps in identifying any potential issues and addressing them promptly.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage open communication and collaboration between the organization and the vendor. This helps in building trust and ensuring that both parties work together effectively.
Mitigating Risks in Technology Sourcing
Technology sourcing involves inherent risks, such as vendor performance issues, security breaches, and cost overruns. Organizations need to implement strategies to mitigate these risks and ensure successful outcomes.
- Conduct Due Diligence: Thoroughly vet potential vendors to assess their financial stability, technical expertise, and reputation. This helps in reducing the risk of selecting a vendor that may not be able to deliver on its promises.
- Negotiate Strong Contracts: Establish clear and comprehensive contracts that define the scope of work, payment terms, and responsibilities. This helps in protecting the organization’s interests and minimizing the risk of disputes.
- Implement Security Measures: Ensure that appropriate security measures are in place to protect sensitive data and systems. This may involve data encryption, access control, and regular security audits.
- Establish Exit Strategies: Plan for potential scenarios where the vendor relationship may need to be terminated. This may involve developing contingency plans, negotiating termination clauses, and ensuring data portability.
Emerging Trends in Technology Sourcing

The landscape of technology sourcing is rapidly evolving, driven by the emergence of transformative technologies like cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These innovations are fundamentally altering how organizations procure and manage their technology needs, leading to a new era of dynamic and agile sourcing strategies.
The Impact of Cloud Computing and Artificial Intelligence
Cloud computing has revolutionized technology sourcing by offering a flexible and scalable platform for organizations to access computing resources on demand. This has significantly reduced the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, enabling businesses to scale their technology resources as required.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also transforming technology sourcing by automating various tasks, from identifying potential vendors to negotiating contracts. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify the most suitable vendors based on specific criteria, streamline the sourcing process, and even predict future technology needs.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Technology Sourcing
Several key trends are shaping the future of technology sourcing, reflecting the changing dynamics of the technology landscape and evolving business needs.
- Increased Focus on Digital Transformation: Organizations are increasingly prioritizing digital transformation initiatives, driving the need for flexible and agile technology solutions. This trend is accelerating the adoption of cloud-based services and the use of emerging technologies, such as AI and machine learning.
- Rise of the Gig Economy: The rise of the gig economy has introduced new models for technology sourcing, allowing organizations to tap into a global pool of skilled professionals on a project basis. This approach offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness, particularly for specialized or short-term projects.
- Growing Importance of Cybersecurity: With the increasing reliance on technology, cybersecurity has become a paramount concern for organizations. This trend is driving the demand for robust cybersecurity solutions and services, including threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident response.
- Emphasis on Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Organizations are increasingly leveraging data analytics and business intelligence tools to gain insights into their operations and make data-driven decisions. This trend is driving the demand for data-driven technology solutions and services, including data warehousing, data visualization, and predictive analytics.
- Shift Towards Outcome-Based Sourcing: Traditional technology sourcing models are being replaced by outcome-based approaches, where organizations focus on achieving specific business outcomes rather than simply procuring technology solutions. This shift emphasizes the importance of aligning technology investments with strategic business goals.
Evolution of Technology Sourcing Over Time
[Diagram or infographic depicting the evolution of technology sourcing over time, highlighting key milestones and trends.]
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, technology sourcing is an essential element of modern business success, offering a range of benefits while presenting unique challenges. By embracing best practices, staying abreast of emerging trends, and carefully navigating the complexities of vendor management and security, organizations can harness the power of technology sourcing to drive innovation, enhance agility, and achieve sustainable growth.
Technology sourcing is a crucial aspect of any business, ensuring access to the right tools and resources to stay competitive. This process involves navigating a complex landscape of vendors, contracts, and technology options. For those interested in a career that bridges the gap between business needs and technological solutions, consider pursuing a path in business technology management careers.
These professionals play a vital role in evaluating, selecting, and implementing technology solutions, making them key players in the technology sourcing process.