OCR Tracking Technologies: Revolutionizing Efficiency
OCR tracking technologies set the stage for a revolution in efficiency, offering businesses a powerful tool to streamline operations and unlock new levels of automation. By leveraging the power of […]

OCR tracking technologies set the stage for a revolution in efficiency, offering businesses a powerful tool to streamline operations and unlock new levels of automation. By leveraging the power of optical character recognition (OCR) and image analysis, these technologies can extract valuable data from physical documents and images, transforming information into actionable insights.
From tracking packages in logistics to automating document processing in offices, OCR tracking technologies are transforming industries across the globe. These technologies are constantly evolving, with advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning pushing the boundaries of what is possible. This article delves into the fascinating world of OCR tracking technologies, exploring their history, components, applications, and future potential.
Introduction to OCR Tracking Technologies
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) tracking technologies have revolutionized how we interact with and analyze data. These technologies use software to convert images of text into machine-readable formats, enabling automated data extraction and analysis.
OCR tracking technologies have become an indispensable tool in various industries, offering significant benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Historical Development and Evolution of OCR Tracking Technologies
OCR technology has a long and fascinating history, evolving from early attempts to automate character recognition to sophisticated algorithms used in modern applications.
The development of OCR tracking technologies can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with early efforts focusing on recognizing handwritten characters. These early systems were limited in their capabilities and accuracy, relying on simple pattern matching techniques.
The development of computers and digital image processing techniques in the 1970s and 1980s significantly advanced OCR technology. Researchers developed more sophisticated algorithms, including statistical methods and neural networks, which improved the accuracy and speed of character recognition.
The advent of the internet and the widespread use of digital documents further fueled the growth of OCR tracking technologies. Today, OCR software is readily available and integrated into various applications, from document management systems to mobile devices.
Real-World Examples of OCR Tracking Technologies
OCR tracking technologies are widely used across various industries, offering significant benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
- Document Management: OCR technology is used to digitize paper documents, making them searchable and easily accessible. This is particularly beneficial for businesses that deal with large volumes of documents, such as insurance companies, banks, and government agencies.
- Data Extraction: OCR can extract data from images of documents, such as invoices, receipts, and forms, automating data entry processes and reducing manual errors.
- Customer Service: OCR technology is used to automate customer support tasks, such as processing insurance claims or handling customer inquiries. By extracting information from documents, OCR can help businesses respond to customer requests more efficiently and accurately.
- Healthcare: OCR technology is used to digitize patient records, enabling faster access to medical information and improved patient care. OCR can also be used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and scans, to detect anomalies and assist in diagnosis.
- Retail: OCR technology is used to track inventory levels, analyze sales data, and improve supply chain management. By reading product labels and barcodes, OCR can automate stocktaking processes and provide real-time insights into inventory levels.
Key Components of OCR Tracking Systems
OCR tracking systems are built upon a foundation of interconnected components that work together to transform visual data into actionable information. These components are essential for capturing, processing, and interpreting images to extract meaningful data.
Image Capture and Pre-processing
Image capture and pre-processing are the initial steps in OCR tracking, laying the groundwork for accurate character recognition. Image capture involves acquiring images of the target objects or documents, while pre-processing prepares these images for analysis.
- Image Capture: Image capture methods can range from simple digital cameras to specialized scanners and even live video feeds. The quality of the captured image directly impacts the accuracy of subsequent processing steps. Factors such as lighting, camera angle, and resolution influence the effectiveness of image capture.
- Pre-processing: Pre-processing involves a series of techniques designed to enhance image quality and prepare it for character recognition. Common pre-processing steps include:
- Noise Reduction: Eliminating random disturbances in the image, such as speckles or blur, to improve clarity.
- Image Enhancement: Adjusting brightness, contrast, and sharpness to enhance the visibility of characters.
- Image Segmentation: Dividing the image into smaller regions, isolating characters or text blocks for individual analysis.
Character Recognition and Data Extraction
Character recognition is the core of OCR tracking, where the system identifies individual characters within the pre-processed image. This process relies on sophisticated algorithms and pattern recognition techniques to translate visual information into digital text.
- Character Recognition Algorithms: Various algorithms are employed for character recognition, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some commonly used algorithms include:
- Template Matching: Comparing the image of a character to a library of pre-defined templates to find the closest match.
- Neural Networks: Using machine learning models trained on large datasets of characters to recognize patterns and classify characters.
- Data Extraction: Once characters are recognized, the system extracts the identified text and converts it into a structured format, such as plain text or a spreadsheet. This extracted data can be used for further analysis, processing, or storage.
Types of OCR Tracking Technologies
OCR tracking technologies are essential for automating data extraction and analysis in various industries. These technologies use advanced algorithms to recognize and interpret characters from images, enabling efficient tracking and management of information.
Types of OCR Tracking Technologies
OCR tracking technologies encompass a range of methods, each with its unique strengths, weaknesses, and applications. Here’s a table comparing some common types:
| Technology Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Examples of Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Character Recognition (OCR) | OCR technology converts images of text into machine-readable text formats. It can recognize various fonts, styles, and layouts, making it suitable for diverse documents. | High accuracy in recognizing text, versatile for various document types, widely available, cost-effective. | May struggle with handwritten text, complex layouts, and images with low quality or noise. | Digitizing paper documents, extracting data from invoices, automating form processing. |
| Barcode Scanning | Barcode scanning uses specialized readers to interpret barcodes, which contain encoded data representing products, locations, or other information. | Fast and efficient data capture, high accuracy in barcode reading, widely used in inventory management and retail. | Limited to specific barcode types, requires dedicated barcode scanners, susceptible to damage or wear on barcodes. | Inventory tracking, point-of-sale systems, supply chain management. |
| Image-Based Tracking | Image-based tracking uses computer vision algorithms to analyze images and identify objects or patterns. It can track movements, recognize objects, and extract information from images. | Can handle complex scenes and objects, adaptable to various environments, suitable for real-time tracking. | Requires powerful processing capabilities, susceptible to environmental factors like lighting and occlusion, may require extensive training data. | Autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, object detection in industrial settings. |
Applications of OCR Tracking Technologies
OCR tracking technologies have become ubiquitous in various industries, transforming the way information is captured, processed, and analyzed. These technologies offer numerous applications, improving efficiency, accuracy, and security in various sectors.
Applications in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
OCR tracking plays a crucial role in optimizing logistics and supply chain operations by enabling real-time visibility and efficient inventory management.
- Package Tracking: OCR technology is used to scan and track packages throughout the supply chain, from origin to destination. This allows for real-time monitoring of package location, ensuring timely delivery and minimizing delays.
- Inventory Management: OCR tracking can be used to automate inventory management processes, such as receiving, storing, and shipping goods. By scanning barcodes and labels, OCR systems can accurately track inventory levels, identify discrepancies, and generate reports for optimal stock management.
- Shipping Container Tracking: OCR tracking is used to track shipping containers, ensuring efficient loading, unloading, and movement. This helps in streamlining transportation processes and reducing the risk of lost or misplaced containers.
Applications in Document Processing and Automation
OCR tracking is essential in automating document processing tasks, streamlining workflows, and improving accuracy.
- Data Extraction: OCR technology enables the extraction of data from scanned documents, such as invoices, receipts, and forms. This extracted data can be used to automate accounting processes, create databases, and generate reports.
- Document Indexing and Classification: OCR tracking can be used to index and classify documents based on their content. This helps in organizing and retrieving documents efficiently, facilitating easy access to relevant information.
- Workflow Automation: OCR tracking can be used to automate document workflows, such as routing documents for approval, generating notifications, and archiving documents. This reduces manual effort and improves efficiency in document management processes.
Applications in Security and Surveillance Systems
OCR tracking plays a crucial role in enhancing security and surveillance systems by providing real-time identification and tracking capabilities.
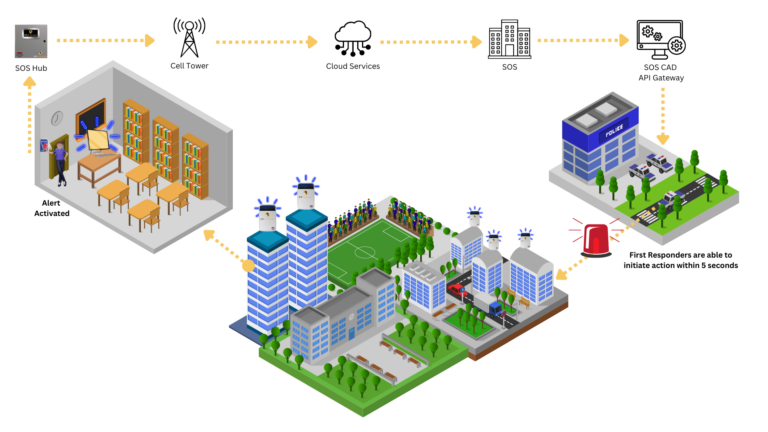
- Facial Recognition: OCR technology is used in facial recognition systems to identify individuals based on their facial features. This can be used for access control, security screening, and crime prevention.
- License Plate Recognition: OCR tracking is used to identify vehicles by scanning and recognizing their license plates. This can be used for traffic monitoring, toll collection, and law enforcement purposes.
- Surveillance Systems: OCR technology can be used to analyze video footage, identifying objects and individuals in real-time. This can be used to monitor public spaces, detect suspicious activity, and provide evidence in investigations.
Future Trends in OCR Tracking Technologies
The field of OCR tracking is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud computing. These technologies are poised to revolutionize OCR tracking, leading to significant improvements in accuracy, speed, and efficiency.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Ocr tracking technologies
AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in enhancing OCR tracking capabilities. By leveraging these technologies, OCR systems can learn from vast datasets of images and text, enabling them to:
- Improve accuracy: AI and ML algorithms can identify patterns and nuances in images, leading to more accurate character recognition and text extraction. This is particularly important for complex or handwritten text, where traditional OCR methods struggle.
- Enhance robustness: AI-powered OCR systems are better equipped to handle challenging scenarios, such as images with low resolution, noise, or distortions. This is crucial for real-world applications where image quality can vary.
- Enable real-time processing: AI and ML algorithms can process images and extract text in real time, making OCR tracking more responsive and efficient. This is particularly useful for applications requiring immediate data analysis, such as video surveillance or live document processing.
Advancements in OCR Accuracy and Speed
AI and ML are driving significant advancements in OCR accuracy and speed. For example, deep learning models have achieved remarkable accuracy in character recognition, surpassing traditional OCR methods in many scenarios.
- Improved character recognition: Deep learning models have significantly improved the accuracy of character recognition, particularly for complex or handwritten text. This is due to their ability to learn intricate patterns and features from large datasets.
- Faster processing times: AI and ML algorithms can process images and extract text much faster than traditional methods, enabling real-time OCR tracking applications. This is achieved through parallel processing and optimized algorithms.
- Enhanced language support: AI-powered OCR systems can support a wider range of languages, including those with complex scripts or limited data availability. This is made possible by training models on diverse datasets.
Impact of Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
Cloud computing and edge computing are transforming OCR tracking technologies by providing scalable and flexible infrastructure for data processing and storage.
- Scalability and flexibility: Cloud computing allows for the deployment of powerful OCR systems with minimal upfront investment. This scalability makes it easier to handle large volumes of data and adjust resources based on demand.
- Reduced latency: Edge computing enables OCR processing closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This is particularly important for applications requiring real-time analysis, such as video surveillance or autonomous vehicles.
- Enhanced security: Cloud computing and edge computing offer robust security measures, protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Final Thoughts

As OCR tracking technologies continue to evolve, their impact on our world will only grow. With the ability to automate processes, improve accuracy, and unlock valuable data, OCR tracking is poised to become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge. From revolutionizing logistics to streamlining administrative tasks, the future of OCR tracking holds immense promise, ushering in a new era of efficiency and innovation.
OCR tracking technologies are crucial for streamlining workflows in various industries. From automating data entry to improving document management, OCR plays a vital role in boosting efficiency. In the realm of newsroom technology , OCR can be used to automatically transcribe audio and video recordings, making it easier for journalists to create accurate and timely content.
These applications demonstrate how OCR tracking technologies can significantly impact various sectors, including the media industry.