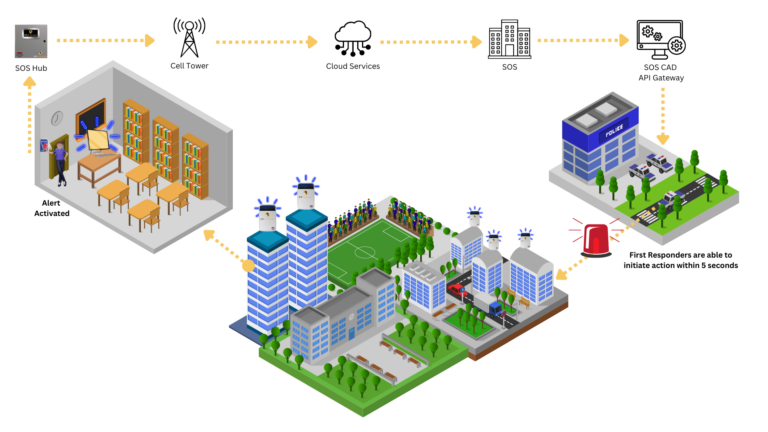
Next Technology: Shaping Our Future
Next technology is not just a buzzword; it represents a wave of innovation poised to transform our world. From artificial intelligence to quantum computing, these advancements are pushing the boundaries […]
Next technology is not just a buzzword; it represents a wave of innovation poised to transform our world. From artificial intelligence to quantum computing, these advancements are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, creating opportunities and challenges that will shape the future of humanity.
This exploration delves into the key areas of next technology development, examining the current state, potential applications, and the impact these technologies will have on various sectors. We will also consider the ethical implications and responsible innovation frameworks needed to guide their development and deployment.
Defining “Next Technology”
The term “next technology” encompasses the emerging technologies that are poised to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. These technologies are characterized by their disruptive potential, transformative impact, and long-term implications, shaping the future of society, economy, and human interaction.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Society
Emerging technologies are innovations that are still under development or in their early stages of adoption. They have the potential to disrupt existing industries, create new markets, and transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world. These technologies often arise from advancements in science, engineering, and computing, leading to new possibilities and solutions to pressing societal challenges.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming industries by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing customer experiences. Examples include self-driving cars, personalized medicine, and fraud detection systems.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain enables secure and transparent transactions, enhancing trust and efficiency in various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and digital identity.
- Biotechnology: Advancements in biotechnology are revolutionizing healthcare, agriculture, and energy production. Examples include gene editing, personalized medicine, and sustainable biofuels.
Factors Driving Technological Advancement
Technological advancement is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including scientific breakthroughs, societal needs, and market trends.
- Scientific Breakthroughs: Scientific discoveries and technological innovations often fuel the development of new technologies. For example, the discovery of the structure of DNA led to the development of genetic engineering, while the invention of the transistor paved the way for the modern computer.
- Societal Needs: Technological advancements are often driven by the need to address societal challenges, such as climate change, healthcare disparities, and poverty. For instance, the development of renewable energy technologies is driven by the need to mitigate climate change.
- Market Trends: Market demand and competition also play a significant role in driving technological innovation. Companies invest in research and development to create products and services that meet evolving customer needs and gain a competitive advantage.
Key Characteristics of “Next Technology”
“Next technology” is characterized by its disruptive potential, transformative impact, and long-term implications.
- Disruptive Potential: “Next technology” often disrupts existing industries and business models, creating new markets and opportunities. For example, the rise of e-commerce disrupted the traditional retail industry, while the advent of smartphones disrupted the mobile phone market.
- Transformative Impact: “Next technology” has the potential to transform various aspects of our lives, from the way we work and communicate to the way we access information and healthcare. For instance, AI is transforming industries by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing customer experiences.
- Long-Term Implications: “Next technology” has far-reaching and long-term implications for society, economy, and the environment. It is crucial to consider the ethical, social, and economic consequences of these technologies to ensure their responsible development and deployment.
Key Areas of Next Technology Development
The field of technology is constantly evolving, with new breakthroughs and advancements emerging at an unprecedented pace. These advancements are shaping the future across various industries, impacting how we live, work, and interact with the world around us. This section will delve into key areas of next technology development, exploring the current state of these technologies, the challenges they face, and their potential applications.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is transforming industries and influencing how we interact with technology. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing.
- Machine learning involves training algorithms on large datasets to enable them to learn patterns and make predictions. Applications range from image recognition and fraud detection to personalized recommendations and self-driving cars.
- Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to process complex data. This technology powers advancements in computer vision, speech recognition, and natural language understanding.
- Natural language processing (NLP) focuses on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP is used in chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation tools.
AI faces challenges such as data privacy, bias in algorithms, and the ethical implications of its use. Despite these challenges, AI holds immense potential to revolutionize various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and transportation.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology leverages biological processes to create new products and solutions. It encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including genetic engineering, synthetic biology, and bioinformatics.
- Genetic engineering allows for the modification of an organism’s genetic makeup, leading to advancements in agriculture, medicine, and bioremediation.
- Synthetic biology focuses on designing and building new biological systems, with applications in biofuel production, bioremediation, and the development of new drugs and therapies.
- Bioinformatics uses computational tools to analyze and interpret biological data, enabling researchers to understand complex biological processes and develop new treatments for diseases.
Biotechnology has the potential to address global challenges such as food security, disease prevention, and environmental sustainability. However, it also raises ethical concerns related to genetic manipulation and the potential for unintended consequences.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to solve problems that are intractable for classical computers.
- Quantum bits (qubits), the fundamental units of information in quantum computing, can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling quantum computers to perform calculations at a much faster rate than classical computers.
- Quantum algorithms, specifically designed for quantum computers, can solve complex problems in fields such as cryptography, drug discovery, and materials science.
Quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, but it holds the potential to revolutionize various industries, including medicine, finance, and materials science.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular level, enabling the creation of materials with unique properties.
- Nanomaterials, with dimensions in the nanometer range, exhibit enhanced properties such as strength, conductivity, and reactivity, leading to applications in electronics, medicine, and energy.
- Nanodevices, such as nanosensors and nanorobots, are being developed for various applications, including medical diagnostics, drug delivery, and environmental monitoring.
Nanotechnology faces challenges related to safety, toxicity, and ethical considerations. However, it holds immense potential for addressing global challenges such as disease treatment, energy production, and environmental remediation.
Space Exploration
Space exploration continues to push the boundaries of human knowledge and technological innovation.
- Spacecraft development, including reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems, enables exploration of distant planets and celestial bodies.
- Robotics and automation play a crucial role in space exploration, allowing for the collection of data, the construction of infrastructure, and the exploration of hazardous environments.
- Space-based research, conducted in the microgravity environment of space, has the potential to lead to breakthroughs in various fields, including materials science, medicine, and agriculture.
Space exploration has the potential to inspire future generations, drive technological innovation, and contribute to our understanding of the universe.
Impact and Implications of Next Technology
The advent of next technologies, with their transformative capabilities, promises to reshape our world in profound ways. From fostering economic growth and driving social change to raising ethical concerns, these technologies are poised to have a significant impact on various aspects of our lives.
Potential Benefits and Risks
The potential benefits of next technologies are vast and multifaceted. They hold the promise of driving economic growth by creating new industries, improving productivity, and fostering innovation. For example, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are expected to revolutionize various industries, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Furthermore, next technologies have the potential to address pressing global challenges, such as climate change, by enabling the development of sustainable energy solutions and efficient resource management practices.
- In healthcare, next technologies can revolutionize diagnosis, treatment, and personalized medicine, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- The accessibility and affordability of education can be significantly enhanced through the use of next technologies, fostering a more inclusive and equitable learning environment.
However, the adoption of next technologies also comes with inherent risks and ethical considerations.
- One of the primary concerns is the potential displacement of jobs due to automation, which could lead to social and economic inequalities.
- The use of AI and data analytics raises concerns about privacy and data security, as well as the potential for bias and discrimination in decision-making processes.
- The development and deployment of autonomous systems, such as self-driving vehicles, require careful consideration of safety, liability, and ethical implications.
Impact on Various Sectors
The impact of next technologies extends to various sectors, transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world.
Healthcare
Next technologies are poised to revolutionize healthcare, enabling personalized medicine, faster diagnosis, and more effective treatment. Advancements in AI, genomics, and medical imaging are enabling the development of new diagnostic tools and therapies tailored to individual patients. For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images and patient data to detect diseases at earlier stages, leading to more effective treatment and improved patient outcomes.
Education
Next technologies are transforming the educational landscape, creating more engaging and personalized learning experiences. AI-powered learning platforms can adapt to individual learning styles and provide personalized feedback, while virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies offer immersive and interactive learning environments. For instance, VR simulations can provide students with realistic experiences in various fields, such as healthcare, engineering, and aviation, enhancing their practical skills and knowledge.
Transportation
Next technologies are shaping the future of transportation, leading to more efficient, sustainable, and connected mobility solutions. The development of self-driving vehicles has the potential to reduce traffic congestion, improve road safety, and enhance accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges. Advancements in electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies are paving the way for a more sustainable transportation sector.
Energy
Next technologies are crucial for addressing the global energy crisis and transitioning to a more sustainable future. Advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy, are enabling the development of clean and efficient energy sources. AI and data analytics are playing a key role in optimizing energy production, distribution, and consumption, leading to reduced energy costs and environmental impact.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Emerging Technologies
| Technology | Sector | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI | Healthcare, Education, Transportation, Energy | Improved diagnosis, personalized learning, autonomous vehicles, energy optimization | Job displacement, privacy concerns, bias and discrimination |
| Robotics | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Agriculture | Increased productivity, precision tasks, improved safety | Job displacement, ethical concerns, potential for misuse |
| Biotechnology | Healthcare, Agriculture, Environment | Gene therapy, disease prevention, sustainable agriculture | Ethical concerns, potential for misuse, unintended consequences |
| Nanotechnology | Materials science, Medicine, Electronics | Improved materials, targeted drug delivery, advanced electronics | Health risks, environmental concerns, potential for misuse |
| Blockchain | Finance, Supply chain, Healthcare | Secure transactions, transparency, data integrity | Scalability challenges, regulatory uncertainties, potential for misuse |
The Future of Next Technology
The future of next technology is a dynamic landscape shaped by the convergence of emerging trends and research areas. This convergence fosters a future where technological boundaries blur, creating novel solutions and possibilities.
Emerging Trends and Research Areas
Emerging trends and research areas play a crucial role in shaping the future of next technology. These areas push the boundaries of innovation, leading to breakthroughs that redefine our technological landscape.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI continues to evolve rapidly, with advancements in machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. This progress fuels the development of intelligent systems capable of automating complex tasks, enhancing decision-making, and personalizing user experiences. For example, AI-powered chatbots are revolutionizing customer service, providing instant responses and personalized interactions.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to solve problems that are intractable for classical computers. This technology holds immense potential for drug discovery, materials science, and cryptography. For instance, quantum computers could revolutionize drug development by simulating molecular interactions with unprecedented accuracy.
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Advancements in biotechnology and bioengineering are transforming healthcare, agriculture, and environmental science. These fields are leading to innovations such as gene editing, personalized medicine, and sustainable agriculture. For example, CRISPR-Cas9 technology allows scientists to modify genes with precision, offering new possibilities for treating genetic diseases.
- Extended Reality (XR): XR encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), technologies that create immersive experiences by blending the physical and digital worlds. XR is finding applications in gaming, training, healthcare, and design, enabling users to interact with virtual environments and objects in new ways.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data. This technology is driving innovation in smart homes, cities, and industries, enabling greater automation, efficiency, and data-driven insights. For example, smart home devices can automate tasks such as temperature control, lighting, and security.
Convergence and Integration of Technologies, Next technology
The convergence and integration of different technologies are key drivers of the future of next technology. This convergence creates synergistic effects, enabling the development of more powerful and versatile solutions.
- AI and IoT: The integration of AI and IoT allows for intelligent devices that can learn from data and adapt to changing environments. This combination enables smart homes, factories, and cities that can optimize resource usage and improve efficiency.
- XR and AI: XR technologies combined with AI can create immersive and interactive experiences that are tailored to individual users. This convergence has applications in training, education, and entertainment, providing personalized and engaging learning experiences.
- Biotechnology and AI: The integration of biotechnology and AI is accelerating drug discovery, personalized medicine, and diagnostics. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify potential drug targets, predict patient responses to treatments, and develop personalized treatment plans.
Timeline of Key Milestones and Predictions
The future of next technology is characterized by a rapid pace of innovation and a constant stream of breakthroughs. This timeline highlights key milestones and predictions for the future development of next technology.
| Year | Milestone/Prediction | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Widespread adoption of AI-powered assistants | AI assistants will become ubiquitous, providing personalized support in various aspects of life, from scheduling and communication to healthcare and finance. |
| 2030 | Quantum computers solve real-world problems | Quantum computers will begin to address complex problems in fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and cryptography, leading to significant breakthroughs. |
| 2035 | Immersive XR experiences become commonplace | XR technologies will create immersive and interactive experiences in gaming, entertainment, education, and training, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. |
| 2040 | Bioengineered materials revolutionize industries | Bioengineered materials with unique properties will transform industries such as construction, aerospace, and medicine, leading to lighter, stronger, and more sustainable products. |
| 2050 | The emergence of a truly interconnected world | The convergence of next technologies will create a highly interconnected world, where data flows seamlessly and intelligent systems collaborate to address global challenges. |
Responsible Innovation and Ethical Considerations: Next Technology

The rapid advancement of next technologies presents both immense opportunities and significant ethical challenges. It is crucial to consider the potential impact of these technologies on society and ensure that their development and deployment are guided by ethical principles. This section explores some of the key ethical dilemmas associated with next technologies and highlights the importance of responsible innovation.
Ethical Challenges and Dilemmas
The potential misuse of next technologies poses a serious threat to individual privacy, societal well-being, and global security. It is essential to address these ethical concerns proactively and establish robust frameworks to mitigate potential risks.
- Privacy Concerns: Next technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy violations. For example, facial recognition systems can be used for surveillance without individuals’ consent, potentially leading to discriminatory practices or breaches of privacy.
- Bias in AI Algorithms: AI algorithms are trained on large datasets, which can reflect existing societal biases. This can lead to biased outcomes, perpetuating discrimination and inequality. For example, AI-powered hiring systems have been found to discriminate against certain demographic groups based on their gender or ethnicity.
- Potential Misuse of Technology: Next technologies can be misused for malicious purposes, such as creating deepfakes to spread misinformation or developing autonomous weapons systems that could lead to unintended consequences.
Importance of Responsible Innovation
Responsible innovation is essential for ensuring that next technologies are developed and deployed ethically and sustainably. It involves considering the social, environmental, and ethical implications of technological advancements throughout the entire innovation process.
“Responsible innovation is about ensuring that the benefits of technological progress are shared equitably and that the risks are mitigated effectively.” – World Economic Forum
Ethical Frameworks for Next Technology
To address the ethical challenges associated with next technologies, it is crucial to establish clear ethical frameworks that guide their development and deployment. These frameworks should consider principles such as:
- Transparency: The development and deployment of next technologies should be transparent, allowing for public scrutiny and accountability.
- Accountability: Clear lines of accountability should be established for the use and potential misuse of next technologies.
- Fairness: Next technologies should be developed and deployed in a fair and equitable manner, avoiding discrimination or bias.
- Privacy: Individuals’ privacy should be respected and protected in the development and use of next technologies.
- Security: Robust security measures should be implemented to prevent the misuse of next technologies.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Solutions
| Emerging Technology | Ethical Considerations | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Bias in algorithms, privacy violations, job displacement | Develop AI algorithms that are transparent, explainable, and fair. Implement robust data privacy regulations. Provide training and support for workers affected by automation. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Data security breaches, privacy violations, potential for misuse | Implement strong cybersecurity measures. Ensure data is collected and used ethically. Develop clear guidelines for the use of IoT devices. |
| Biotechnology | Genetic engineering, potential for harm, ethical dilemmas | Establish clear ethical guidelines for genetic engineering. Ensure public engagement and transparency in research and development. Develop mechanisms for monitoring and controlling the use of biotechnology. |
| Quantum Computing | Potential for misuse, security risks, economic inequality | Develop robust cybersecurity measures for quantum computers. Promote responsible research and development. Ensure equitable access to the benefits of quantum computing. |
Conclusive Thoughts
As we navigate the exciting and complex landscape of next technology, it’s crucial to approach innovation with a sense of responsibility. By fostering ethical frameworks, promoting collaboration, and embracing the transformative potential of these advancements, we can harness the power of next technology to create a brighter future for all.
Next technology is constantly evolving, and one area that’s experiencing rapid growth is cloud network technology in Singapore. This sector is attracting significant investment and innovation, with companies exploring new ways to leverage the cloud for enhanced connectivity, security, and scalability.
As a result, the future of technology in Singapore, and beyond, looks incredibly bright.