Millimeter Wave Technology Body Scanners: A Look Inside
Millimeter wave technology body scanners, a recent advancement in security screening, are revolutionizing how we detect potential threats. This technology, using non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation, creates detailed images of a person’s […]

Millimeter wave technology body scanners, a recent advancement in security screening, are revolutionizing how we detect potential threats. This technology, using non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation, creates detailed images of a person’s body without exposing them to harmful X-rays. It’s a powerful tool with applications beyond airport security, ranging from healthcare to law enforcement.
Millimeter wave scanners work by emitting radio waves that bounce off the surface of the body, creating a detailed image. These scanners can differentiate between organic and inorganic materials, allowing security personnel to identify objects hidden beneath clothing. This technology is incredibly sensitive, capable of detecting even the smallest items, like a small knife or a cell phone.
Introduction to Millimeter Wave Technology

Millimeter wave (mmWave) technology is a form of electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). These waves are much shorter than traditional microwaves, allowing for higher bandwidth and data transfer rates. In recent years, mmWave technology has emerged as a promising solution for various applications, including high-speed wireless communication, imaging, and security screening.
Millimeter waves interact with objects differently than lower frequency waves. They are absorbed by water and organic materials, making them ideal for imaging and detecting objects hidden under clothing. This unique property has led to the development of mmWave body scanners, which are increasingly used in airports and other security checkpoints.
Principles of Millimeter Wave Technology
Millimeter wave technology operates by transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves in the millimeter wavelength range. The waves are emitted from an antenna and reflected back by objects in their path. The reflected waves are then processed to create an image of the object. The intensity of the reflected waves is dependent on the object’s material properties, such as its density, water content, and dielectric constant.
The image produced by a mmWave scanner is not a photographic image but rather a representation of the object’s reflectivity. This type of image is called a “backscatter” image. Backscatter images are often displayed in grayscale, with darker areas representing higher reflectivity and lighter areas representing lower reflectivity.
Advantages of Millimeter Wave Technology in Body Scanners
Millimeter wave technology offers several advantages over traditional metal detectors and X-ray scanners for security screening purposes.
- Non-invasive: Millimeter wave scanners do not use ionizing radiation, which is known to be harmful to human health. This makes them safer for frequent use, especially for children and pregnant women.
- High resolution: The short wavelengths of millimeter waves allow for high-resolution imaging, enabling the detection of small objects that may be missed by other security technologies.
- Penetration through clothing: Millimeter waves can penetrate through most clothing materials, allowing for the detection of concealed weapons and other prohibited items.
- Fast scanning: Millimeter wave scanners can scan individuals quickly, minimizing wait times at security checkpoints.
Disadvantages of Millimeter Wave Technology in Body Scanners
Despite their advantages, millimeter wave body scanners also have some limitations.
- Privacy concerns: The ability of millimeter wave scanners to create detailed images of the human body has raised privacy concerns. Critics argue that the technology could be used to obtain sensitive information about individuals, such as their body shape and clothing.
- False positives: Millimeter wave scanners can sometimes produce false positives, which can lead to delays and inconvenience for travelers. This is due to the fact that the technology is sensitive to variations in body composition and clothing materials.
- Cost: Millimeter wave body scanners are relatively expensive to purchase and operate, which can be a barrier to their widespread adoption.
Real-World Applications of Millimeter Wave Technology
Beyond security screening, millimeter wave technology has a wide range of applications in various fields.
- Wireless communication: Millimeter waves offer high bandwidth and low latency, making them ideal for next-generation wireless communication networks, such as 5G and beyond.
- Medical imaging: Millimeter wave imaging is used in medical applications, such as breast cancer screening and non-invasive monitoring of vital signs.
- Industrial inspection: Millimeter wave technology is used for non-destructive testing of materials, such as detecting defects in aircraft parts and inspecting pipelines.
- Autonomous vehicles: Millimeter wave sensors are used in autonomous vehicles for object detection and navigation in challenging weather conditions.
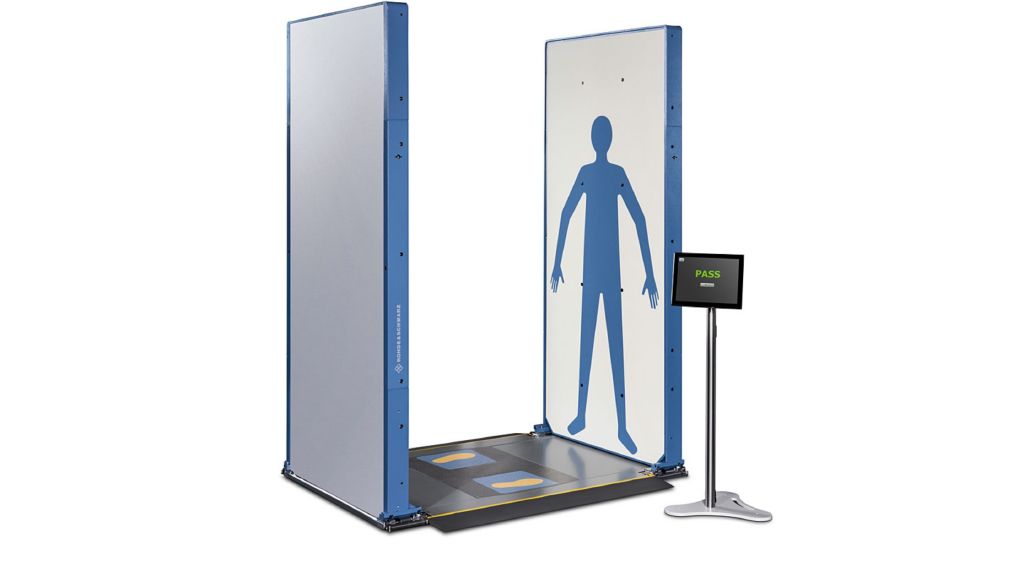
Millimeter Wave Body Scanners
Millimeter wave body scanners are a type of security screening technology used in airports and other high-security locations. These scanners use non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation in the millimeter wave range to create an image of a person’s body without exposing them to harmful X-rays.
How Millimeter Wave Body Scanners Work
Millimeter wave body scanners emit a low-power beam of millimeter waves that are reflected back from the person being scanned. The scanner’s antenna then captures these reflected waves, which are processed by a computer to create a 3D image of the person’s body.
The image produced by the scanner shows the general Artikel of the person’s body, including clothing and any objects concealed beneath it. However, the image does not reveal any personal details, such as the person’s face, skin color, or gender.
Components of a Millimeter Wave Body Scanner
A typical millimeter wave body scanner consists of the following components:
- Millimeter wave emitter: This component generates the millimeter wave beam that is used to scan the person.
- Antenna: This component receives the reflected millimeter waves from the person being scanned.
- Signal processor: This component processes the received signals and converts them into a 3D image of the person’s body.
- Display: This component displays the 3D image of the person’s body to the security officer.
- Control panel: This component allows the security officer to control the scanner and adjust its settings.
Differentiating Between Organic and Inorganic Materials, Millimeter wave technology body scanner
Millimeter waves interact differently with organic and inorganic materials. Organic materials, such as skin, flesh, and clothing, absorb millimeter waves, while inorganic materials, such as metal and plastic, reflect millimeter waves. This difference in interaction allows the scanner to distinguish between organic and inorganic materials in the human body.
For example, if a person is carrying a metal object, such as a gun, the scanner will detect the metal object as a distinct anomaly on the 3D image. This is because the metal object will reflect the millimeter waves differently than the surrounding organic materials.
The scanner’s ability to differentiate between organic and inorganic materials is crucial for its effectiveness as a security screening tool. It allows security officers to identify potential threats, such as weapons, explosives, and other contraband, that may be concealed beneath a person’s clothing.
Applications of Millimeter Wave Body Scanners
Millimeter wave body scanners are rapidly gaining popularity across various industries and sectors due to their non-invasive nature and ability to detect concealed objects. These scanners are proving to be a valuable tool in enhancing security, improving healthcare practices, and facilitating efficient operations.
Applications in Different Sectors
The use of millimeter wave body scanners extends beyond traditional security applications. Here are some key sectors where these scanners are making a significant impact:
- Airports: Airports are one of the primary users of millimeter wave body scanners, playing a crucial role in passenger screening and security. These scanners effectively detect concealed weapons, explosives, and other prohibited items, significantly enhancing airport security.
- Prisons: In prisons, millimeter wave body scanners are used for contraband detection, helping to maintain a safe and secure environment for both inmates and staff. These scanners can detect concealed weapons, drugs, and other prohibited items that could be smuggled into the prison.
- Hospitals: Millimeter wave body scanners are increasingly being used in hospitals for patient screening and security. These scanners can detect concealed weapons or other prohibited items that could pose a threat to patients, staff, or visitors.
- Courthouses: Millimeter wave body scanners are also used in courthouses to screen individuals entering the building for weapons or other prohibited items, ensuring a safe and secure environment for legal proceedings.
- Schools and Universities: Some schools and universities are using millimeter wave body scanners to enhance security and prevent the entry of weapons or other prohibited items onto school grounds.
- Stadiums and Events: Millimeter wave body scanners are increasingly being used at large-scale events like concerts, sporting events, and conferences to enhance security and prevent the entry of prohibited items.
Benefits and Challenges of Millimeter Wave Body Scanners
Millimeter wave body scanners offer numerous benefits in various settings, but it is important to acknowledge the challenges associated with their use:
Benefits
- Non-Invasive: Unlike traditional metal detectors, millimeter wave body scanners do not require physical contact, making them a more comfortable and less intrusive screening method.
- High Detection Rate: These scanners are highly effective at detecting a wide range of concealed objects, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and explosives.
- Speed and Efficiency: Millimeter wave body scanners can quickly and efficiently screen large numbers of individuals, making them ideal for high-traffic areas like airports and prisons.
- Privacy-Preserving: Millimeter wave body scanners do not produce detailed images of the individual’s body, ensuring privacy and minimizing the risk of embarrassing situations.
Challenges
- Cost: Millimeter wave body scanners can be expensive to purchase and maintain, which may be a significant barrier for some organizations.
- False Positives: Like any screening technology, millimeter wave body scanners can produce false positives, requiring additional inspection and potentially delaying the screening process.
- Privacy Concerns: Despite the technology’s privacy-preserving nature, some individuals may have concerns about the use of millimeter wave body scanners, especially regarding the potential for misuse or data breaches.
- Technical Complexity: Millimeter wave body scanners require specialized training and expertise to operate and maintain effectively.
Case Studies of Successful Deployments
Millimeter wave body scanners have been successfully deployed in various settings, demonstrating their effectiveness in enhancing security and improving operational efficiency.
Airports
- The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) in the United States: The TSA has deployed millimeter wave body scanners at major airports across the country, significantly enhancing airport security and reducing the number of prohibited items being smuggled onto airplanes.
Prisons
- The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) in the United States: The BOP has implemented millimeter wave body scanners in several federal prisons, effectively reducing the smuggling of contraband and enhancing the safety of both inmates and staff.
Hospitals
- The University of Pennsylvania Hospital: The University of Pennsylvania Hospital has deployed millimeter wave body scanners to screen visitors and ensure the safety of patients and staff. The scanners have been effective in detecting concealed weapons and other prohibited items, improving the security of the hospital environment.
Privacy and Security Considerations: Millimeter Wave Technology Body Scanner
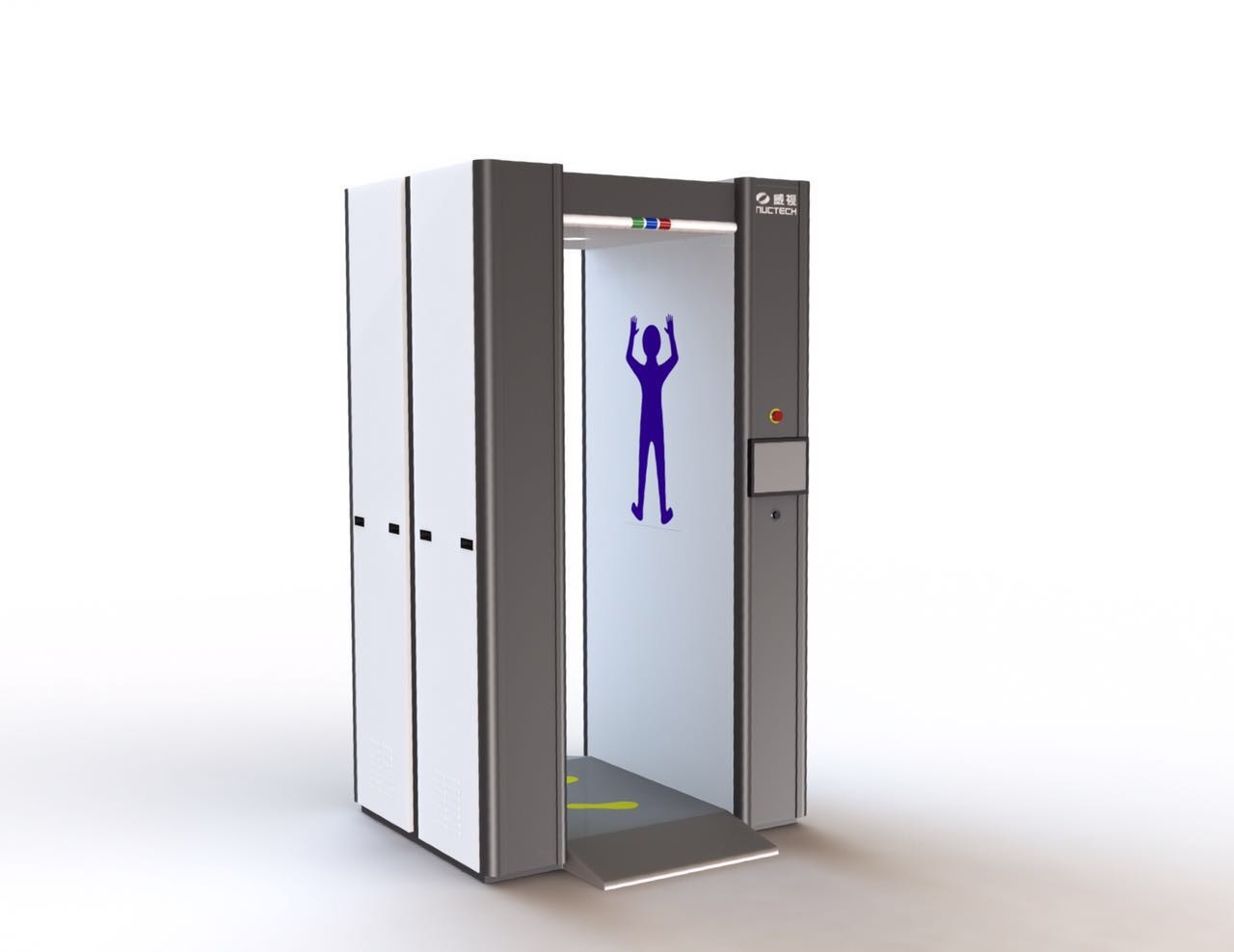

Millimeter wave body scanners, while offering numerous benefits, raise valid concerns about privacy and security. The technology’s ability to create detailed images of individuals’ bodies, albeit non-invasive, raises questions about the potential for misuse and the need for robust safeguards to protect personal information.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns arise from the detailed images generated by millimeter wave scanners. The images can reveal personal details, including clothing, body shape, and even medical conditions. There are potential concerns regarding the storage, access, and potential misuse of these images.
- Unintentional Disclosure: There’s a risk of unintentional disclosure of sensitive information if security protocols are not robust enough. Unauthorized access to stored images could lead to privacy violations.
- Data Retention Policies: Clear guidelines and policies on data retention are crucial to ensure that personal information is not stored for longer than necessary. The potential for misuse increases if data is retained indefinitely.
- Purpose and Scope: The purpose and scope of data collection must be clearly defined and communicated to individuals being scanned. Transparent procedures and informed consent are essential to address privacy concerns.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations surrounding data collection and storage from millimeter wave scans are paramount. It is crucial to ensure that the technology is used responsibly and ethically, respecting individual privacy and autonomy.
- Informed Consent: Individuals should be fully informed about the technology’s capabilities, data collection practices, and the potential risks associated with scanning. Obtaining informed consent is crucial to ensure ethical use.
- Data Minimization: Only essential data should be collected and stored, minimizing the potential for misuse and safeguarding privacy. This principle emphasizes the importance of collecting only the necessary information.
- Data Anonymization: Measures should be implemented to anonymize data, removing any identifiable information. This practice reduces the risk of personal information being linked to specific individuals, protecting their privacy.
Security Measures
Robust security measures are essential to protect the privacy and confidentiality of individuals scanned using millimeter wave technology. These measures aim to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse of personal information.
- Encryption: All data collected and stored should be encrypted using strong algorithms to prevent unauthorized access. Encryption safeguards data during transmission and storage.
- Access Control: Access to scanned images and data should be restricted to authorized personnel with legitimate reasons for accessing the information. Strict access control mechanisms are crucial to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits should be conducted to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Audits ensure that security measures are effective and updated to address emerging threats.
Future Developments and Trends
Millimeter wave body scanning technology is a rapidly evolving field with significant potential for future advancements. The ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance its capabilities, improve user experience, and expand its applications beyond security screening.
Advancements in Millimeter Wave Technology
Several exciting advancements are shaping the future of millimeter wave body scanning.
- Enhanced Image Resolution and Accuracy: Researchers are continuously improving the resolution and accuracy of millimeter wave imaging by developing more sophisticated algorithms and using advanced antenna designs. This leads to clearer and more detailed images, enabling more precise detection of concealed objects. For example, recent research has explored the use of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to enhance image processing, resulting in improved object identification and reduced false alarms.
- Real-time Image Analysis: The integration of real-time image analysis capabilities is another crucial development. By incorporating AI and machine learning, millimeter wave scanners can automatically analyze images and detect potential threats in real time. This eliminates the need for manual inspection and speeds up the screening process.
- Miniaturization and Portability: Efforts are underway to miniaturize millimeter wave technology, making it more portable and adaptable for diverse applications. This trend is driven by the increasing demand for on-the-go security solutions, such as personal security devices and mobile scanners.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing millimeter wave technology by enabling more intelligent and efficient screening processes.
- Automated Threat Detection: AI algorithms can be trained to identify specific objects or patterns associated with potential threats. This enables automated threat detection, reducing the workload of security personnel and minimizing the risk of human error. For instance, AI can be trained to distinguish between harmless items and weapons, leading to more accurate and efficient screening.
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency: AI-powered algorithms can analyze large volumes of data and identify subtle patterns that might be missed by human operators. This results in improved accuracy and efficiency in detecting concealed objects, leading to faster screening times and fewer false alarms. A real-life example is the use of AI in airport security, where it helps identify suspicious objects with greater accuracy, reducing the need for manual inspection and improving overall efficiency.
- Personalized Screening: AI can be used to personalize screening processes based on individual risk profiles. This allows for more targeted and efficient screening, reducing the need for unnecessary scans and improving the overall user experience. For example, frequent travelers with a low-risk profile could benefit from faster and more streamlined screening processes, while individuals with a higher risk profile might require more thorough scans.
Applications Beyond Security Screening
Millimeter wave technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries beyond security screening.
- Medical Imaging: Millimeter wave technology can be used for non-invasive medical imaging, providing detailed information about internal organs and tissues without the use of ionizing radiation. This has the potential to revolutionize medical diagnostics and treatment planning, leading to earlier detection of diseases and more effective treatment options.
- Industrial Inspection: Millimeter wave technology can be used for non-destructive testing in industrial settings, allowing for the inspection of materials and structures without causing damage. This is particularly useful for identifying defects in complex structures, such as bridges and aircraft, ensuring safety and reliability.
- Environmental Monitoring: Millimeter wave technology can be used for remote sensing and environmental monitoring, providing valuable information about atmospheric conditions, pollution levels, and other environmental factors. This data can be used to develop more effective environmental management strategies and protect the environment.
Conclusion
Millimeter wave technology body scanners represent a significant step forward in security screening. While concerns about privacy exist, advancements in data protection and ethical considerations are continuously being addressed. As technology evolves, we can expect even more innovative applications of millimeter wave technology, impacting various sectors and improving safety in the future.
Millimeter wave technology body scanners are becoming increasingly popular for security purposes, offering a non-invasive way to detect concealed objects. These scanners use high-frequency radio waves to create detailed images of a person’s body, which can be analyzed for potential threats.
Companies like spec technologies are leading the way in developing advanced millimeter wave technology for a variety of applications, including airport security, law enforcement, and even healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for millimeter wave body scanners in the future.