HR Technology Stack: Building a Modern HR Ecosystem
HR Technology Stack, a term that encompasses the array of software and tools used by HR departments to manage and optimize all aspects of the employee lifecycle, has become a […]
HR Technology Stack, a term that encompasses the array of software and tools used by HR departments to manage and optimize all aspects of the employee lifecycle, has become a cornerstone of modern organizations. From recruiting and onboarding to performance management and employee engagement, these technologies streamline processes, improve efficiency, and empower HR professionals to make data-driven decisions.
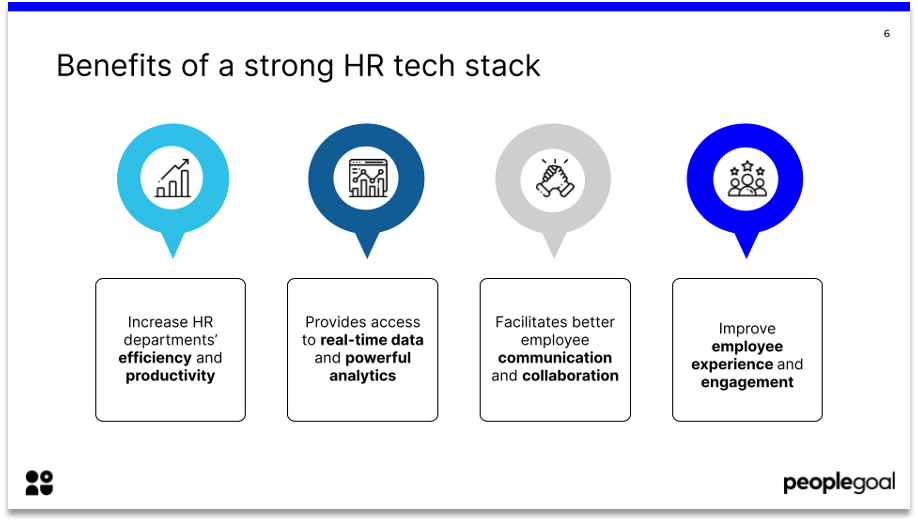
The HR technology stack has evolved significantly over the years, moving from isolated, single-purpose applications to integrated platforms that connect different HR functions. This shift has been driven by the increasing need for data-driven insights, automation, and seamless integration across the HR ecosystem. Today’s modern HR technology stacks often include core HR systems, recruiting and talent acquisition tools, learning and development platforms, employee engagement and communication software, and data analytics solutions.
Introduction to HR Technology Stack
In the dynamic world of human resources, technology plays a crucial role in streamlining processes, enhancing efficiency, and improving employee experiences. The concept of an HR technology stack encompasses the suite of software tools and applications that HR departments use to manage various aspects of their operations.
This stack has evolved significantly over time, adapting to the changing needs of businesses and the rise of new technologies. The evolution of HR technology stacks has been driven by several factors, including:
Evolution of HR Technology Stacks
The evolution of HR technology stacks can be traced back to the early days of computerized payroll and personnel management systems. Over time, the stack has expanded to include a wide range of functionalities, encompassing talent acquisition, performance management, learning and development, compensation and benefits, and employee engagement.
- Early Days: Initially, HR technology stacks were primarily focused on automating administrative tasks such as payroll processing and employee record-keeping. These systems were typically standalone and lacked integration capabilities.
- Emergence of Integrated Solutions: The introduction of integrated HR software suites, such as SAP SuccessFactors and Oracle HCM Cloud, marked a significant shift. These solutions offered a comprehensive suite of modules covering various HR functions, facilitating data sharing and process automation across different departments.
- Rise of Cloud Computing: The advent of cloud computing further revolutionized HR technology stacks. Cloud-based solutions offered greater flexibility, scalability, and affordability, making them accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- Focus on Employee Experience: Modern HR technology stacks prioritize employee engagement and experience. This includes features like employee self-service portals, mobile-friendly applications, and personalized communication tools.
- Integration with Other Business Systems: The integration of HR technology stacks with other business systems, such as CRM and ERP, has become increasingly important. This enables data sharing and process automation across different departments, creating a more holistic view of the workforce.
Key Components of a Modern HR Technology Stack
A modern HR technology stack typically includes the following key components:
- Applicant Tracking System (ATS): This software helps organizations manage the recruitment process, from job postings to candidate screening and onboarding. Examples include Greenhouse, Workday Recruiting, and Taleo.
- Human Capital Management (HCM) System: An HCM system provides a comprehensive suite of modules for managing core HR functions, such as payroll, benefits, talent management, and employee performance. Examples include Workday, Oracle HCM Cloud, and SAP SuccessFactors.
- Learning Management System (LMS): An LMS facilitates the delivery and tracking of training programs, online courses, and other learning materials. Examples include Cornerstone OnDemand, LinkedIn Learning, and Moodle.
- Performance Management System: This software enables organizations to set goals, track progress, provide feedback, and conduct performance reviews. Examples include Lattice, BambooHR, and 15Five.
- Employee Engagement Platform: An employee engagement platform provides tools for communication, collaboration, and recognition. Examples include Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Culture Amp.
- Compensation and Benefits Management System: This software helps organizations manage compensation plans, benefits programs, and payroll. Examples include Paychex, ADP, and Zenefits.
- Talent Acquisition Analytics: These tools provide insights into recruitment metrics, such as time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, and candidate source effectiveness. Examples include Google Analytics, Tableau, and Power BI.
- HR Chatbots: HR chatbots are AI-powered tools that can automate common HR tasks, such as answering employee questions, scheduling appointments, and processing requests. Examples include Olivia, Ada, and Kasisto.
Core HR Technology Solutions
Core HR technology solutions are the foundation of any modern HR department. They encompass systems that manage essential HR functions, such as payroll, benefits, and talent management. These solutions streamline administrative tasks, improve data accuracy, and provide valuable insights into the workforce.
The Role of Core HR Systems
Core HR systems play a crucial role in managing various HR functions.
- Payroll: Payroll systems automate the process of calculating and distributing employee salaries, deductions, and taxes. They ensure timely and accurate payments, comply with tax regulations, and provide comprehensive reporting.
- Benefits: Benefits management systems handle the administration of employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and life insurance. They allow employees to enroll in benefits, track usage, and manage their benefit information.
- Talent Management: Talent management systems encompass a range of functionalities, including recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and learning and development. They help organizations attract, retain, and develop their workforce.
Benefits of Cloud-Based HR Solutions
Cloud-based HR solutions offer numerous benefits, including:
- Accessibility: Employees can access HR information and services from any device with an internet connection. This eliminates the need for on-premise software and physical infrastructure.
- Scalability: Cloud-based solutions can easily scale up or down as an organization’s needs change. This eliminates the need for expensive hardware upgrades.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based solutions typically have lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premise systems. They also offer a predictable monthly subscription fee.
- Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Regular Updates: Cloud-based solutions are automatically updated with the latest features and security patches. This ensures that users have access to the most up-to-date functionality.
Challenges of Cloud-Based HR Solutions
While cloud-based HR solutions offer numerous benefits, they also present some challenges:
- Internet Dependency: Cloud-based solutions rely on a stable internet connection. Interruptions in connectivity can disrupt access to HR information and services.
- Data Security Concerns: While cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, there is always a risk of data breaches. It is important to choose a reputable cloud provider with strong security protocols.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating cloud-based HR solutions with other HR technology solutions can be complex. Organizations need to carefully consider compatibility and ensure seamless data flow.
- Vendor Lock-In: Switching cloud providers can be difficult and expensive. Organizations should carefully evaluate their options and choose a provider that meets their long-term needs.
Integration of Core HR Systems
Core HR systems need to seamlessly integrate with other HR technology solutions to create a comprehensive and efficient HR ecosystem. This integration enables data sharing, reduces manual processes, and provides a unified view of the workforce.
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS): Integrating core HR systems with ATS allows for a smooth transition from candidate applications to employee onboarding.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Integration with LMS enables organizations to track employee training and development activities and link them to performance evaluations.
- Performance Management Systems: Integration with performance management systems allows for real-time performance tracking and feedback, facilitating employee growth and development.
- Compensation and Benefits Systems: Integration with compensation and benefits systems ensures accurate and timely payments and provides employees with access to their benefit information.
Recruiting and Talent Acquisition Technology
In today’s competitive job market, HR departments rely heavily on technology to streamline the recruiting process and attract top talent. Recruiting and talent acquisition technology encompasses a range of tools designed to automate and enhance various stages of the hiring process, from candidate sourcing to onboarding.
Candidate Sourcing and Screening Tools
Candidate sourcing and screening tools are essential for identifying and evaluating potential candidates. These tools leverage various methods to reach out to qualified individuals and assess their suitability for open positions.
- Job Boards: Websites like Indeed, LinkedIn, Monster, and CareerBuilder allow employers to post job openings and attract a large pool of applicants. These platforms offer advanced search filters and candidate management features.
- Social Media: Social media platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter are increasingly used for talent acquisition. Companies can leverage these platforms to connect with potential candidates, share job openings, and build employer branding.
- Employee Referral Programs: Encouraging current employees to refer qualified candidates is a cost-effective and efficient way to find talent. Employee referral programs often offer incentives for successful referrals.
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS): ATS are software applications that manage the entire recruiting process, from application submission to candidate selection. They automate tasks like screening resumes, scheduling interviews, and tracking candidate progress. ATS can also help companies analyze candidate data and identify potential hiring biases.
- Pre-employment Assessments: Pre-employment assessments are standardized tests used to evaluate candidates’ skills, knowledge, and personality traits. These assessments can help companies identify candidates who are best suited for specific roles.
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), Hr technology stack
Applicant tracking systems (ATS) are widely used by organizations to manage the recruiting process. They streamline tasks and provide valuable insights into candidate data.
- Resume Parsing: ATS automatically extract key information from resumes, such as skills, experience, and education, and store it in a database. This allows recruiters to quickly search and filter candidates based on specific criteria.
- Candidate Communication: ATS automate communication with candidates, sending automated emails and notifications about application status, interview scheduling, and job offers.
- Candidate Pipelines: ATS create and manage candidate pipelines, tracking the progress of each candidate through the hiring process. This helps recruiters stay organized and avoid missing deadlines.
- Data Analytics: ATS provide data analytics capabilities, allowing companies to track key metrics such as time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, and candidate source. This data can be used to optimize the recruiting process and identify areas for improvement.
Social Media for Talent Acquisition
Social media platforms have become an integral part of talent acquisition strategies. Companies leverage social media to connect with potential candidates, build employer branding, and promote job openings.
- LinkedIn: LinkedIn is a professional networking platform that allows companies to connect with potential candidates, share job openings, and build their employer brand. Companies can use LinkedIn to search for qualified candidates, post job openings, and engage with potential employees.
- Facebook: Facebook’s large user base and targeted advertising options make it a valuable platform for reaching potential candidates. Companies can create Facebook pages to share job openings, engage with potential employees, and build their employer brand.
- Twitter: Twitter is a real-time platform that allows companies to share job openings, engage with potential candidates, and build their employer brand. Companies can use Twitter to participate in industry conversations, share company news, and promote job openings.
Data Analytics and Reporting in HR
In today’s competitive business landscape, data-driven decision-making is crucial for HR departments to optimize their operations and achieve strategic goals. By leveraging data analytics, HR can gain valuable insights into their workforce, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions that drive business success.
The Importance of Data-Driven Decision-Making in HR
Data-driven decision-making in HR allows organizations to move beyond gut feelings and anecdotal evidence, enabling them to make informed decisions based on objective data. By analyzing data, HR professionals can gain a deeper understanding of their workforce, identify trends, and measure the effectiveness of their programs and initiatives. This approach helps HR departments to:
- Improve workforce planning and talent acquisition: Data can help HR teams understand current workforce demographics, identify future talent needs, and predict potential talent shortages. This information can be used to develop targeted recruitment strategies and ensure the organization has the right skills and talent to meet its business objectives.
- Optimize employee performance and engagement: HR analytics can be used to identify factors that contribute to employee engagement and performance. This information can be used to develop targeted training programs, improve employee communication, and create a more positive work environment.
- Reduce employee turnover: By analyzing data on employee turnover, HR can identify the root causes of attrition and implement strategies to retain valuable employees. This can include targeted retention programs, addressing employee concerns, and creating a more positive work environment.
- Improve HR efficiency and effectiveness: Data analytics can help HR teams automate routine tasks, streamline processes, and improve the efficiency of their operations. This frees up time for HR professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Using HR Analytics Tools to Measure Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
HR analytics tools provide a powerful platform for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing HR data. These tools can be used to track key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure the effectiveness of HR programs and initiatives. Examples of important KPIs include:
- Time to fill: This metric measures the average time it takes to fill open positions. A shorter time to fill indicates an efficient recruitment process.
- Employee turnover rate: This metric measures the percentage of employees who leave the organization within a specific period. A lower turnover rate indicates higher employee retention.
- Employee engagement scores: This metric measures employee satisfaction and commitment to the organization. Higher engagement scores indicate a more positive work environment.
- Training effectiveness: This metric measures the impact of training programs on employee performance and knowledge acquisition.
- Diversity and inclusion metrics: These metrics track the representation of different groups within the workforce and measure progress towards diversity and inclusion goals.
Examples of How Data Can Be Used to Improve HR Processes and Outcomes
Here are some examples of how data can be used to improve HR processes and outcomes:
- Identifying high-potential employees: HR analytics can be used to identify employees who have the potential for future leadership roles. This can be done by analyzing data on performance, engagement, and skills development.
- Personalizing employee development plans: Data can be used to tailor employee development plans to individual needs and career aspirations. This can include identifying skills gaps, recommending relevant training programs, and providing personalized career guidance.
- Optimizing compensation and benefits: HR analytics can be used to ensure that compensation and benefits packages are competitive and aligned with market trends. This can help attract and retain top talent.
- Improving employee communication: Data can be used to identify communication gaps and develop more effective communication strategies. This can include using data to understand employee preferences for communication channels and tailoring messages accordingly.
Implementing and Managing an HR Technology Stack

Successfully implementing and managing an HR technology stack requires careful planning, consideration of various factors, and a strategic approach. This section will delve into the challenges and considerations involved in selecting and implementing HR technology, providing guidance on integrating HR technology with existing systems and processes, and analyzing the importance of data security and compliance in managing an HR technology stack.
Challenges and Considerations in Selecting and Implementing HR Technology
Selecting and implementing HR technology involves various challenges and considerations. It’s essential to understand these factors to make informed decisions and ensure a successful implementation.
- Defining Clear Business Objectives: Before embarking on the selection process, clearly define your business objectives and how HR technology can contribute to achieving them. This includes identifying specific pain points, areas for improvement, and desired outcomes.
- Budget and Resource Allocation: Determine the budget allocated for HR technology and allocate resources effectively. Consider the cost of software licenses, implementation services, training, and ongoing maintenance.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Evaluate the compatibility of the chosen HR technology with your existing systems, such as payroll, benefits, and learning management systems. Seamless integration is crucial for data consistency and operational efficiency.
- Data Security and Compliance: Prioritize data security and compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Choose HR technology solutions that adhere to industry best practices and offer robust security measures.
- User Adoption and Training: Ensure that the chosen HR technology is user-friendly and intuitive. Provide adequate training and support to employees to facilitate adoption and maximize its effectiveness.
- Vendor Selection and Evaluation: Carefully evaluate potential vendors based on their reputation, experience, customer support, and product features. Consider conducting proof-of-concept trials and seeking references from other organizations.
Integrating HR Technology with Existing Systems and Processes
Successful integration of HR technology with existing systems and processes is critical for a smooth transition and optimal utilization. Here’s a breakdown of the key considerations:
- Data Mapping and Migration: Develop a comprehensive data mapping plan to ensure accurate data transfer from existing systems to the new HR technology platform. This involves identifying data fields, data formats, and potential data discrepancies.
- Process Re-engineering: Evaluate current HR processes and identify areas for optimization and automation using the new technology. Streamline workflows and eliminate redundant tasks to improve efficiency.
- Change Management and Communication: Implement a robust change management plan to effectively communicate the benefits of the new technology to employees. Provide clear instructions, training, and ongoing support to minimize resistance and ensure smooth adoption.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regularly monitor the performance of the integrated HR technology stack and identify areas for improvement. Collect user feedback, analyze data, and make adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
Data Security and Compliance in Managing an HR Technology Stack
Data security and compliance are paramount in managing an HR technology stack. Organizations must implement robust measures to protect sensitive employee data and comply with relevant regulations.
- Data Encryption and Access Control: Implement strong data encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive employee information stored in the HR technology stack. Implement robust access control measures to limit access to authorized personnel.
- Regular Security Audits and Updates: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary security updates to mitigate risks. Ensure the HR technology platform is regularly patched and updated with the latest security measures.
- Compliance with Data Protection Regulations: Adhere to relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Ensure the HR technology platform complies with these regulations and implements appropriate data retention policies.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Establish comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure data integrity and availability in case of unforeseen events. Implement regular backups and test disaster recovery procedures to ensure data can be restored quickly and efficiently.
Case Studies and Best Practices: Hr Technology Stack
Successful HR technology implementations demonstrate the potential of technology to transform HR functions and enhance organizational performance. Examining these case studies reveals key factors contributing to the effectiveness of an HR technology stack and its role in achieving strategic HR goals.
Successful HR Technology Implementations
Real-world examples illustrate the transformative impact of HR technology on organizations.
- Netflix, a leading streaming service, uses a data-driven approach to talent management. Their HR technology stack supports performance reviews, talent development, and compensation decisions based on data and analytics. This approach helps them attract and retain top talent, fostering a culture of innovation and high performance.
- Adobe, a software company, leverages HR technology to streamline recruitment and onboarding processes. Their applicant tracking system automates tasks like candidate screening and communication, improving efficiency and reducing time-to-hire. Their onboarding platform provides a seamless experience for new hires, ensuring they are quickly integrated into the organization.
- Google, a technology giant, utilizes HR technology for employee engagement and development. Their performance management system encourages regular feedback and development goals, while their learning platform provides access to a wide range of training resources. These initiatives contribute to a highly engaged and productive workforce.
Factors Contributing to Effective HR Technology Stacks
Several key factors contribute to the success of HR technology implementations:
- Alignment with Business Goals: HR technology should be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. This ensures that the technology supports the achievement of key business goals, such as talent acquisition, employee engagement, and performance improvement.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: HR technology enables organizations to gather and analyze data on various HR metrics. This data can be used to inform decision-making, leading to more effective and data-driven HR practices.
- User-Friendly Interface: User-friendly technology is essential for adoption and engagement. Employees should find the technology intuitive and easy to use, maximizing its impact on their work.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating HR technology with other systems, such as payroll or learning management systems, ensures seamless data flow and avoids duplication of effort.
- Continuous Improvement: HR technology should be continuously evaluated and improved to meet evolving needs. Regular updates and enhancements ensure the technology remains relevant and effective over time.
Technology’s Role in Achieving Strategic HR Goals
HR technology plays a crucial role in achieving strategic HR goals:
- Talent Acquisition: HR technology can automate tasks like candidate screening and communication, reducing time-to-hire and improving the quality of hires. It can also enhance the candidate experience, attracting top talent.
- Employee Engagement: HR technology can facilitate employee communication, provide access to learning resources, and streamline performance management processes. These features contribute to a more engaged and productive workforce.
- Performance Management: HR technology enables organizations to track performance metrics, provide regular feedback, and identify areas for development. This data-driven approach improves employee performance and supports career growth.
- Organizational Culture: HR technology can support the creation and maintenance of a positive organizational culture. For example, employee communication platforms can foster collaboration and transparency, while employee recognition tools can boost morale and engagement.
Ultimate Conclusion
By strategically implementing and managing an HR technology stack, organizations can gain a competitive edge in attracting and retaining top talent, improving employee engagement, and driving business success. As technology continues to advance, the HR technology landscape will continue to evolve, offering new opportunities for HR professionals to innovate and optimize their operations. The future of HR is undoubtedly intertwined with technology, and those who embrace these advancements will be best positioned to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the modern workplace.
An HR technology stack encompasses various tools that streamline HR processes, from recruitment and onboarding to performance management and payroll. The rapid evolution of technology in other industries, like the one showcased at the ADAS & Autonomous Vehicle Technology Expo , is a reminder that HR technology needs to constantly adapt and innovate to remain relevant and competitive.
As AI and automation continue to reshape the workplace, HR technology stacks will need to embrace these advancements to effectively support the changing needs of organizations and their employees.