Strategic Management of Technological Innovation: A Roadmap for Success
Strategic management of technological innovation takes center stage as businesses navigate an ever-changing landscape. This dynamic field requires a blend of foresight, strategic planning, and agile execution to harness the […]

Strategic management of technological innovation takes center stage as businesses navigate an ever-changing landscape. This dynamic field requires a blend of foresight, strategic planning, and agile execution to harness the transformative power of technology. From identifying emerging trends to cultivating a culture of innovation, organizations must embrace a strategic approach to thrive in this competitive environment.
The success of any organization hinges on its ability to adapt and innovate. This is especially true in the face of rapid technological advancements. Strategic management of technological innovation provides a framework for organizations to identify, evaluate, and capitalize on emerging technologies, ultimately driving growth and competitive advantage.
Defining Strategic Management of Technological Innovation
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, technological innovation is no longer a mere option but a critical driver of competitive advantage. To harness the transformative power of technology, companies must adopt a strategic approach to innovation, aligning their technological endeavors with their overall business goals. This is where strategic management of technological innovation comes into play.
The Significance of Strategic Management in Technological Innovation
Strategic management of technological innovation involves a deliberate and systematic process of identifying, evaluating, and implementing technological opportunities that align with a company’s long-term vision, goals, and resources. It’s not simply about adopting the latest technology; it’s about understanding how technology can be leveraged to create sustainable competitive advantage.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: A strategic approach provides a framework for evaluating the potential impact of technological innovations on various aspects of the business, from product development and manufacturing to marketing and customer service. This enables informed decision-making regarding resource allocation and investment priorities.
- Improved Innovation Success Rates: By aligning innovation efforts with business goals, companies can focus on developing technologies that are more likely to resonate with their target market and contribute to revenue growth. This reduces the risk of investing in technologies that are not aligned with their strategic direction.
- Sustainable Competitive Advantage: Strategic management of technological innovation helps companies build and maintain a sustainable competitive advantage by creating new products, services, or business models that are difficult for competitors to replicate. This is particularly important in industries characterized by rapid technological change.
Key Elements of a Strategic Approach to Technological Innovation
A successful strategic approach to technological innovation encompasses several key elements.
- Clear Vision and Goals: Companies must have a clear vision of their desired future state and define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for their innovation efforts. This provides direction and alignment across the organization.
- Market Analysis and Opportunity Identification: Thorough market research is essential to identify emerging technologies, understand customer needs and preferences, and identify potential opportunities for innovation. This includes analyzing competitive landscapes, market trends, and technological advancements.
- Resource Allocation and Prioritization: Companies need to allocate resources strategically to support their innovation initiatives. This includes financial investments, human capital, and other essential resources. Prioritization ensures that the most promising innovations receive the necessary attention and support.
- Innovation Process Management: Establishing a structured innovation process is crucial for managing the development, testing, and implementation of new technologies. This process should include steps such as idea generation, feasibility analysis, prototyping, testing, and commercialization.
- Organizational Culture and Structure: A culture that encourages innovation, experimentation, and collaboration is essential for fostering a successful innovation environment. Companies need to create structures and processes that support open communication, knowledge sharing, and cross-functional collaboration.
- Risk Management and Mitigation: Technological innovation inherently involves risk. Companies need to develop strategies for identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks associated with new technologies. This includes considering factors such as market uncertainty, technological obsolescence, and regulatory changes.
- Measurement and Evaluation: Regularly tracking and evaluating the progress and impact of innovation initiatives is essential for making informed decisions and ensuring that efforts are aligned with strategic goals. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to measure the success of innovation initiatives.
Examples of Companies that Have Successfully Implemented Strategic Technological Innovation
Several companies have successfully implemented strategic technological innovation to achieve significant competitive advantages.
- Amazon: Amazon’s strategic approach to technological innovation has been instrumental in its success. The company has consistently invested in technologies such as cloud computing (Amazon Web Services), e-commerce platforms, and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance its customer experience, optimize operations, and expand into new markets. This strategic approach has enabled Amazon to become a global leader in e-commerce and cloud computing.
- Tesla: Tesla’s commitment to electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies has revolutionized the automotive industry. The company’s strategic focus on innovation has enabled it to develop groundbreaking technologies and capture a significant market share in the electric vehicle segment. Tesla’s success demonstrates the power of strategic technological innovation in disrupting established industries.
- Netflix: Netflix’s strategic approach to streaming video content has transformed the entertainment industry. The company’s early adoption of streaming technology and its focus on personalized recommendations have enabled it to become a global leader in video streaming. Netflix’s success highlights the importance of embracing emerging technologies and adapting to changing consumer preferences.
Identifying and Assessing Technological Opportunities

Identifying and assessing technological opportunities is a critical step in strategic management of technological innovation. It involves systematically exploring emerging technologies and their potential impact on the organization’s operations, products, services, and competitive landscape. This process requires a deep understanding of current and future technological trends, as well as the ability to analyze and evaluate the feasibility and viability of potential innovations.
Methods for Identifying Emerging Technologies
Identifying emerging technologies is the first step in the process. It involves scanning the technological landscape for new developments, trends, and breakthroughs that could have a significant impact on the organization’s industry or market. Here are some common methods:
- Trend Analysis: This involves monitoring industry publications, research reports, and expert opinions to identify emerging trends and technologies. It can help in understanding the direction of technological development and its potential impact on the industry.
- Competitive Intelligence: This involves analyzing the activities and strategies of competitors, including their investments in research and development, partnerships, and product launches. This can provide insights into emerging technologies that competitors are using or developing.
- Patents and Publications: Monitoring patent applications and scientific publications can reveal new technologies being developed and their potential applications. This can provide early insights into emerging technologies before they are widely known.
- Networking and Conferences: Attending industry conferences, workshops, and seminars, and networking with experts and researchers can provide access to the latest technological advancements and insights.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media platforms and online forums can reveal emerging trends and technologies that are gaining traction and generating buzz among industry experts and consumers.
Factors to Consider When Assessing Technological Opportunities
Once emerging technologies are identified, it is crucial to assess their feasibility and viability. This involves evaluating the technology’s potential impact on the organization’s business model, market position, and competitive landscape. Here are some factors to consider:
- Market Size and Growth Potential: Evaluate the size and growth potential of the market for the proposed innovation. A large and growing market can offer significant opportunities for revenue and profitability.
- Technological Feasibility: Assess the technical feasibility of developing and implementing the innovation. Consider the availability of necessary resources, expertise, and infrastructure.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the competitive landscape and identify potential competitors who may be developing or offering similar technologies. Assess the organization’s competitive advantage and its ability to differentiate itself from competitors.
- Financial Viability: Evaluate the financial viability of the innovation. Consider the costs of development, production, marketing, and distribution, as well as the potential for return on investment.
- Regulatory Environment: Consider the regulatory environment and any potential legal or ethical challenges that may arise from developing or implementing the innovation.
Frameworks for Evaluating Technological Opportunities
Various frameworks can be used to evaluate technological opportunities and prioritize them based on their potential impact and feasibility. These frameworks provide a structured approach for analyzing and comparing different opportunities. Here are some common frameworks:
- SWOT Analysis: This framework involves identifying the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It helps in evaluating the potential impact of a technological opportunity on the organization’s internal capabilities and external environment.
- Porter’s Five Forces: This framework analyzes the competitive forces within an industry, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, and the rivalry among existing competitors. It helps in understanding the competitive landscape and the potential impact of a technological opportunity on the organization’s market position.
- Value Chain Analysis: This framework examines the activities involved in creating, producing, delivering, and supporting a product or service. It helps in identifying the potential impact of a technological opportunity on different stages of the value chain and the organization’s cost structure and value proposition.
- The Technology Adoption Curve: This framework analyzes the rate of adoption of a new technology by different groups of consumers. It helps in understanding the potential market for a technological innovation and its expected growth trajectory.
Developing a Technological Innovation Strategy
A technological innovation strategy Artikels how an organization will leverage technology to achieve its business objectives. It is a critical element of any company’s strategic plan, particularly in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape. A well-defined strategy helps businesses navigate the complexities of technological advancements, identify opportunities for growth, and stay ahead of the competition.
Steps Involved in Developing a Technological Innovation Strategy
Developing a comprehensive technological innovation strategy involves a series of well-defined steps. These steps provide a structured approach to ensure that the strategy aligns with the company’s overall goals and addresses the specific challenges and opportunities presented by the technological environment.
- Define the organization’s vision and strategic goals: The first step is to clarify the organization’s vision for the future and establish clear strategic goals that are aligned with this vision. This involves considering the company’s competitive landscape, market trends, and the potential impact of technological advancements.
- Conduct a thorough internal and external analysis: This step involves assessing the organization’s current technological capabilities, resources, and infrastructure. It also entails analyzing the external environment, including market trends, competitor activities, and emerging technologies. This analysis helps identify areas for improvement, potential threats, and opportunities for innovation.
- Identify key technological trends and opportunities: Organizations must stay abreast of emerging technologies and their potential impact on their industry. This includes identifying trends that could disrupt existing business models, create new market opportunities, or enhance existing products and services.
- Develop a roadmap for technological innovation: Once key technological trends and opportunities have been identified, organizations must develop a roadmap that Artikels the specific steps they will take to leverage these opportunities. This roadmap should include timelines, resource allocation, and key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring progress.
- Establish a culture of innovation: Cultivating a culture of innovation is essential for successful technological innovation. This involves fostering an environment where employees feel empowered to experiment, take risks, and share ideas. It also requires providing employees with the necessary training and resources to develop their technological skills.
- Implement and monitor the strategy: Once the technological innovation strategy is developed, it must be implemented and closely monitored. This involves tracking progress against the established KPIs, adapting the strategy as needed, and ensuring that the organization is constantly learning and evolving.
Key Components of a Successful Technological Innovation Strategy
A successful technological innovation strategy encompasses several key components that contribute to its effectiveness and ensure alignment with the organization’s overall goals.
- Clear vision and strategic alignment: The strategy must be clearly aligned with the organization’s overall vision and strategic goals. This ensures that innovation efforts are focused on achieving the company’s objectives and creating long-term value.
- Focus on customer needs: The strategy should be driven by a deep understanding of customer needs and how technology can be used to enhance their experience. This customer-centric approach ensures that innovation efforts are relevant and valuable to the target market.
- Resource allocation and prioritization: Organizations must allocate resources effectively and prioritize innovation projects based on their potential impact and alignment with the strategic goals. This ensures that resources are used wisely and that the most promising opportunities are pursued.
- Collaboration and partnerships: Successful technological innovation often requires collaboration with external partners, such as universities, research institutions, or technology companies. This allows organizations to access specialized expertise, resources, and technologies that may not be available internally.
- Continuous learning and adaptation: The technological landscape is constantly evolving, so organizations must embrace continuous learning and adapt their strategies accordingly. This includes staying informed about emerging trends, evaluating new technologies, and adjusting the innovation roadmap as needed.
Examples of Technological Innovation Strategies
Different organizations employ various technological innovation strategies depending on their industry, business model, and strategic goals. Here are some examples of common technological innovation strategies:
- Disruptive Innovation: This strategy focuses on developing new technologies or products that disrupt existing markets and create new opportunities. For example, Uber disrupted the traditional taxi industry by leveraging technology to connect passengers with drivers through a mobile app.
- Incremental Innovation: This strategy involves making gradual improvements to existing products, services, or processes. For example, Apple continuously updates its iPhone with new features and capabilities, offering incremental improvements to its flagship product.
- Open Innovation: This strategy involves collaborating with external partners, such as universities, startups, or other companies, to develop new technologies or products. For example, Google’s Android operating system is based on open-source software, allowing developers worldwide to contribute to its development.
- Strategic Acquisitions: This strategy involves acquiring companies that possess valuable technologies or intellectual property. For example, Facebook acquired Instagram to gain access to its popular photo-sharing platform.
Organizational Structures and Cultures for Technological Innovation
The organizational structure and culture play a crucial role in fostering and promoting technological innovation within an organization. A conducive environment encourages experimentation, collaboration, and risk-taking, ultimately leading to successful innovation. This section will delve into the intricate relationship between organizational structures, cultures, and technological innovation, exploring how each element influences the other.
The Role of Organizational Structure in Fostering Technological Innovation
Organizational structure refers to the formal arrangement of tasks, roles, and reporting relationships within an organization. It determines how information flows, decisions are made, and resources are allocated. A structure that encourages innovation should be flexible, decentralized, and collaborative.
- Flat Hierarchies: Flat hierarchies promote open communication and quicker decision-making, allowing ideas to flow freely without being stifled by layers of bureaucracy.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Cross-functional teams bring together individuals from different departments, fostering collaboration and diverse perspectives. This allows for the integration of various skills and knowledge, leading to more innovative solutions.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Decentralized decision-making empowers employees at all levels to take ownership of their work and make decisions related to innovation without excessive oversight. This fosters a sense of autonomy and responsibility, encouraging creativity and experimentation.
The Impact of Organizational Culture on the Adoption and Success of Technological Innovation
Organizational culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and assumptions that guide employee behavior and decision-making. A culture that embraces innovation is characterized by risk-taking, experimentation, and a willingness to learn from failures.
- Openness to New Ideas: An innovative culture welcomes new ideas, even those that may seem unconventional or risky. It encourages employees to share their thoughts and suggestions, fostering a collaborative environment where ideas can be freely exchanged and developed.
- Tolerance for Failure: Failure is an integral part of the innovation process. A culture that embraces failure allows employees to learn from their mistakes, fostering a sense of experimentation and exploration.
- Rewarding Innovation: Organizations that reward innovation, both financially and through recognition, motivate employees to pursue new ideas and solutions. This reinforces the importance of innovation within the organization and encourages continued pursuit of novel ideas.
Key Characteristics of Organizations that are Highly Innovative
Organizations that consistently achieve technological breakthroughs often share several key characteristics that foster a culture of innovation. These include:
- Strong Leadership: Leaders who are passionate about innovation and actively champion new ideas are crucial in driving organizational change. They set the tone for the culture and inspire employees to embrace innovation.
- Continuous Learning: Highly innovative organizations prioritize continuous learning and development. They invest in training and education, encouraging employees to stay abreast of the latest technological advancements and trends.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for innovation. Organizations foster a culture of open communication and knowledge exchange, allowing ideas to be shared and developed collectively.
Innovation Processes and Methods
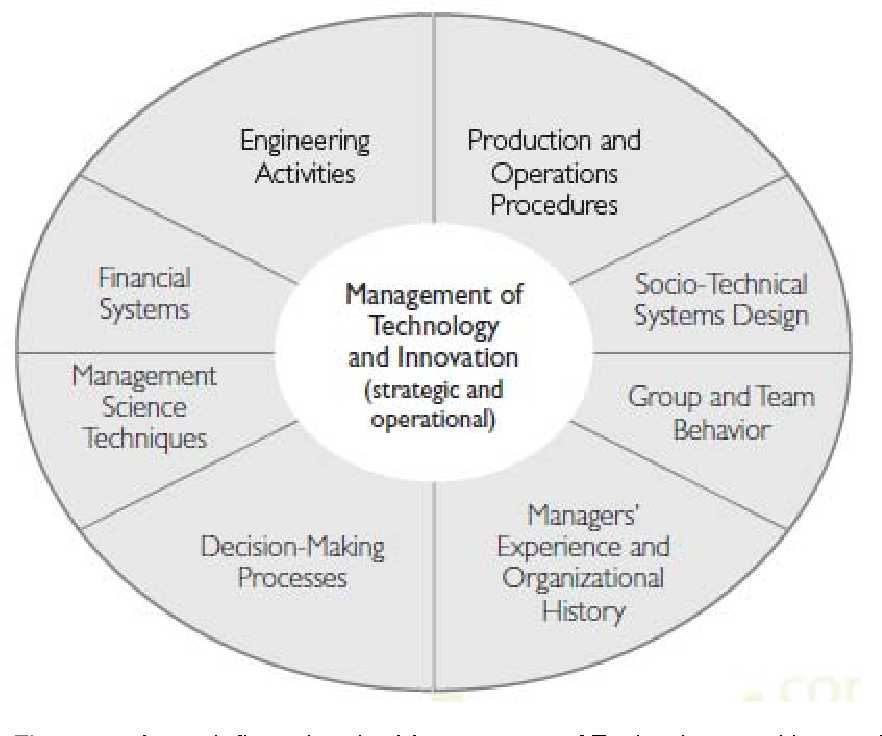
Understanding the innovation process is crucial for companies seeking to leverage technological advancements. This process involves a series of steps that transform an idea into a commercially viable product or service. Moreover, various methodologies and tools can be employed to manage innovation effectively, ensuring a systematic approach to developing and implementing new ideas.
Stages of the Innovation Process
The innovation process can be broadly divided into distinct stages, each with its own objectives and challenges. These stages are often interconnected and iterative, meaning that companies may revisit earlier stages as they progress through the process.
Strategic management of technological innovation involves understanding the market and identifying opportunities for growth. This can include exploring new technologies, such as the wilspec technologies pressure switch , which can be integrated into existing systems to improve efficiency and performance.
By strategically incorporating such innovations, companies can gain a competitive edge and stay ahead of the curve in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
- Idea Generation: This initial stage involves identifying potential opportunities and generating new ideas. Techniques like brainstorming, market research, and trend analysis are employed to spark creativity and uncover promising concepts. This stage is often characterized by a high volume of ideas, many of which may not be feasible or desirable.
- Idea Screening: Once a pool of ideas is generated, it’s essential to evaluate their potential and prioritize those most likely to succeed. This involves assessing factors like market demand, technological feasibility, resource availability, and potential profitability. The goal is to eliminate ideas that are not aligned with the company’s strategic goals or lack the necessary viability.
- Concept Development: This stage involves refining promising ideas into detailed concepts. This may include developing prototypes, conducting feasibility studies, and gathering feedback from potential customers. The focus is on translating initial ideas into concrete proposals with a clear understanding of their technical specifications, target market, and potential benefits.
- Business Planning: Once a concept is developed, a comprehensive business plan is required. This plan Artikels the commercialization strategy, including marketing, sales, production, and financial projections. It also addresses potential risks and mitigation strategies, ensuring a sound business foundation for the innovation.
- Product Development: This stage involves translating the concept into a tangible product or service. This may involve engineering design, prototyping, testing, and refinement. The goal is to develop a product that meets the desired specifications, is reliable, and addresses the identified market needs.
- Commercialization: The final stage involves launching the product or service to the market. This may involve marketing campaigns, distribution strategies, and customer support. The focus is on achieving successful adoption and generating positive returns on the investment made in the innovation.
Innovation Methodologies
Different innovation methodologies offer structured approaches to managing the innovation process. Each methodology emphasizes specific principles and tools, catering to different organizational contexts and innovation goals.
- Design Thinking: This human-centered approach focuses on understanding user needs and developing solutions that are both desirable and feasible. It emphasizes empathy, ideation, prototyping, and testing, fostering a collaborative and iterative process.
- Lean Startup: This methodology emphasizes rapid experimentation and learning. It encourages building a minimum viable product (MVP) and iteratively refining it based on customer feedback. The goal is to validate product-market fit and minimize the risk of developing a product that doesn’t meet customer needs.
- Agile Development: This iterative and incremental approach to software development focuses on delivering value quickly and continuously. It emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and responsiveness to change. Agile development is particularly effective for projects with evolving requirements and a need for frequent updates.
Comparison of Innovation Methodologies
| Methodology | Focus | Key Principles | Tools and Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design Thinking | User needs and experience | Empathy, ideation, prototyping, testing | User research, brainstorming, sketching, prototyping, user testing |
| Lean Startup | Product-market fit and rapid learning | Build-measure-learn, minimum viable product (MVP), customer feedback | Customer discovery, A/B testing, data analysis, customer interviews |
| Agile Development | Iterative and incremental development | Collaboration, flexibility, continuous delivery | Scrum, Kanban, user stories, sprints, daily stand-ups |
Managing Technological Risk and Uncertainty: Strategic Management Of Technological Innovation
Technological innovation is inherently risky. It involves venturing into uncharted territory, where success is not guaranteed, and the potential for failure is always present. Effectively managing technological risk is crucial for organizations to achieve their innovation goals and ensure long-term sustainability.
Identifying and Analyzing Technological Risks
Technological risks can be categorized into several key areas, each with its unique characteristics and potential impact on innovation projects.
- Technical Risks: These risks arise from the uncertainties associated with the technical feasibility and performance of the innovation. Examples include challenges in developing new technologies, integrating existing systems, and ensuring the reliability and scalability of the solution.
- Market Risks: These risks stem from the uncertainties surrounding the market demand for the innovation, its competitive landscape, and the potential for market acceptance. Factors such as customer preferences, regulatory changes, and the emergence of substitute technologies can significantly impact the success of an innovation.
- Financial Risks: These risks relate to the financial viability of the innovation project, including the costs of development, manufacturing, and marketing, as well as the potential for return on investment. Funding constraints, cost overruns, and delays in product launch can pose significant financial challenges.
- Organizational Risks: These risks are associated with the internal capabilities and resources of the organization to successfully implement and manage the innovation. Examples include inadequate infrastructure, lack of skilled personnel, and resistance to change within the organization.
A thorough risk assessment process should be conducted to identify, analyze, and prioritize the risks associated with a specific technological innovation. This process typically involves:
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential risks through brainstorming, expert opinions, and analysis of past projects.
- Risk Analysis: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of each risk, considering factors such as severity, frequency, and duration.
- Risk Prioritization: Ranking risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, focusing on those with the highest combined risk score.
Strategies for Mitigating and Managing Technological Risk
Once the key risks have been identified and analyzed, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate and manage them. These strategies can include:
- Risk Avoidance: This involves avoiding activities or projects that pose high levels of risk. For example, an organization may choose not to pursue a particular innovation if the technical challenges are deemed insurmountable or the market demand is uncertain.
- Risk Reduction: This involves taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks. Examples include investing in research and development to improve the technical feasibility of the innovation, conducting market research to validate demand, and building strong partnerships to access critical resources.
- Risk Transfer: This involves transferring the risk to another party, such as through insurance or outsourcing. For example, an organization may purchase insurance to cover potential losses from product liability claims.
- Risk Acceptance: This involves accepting the risk and developing contingency plans to manage its potential consequences. For example, an organization may accept the risk of market failure for a new product but develop a plan to quickly adapt or pivot if the product does not meet expectations.
Risk Assessment and Management Process
- Define the Scope of the Innovation: Clearly define the objectives, timeline, and resources associated with the innovation project.
- Identify Potential Risks: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify all potential risks associated with the innovation, including technical, market, financial, and organizational risks.
- Analyze the Risks: Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each risk, considering factors such as severity, frequency, and duration.
- Prioritize the Risks: Rank risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, focusing on those with the highest combined risk score.
- Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies: Develop specific strategies to address each prioritized risk, including risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk acceptance.
- Implement and Monitor Risk Mitigation Strategies: Put the risk mitigation strategies into action and monitor their effectiveness over time.
- Review and Update Risk Assessment: Regularly review and update the risk assessment process to account for changing circumstances and emerging risks.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaboration
In the dynamic landscape of technological innovation, forging strategic partnerships has become a critical success factor. By collaborating with other organizations, businesses can access complementary resources, expertise, and market reach, accelerating their innovation journey and unlocking new opportunities.
Types of Strategic Partnerships
Strategic partnerships in technological innovation can take various forms, each offering unique advantages.
- Joint Ventures: Involve two or more companies pooling resources and expertise to create a new entity for a specific project or venture. This allows for shared risks and rewards, leveraging complementary strengths.
- Research and Development Partnerships: Collaborations focused on joint research and development activities, sharing knowledge and resources to advance technological frontiers. This can lead to breakthroughs and innovations that might not be possible individually.
- Licensing Agreements: Granting another company the right to use a company’s intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or technologies, in exchange for royalties or other considerations. This allows for wider market penetration and faster commercialization of innovations.
- Strategic Alliances: Long-term partnerships between companies that share common goals and interests, collaborating on various aspects of their businesses, including innovation, marketing, and distribution.
Benefits of Strategic Partnerships
Strategic partnerships offer numerous benefits for companies seeking to innovate:
- Access to Expertise and Resources: Partnering with companies possessing specialized knowledge, skills, or resources can overcome internal limitations and accelerate innovation.
- Reduced Development Costs and Risks: Sharing development costs and risks through partnerships can make innovation more financially viable and reduce the burden on individual companies.
- Faster Time to Market: Collaboration can expedite the development and commercialization of innovations, enabling companies to seize market opportunities quickly.
- Increased Market Reach and Access: Partnering with companies operating in complementary markets can expand a company’s customer base and distribution channels.
- Enhanced Innovation Capabilities: Collaboration can foster cross-fertilization of ideas and perspectives, leading to more innovative solutions and breakthroughs.
Examples of Successful Partnerships
Numerous examples showcase the effectiveness of strategic partnerships in technological innovation:
- Google and NASA: Their partnership has led to advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and Earth observation, leveraging each other’s strengths in research and development.
- Apple and Samsung: Despite being competitors, these companies collaborate in specific areas, such as component manufacturing and technology licensing, demonstrating the potential for partnerships even between rivals.
- IBM and the OpenStack Foundation: This partnership has fostered open-source collaboration in cloud computing, leading to the development of a robust and widely adopted cloud platform.
The Future of Technological Innovation

The landscape of technological innovation is constantly evolving, driven by rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and other disruptive technologies. Understanding the emerging trends and challenges in this dynamic environment is crucial for businesses to navigate the future of innovation effectively.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The emergence of AI, automation, and other disruptive technologies is transforming industries and shaping the future of innovation. These technologies are creating new possibilities for businesses to enhance efficiency, improve customer experiences, and develop entirely new products and services.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is rapidly transforming industries by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and personalizing customer experiences. AI-powered systems are capable of learning from data and adapting to changing conditions, making them increasingly valuable in areas such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
- Automation: Automation is another transformative technology that is automating tasks and processes across various industries. From robotic process automation (RPA) to industrial robots, automation is increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving productivity.
- Other Disruptive Technologies: Emerging technologies such as blockchain, quantum computing, and biotechnology are also driving innovation and creating new opportunities. Blockchain offers secure and transparent data management, quantum computing promises unprecedented computational power, and biotechnology is revolutionizing healthcare and agriculture.
Navigating the Future of Technological Innovation, Strategic management of technological innovation
Strategic management plays a crucial role in navigating the future of technological innovation. Businesses need to adopt a proactive and adaptive approach to stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Embrace a Culture of Innovation: Businesses need to foster a culture that encourages experimentation, risk-taking, and continuous learning. This requires creating an environment where employees feel empowered to explore new ideas and challenge the status quo.
- Develop a Clear Innovation Strategy: A well-defined innovation strategy Artikels the organization’s goals, priorities, and approach to technological innovation. This strategy should align with the overall business strategy and consider the impact of emerging technologies.
- Invest in Research and Development: Investing in research and development (R&D) is essential for staying ahead of the innovation curve. Businesses need to allocate resources to explore new technologies, develop prototypes, and test innovative solutions.
- Foster Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with other organizations, universities, and research institutions can accelerate innovation and access new knowledge and expertise. Strategic partnerships can provide access to cutting-edge technologies, talent, and market insights.
Concluding Remarks
As we conclude our exploration of strategic management of technological innovation, it’s clear that this is not just a business strategy, but a critical driver of progress. By embracing a strategic approach, organizations can unlock the full potential of innovation, shaping a future where technology empowers growth and creates lasting value.