Endpoint Technologies: Shaping Modern IT Infrastructure
Endpoint technologies, the diverse range of devices connecting to a network, are the cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure. From personal computers and smartphones to servers and IoT devices, these endpoints […]
Endpoint technologies, the diverse range of devices connecting to a network, are the cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure. From personal computers and smartphones to servers and IoT devices, these endpoints have revolutionized the way we work, communicate, and access information. The evolution of endpoint technologies has been marked by significant milestones, from the advent of personal computing to the rise of mobile devices and the Internet of Things. This dynamic landscape presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring a comprehensive understanding of endpoint security, management, and emerging trends.
Endpoint technologies have become integral to every industry, transforming how businesses operate and individuals interact with the digital world. In healthcare, for instance, medical devices and patient monitoring systems rely on endpoint technologies, while financial institutions leverage them for secure transactions and data analysis. The education sector utilizes endpoints for online learning platforms, student management systems, and research initiatives. As we navigate the digital age, understanding the complexities and potential of endpoint technologies is crucial for success.
Introduction to Endpoint Technologies

Endpoint technologies are the devices and software that connect to a network, allowing users to access and interact with data and applications. These technologies are fundamental to modern IT infrastructure, enabling communication, collaboration, and data sharing across organizations.
Endpoint technologies have evolved significantly over the years, reflecting advancements in computing power, network connectivity, and user needs. This evolution has been marked by several key milestones and trends, including the shift from desktop computers to mobile devices, the emergence of cloud computing, and the increasing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Types of Endpoint Devices
Endpoint technologies encompass a diverse range of devices, each serving specific purposes and catering to different user requirements. Here are some examples:
- Personal Computers (PCs): Desktop computers and laptops are traditional endpoint devices, providing users with a powerful platform for accessing and managing data, running applications, and connecting to the internet.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones and tablets have become ubiquitous endpoint devices, offering users mobility, connectivity, and access to a wide range of applications.
- Printers: Printers are essential endpoint devices for document printing, providing a physical output for digital data.
- Servers: Servers are specialized endpoint devices that host and manage data and applications, providing resources to other devices on the network.
- IoT Devices: The Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced a new category of endpoint devices, such as smart home appliances, wearable fitness trackers, and industrial sensors. These devices collect and transmit data, enabling automation and remote monitoring.
Endpoint Security and Management
Endpoint security and management are critical aspects of cybersecurity, particularly in today’s evolving threat landscape. As more organizations embrace remote work and adopt cloud-based technologies, endpoints have become increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Endpoint Security Vulnerabilities
Endpoint security vulnerabilities are weaknesses in endpoint devices and their associated software that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or compromise the system. These vulnerabilities can arise from various sources, including:
- Operating System Weaknesses: Operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, can contain security flaws that attackers can exploit to gain control of the device. For example, the “EternalBlue” exploit targeted a vulnerability in the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol in Windows operating systems, allowing attackers to gain remote code execution on vulnerable machines.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Applications and software installed on endpoints, such as browsers, email clients, and productivity tools, can also have security vulnerabilities. For instance, the “Heartbleed” vulnerability affected OpenSSL, a widely used cryptographic library, allowing attackers to steal sensitive data from vulnerable servers.
- Misconfigurations: Improper configuration of endpoint security settings, such as weak passwords, disabled firewalls, and outdated antivirus software, can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. For example, an attacker could exploit a misconfigured firewall to bypass security controls and gain access to the endpoint.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Phishing attacks, which involve tricking users into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments, can compromise endpoints. Similarly, social engineering attacks exploit human psychology to manipulate users into divulging sensitive information or granting unauthorized access.
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, can infect endpoints and steal data, disrupt operations, or demand ransom payments.
Best Practices for Endpoint Security and Management, Endpoint technologies
Organizations must implement robust endpoint security and management practices to mitigate these vulnerabilities and protect their data and systems.
- Software Updates: Regular software updates are essential to patch vulnerabilities and enhance endpoint security. Organizations should implement a centralized patch management system to ensure that all endpoints receive timely updates.
- Security Configurations: Secure endpoint configurations, such as strong passwords, enabled firewalls, and anti-malware software, can significantly reduce the risk of attacks. Organizations should establish and enforce standardized security configurations across all endpoints.
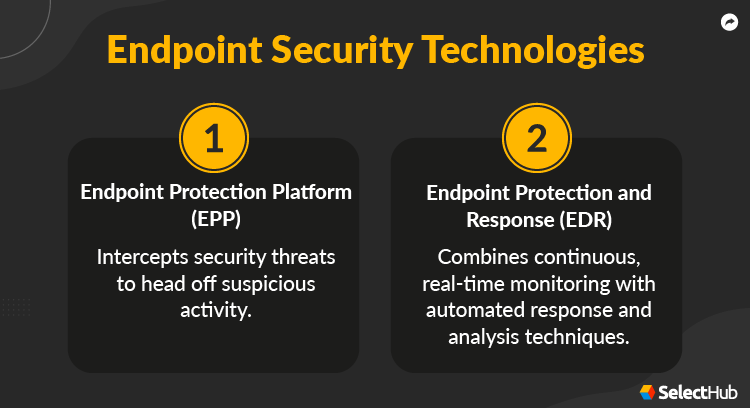
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring and threat detection capabilities, enabling organizations to identify and respond to attacks quickly. EDR solutions can detect suspicious activity, isolate infected endpoints, and prevent further damage.
- User Education and Awareness: User education and awareness training can help employees recognize and avoid phishing attacks, malware, and other threats.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data stored on endpoints helps protect it from unauthorized access, even if the device is lost or stolen.
- Network Segmentation: Network segmentation can isolate sensitive systems and data from other parts of the network, limiting the impact of a successful attack.
- Regular Security Assessments: Organizations should conduct regular security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities and ensure that security controls are effective.
Closing Notes: Endpoint Technologies
In conclusion, endpoint technologies have become an indispensable part of our interconnected world, driving innovation and transforming how we work, learn, and interact. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is essential to prioritize endpoint security, implement robust management solutions, and embrace emerging trends to harness their full potential. By understanding the nuances of endpoint technologies, we can navigate the digital landscape effectively and unlock a world of possibilities.
Endpoint technologies are crucial for securing and managing devices in today’s interconnected world. If you’re passionate about technology and want to make a difference, consider exploring opportunities in technology volunteer jobs. These roles often involve supporting individuals and organizations with their endpoint devices, providing valuable experience in troubleshooting, security, and software deployment.








