Technology Control Plan Template: A Guide to Secure Operations
Technology Control Plan Template: A Guide to Secure Operations, delves into the crucial realm of safeguarding your organization’s technological assets. It Artikels a comprehensive framework for implementing effective technology controls, […]
Technology Control Plan Template: A Guide to Secure Operations, delves into the crucial realm of safeguarding your organization’s technological assets. It Artikels a comprehensive framework for implementing effective technology controls, ensuring the protection of your data, systems, and operations from potential threats.
This guide provides a clear and concise template that can be adapted to fit the specific needs of any organization, regardless of size or industry. It covers essential elements like network security, data security, user access management, incident response, and business continuity planning.
Implementation and Maintenance
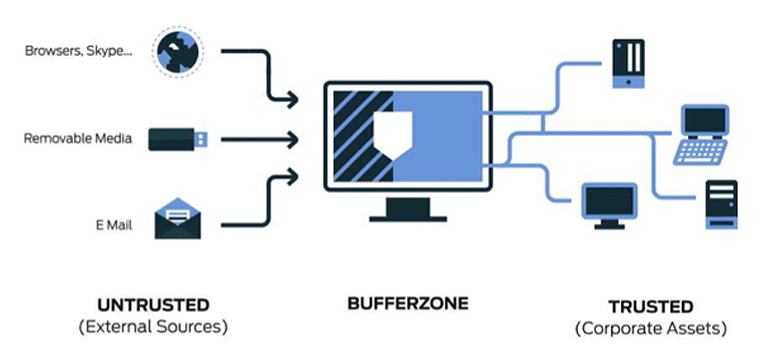
Implementing a technology control plan is crucial for ensuring its effectiveness in safeguarding sensitive data and systems. It requires a structured approach that involves careful planning, resource allocation, and ongoing monitoring.
Implementation Steps
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly assign roles and responsibilities to individuals or teams for implementing and maintaining the technology control plan. This ensures accountability and efficient execution.
- Develop Training Programs: Provide comprehensive training to all stakeholders, including employees, contractors, and third-party vendors, on the technology control plan’s policies, procedures, and best practices. This promotes understanding and compliance.
- Establish Monitoring and Reporting Mechanisms: Implement robust monitoring systems to track the effectiveness of technology controls. Regularly collect and analyze data to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. This ensures continuous improvement.
- Conduct Regular Audits and Assessments: Regularly audit and assess the technology control plan to ensure its effectiveness in mitigating risks. These assessments can involve internal audits, external reviews, or penetration testing to identify weaknesses and areas for enhancement.
- Integrate Technology Controls into Business Processes: Seamlessly integrate technology controls into existing business processes to minimize disruptions and maximize effectiveness. This ensures that security measures are ingrained in daily operations.
Ongoing Monitoring and Review, Technology control plan template
Continuous monitoring and review are essential for maintaining the effectiveness of a technology control plan. This involves:
- Tracking Control Effectiveness: Regularly monitor the performance of technology controls and analyze their impact on security posture. This allows for early detection of vulnerabilities and proactive remediation.
- Identifying Emerging Threats: Stay abreast of emerging threats and vulnerabilities in the cybersecurity landscape. Proactively update the technology control plan to address new risks and ensure ongoing protection.
- Evaluating Control Performance: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of implemented controls against established metrics and benchmarks. This helps identify areas for improvement and optimize the plan for better security outcomes.
- Documenting Changes and Updates: Maintain a comprehensive record of all changes and updates made to the technology control plan. This ensures transparency, accountability, and effective communication across stakeholders.
Updating and Revising the Plan
The technology control plan should be a dynamic document that adapts to changing security needs and emerging threats. This requires regular review and updating.
- Conduct Periodic Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews of the technology control plan to assess its relevance, effectiveness, and alignment with current business needs and security requirements.
- Incorporate New Technologies: Incorporate new technologies and security solutions into the technology control plan as they become available. This ensures that the plan remains up-to-date and effective in addressing evolving threats.
- Address Identified Deficiencies: Address any identified deficiencies or vulnerabilities in the technology control plan promptly. This includes implementing corrective actions, updating policies, and enhancing controls to mitigate risks.
- Communicate Changes: Effectively communicate any changes or updates to the technology control plan to all stakeholders. This ensures that everyone is aware of the latest security practices and procedures.
Stakeholder Roles
Stakeholder engagement is critical for successful implementation and maintenance of a technology control plan.
- Management: Provides leadership, resources, and support for the implementation and maintenance of the technology control plan. They also ensure alignment with business objectives and security goals.
- IT Department: Responsible for implementing and maintaining technical controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. They also provide technical expertise and support for the plan.
- Employees: Responsible for following the technology control plan’s policies and procedures. They also play a vital role in reporting suspicious activities and potential security breaches.
- Security Professionals: Provide specialized expertise in security assessments, vulnerability management, and incident response. They help identify and mitigate risks, and ensure the plan’s effectiveness.
Best Practices and Resources
Developing and implementing effective technology control plans requires a strategic approach that leverages industry best practices and recognized standards. Adhering to these guidelines ensures a comprehensive and robust control framework, mitigating risks and safeguarding sensitive information.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
These standards and frameworks provide a comprehensive guide for developing and implementing technology control plans, offering valuable insights and best practices.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: This framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), offers a structured approach to cybersecurity risk management. It provides a set of activities, processes, and outcomes for organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework focuses on five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- ISO 27001: This international standard specifies requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a documented Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides a framework for managing information security risks, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. ISO 27001 encompasses a broad range of security controls, covering areas such as access control, encryption, incident management, and data backup.
- COBIT 5: This framework, developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association), provides a comprehensive set of governance and management principles and practices for Information Technology (IT). It emphasizes aligning IT with business goals, managing IT risks, and optimizing IT resources. COBIT 5 covers various aspects of IT governance, including strategy, planning, implementation, monitoring, and reporting.
Benefits of Adhering to Standards and Guidelines
Adhering to these standards and guidelines offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security Posture: Implementing these frameworks strengthens the organization’s overall security posture by providing a comprehensive and structured approach to risk management and control.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: By implementing robust security controls and best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Improved Compliance: These standards and guidelines often align with regulatory requirements, simplifying compliance efforts and minimizing potential penalties.
- Increased Trust and Confidence: Demonstrating adherence to industry-recognized standards builds trust and confidence among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Implementing a well-defined technology control plan can improve operational efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing errors, and optimizing resource allocation.
Final Review: Technology Control Plan Template

By implementing a robust technology control plan, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance operational efficiency, and build a strong foundation for long-term success. This template serves as a valuable resource for developing and maintaining a secure and resilient technology environment, ensuring that your organization is well-equipped to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
A technology control plan template is a valuable tool for churches, helping them manage their technology assets and ensure responsible use. To help with funding for technology upgrades, churches can explore technology grants for churches , which can provide financial support for new equipment and software.
Once funding is secured, a well-defined technology control plan template can help churches effectively manage their technology investments and maximize their impact.