Smart Grid Technology Companies: Shaping the Future of Energy
Smart grid technology companies are at the forefront of revolutionizing the energy sector, ushering in a new era of efficiency, sustainability, and reliability. These companies develop and implement cutting-edge technologies […]

Smart grid technology companies are at the forefront of revolutionizing the energy sector, ushering in a new era of efficiency, sustainability, and reliability. These companies develop and implement cutting-edge technologies that enable smarter grids, allowing for better energy management, increased renewable energy integration, and enhanced grid resilience.
The concept of smart grids involves the integration of advanced technologies, such as communication networks, sensors, and automation systems, into traditional power grids. This integration enables real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of energy flow, leading to significant improvements in grid performance and overall energy efficiency.
Smart Grid Technology Companies

The smart grid market is a dynamic and rapidly growing industry, driven by the increasing demand for reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy systems. Several companies play a crucial role in developing and implementing smart grid technologies, shaping the future of energy infrastructure.
Major Players in the Smart Grid Market
The smart grid market is characterized by a diverse range of companies, each specializing in different aspects of the technology. These companies can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
- Technology Providers: These companies develop and supply core technologies like advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), distribution automation systems, energy storage solutions, and communication networks. Examples include:
- ABB: A global technology leader in electrification, automation, and robotics, ABB provides a wide range of smart grid solutions, including substation automation, grid monitoring, and energy storage systems.
- Siemens: A leading technology company, Siemens offers comprehensive smart grid solutions, including grid control systems, energy management platforms, and smart metering solutions.
- Schneider Electric: A global specialist in energy management and automation, Schneider Electric provides smart grid solutions like advanced metering, distribution automation, and energy efficiency optimization.
- Software and Services Providers: These companies focus on developing software applications and providing services for managing and optimizing smart grid operations. Examples include:
- Oracle: A leading cloud computing and software company, Oracle offers software solutions for managing and analyzing smart grid data, including energy consumption patterns and grid performance.
- IBM: A global technology giant, IBM provides solutions for smart grid analytics, data management, and cybersecurity.
- GE Digital: A subsidiary of General Electric, GE Digital offers software solutions for managing and optimizing energy assets, including power generation and distribution.
- System Integrators: These companies integrate different technologies and components to create complete smart grid solutions. Examples include:
- Accenture: A global consulting and technology services company, Accenture provides smart grid implementation services, including system design, integration, and testing.
- Capgemini: A global technology and consulting company, Capgemini offers smart grid consulting and implementation services, focusing on grid modernization and energy efficiency.
- Atos: A global technology company, Atos provides smart grid solutions, including grid management systems, cybersecurity, and data analytics.
- Utilities: These companies are the end users of smart grid technologies, deploying these solutions to improve grid efficiency, reliability, and customer service. Examples include:
- Duke Energy: A leading US energy company, Duke Energy has implemented smart grid technologies to improve grid reliability, enhance customer service, and integrate renewable energy sources.
- Southern Company: A major US energy company, Southern Company has invested in smart grid technologies to improve grid efficiency, reduce outages, and integrate distributed energy resources.
- Exelon: A US energy company, Exelon has implemented smart grid technologies to improve grid reliability, enhance customer service, and reduce carbon emissions.
Key Smart Grid Technology Companies
| Company Name | Focus Area | Offerings | Key Projects |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABB | Grid Automation, Energy Storage, Electrification | Substation Automation, Grid Monitoring, Energy Storage Systems | Smart Grid projects in Switzerland, Germany, and the United States |
| Siemens | Grid Control, Energy Management, Smart Metering | Grid Control Systems, Energy Management Platforms, Smart Metering Solutions | Smart Grid projects in Germany, China, and the United States |
| Schneider Electric | Advanced Metering, Distribution Automation, Energy Efficiency | Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Distribution Automation Systems, Energy Efficiency Optimization Solutions | Smart Grid projects in France, Brazil, and the United States |
| Oracle | Smart Grid Data Management, Analytics | Software solutions for managing and analyzing smart grid data | Smart Grid projects with utilities in North America and Europe |
| IBM | Smart Grid Analytics, Data Management, Cybersecurity | Solutions for smart grid analytics, data management, and cybersecurity | Smart Grid projects with utilities in the United States and Asia |
| GE Digital | Energy Asset Management, Optimization | Software solutions for managing and optimizing energy assets | Smart Grid projects with utilities in the United States and Europe |
| Accenture | Smart Grid Implementation, System Integration | Smart grid implementation services, including system design, integration, and testing | Smart Grid projects with utilities in the United States and Europe |
| Capgemini | Smart Grid Consulting, Implementation | Smart grid consulting and implementation services, focusing on grid modernization and energy efficiency | Smart Grid projects with utilities in Europe and Asia |
| Atos | Grid Management, Cybersecurity, Data Analytics | Grid management systems, cybersecurity solutions, and data analytics platforms | Smart Grid projects with utilities in Europe and Asia |
| Duke Energy | Grid Reliability, Customer Service, Renewable Integration | Smart grid technologies for improving grid reliability, enhancing customer service, and integrating renewable energy sources | Smart Grid projects in the Carolinas and the Midwest |
| Southern Company | Grid Efficiency, Outage Reduction, Distributed Energy Resources | Smart grid technologies for improving grid efficiency, reducing outages, and integrating distributed energy resources | Smart Grid projects in the Southeast |
| Exelon | Grid Reliability, Customer Service, Carbon Emission Reduction | Smart grid technologies for improving grid reliability, enhancing customer service, and reducing carbon emissions | Smart Grid projects in the Midwest and the Northeast |
Competitive Landscape of the Smart Grid Industry
The smart grid industry is highly competitive, with numerous companies vying for market share. Key factors driving competition include:
- Technological Innovation: Companies are constantly innovating to develop new and advanced smart grid technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for grid optimization and cybersecurity solutions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Companies are focused on developing cost-effective solutions that can be implemented by utilities with limited budgets. This includes optimizing existing infrastructure and leveraging open-source technologies.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Companies are increasingly forming partnerships and collaborations to develop comprehensive smart grid solutions. This allows them to leverage each other’s expertise and resources.
- Government Policies and Regulations: Government policies and regulations are playing a significant role in shaping the smart grid industry. Incentives and regulations are driving the adoption of smart grid technologies and encouraging innovation.
- Customer Demand: Increasing customer demand for reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy is driving the adoption of smart grid technologies. Utilities are investing in smart grid solutions to meet these demands and improve customer satisfaction.
Smart Grid Solutions and Applications
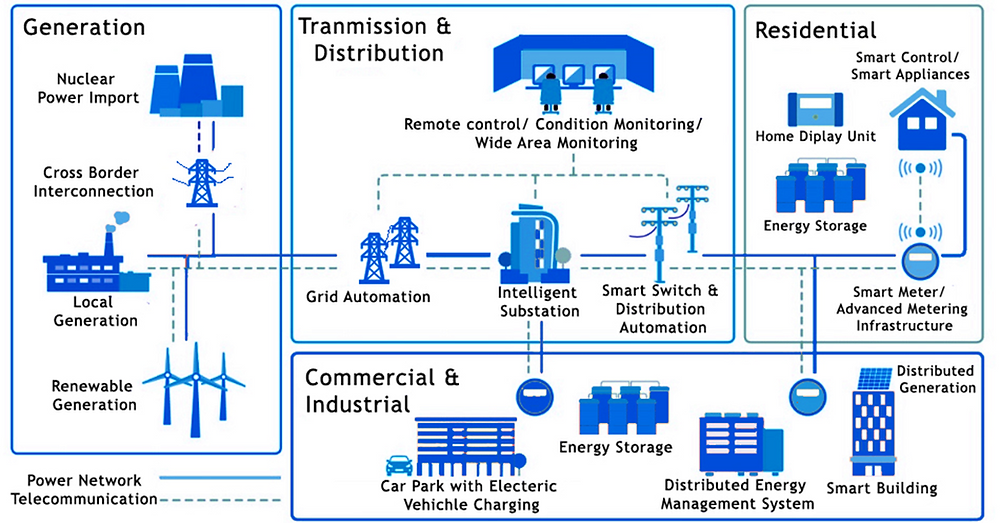
Smart grids are an integral part of the modern energy landscape, offering numerous solutions and applications to address challenges related to energy efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. These advanced grids utilize digital technologies to optimize energy flow, enhance grid management, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources.
Renewable Energy Integration
Smart grids play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the existing power grid. They enable the seamless and efficient flow of energy from these intermittent sources, addressing their inherent variability.
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Smart meters provide real-time data on energy consumption and generation, allowing utilities to monitor and manage the integration of renewable energy sources effectively.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DER) Management: Smart grids facilitate the management of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar panels, allowing them to contribute to the grid and enhance its reliability.
- Demand Response Programs: Smart grids enable utilities to incentivize consumers to reduce their energy consumption during peak demand periods, thereby mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
Energy Efficiency and Demand Response, Smart grid technology companies
Smart grids enhance energy efficiency by providing real-time information to consumers, allowing them to make informed decisions about their energy usage. This information can be used to reduce energy consumption during peak demand periods, thereby lowering energy costs and reducing strain on the grid.
- Real-Time Pricing: Smart grids enable utilities to offer dynamic pricing based on real-time energy demand, incentivizing consumers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours.
- Demand Response Programs: These programs allow utilities to remotely control appliances and devices in homes and businesses, reducing energy consumption during peak demand periods.
- Energy Management Systems: Smart grids enable the integration of energy management systems in homes and businesses, allowing consumers to monitor and control their energy usage in real-time.
Electric Vehicle Charging
Smart grids are essential for managing the increasing demand for electric vehicle charging infrastructure. They enable the efficient and reliable charging of electric vehicles while minimizing the impact on the grid.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: Smart grids allow electric vehicles to act as distributed energy storage systems, enabling them to discharge energy back to the grid during peak demand periods.
- Smart Charging Management: Smart grids enable utilities to manage the charging of electric vehicles, optimizing charging times to minimize strain on the grid and reduce energy costs.
- Charging Infrastructure Integration: Smart grids facilitate the integration of electric vehicle charging infrastructure into the grid, ensuring reliable and efficient charging for electric vehicles.
Grid Modernization and Resilience
Smart grids play a vital role in modernizing and enhancing the resilience of the electric grid. They enable utilities to detect and respond to outages more quickly, improving grid reliability and reducing the impact of disruptions.
- Advanced Distribution Management Systems (ADMS): Smart grids utilize ADMS to monitor and control the distribution grid, enabling utilities to identify and address potential problems proactively.
- Microgrids: Smart grids facilitate the development of microgrids, which are small, localized grids that can operate independently from the main grid, enhancing resilience during outages.
- Cybersecurity: Smart grids require robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cyberattacks and ensure the integrity of grid operations.
Last Point: Smart Grid Technology Companies
As the demand for sustainable and reliable energy solutions continues to grow, smart grid technology companies play a crucial role in shaping the future of the energy landscape. Their innovative solutions are driving the transition to a more efficient, resilient, and environmentally friendly energy system, paving the way for a brighter and more sustainable future.
Smart grid technology companies are constantly innovating to improve efficiency and reliability in the energy sector. A key aspect of this innovation lies in the realm of digital info technology , which enables real-time monitoring, data analytics, and automated control systems.
By leveraging these advanced technologies, smart grid companies can optimize energy distribution, reduce outages, and empower consumers to manage their energy consumption more effectively.





