Technology for Brokers: Shaping the Future of Finance
Technology for brokers has revolutionized the financial landscape, transforming how brokers operate and interact with clients. From automated trading platforms to sophisticated data analytics, technology has empowered brokers with tools […]

Technology for brokers has revolutionized the financial landscape, transforming how brokers operate and interact with clients. From automated trading platforms to sophisticated data analytics, technology has empowered brokers with tools to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and provide personalized client experiences.
This comprehensive guide explores the evolution of technology in brokerage, examines key tools and platforms, and delves into the impact of automation, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity on the industry. We’ll also discuss future trends shaping the brokerage landscape and the implications for broker-client relationships in this evolving digital world.
Evolution of Technology for Brokers
The brokerage industry has undergone a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements that have revolutionized how brokers operate and interact with clients. From the days of manual trading and paper-based records to the sophisticated digital platforms of today, the evolution of technology has significantly impacted the brokerage landscape.
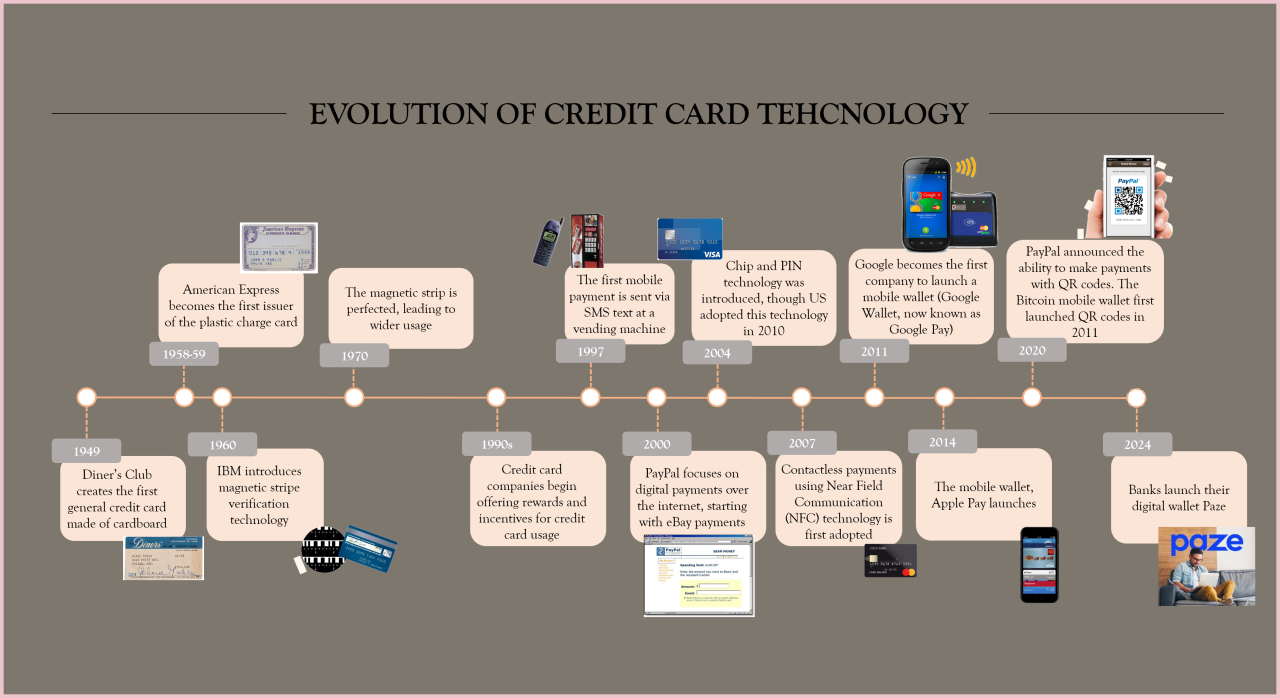
Historical Evolution of Brokerage Technology
The history of brokerage technology is marked by several key milestones and innovations that have shaped the industry.
- Early Days (Pre-1970s): Brokers relied heavily on manual processes, using telephones, telex machines, and physical trading floors to execute trades. Information dissemination was limited, and clients often had to rely on brokers for market insights.
- The Rise of Electronic Trading (1970s-1990s): The introduction of electronic trading systems, such as the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation (NASDAQ) system in 1971, ushered in a new era of efficiency and speed. Brokers could now execute trades electronically, reducing the reliance on physical trading floors and increasing trading volume.
- The Internet Revolution (1990s-Present): The internet’s arrival transformed the brokerage industry, allowing for online trading platforms, real-time market data, and increased access to financial information. This period witnessed the emergence of discount brokers, who offered lower commission fees and greater accessibility for retail investors.
- Mobile Trading and Fintech Innovations (2000s-Present): The rise of smartphones and mobile technology further democratized trading, enabling investors to access their accounts and execute trades anytime, anywhere. The emergence of fintech companies, specializing in financial technology, introduced innovative solutions such as robo-advisors, algorithmic trading, and blockchain-based platforms.
Comparison of Traditional and Modern Brokerage Methods
Traditional brokerage methods, characterized by face-to-face interactions and manual processes, have been largely replaced by modern, tech-driven approaches.
- Trading Execution: Traditional brokers relied on physical trading floors and phone calls to execute trades, which could be time-consuming and prone to errors. Modern brokers leverage electronic trading platforms that allow for instant trade execution, reducing transaction costs and improving efficiency.
- Information Access: In the past, clients relied heavily on brokers for market information, which was often limited and delayed. Today, online platforms provide real-time market data, news feeds, and research reports, empowering investors to make informed decisions.
- Client Interaction: Traditional brokerage relationships were often based on personal connections and trust. Modern brokers increasingly rely on digital channels, such as online chatbots, mobile apps, and social media platforms, to engage with clients and provide personalized services.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have profoundly impacted the brokerage industry, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced client experiences.
- Increased Efficiency: Electronic trading platforms and automated processes have significantly improved the efficiency of trade execution, reducing the time and resources required to complete transactions.
- Reduced Costs: Online platforms and automated processes have lowered operational costs for brokers, enabling them to offer lower commission fees and more competitive pricing to clients.
- Enhanced Client Experiences: Modern brokers provide clients with access to real-time market data, personalized investment advice, and user-friendly mobile apps, creating a more engaging and convenient trading experience.
Technology Tools and Platforms for Brokers
Brokers leverage a variety of technology tools and platforms to streamline operations, enhance client interactions, and improve efficiency. These tools cater to different aspects of their business, from managing client relationships to executing trades and analyzing market data.
CRM Systems
CRM systems are essential for brokers to manage client relationships effectively. These systems provide a centralized platform for storing and managing client information, tracking interactions, and automating tasks.
- Functionality: CRM systems typically offer features such as contact management, lead tracking, opportunity management, communication tracking, and reporting. They can be integrated with other tools, such as email marketing platforms and social media, to provide a comprehensive view of client interactions.
- Benefits: CRM systems help brokers improve client satisfaction, increase sales, and gain valuable insights into client behavior. They streamline communication, automate tasks, and provide a centralized repository for client data.
- Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Trading Platforms
Trading platforms provide brokers with the tools they need to execute trades on behalf of their clients. These platforms offer various functionalities, including order placement, real-time market data, charting tools, and trade analysis.
- Functionality: Trading platforms allow brokers to place orders, monitor market activity, analyze trade performance, and manage client accounts. They often offer advanced features such as algorithmic trading, backtesting, and real-time news feeds.
- Benefits: Trading platforms enhance trading efficiency, improve order execution speed, and provide brokers with access to sophisticated trading tools. They enable brokers to offer clients a wide range of trading instruments and functionalities.
- Examples: MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), TradingView, NinjaTrader.
Research Tools
Research tools are essential for brokers to provide clients with insightful market analysis and investment recommendations. These tools offer access to a wide range of data sources, including fundamental data, technical indicators, and market news.
- Functionality: Research tools provide brokers with access to market data, financial statements, analyst reports, and other relevant information. They often offer advanced features such as screening tools, backtesting capabilities, and portfolio optimization algorithms.
- Benefits: Research tools enable brokers to conduct thorough market analysis, generate investment ideas, and provide clients with informed recommendations. They also help brokers stay up-to-date on market trends and identify potential investment opportunities.
- Examples: Bloomberg Terminal, Refinitiv Eikon, FactSet, Morningstar.
Portfolio Management Software
Portfolio management software helps brokers manage client portfolios, track performance, and generate reports. These tools offer a variety of features, including account aggregation, performance tracking, and risk analysis.
- Functionality: Portfolio management software enables brokers to track client holdings, monitor performance, generate reports, and analyze risk. They often offer features such as rebalancing tools, performance attribution analysis, and asset allocation strategies.
- Benefits: Portfolio management software helps brokers provide clients with comprehensive portfolio insights, improve portfolio performance, and reduce risk. They also streamline portfolio management tasks and provide clients with regular updates on their investments.
- Examples: Advent Software, Tamarac, Black Knight, Orion Advisor Services.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Brokerage
The rise of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the brokerage industry, enabling brokers to optimize their operations, enhance client experiences, and gain a competitive edge. These technologies are automating tasks, improving efficiency, and unlocking new possibilities for brokers.
AI-Powered Tools and Platforms for Brokers
AI-powered tools and platforms are being widely adopted by brokers to streamline various aspects of their operations. These platforms utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze vast amounts of data, automate processes, and personalize client interactions.
- Robo-Advisors: These automated platforms use algorithms to create and manage investment portfolios based on client risk tolerance and financial goals. They provide personalized investment advice and automate portfolio rebalancing, offering cost-effective solutions for investors.
- Trading Bots: These AI-driven programs execute trades automatically based on predefined rules and parameters. They can analyze market data in real-time, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades at optimal times, potentially improving trading efficiency and returns.
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots provide instant customer support, answer frequently asked questions, and assist with basic tasks. They can be integrated into websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms, offering 24/7 availability and enhancing the client experience.
- Sentiment Analysis Tools: These tools use AI to analyze market news, social media posts, and other data sources to gauge investor sentiment and identify potential market trends. This information can help brokers make more informed trading decisions and provide valuable insights to clients.
AI Applications in Brokerage
The use of AI in brokerage is expanding rapidly, with various applications across different aspects of the industry.
| Task Automated | Benefits Achieved | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Data analysis and market research | Faster and more accurate insights, identification of trading opportunities, improved risk management | Bias in AI algorithms, potential for misinterpretation of data, need for human oversight |
| Trade execution and order routing | Improved execution speed and efficiency, reduced transaction costs, enhanced order fulfillment | Technical glitches and system errors, potential for market manipulation, need for robust security measures |
| Client communication and support | Personalized recommendations, 24/7 availability, improved customer satisfaction | Potential for impersonal interactions, lack of human touch, need for clear communication and transparency |
| Fraud detection and risk management | Proactive identification of suspicious activity, improved compliance with regulations, reduced financial losses | False positives, potential for discrimination, need for ongoing monitoring and adjustments |
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy in Brokerage: Technology For Brokers
The brokerage industry operates in a highly digital environment, making cybersecurity and data privacy paramount. Brokers handle sensitive client information, including financial details, investment strategies, and personal data, which are vulnerable to various cyber threats. Protecting this information is crucial for maintaining client trust, regulatory compliance, and the overall reputation of the brokerage firm.
Cybersecurity Risks and Vulnerabilities
Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to brokerage firms, potentially leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. These risks can be categorized as follows:
- Data Breaches: Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks to steal client data, including account details, trading history, and personal information. This can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and loss of client trust.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to disrupt the availability of brokerage services by overwhelming their systems with traffic. This can cause significant downtime, hindering trading activities and impacting client access.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can infiltrate brokerage systems, steal data, or manipulate trading activities. This can lead to financial losses for clients and the firm, as well as potential regulatory sanctions.
- Insider Threats: Employees with access to sensitive data can pose a risk, intentionally or unintentionally compromising security. This highlights the importance of robust employee training and access control measures.
Data Privacy Regulations and Compliance
Brokerage firms are subject to strict data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These regulations impose obligations on firms to protect client data, including:
- Data Minimization: Only collect and process data that is necessary for legitimate business purposes.
- Transparency and Consent: Clearly inform clients about how their data is collected, used, and shared, and obtain their consent for data processing.
- Data Security: Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect client data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- Data Subject Rights: Grant clients the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict, and transfer their personal data.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Brokerage firms must adopt a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity and data privacy, incorporating the following best practices:
- Strong Password Policies: Implement robust password policies that require complex passwords, regular changes, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing sensitive systems.
- Network Security: Secure the firm’s network infrastructure with firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and regular vulnerability assessments.
- Endpoint Security: Protect all devices connected to the network with antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and regular security updates.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest, using strong encryption algorithms and key management practices.
- Employee Training: Provide employees with regular cybersecurity awareness training to educate them about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and best practices for handling sensitive data.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and test a comprehensive incident response plan to address cybersecurity incidents promptly and effectively.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Cybersecurity Incidents in Brokerage
Several high-profile cybersecurity incidents have affected brokerage firms, highlighting the importance of robust security measures.
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): This incident involved the theft of personal data, including Social Security numbers, of millions of customers from the credit reporting agency Equifax. While not directly targeting a brokerage firm, it demonstrated the potential for large-scale data breaches and their significant impact on individuals and businesses.
- Robinhood Data Breach (2020): In this incident, hackers gained access to personal data of millions of Robinhood users, including email addresses and names. This breach highlighted the vulnerability of online trading platforms to cyberattacks and the importance of robust security measures to protect client data.
Future Trends in Technology for Brokers
The brokerage industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology. Emerging technologies are poised to transform how brokers operate, interact with clients, and deliver services. This section explores some of the most significant trends shaping the future of brokerage.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure platform for recording transactions, making it an attractive solution for the brokerage industry. The potential benefits of blockchain include increased transparency, reduced costs, and improved efficiency. Blockchain can be used to streamline processes like trade execution, settlement, and custody, enhancing the overall client experience.
Potential Impact of Blockchain on Brokerage
- Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of transactions, fostering trust and accountability between brokers and clients.
- Reduced Costs: By automating processes and eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can help brokers reduce operational costs.
- Improved Efficiency: Blockchain enables faster and more efficient trade execution and settlement, improving the overall trading experience.
- Increased Security: The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it resistant to fraud and manipulation, enhancing data security.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a flexible and scalable infrastructure for brokers, enabling them to access resources on demand. This technology allows brokers to reduce their IT costs, enhance data storage and security, and improve accessibility for clients. Cloud-based platforms provide a more agile and responsive environment, facilitating innovation and rapid adaptation to market changes.
Potential Impact of Cloud Computing on Brokerage
- Cost Reduction: Cloud computing eliminates the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, leading to lower IT costs.
- Enhanced Scalability: Brokers can easily scale their operations up or down as needed, adapting to changing market demands and client requirements.
- Improved Data Security: Cloud providers offer robust security measures, protecting sensitive data from breaches and cyberattacks.
- Increased Accessibility: Clients can access brokerage services from anywhere with an internet connection, improving convenience and accessibility.
Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics empowers brokers to gain deeper insights from data, leading to more informed decisions and personalized client experiences. By leveraging big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms, brokers can analyze market trends, identify investment opportunities, and tailor their services to individual client needs.
Potential Impact of Advanced Analytics on Brokerage
- Improved Investment Strategies: Data analysis helps brokers identify investment opportunities, manage risk, and optimize portfolio performance.
- Personalized Client Experiences: Advanced analytics allows brokers to personalize investment recommendations, financial planning, and communication based on client preferences and goals.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Data-driven insights enable brokers to better assess and manage risk, protecting client investments and ensuring financial stability.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Advanced analytics can optimize processes like client onboarding, trade execution, and compliance, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings.
Future Trends in Technology for Brokers
| Technology | Potential Impact | Estimated Timeframe for Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | Increased transparency, reduced costs, improved efficiency, enhanced security | 5-10 years |
| Cloud Computing | Cost reduction, enhanced scalability, improved data security, increased accessibility | 3-5 years |
| Advanced Analytics | Improved investment strategies, personalized client experiences, enhanced risk management, improved operational efficiency | 2-5 years |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Automated trading, personalized financial advice, fraud detection, customer service automation | 2-5 years |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Real-time data collection, automated trading, personalized financial advice, enhanced security | 5-10 years |
The Impact of Technology on Broker-Client Relationships
The rapid evolution of technology has fundamentally reshaped the way brokers interact with their clients. Gone are the days of solely relying on phone calls and in-person meetings. Now, brokers have a wide array of digital tools and platforms at their disposal, enabling them to engage with clients in a more personalized and efficient manner. This shift towards digital communication channels has brought about both benefits and challenges, influencing client satisfaction and trust in the brokerage industry.
Personalized Communication and Digital Engagement
Technology has empowered brokers to tailor their communication strategies to individual client needs and preferences. With the help of sophisticated CRM systems, brokers can track client interactions, gather insights into their investment goals, and personalize their outreach. This personalized approach allows brokers to provide more relevant and timely information, enhancing the overall client experience.
- Targeted Email Campaigns: Brokers can leverage email marketing platforms to segment their client base and send targeted messages based on individual preferences and investment strategies. This ensures that clients receive relevant information that resonates with their needs.
- Automated Investment Updates: Platforms like robo-advisors and portfolio management tools can provide clients with regular updates on their investments, including performance reports, market insights, and personalized recommendations. This transparency and accessibility empower clients to stay informed about their portfolios.
- Interactive Chatbots: Chatbots powered by AI can provide clients with instant answers to common questions, helping them access information 24/7. This reduces wait times and improves client satisfaction by offering immediate support and assistance.
Regulation and Compliance in the Tech-Driven Brokerage Industry
The rapid evolution of technology in the brokerage industry has significantly reshaped the landscape, leading to innovative trading platforms, automated services, and data-driven insights. However, this technological advancement has also brought about new challenges related to regulation and compliance. Regulatory bodies worldwide are actively adapting their frameworks to address the unique risks and opportunities presented by tech-driven brokerage.
Data Privacy and Security Regulations
Data privacy and security are paramount in the brokerage industry, where sensitive client information is handled. Regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States have established stringent requirements for data protection.
Brokers are obligated to implement robust security measures to safeguard client data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. This includes:
- Data encryption and secure storage
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
- Employee training on data privacy and security best practices
- Incident response plans for data breaches
Brokers must also obtain explicit consent from clients for data collection and processing, ensuring transparency and control over their personal information.
Final Summary

As technology continues to advance, the brokerage industry is poised for further transformation. Embracing innovation and adapting to emerging trends will be crucial for brokers to thrive in this dynamic environment. By leveraging technology effectively, brokers can unlock new opportunities, enhance client satisfaction, and secure their position in the future of finance.
Technology is revolutionizing the brokerage industry, and brokers who embrace these advancements gain a competitive edge. One key area of focus is educational technology, and professionals in this field can gain valuable credentials by pursuing an educational technology specialist certification.
This certification demonstrates a deep understanding of educational technology tools and strategies, which can be invaluable for brokers looking to enhance their client services and leverage technology for improved communication and efficiency.