Subscription-Based IT Arrangements: A Modern Approach
Subscription-based information technology arrangements have revolutionized how businesses access and utilize technology. This model, often referred to as “IT as a service,” offers a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional […]
Subscription-based information technology arrangements have revolutionized how businesses access and utilize technology. This model, often referred to as “IT as a service,” offers a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional IT ownership, allowing organizations of all sizes to leverage cutting-edge technology without significant upfront investments.
This approach encompasses various models, including Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Managed Services, each catering to specific business needs. By subscribing to these services, businesses gain access to a range of benefits, including scalability, agility, and reduced operational overhead. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the potential challenges, such as vendor lock-in, data security, and service level agreements, before committing to a subscription-based IT arrangement.
Definition and Types
Subscription-based information technology arrangements, often referred to as cloud computing, have revolutionized the way businesses access and utilize IT resources. This model allows organizations to leverage technology without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware, software, or infrastructure.
Types of Subscription-Based IT Arrangements
Subscription-based IT arrangements encompass various models, each offering distinct advantages and catering to specific needs.
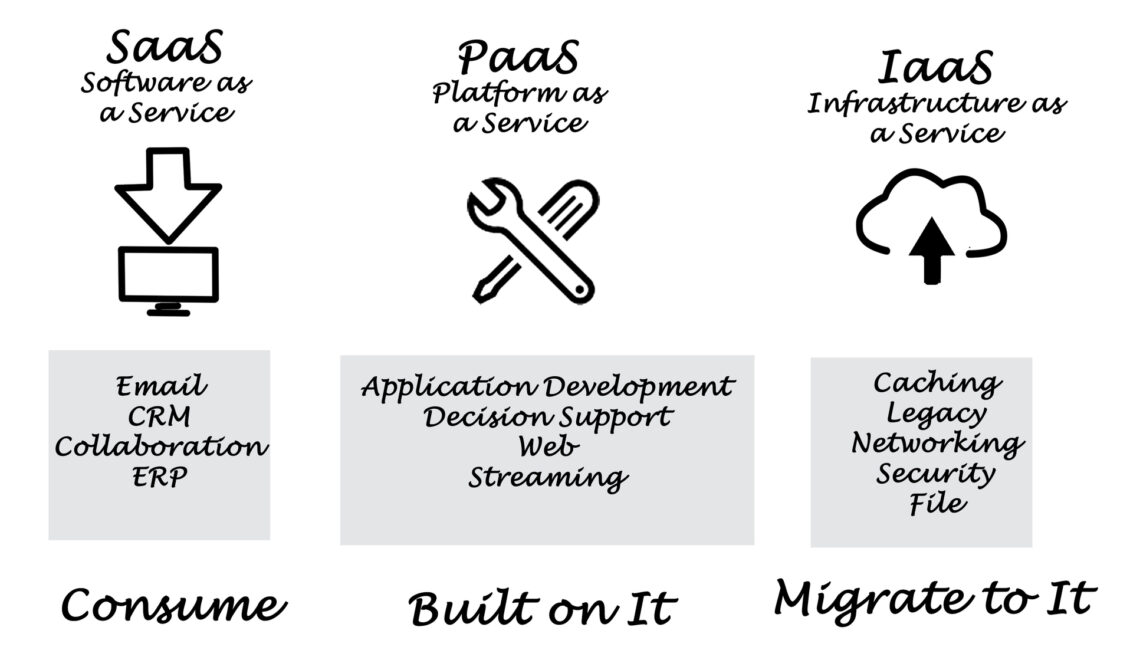
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, enabling users to access and utilize them from any device with an internet connection. Instead of installing and maintaining software on local servers, users subscribe to a service that provides access to the application and its updates.
- Example: Popular SaaS applications include Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
- Real-world applications: SaaS is widely used for email, productivity tools, customer relationship management (CRM), and collaboration platforms. Businesses of all sizes can leverage SaaS to streamline operations, improve communication, and enhance productivity.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides access to computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis. Users can provision and manage virtualized infrastructure through a self-service portal, allowing them to scale resources up or down as needed.
- Example: Leading IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Real-world applications: IaaS is particularly beneficial for businesses with fluctuating workloads, demanding high scalability, or requiring flexibility in their IT infrastructure. Examples include web hosting, database management, and application deployment.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a development platform in the cloud, providing tools and services for building, testing, and deploying applications. It eliminates the need for developers to manage underlying infrastructure, allowing them to focus on application development.
- Example: Popular PaaS platforms include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
- Real-world applications: PaaS is ideal for software developers and businesses seeking to accelerate application development and deployment. It enables rapid prototyping, agile development, and continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) processes.
Managed Services
Managed services provide a comprehensive suite of IT services, including infrastructure management, application support, and security monitoring. Organizations can outsource these functions to specialized providers, allowing them to focus on their core business operations.
- Example: Managed services providers offer a wide range of services, including data center management, network security, and cloud migration assistance.
- Real-world applications: Managed services are particularly valuable for businesses seeking to reduce IT costs, enhance security, and improve operational efficiency. They can provide 24/7 support, expertise, and scalability to meet evolving IT needs.
Benefits and Challenges

Subscription-based IT arrangements, also known as ITaaS (IT as a Service), have become increasingly popular in recent years, offering businesses a more flexible and cost-effective way to manage their IT infrastructure. This approach presents both advantages and challenges that businesses need to carefully consider before adopting it.
Benefits of Subscription-Based IT Arrangements
Subscription-based IT arrangements offer several benefits to businesses, making them an attractive alternative to traditional IT ownership models.
- Reduced upfront costs: Subscription models eliminate the need for large capital expenditures on hardware, software, and infrastructure, making IT more accessible to businesses with limited budgets. This allows businesses to allocate their resources to other strategic initiatives.
- Predictable and manageable costs: Subscription fees are typically fixed, providing businesses with predictable monthly expenses and eliminating the risk of unexpected costs associated with hardware upgrades, maintenance, and repairs.
- Scalability and flexibility: Subscription-based IT arrangements allow businesses to easily scale their IT resources up or down based on their changing needs. This is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in demand.
- Access to the latest technology: Subscription providers typically offer access to the latest software and hardware, ensuring that businesses are always using cutting-edge technology. This eliminates the need for businesses to invest in costly upgrades and ensures they remain competitive in the market.
- Reduced IT management burden: Subscription-based IT arrangements relieve businesses of the responsibility for managing their IT infrastructure, freeing up internal resources to focus on core business operations. This includes tasks such as hardware maintenance, software updates, and security management.
- Improved security and compliance: Subscription providers typically have robust security measures and compliance protocols in place, ensuring that businesses’ data is protected and their systems meet regulatory requirements. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses in highly regulated industries.
Challenges of Subscription-Based IT Arrangements
While subscription-based IT arrangements offer numerous benefits, they also present some challenges that businesses need to be aware of.
- Vendor lock-in: Businesses may find it difficult to switch providers if they are unhappy with the service or if the subscription costs increase significantly. This can limit their flexibility and bargaining power.
- Limited customization: Subscription models often provide standardized IT solutions that may not fully meet the specific needs of all businesses. This can lead to compromises and may require businesses to adapt their processes to fit the provider’s offerings.
- Dependence on internet connectivity: Subscription-based IT arrangements rely heavily on internet connectivity, which can be a challenge for businesses with unreliable internet access or those operating in remote locations.
- Potential for data security breaches: While subscription providers typically have strong security measures in place, there is always a risk of data breaches, especially if the provider experiences a security lapse. Businesses need to carefully evaluate the provider’s security protocols and track record.
- Lack of control over infrastructure: Businesses lose some control over their IT infrastructure when they adopt a subscription model. This can be a concern for businesses that require specific configurations or have unique security requirements.
Comparison with Traditional IT Ownership Models
Subscription-based IT arrangements offer several advantages over traditional IT ownership models, such as:
- Lower upfront costs: Subscription models eliminate the need for significant capital investment, making IT more accessible to businesses with limited budgets.
- Predictable costs: Subscription fees provide businesses with predictable monthly expenses, eliminating the risk of unexpected costs associated with hardware upgrades and maintenance.
- Flexibility and scalability: Subscription models allow businesses to easily adjust their IT resources based on their changing needs.
- Access to latest technology: Subscription providers typically offer access to the latest software and hardware, ensuring that businesses remain competitive.
- Reduced IT management burden: Subscription models relieve businesses of the responsibility for managing their IT infrastructure, freeing up internal resources.
However, traditional IT ownership models also offer some advantages, such as:
- Greater control over infrastructure: Businesses have complete control over their IT infrastructure and can customize it to meet their specific needs.
- Potential for long-term cost savings: While traditional models require upfront investments, businesses can potentially save money in the long run by avoiding recurring subscription fees.
- No vendor lock-in: Businesses have the freedom to switch vendors or upgrade their equipment as needed.
Ultimately, the best IT model for a business depends on its specific needs, budget, and risk tolerance.
Key Considerations
Adopting a subscription-based IT arrangement requires careful evaluation of various factors to ensure it aligns with your business needs and goals. Here are some key considerations that businesses should carefully assess:
Service Level Agreements
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are crucial for defining the specific performance expectations, responsibilities, and remedies for any service disruptions. They provide a clear framework for both the provider and the business to understand their obligations and ensure the agreed-upon level of service is delivered.
- Availability: SLAs should clearly define the expected uptime and downtime of the IT services. For instance, they might specify a 99.9% uptime guarantee, meaning the service should be available for 99.9% of the time.
- Performance: SLAs should Artikel performance metrics, such as response times, data transfer rates, and application performance. These metrics help ensure the IT services meet the business’s performance requirements.
- Response Times: SLAs should define the expected response times for support requests and incident resolution. This ensures timely support and problem resolution to minimize business disruptions.
- Reporting and Monitoring: SLAs should include provisions for regular reporting and monitoring of service performance. This allows the business to track the provider’s adherence to the agreed-upon service levels.
Security Considerations
Data security is paramount, especially when outsourcing IT services. Businesses must ensure that the provider has robust security measures in place to protect sensitive data and comply with relevant regulations.
- Data Encryption: The provider should encrypt data both in transit and at rest, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
- Access Control: The provider should implement strict access controls to restrict unauthorized access to data and systems.
- Regular Security Audits: The provider should conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response: The provider should have a well-defined incident response plan to handle security breaches effectively and minimize the impact on the business.
Vendor Lock-in and Data Portability
Vendor lock-in is a potential concern with subscription-based IT arrangements. It refers to the difficulty or cost associated with switching providers due to proprietary technologies or data formats. Businesses should carefully evaluate the potential for vendor lock-in and ensure data portability options exist.
- Open Standards: The provider should utilize open standards and protocols to ensure compatibility with other systems and facilitate data migration if needed.
- Data Export Options: The provider should offer options to export data in standard formats to enable easy transfer to other platforms.
- Exit Clauses: The contract should include clear exit clauses that Artikel the process and terms for terminating the agreement and transferring data.
Implementation and Management
Implementing a subscription-based IT arrangement requires a structured approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximize its benefits. It involves careful planning, coordination, and ongoing management to achieve optimal performance and value.
Implementation Steps
Implementing a subscription-based IT arrangement requires a well-defined process. Here are the key steps involved:
- Define Scope and Requirements: Clearly define the scope of the arrangement, including the specific IT services, applications, and infrastructure components to be covered. This involves identifying business needs, performance expectations, and security requirements.
- Vendor Selection and Contract Negotiation: Conduct a thorough vendor evaluation process, considering factors such as reputation, experience, pricing, service level agreements (SLAs), and support capabilities. Negotiate a comprehensive contract that Artikels the terms and conditions of the subscription, including pricing, service levels, and termination clauses.
- Technical Integration and Configuration: Integrate the subscribed IT services and applications with existing systems and infrastructure. This may involve configuring network settings, user accounts, and data synchronization processes.
- User Training and Onboarding: Provide comprehensive training to end users on how to access and utilize the subscribed services and applications effectively. This includes familiarizing them with the user interface, features, and best practices.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Deploy the subscribed services and applications according to a planned schedule, ensuring a smooth transition and minimal disruption to operations. Conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure functionality and performance meet expectations.
Implementation Checklist
A comprehensive checklist ensures that all critical aspects of implementation are addressed:
- Business Requirements Documentation: Clearly define business needs, objectives, and expected outcomes from the subscription-based IT arrangement.
- Vendor Evaluation and Selection: Conduct a rigorous vendor evaluation process, considering factors such as technical expertise, industry experience, pricing, and support capabilities.
- Contract Negotiation and Agreement: Secure a comprehensive contract that Artikels the terms and conditions of the subscription, including pricing, service levels, and termination clauses.
- Technical Integration and Configuration: Plan and execute the integration of subscribed services and applications with existing systems and infrastructure.
- User Training and Onboarding: Develop and deliver comprehensive training programs to ensure users are proficient in using the subscribed services and applications.
- Deployment and Go-Live Planning: Establish a detailed deployment plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and testing procedures.
- Change Management and Communication: Effectively manage change processes and communicate updates to stakeholders throughout the implementation process.
Management Best Practices
Managing subscription-based IT arrangements requires a proactive approach to ensure optimal performance, cost-effectiveness, and continuous improvement:
- Monitoring and Performance Measurement: Regularly monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to track service levels, resource utilization, and overall performance. This involves analyzing data from various sources, such as usage logs, system metrics, and user feedback.
- Optimization and Cost Control: Identify opportunities to optimize resource allocation, streamline processes, and reduce costs associated with the subscription-based IT arrangement. This may involve adjusting service levels, negotiating pricing, or exploring alternative solutions.
- Vendor Management and Relationship Building: Establish a strong relationship with the vendor, fostering open communication and collaboration. Regularly review the contract and service level agreements (SLAs), ensuring compliance and addressing any issues promptly.
- Security and Compliance: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. This includes regular security assessments, vulnerability scans, and incident response planning.
- Continuous Improvement and Innovation: Stay abreast of industry trends and advancements in IT services and technologies. Explore opportunities to leverage new solutions and enhance the value derived from the subscription-based arrangement.
Future Trends
The landscape of subscription-based IT arrangements is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Emerging trends, such as the rise of cloud-native applications and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), are shaping the future of this model.
Impact of Cloud-Native Applications, Subscription-based information technology arrangements
Cloud-native applications, designed specifically for cloud environments, are becoming increasingly popular. These applications are built with microservices architecture, enabling scalability, flexibility, and rapid deployment. Subscription-based IT arrangements are well-suited for cloud-native applications, offering a flexible and cost-effective way to access and manage these applications.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Subscription models align with the pay-as-you-go pricing structure of cloud services, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they consume. This eliminates the need for upfront capital investments and reduces operational costs.
- Scalability and agility: Cloud-native applications are highly scalable, allowing businesses to adjust their IT resources based on demand. Subscription-based arrangements provide the flexibility to scale up or down as needed, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Faster innovation: Cloud-native applications enable rapid development and deployment cycles, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to changing market conditions. Subscription models support this agility by providing access to the latest technologies and updates.
Impact of AI Integration
AI is transforming various industries, and its integration into IT arrangements is accelerating. AI-powered tools and services are being incorporated into subscription-based models, offering enhanced capabilities and value to businesses.
- Automated IT management: AI can automate routine IT tasks, such as monitoring, troubleshooting, and security management. This frees up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives and improves operational efficiency.
- Personalized IT services: AI can analyze user behavior and preferences to provide personalized IT experiences. Subscription-based arrangements can leverage AI to deliver tailored solutions and enhance user satisfaction.
- Predictive analytics: AI can analyze historical data to predict future IT needs and proactively address potential issues. This enables businesses to optimize resource allocation and minimize downtime.
Ultimate Conclusion: Subscription-based Information Technology Arrangements
In conclusion, subscription-based information technology arrangements are reshaping the IT landscape, providing businesses with unprecedented flexibility, cost-efficiency, and access to advanced technologies. By understanding the various types of arrangements, weighing the benefits and challenges, and carefully considering the key factors involved, organizations can leverage this innovative model to achieve their IT goals and gain a competitive edge in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve, subscription-based IT arrangements are poised to become even more prevalent, offering businesses a dynamic and adaptable approach to meeting their technology needs.
Subscription-based information technology arrangements are becoming increasingly popular, offering businesses a flexible and cost-effective way to access the latest technology. One example of this trend is the adoption of gol pump technology , which provides real-time data and insights into fuel consumption and efficiency.
This type of data can be invaluable for businesses looking to optimize their operations and reduce costs, demonstrating how subscription-based models can empower businesses to leverage cutting-edge technology without significant upfront investment.







