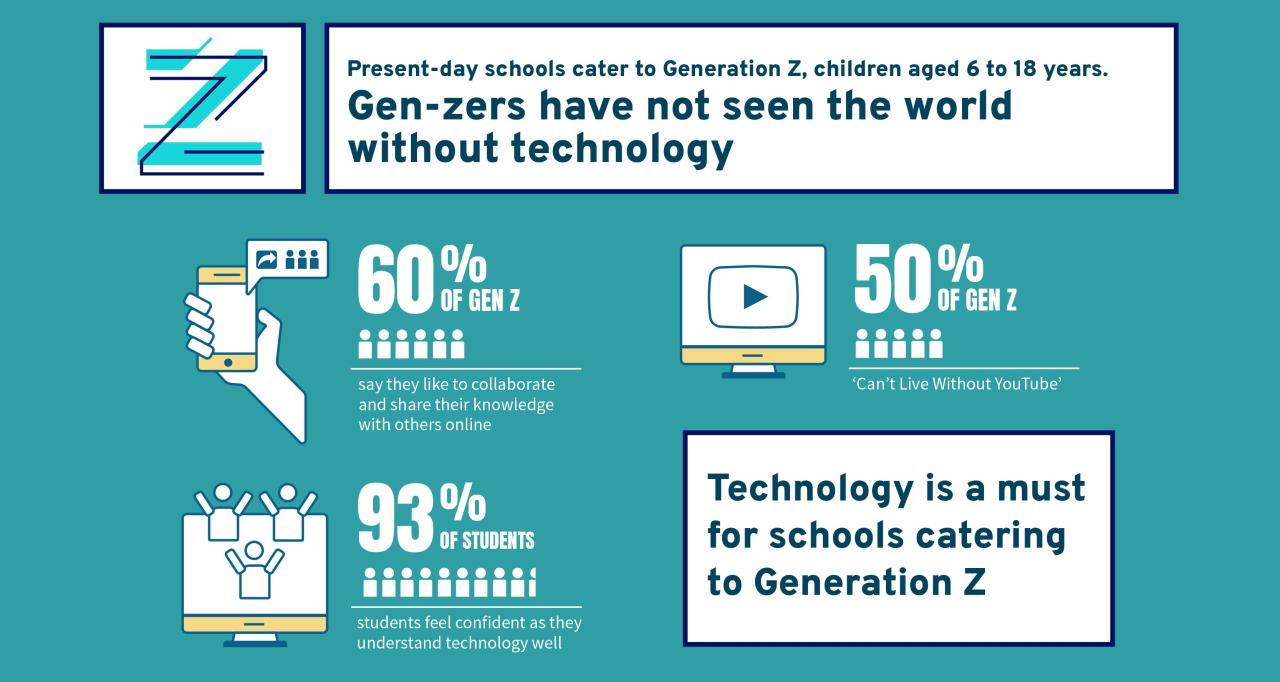
Click Technologies: Shaping User Interactions
Click technologies, the unseen force behind our digital interactions, have revolutionized how we engage with computers. From the simple click of a mouse to the intuitive gestures on a touchscreen, […]

Click technologies, the unseen force behind our digital interactions, have revolutionized how we engage with computers. From the simple click of a mouse to the intuitive gestures on a touchscreen, these technologies have evolved alongside our understanding of user interfaces, shaping how we navigate the digital world.
This exploration delves into the history, types, applications, and future of click technologies, uncovering the intricate web of innovations that have transformed our interactions with technology.
Definition and Evolution of Click Technologies
Click technologies encompass the various methods and tools that allow users to interact with digital systems through discrete actions, typically by clicking, tapping, or selecting elements on a screen. These technologies are the foundation of modern user interfaces, facilitating navigation, data input, and control over digital devices and software.
Evolution of Click Technologies
Click technologies have evolved significantly since their inception, driven by advancements in hardware, software, and user interaction models. This evolution has led to more intuitive, efficient, and diverse ways for users to interact with digital environments.
- Early Click Technologies: The first iterations of click technologies emerged with the development of the computer mouse in the 1960s. The mouse, initially a physical device connected to a computer, enabled users to interact with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) by clicking on icons and menus. This marked a shift from text-based command-line interfaces to more visually intuitive interfaces. The mouse, paired with the GUI, revolutionized how users interacted with computers, paving the way for the widespread adoption of personal computers.
- Touchscreen Interfaces: The introduction of touchscreens in the late 20th century brought about a new era of click technologies. Touchscreens allowed users to interact with digital devices directly by touching the screen, eliminating the need for a separate input device like a mouse. This intuitive and direct interaction model gained popularity with the advent of smartphones and tablets, leading to the widespread adoption of touchscreens in various devices. Touchscreens have become an integral part of modern user interfaces, offering a more natural and accessible way to interact with digital devices.
- Gesture Recognition: As technology advanced, click technologies evolved beyond simple clicks and taps. Gesture recognition technologies emerged, enabling users to interact with devices using hand movements and gestures. This technology utilizes sensors and algorithms to interpret user gestures, allowing for more complex and intuitive interactions. Gesture recognition is commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and other devices to perform actions like scrolling, zooming, and navigating through menus. It has also found applications in gaming, virtual reality, and other fields, expanding the possibilities of user interaction.
Types of Click Technologies

Click technologies are the methods used to interact with computer systems and devices. These technologies have evolved significantly over time, from the traditional mouse click to more advanced methods like touch screens and voice commands. The choice of click technology depends on the context, user preferences, and the capabilities of the device.
Mouse Clicks
Mouse clicks are the most basic and widely used click technology. They involve using a physical mouse to interact with a computer by clicking buttons. The mouse typically has two or three buttons, each with a specific function.
Mouse clicks are versatile and can be used for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Selecting and opening files and folders
- Navigating through web pages
- Editing text and images
- Launching applications
- Playing games
The advantages of mouse clicks include:
- Accuracy: Mouse clicks provide precise control over the cursor, allowing for accurate selection and manipulation of objects.
- Familiarity: Mouse clicks are a familiar and intuitive way to interact with computers for most users.
- Affordability: Mice are relatively inexpensive and readily available.
However, mouse clicks also have limitations:
- Physical constraints: Using a mouse requires a physical workspace and can be cumbersome in some situations, such as when working on a small laptop or in a crowded environment.
- Limited accessibility: Mouse clicks can be challenging for individuals with disabilities, such as those with limited hand mobility.
Touch Screen Interactions
Touch screen interactions allow users to interact with a device by directly touching the screen. This technology has become increasingly popular with the rise of smartphones and tablets.
Touch screens offer a variety of interaction methods, including:
- Taps: A single tap on the screen can be used to select an item or open an application.
- Swipes: Swiping across the screen can be used to navigate through menus, scroll through lists, or change pages.
- Gestures: More complex gestures, such as pinching to zoom or rotating an image, can be used for more advanced interactions.
Touch screens have several advantages:
- Intuitiveness: Touch screen interactions are natural and easy to learn, even for users who are not familiar with computers.
- Portability: Touch screens are typically found on portable devices, making them convenient for on-the-go use.
- Accessibility: Touch screens can be more accessible for individuals with disabilities, as they can be used with a variety of assistive technologies.
However, touch screens also have limitations:
- Accuracy: Touch screens can be less accurate than mouse clicks, especially for tasks that require fine motor control.
- Fingerprint smudges: Touch screens are prone to fingerprint smudges, which can be distracting and require regular cleaning.
- Limited functionality: Some tasks, such as gaming or complex design work, may be better suited for a mouse and keyboard.
Voice Commands
Voice commands allow users to interact with devices by speaking commands. This technology has become increasingly sophisticated and is now widely used in smartphones, smart home devices, and other applications.
Voice commands offer several advantages:
- Hands-free interaction: Voice commands allow users to interact with devices without having to use their hands, making them ideal for tasks such as driving or cooking.
- Accessibility: Voice commands can be a valuable tool for individuals with disabilities who have difficulty using traditional input methods.
- Convenience: Voice commands can be faster and more convenient than typing or using a mouse, especially for simple tasks.
However, voice commands also have limitations:
- Accuracy: Voice recognition software is not always accurate, especially in noisy environments or when dealing with unusual accents.
- Privacy concerns: Using voice commands raises privacy concerns, as the device is constantly listening for commands.
- Limited functionality: Voice commands are not always suitable for complex tasks that require precise input.
Gesture Recognition
Gesture recognition allows users to interact with devices by performing physical gestures in front of a camera or sensor. This technology is often used in gaming, virtual reality, and other applications where natural and intuitive interaction is desired.
Gesture recognition offers several advantages:
- Intuitiveness: Gestures are a natural and intuitive way to interact with devices, making them easy to learn and use.
- Immersive experience: Gesture recognition can enhance the immersive experience in applications such as virtual reality and gaming.
- Hands-free control: Gesture recognition allows users to control devices without having to touch them, making them ideal for tasks such as navigating through menus or controlling a virtual object.
However, gesture recognition also has limitations:
- Accuracy: Gesture recognition software can be unreliable, especially in noisy environments or when dealing with unusual movements.
- Limited functionality: Gesture recognition is not yet as versatile as other click technologies and is primarily used for specific tasks.
- Technical requirements: Gesture recognition systems require specialized hardware and software, which can be expensive and complex to set up.
Applications of Click Technologies
Click technologies have revolutionized various industries and domains, transforming the way we interact with the world around us. From enhancing user experiences to improving accessibility and productivity, these technologies have a profound impact on our daily lives. Let’s delve into the diverse applications of click technologies and explore their transformative potential.
Impact on User Experience
Click technologies have significantly improved user experiences across various platforms and applications. The intuitive and responsive nature of click interactions has made technology more accessible and engaging.
- Enhanced Navigation: Click technologies enable seamless navigation through websites, applications, and digital environments. Users can easily navigate menus, explore content, and access information with a simple click, creating a more intuitive and user-friendly experience.
- Interactive Content: Click technologies facilitate the creation of interactive content, such as quizzes, polls, and games, that engage users and provide a more immersive experience. These interactive elements enhance user engagement and make information more memorable.
- Personalized Experiences: Click technologies enable personalized experiences by collecting user data and preferences. This data can be used to tailor content, recommendations, and user interfaces to individual needs, creating a more relevant and engaging experience.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Click technologies play a crucial role in making technology more accessible to people with disabilities.
- Assistive Technologies: Click technologies are used in assistive technologies, such as screen readers and voice control software, to provide alternative input methods for users with visual or motor impairments. These technologies enable individuals with disabilities to interact with computers and mobile devices more easily.
- Universal Design: Click technologies contribute to universal design principles by providing intuitive and accessible interfaces that cater to a wider range of users, regardless of their abilities. This ensures that technology is inclusive and accessible to all.
Productivity Enhancement
Click technologies have significantly enhanced productivity in various industries by streamlining workflows and automating tasks.
- Workflow Automation: Click technologies are used to automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry and document processing, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic and creative work. This increased efficiency leads to higher productivity and reduced errors.
- Real-time Collaboration: Click technologies facilitate real-time collaboration by enabling users to share and edit documents, presentations, and other files simultaneously. This fosters seamless teamwork and accelerates project completion.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Click technologies are used in data analysis and visualization tools to provide insights and patterns from large datasets. This enables businesses to make informed decisions and optimize operations based on data-driven insights.
Innovative Applications
Click technologies are at the forefront of innovation, driving the development of cutting-edge applications in various fields.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Click technologies are integral to VR experiences, enabling users to interact with virtual environments and objects. By clicking on objects or navigating menus, users can explore virtual worlds, engage in immersive simulations, and experience new realities.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Click technologies enhance AR experiences by allowing users to interact with digital overlays on the real world. Users can click on objects to access information, control virtual elements, and engage with augmented content.
- Wearable Technology: Click technologies are used in wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, to provide intuitive and personalized experiences. Users can click on buttons or touchscreens to control functions, access data, and interact with their devices.
Click Technologies in User Interfaces

Click technologies have played a pivotal role in shaping user interfaces (UIs) and user interactions, revolutionizing how we navigate and interact with digital environments. From the humble mouse click to the complex touch gestures, click technologies have made UIs more intuitive, accessible, and engaging.
Impact on User-Friendliness and Intuitiveness
Click technologies have significantly contributed to user-friendliness and intuitiveness in UIs. The simple act of clicking or tapping on a screen element provides a clear and immediate feedback mechanism, making interactions more predictable and less prone to errors.
For instance, the introduction of the mouse and the click action made it easier for users to select, manipulate, and interact with objects on a computer screen, eliminating the need for complex commands or cryptic codes. This direct interaction made computer interfaces more accessible to a wider audience, paving the way for the widespread adoption of personal computers.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Click technologies have also played a crucial role in enhancing accessibility and inclusivity in UI design.
For example, the advent of touchscreens has made devices more accessible to individuals with disabilities who may find traditional input methods challenging. Touch gestures, like swiping and pinching, provide alternative ways to navigate and interact with devices, enabling individuals with motor impairments to use technology more effectively.
Design Principles and Considerations
The effective incorporation of click technologies into UI design requires careful consideration of several key design principles.
- Clear and Consistent Feedback: Click actions should provide clear and immediate feedback to users, indicating that their interaction has been registered and acknowledged. This feedback can be visual, auditory, or haptic, depending on the context and the user’s preferences.
- Intuitive and Predictable Interactions: Click technologies should be used in a way that is intuitive and predictable for users. Actions should be consistent across different interfaces and contexts, minimizing the learning curve and reducing the potential for confusion.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: UI designers should consider the needs of diverse users, including individuals with disabilities. Click technologies should be implemented in a way that is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or limitations.
- User-Centered Design: The design of click interactions should be guided by user research and testing. Understanding user needs, preferences, and behaviors is crucial for creating effective and engaging interfaces.
Future Trends in Click Technologies

Click technologies are constantly evolving, driven by advancements in hardware, software, and user interface design. This evolution is leading to a future where interactions with technology will be more intuitive, immersive, and personalized than ever before.
Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback is a powerful tool for enhancing user experiences by providing tactile sensations that complement visual and auditory cues. This technology allows users to feel the effects of their actions in the digital world, creating a more realistic and engaging experience.
- Enhanced Realism: Haptic feedback can create a more realistic sense of touch in virtual environments, making them more immersive and believable. For example, in a virtual reality game, players can feel the impact of a punch or the texture of a surface they’re touching.
- Improved User Feedback: Haptic feedback can provide users with immediate feedback on their actions, such as the click of a button or the vibration of a notification. This can improve user efficiency and satisfaction by reducing ambiguity and providing clear confirmation.
- Accessibility: Haptic feedback can be particularly beneficial for users with visual or auditory impairments, providing an alternative way to interact with and understand digital information.
Brain-Computer Interfaces, Click technologies
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are emerging technologies that allow users to control computers and other devices using their brainwaves. This technology has the potential to revolutionize click technologies by enabling direct interaction with devices without the need for physical input.
- Intuitive Control: BCIs could allow users to control devices with their thoughts, eliminating the need for traditional input methods like keyboards and mice. This could lead to more natural and efficient interactions with technology.
- Accessibility: BCIs could provide a new avenue for individuals with physical disabilities to interact with technology.
- Enhanced Creativity: BCIs could enable users to express themselves in new and innovative ways, potentially leading to new forms of art and communication.
Holographic Interfaces
Holographic interfaces are three-dimensional displays that project images and information into the real world. These interfaces can create immersive experiences by allowing users to interact with digital content in a more realistic and tangible way.
- Enhanced Visualization: Holographic interfaces can provide a more intuitive and immersive way to visualize complex data and information. This can be particularly beneficial in fields like medicine, engineering, and education.
- Interactive Experiences: Holographic interfaces allow users to interact with digital content in a more natural and intuitive way. This could lead to new forms of entertainment, education, and collaboration.
- Remote Collaboration: Holographic interfaces can facilitate remote collaboration by allowing users to interact with digital content in a shared virtual space. This could lead to more efficient and effective teamwork.
End of Discussion: Click Technologies
As click technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more intuitive and immersive experiences. The future holds exciting possibilities, from brain-computer interfaces to holographic displays, promising a seamless integration of technology into our lives. By understanding the evolution and potential of click technologies, we can better anticipate and shape the future of human-computer interactions.
Click technologies, encompassing everything from online advertising to user interfaces, are constantly evolving. The legal landscape surrounding these technologies is equally dynamic, making it crucial to stay informed about the latest developments. The technology law conference provides an excellent platform for professionals to engage with these issues and gain valuable insights.
By understanding the legal framework governing click technologies, we can ensure their responsible and ethical implementation.