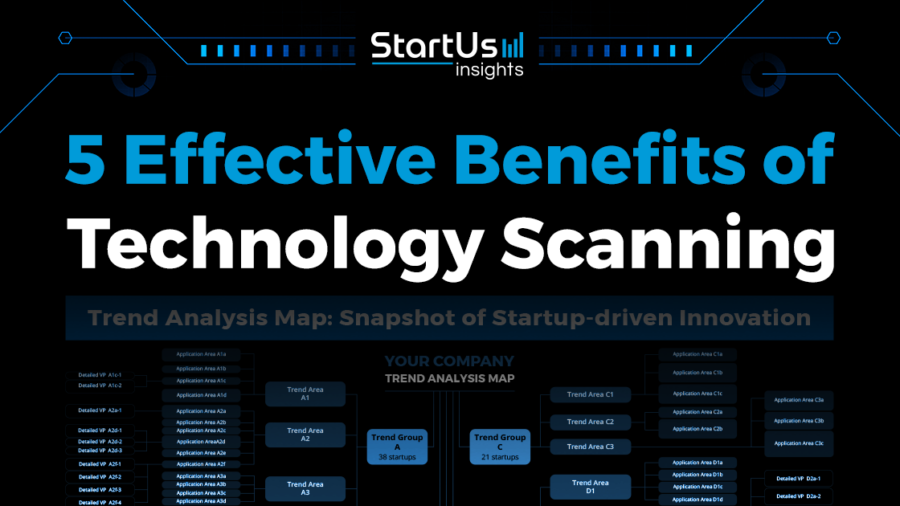
Technology Scanning: Understanding Business Innovation
Technology scanning is the process of systematically searching for and analyzing emerging technologies that can impact a business. It involves identifying trends, evaluating potential disruptions, and discovering new opportunities. This […]
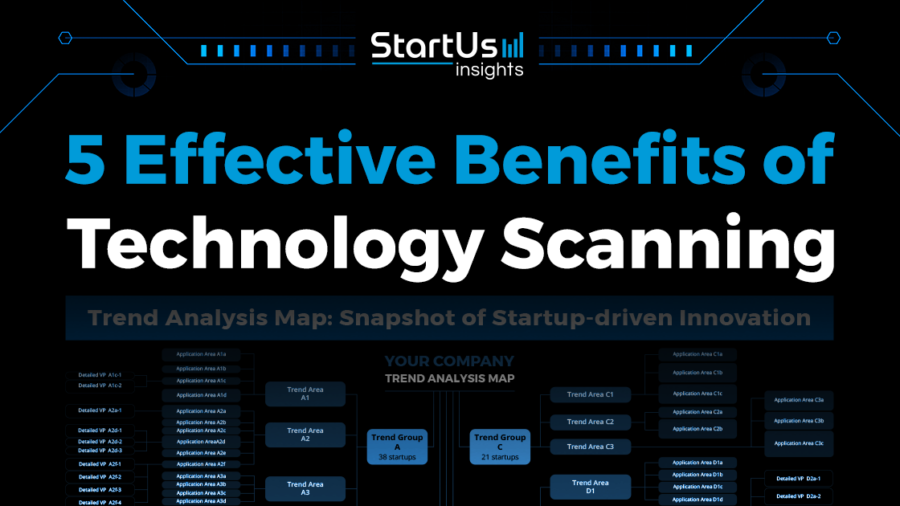
Technology scanning is the process of systematically searching for and analyzing emerging technologies that can impact a business. It involves identifying trends, evaluating potential disruptions, and discovering new opportunities. This process is essential for organizations looking to stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape.
By understanding the latest advancements and their potential implications, businesses can make informed decisions about product development, strategic planning, and risk management. Technology scanning helps companies identify new markets, develop innovative products and services, and anticipate future challenges. It is a proactive approach that empowers businesses to adapt to change and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Technology Scanning
Technology scanning is a strategic process that businesses employ to identify and analyze emerging technologies and their potential impact on their industry. It involves a systematic and comprehensive exploration of the technological landscape, seeking to understand the latest trends, advancements, and innovations. By understanding the potential of new technologies, businesses can make informed decisions about their future direction, adapt to changing market dynamics, and stay ahead of the competition.
The Importance of Technology Scanning
Technology scanning is essential for businesses that want to remain competitive and innovative. It allows them to:
- Identify Emerging Trends: Technology scanning helps businesses stay ahead of the curve by identifying emerging trends that could disrupt their industry or create new opportunities. For example, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. By scanning for AI-related advancements, businesses can understand how these technologies will impact their operations and develop strategies to leverage them.
- Evaluate Potential Disruptions: Disruptive technologies can completely change the competitive landscape, making it essential for businesses to understand their potential impact. For example, the emergence of ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft has disrupted the traditional taxi industry. By scanning for disruptive technologies, businesses can identify potential threats and develop strategies to mitigate their impact.
- Discover New Opportunities: Technology scanning can also help businesses discover new opportunities for growth and innovation. For example, the development of 3D printing technology has created new possibilities for manufacturing, design, and healthcare. By scanning for emerging technologies, businesses can identify potential applications that could lead to new products, services, or business models.
Technology Scanning in Different Industries
Technology scanning is crucial for businesses in various industries, including:
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging that improve patient care, streamline processes, and reduce costs. Technology scanning helps healthcare providers stay informed about advancements in areas such as telemedicine, genomics, and medical imaging.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing industry is undergoing a digital transformation, with new technologies such as robotics, automation, and the Internet of Things (IoT) changing the way products are designed, manufactured, and distributed. Technology scanning helps manufacturers stay abreast of these advancements and implement them to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Finance: The financial services industry is rapidly adopting new technologies to enhance customer experiences, improve risk management, and reduce costs. Technology scanning helps financial institutions stay informed about advancements in areas such as blockchain, fintech, and artificial intelligence.
Methods and Techniques for Technology Scanning
Technology scanning involves systematically identifying and analyzing emerging technologies and their potential impact on an organization or industry. This process helps organizations stay ahead of the curve, anticipate future trends, and make informed decisions about innovation, investment, and strategic planning.
Methods for Technology Scanning
Several methods can be employed for technology scanning, each with its strengths and limitations. Understanding these methods allows organizations to choose the most appropriate approach based on their specific needs and resources.
- Literature Reviews: This method involves systematically searching and analyzing published literature, including academic journals, industry reports, and white papers. Literature reviews provide a comprehensive overview of current research and development in specific technology areas.
- Patent Analysis: Analyzing patents reveals insights into emerging technologies, the focus of research and development efforts, and potential future innovations. Patent databases provide information on patent applications, granted patents, and patent holders.
- Industry Conferences: Attending industry conferences provides opportunities to network with experts, learn about the latest technological advancements, and gain insights into emerging trends. Presentations, workshops, and discussions at conferences offer valuable information.
- Expert Interviews: Engaging with experts in specific technology areas through interviews provides valuable insights into emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities. Experts can offer their perspectives on the future direction of technology and its potential impact.
Strengths and Limitations of Technology Scanning Methods
Each technology scanning method has its strengths and limitations. Understanding these aspects helps organizations choose the most effective approach for their specific needs.
Literature Reviews
- Strengths:
- Provides a comprehensive overview of current research and development in specific technology areas.
- Offers insights into the state-of-the-art technologies and their potential applications.
- Can be conducted remotely, making it cost-effective and efficient.
- Limitations:
- Information may be outdated, as publications often have a lag time.
- May not capture emerging technologies that have not yet been published.
- Requires expertise in searching and analyzing scientific literature.
Patent Analysis
- Strengths:
- Provides insights into emerging technologies and the focus of research and development efforts.
- Reveals potential future innovations and the competitive landscape in specific technology areas.
- Offers information on patent holders, which can identify potential collaborators or competitors.
- Limitations:
- Patent applications do not always result in granted patents, so some information may be speculative.
- Patent data can be complex and requires specialized knowledge to interpret.
- May not capture all emerging technologies, as not all innovations are patented.
Industry Conferences
- Strengths:
- Provides opportunities to network with experts and learn about the latest technological advancements.
- Offers insights into emerging trends and the direction of the industry.
- Allows for real-time discussions and the exchange of ideas.
- Limitations:
- Can be expensive and time-consuming to attend.
- May not cover all relevant technology areas.
- Information presented at conferences may be biased or promotional.
Expert Interviews
- Strengths:
- Provides valuable insights into emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Offers perspectives on the future direction of technology and its potential impact.
- Allows for targeted questioning and in-depth discussions.
- Limitations:
- Can be time-consuming and expensive to conduct.
- May be influenced by personal biases or opinions.
- May not be representative of the broader industry or technology landscape.
Table Summarizing Technology Scanning Methods
| Method | Key Characteristics | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Literature Reviews | Systematic analysis of published literature | Gaining a comprehensive overview of current research and development in specific technology areas |
| Patent Analysis | Analyzing patent applications and granted patents | Identifying emerging technologies, the focus of research and development efforts, and potential future innovations |
| Industry Conferences | Networking with experts, attending presentations, and participating in discussions | Learning about the latest technological advancements, gaining insights into emerging trends, and networking with industry leaders |
| Expert Interviews | Engaging with experts in specific technology areas | Gaining valuable insights into emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities, and obtaining perspectives on the future direction of technology |
Data Sources for Technology Scanning
Technology scanning relies heavily on the collection and analysis of data from diverse sources. Identifying and accessing relevant data is crucial for gaining insights into emerging technologies, market trends, and potential disruptions. This section explores key data sources, emphasizing the importance of data quality and reliability, and provides a list of reputable data sources for specific industries.
Academic Journals
Academic journals play a significant role in disseminating cutting-edge research and advancements in various fields. They offer valuable insights into emerging technologies, scientific breakthroughs, and theoretical frameworks.
- Strengths: Rigorous peer-review process ensures the quality and reliability of published research. Provides in-depth analysis and detailed information on specific technologies and their applications.
- Weaknesses: Can be highly specialized and technical, requiring a strong understanding of the subject matter. May not always reflect the practical implications or commercial viability of technologies.
Industry Reports
Industry reports provide valuable insights into market trends, competitive landscapes, and technological advancements within specific sectors. These reports are often commissioned by industry analysts, consulting firms, and research organizations.
- Strengths: Offer market-specific data, including market size, growth rates, key players, and emerging trends. Provide practical insights into the commercialization and adoption of technologies.
- Weaknesses: Can be expensive to access, and some reports may be biased towards specific companies or industries. May not always provide the latest information, as they often have publication delays.
Government Publications
Government agencies and research institutions often publish reports, data sets, and studies related to technological advancements, innovation, and policy. These publications can provide valuable insights into government initiatives, funding opportunities, and regulatory landscapes.
- Strengths: Provide access to publicly funded research and data sets, often with a broader perspective on technological trends. Can be a valuable source of information on government regulations and policies.
- Weaknesses: May not always be readily accessible or easily searchable. Data and information can be presented in a technical or complex format.
Online Databases
Online databases offer a vast collection of information, including scientific articles, patents, news articles, and market data. These databases can be valuable for technology scanning, providing access to a wide range of data sources in a single platform.
- Strengths: Offer comprehensive and searchable databases, allowing for efficient data retrieval and analysis. Can provide real-time updates on technological advancements and industry trends.
- Weaknesses: May require subscriptions or fees for access. Data quality and reliability can vary depending on the database and source of information.
Importance of Data Quality and Reliability
The quality and reliability of data are crucial for effective technology scanning. Inaccurate or biased data can lead to flawed conclusions and misinformed decisions. To ensure data quality, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- Source Credibility: Evaluate the reputation and expertise of the data source. Look for organizations with a strong track record of research and analysis.
- Data Accuracy: Verify the data against other sources and check for consistency and completeness. Look for data that is up-to-date and relevant to the specific technology being scanned.
- Data Bias: Be aware of potential biases in the data, such as industry affiliations or funding sources. Consider multiple perspectives and sources to mitigate bias.
Reputable Data Sources for Specific Industries
The following table lists reputable data sources for various industries, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Technology scanning is essential for staying ahead of the curve in today’s rapidly evolving landscape. Companies like the msr technology group are leading the way in implementing cutting-edge solutions. By proactively identifying emerging trends and technologies, organizations can make informed decisions and capitalize on new opportunities, ultimately achieving greater success in the long run.
| Industry | Data Source | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | ClinicalTrials.gov | Comprehensive database of clinical trials, including information on drugs, devices, and treatments. | May not always include information on early-stage research or pre-clinical trials. |
| Automotive | SAE International | Provides standards, technical papers, and industry news related to automotive engineering and technology. | Focuses primarily on engineering and technical aspects of the industry. |
| Information Technology | Gartner | Offers research and analysis on technology trends, market share, and vendor evaluations. | Can be expensive to access and may not always reflect emerging technologies or niche markets. |
| Energy | International Energy Agency (IEA) | Provides data and analysis on energy markets, technologies, and policies. | May not always include information on emerging renewable energy technologies or distributed energy systems. |
Analyzing and Interpreting Technology Scanning Data

The raw data collected through technology scanning is only the first step. The real value lies in analyzing and interpreting this data to extract meaningful insights. This involves identifying emerging trends, assessing their potential impact, and mapping out opportunities for your organization.
Trend Identification
Trend identification involves recognizing patterns and shifts in the technological landscape. This requires analyzing the data collected from various sources and looking for recurring themes, emerging technologies, and shifts in market dynamics.
- Frequency Analysis: Identify technologies that appear frequently across different sources. This suggests widespread interest and potential for future impact. For example, if you see numerous mentions of “artificial intelligence” in research papers, news articles, and industry reports, it indicates a growing trend.
- Growth Rate Analysis: Examine the rate at which technologies are developing and gaining adoption. Technologies with rapid growth rates indicate a high potential for disruption. For instance, the rapid growth of cloud computing in recent years has significantly impacted businesses and industries.
- Cross-referencing: Compare data from different sources to identify consistent patterns and trends. This approach helps validate findings and build a comprehensive understanding of emerging technologies. For example, if a technology is mentioned in both academic research and industry reports, it suggests a strong potential for practical application.
Impact Assessment
Once trends are identified, the next step is to assess their potential impact on your organization. This involves evaluating the potential benefits and risks associated with each technology.
- Competitive Advantage: Assess how a technology could enhance your organization’s competitive position. For example, implementing artificial intelligence could improve customer service, automate tasks, and gain insights from data, leading to a competitive edge.
- Operational Efficiency: Analyze how a technology could improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. For example, implementing automation technologies could streamline processes and minimize manual labor, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Market Disruption: Consider how a technology could disrupt existing markets or create new opportunities. For example, the emergence of electric vehicles has disrupted the automotive industry, creating new markets for battery technology and charging infrastructure.
Opportunity Mapping
Opportunity mapping involves identifying specific opportunities for your organization to leverage emerging technologies. This requires considering your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, and strategic goals.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensure that the identified opportunities align with your organization’s strategic goals and objectives. For example, if your organization aims to become a leader in sustainability, you should explore opportunities related to renewable energy technologies.
- Resource Availability: Assess whether your organization has the necessary resources (financial, technical, human) to pursue the identified opportunities. For example, investing in artificial intelligence requires expertise in data science and machine learning.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the competitive landscape and identify potential competitors who are already pursuing similar opportunities. This will help you develop a competitive strategy and avoid being overtaken by rivals.
Role of Critical Thinking and Domain Expertise
Critical thinking and domain expertise are crucial for interpreting technology scanning results effectively.
Critical thinking involves questioning assumptions, evaluating evidence, and considering alternative perspectives. Domain expertise provides a deeper understanding of the specific industry and its challenges, enabling you to identify relevant technologies and assess their potential impact.
For example, a technology scanning report might highlight the potential of blockchain technology for supply chain management. However, a critical thinker with expertise in supply chain management would be able to evaluate the specific benefits and challenges of blockchain in this context. They would also be able to assess whether the technology is a viable solution for their organization’s specific needs.
Analyzing Technology Trends: An Example
Let’s consider the example of the growing trend of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is being used in various industries, from healthcare to finance, to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance customer experiences.
- Trend Identification: AI is a frequent topic in research papers, industry reports, and news articles, indicating widespread interest and adoption.
- Impact Assessment: AI has the potential to disrupt industries by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and creating new products and services. For example, AI-powered chatbots are revolutionizing customer service, while AI-driven medical imaging analysis is improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Opportunity Mapping: Organizations can leverage AI to improve their operations, develop new products, and gain a competitive advantage. For example, a healthcare company could use AI to personalize treatment plans and predict patient outcomes, while a financial institution could use AI to detect fraud and improve risk management.
By analyzing technology trends like AI, organizations can identify opportunities for innovation, growth, and competitive advantage.
Applications of Technology Scanning in Business

Technology scanning is a valuable tool that can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions about their future. By understanding the latest trends and emerging technologies, businesses can identify opportunities to innovate, improve their products and services, and gain a competitive advantage.
Applications of Technology Scanning in Business
Technology scanning can be applied to various business functions, such as product development, strategic planning, and risk management.
- Product Development: Technology scanning can help businesses identify new technologies that can be used to create innovative products or improve existing ones. For example, a company that manufactures consumer electronics could use technology scanning to identify new trends in artificial intelligence (AI) or virtual reality (VR) that could be incorporated into its products.
- Strategic Planning: Technology scanning can help businesses develop long-term strategies by identifying potential disruptions and opportunities. For example, a company in the transportation industry could use technology scanning to assess the potential impact of autonomous vehicles on its business and develop strategies to adapt.
- Risk Management: Technology scanning can help businesses identify potential risks associated with emerging technologies. For example, a financial institution could use technology scanning to assess the risks of cyberattacks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Benefits of Technology Scanning
The benefits of technology scanning for businesses include:
- Improved Decision-Making: By understanding the latest trends and emerging technologies, businesses can make more informed decisions about their investments, product development, and strategic planning.
- Increased Innovation: Technology scanning can help businesses identify new opportunities to innovate and create new products and services.
- Enhanced Competitive Advantage: By staying ahead of the curve, businesses can gain a competitive advantage by being the first to market with new products or services that leverage emerging technologies.
Examples of Technology Scanning Applications
The following table provides examples of different business applications of technology scanning, their benefits, and challenges:
| Application | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Product Development | – Development of innovative products and services. – Improved product quality and functionality. – Reduced development costs and time. |
– Difficulty in identifying and evaluating relevant technologies. – High costs associated with research and development. – Risk of technological obsolescence. |
| Strategic Planning | – Development of long-term strategies that anticipate future trends. – Identification of new market opportunities. – Reduced risk of disruption from emerging technologies. |
– Difficulty in predicting the future impact of technologies. – Difficulty in adapting to rapidly changing technological landscapes. – Risk of making decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate information. |
| Risk Management | – Identification of potential risks associated with emerging technologies. – Development of strategies to mitigate risks. – Improved cybersecurity and data privacy. |
– Difficulty in identifying and assessing emerging risks. – High costs associated with risk mitigation strategies. – Risk of overreacting to perceived threats. |
Future Trends in Technology Scanning
The landscape of technology scanning is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and predictive modeling. These trends are poised to significantly impact the way businesses gather, analyze, and interpret technology information.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Technology Scanning
AI is transforming technology scanning by automating tasks and enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of data analysis. AI-powered tools can sift through vast amounts of data from diverse sources, identifying emerging trends, and predicting future technological advancements.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms can analyze unstructured text data, such as news articles, research papers, and social media posts, to extract insights and identify emerging technologies. This capability enables technology scanners to gain a comprehensive understanding of the technological landscape.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms can learn from historical data and identify patterns to predict future technological developments. By analyzing data on past technology adoption rates, market trends, and research and development activities, ML models can provide insights into the trajectory of emerging technologies.
- Computer Vision: Computer vision algorithms can analyze images and videos to identify new technologies and assess their potential impact. For instance, they can analyze images of prototypes, product designs, and manufacturing processes to understand the evolution of technology.
The Impact of Big Data Analytics on Technology Scanning
Big data analytics plays a crucial role in technology scanning by providing insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscape. By analyzing large datasets from various sources, businesses can identify emerging technologies that align with their strategic goals.
- Trend Analysis: Big data analytics can help identify emerging trends by analyzing data on search queries, social media discussions, and online publications. This enables businesses to stay ahead of the curve and identify opportunities for innovation.
- Customer Insights: Big data analytics can provide valuable insights into customer preferences and behavior. By analyzing customer data, businesses can understand the technologies that are most likely to resonate with their target market.
- Competitive Intelligence: Big data analytics can be used to gather competitive intelligence, such as competitor activities, product launches, and market share. This information helps businesses assess the competitive landscape and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Predictive Modeling in Technology Scanning
Predictive modeling utilizes statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms to forecast future technological developments. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, businesses can anticipate future trends and make informed decisions about technology investments.
- Technology Adoption Forecasting: Predictive models can forecast the adoption rates of emerging technologies based on factors such as market size, consumer demand, and technological maturity. This information helps businesses determine the potential impact of new technologies on their operations.
- Innovation Roadmapping: Predictive models can assist in developing technology roadmaps by identifying promising technologies and estimating their time to market. This enables businesses to prioritize their research and development efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- Risk Assessment: Predictive models can assess the potential risks associated with emerging technologies, such as market disruption, regulatory changes, and security vulnerabilities. This information helps businesses mitigate risks and make informed decisions about technology adoption.
Leveraging Emerging Trends for Enhanced Technology Scanning
Businesses can leverage emerging trends in technology scanning to gain a competitive advantage and stay ahead of the curve.
- Invest in AI-powered tools: Businesses should invest in AI-powered tools that automate tasks, enhance data analysis, and provide insights into emerging technologies. This will enable them to scan the technological landscape more efficiently and effectively.
- Embrace big data analytics: Businesses should leverage big data analytics to gain insights into market trends, customer behavior, and the competitive landscape. This will help them identify emerging technologies that align with their strategic goals.
- Utilize predictive modeling: Businesses should utilize predictive modeling to forecast future technological developments and make informed decisions about technology investments. This will help them anticipate future trends and stay ahead of the competition.
- Develop a data-driven culture: Businesses should foster a data-driven culture that encourages the use of data to inform decision-making. This will help them leverage emerging trends in technology scanning and make informed decisions about technology adoption.
Closure: Technology Scanning

In conclusion, technology scanning is a vital tool for businesses seeking to thrive in a world characterized by rapid technological advancement. By understanding the latest trends and their implications, companies can make informed decisions, innovate effectively, and stay ahead of the competition. As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, the importance of technology scanning will only grow in the years to come.