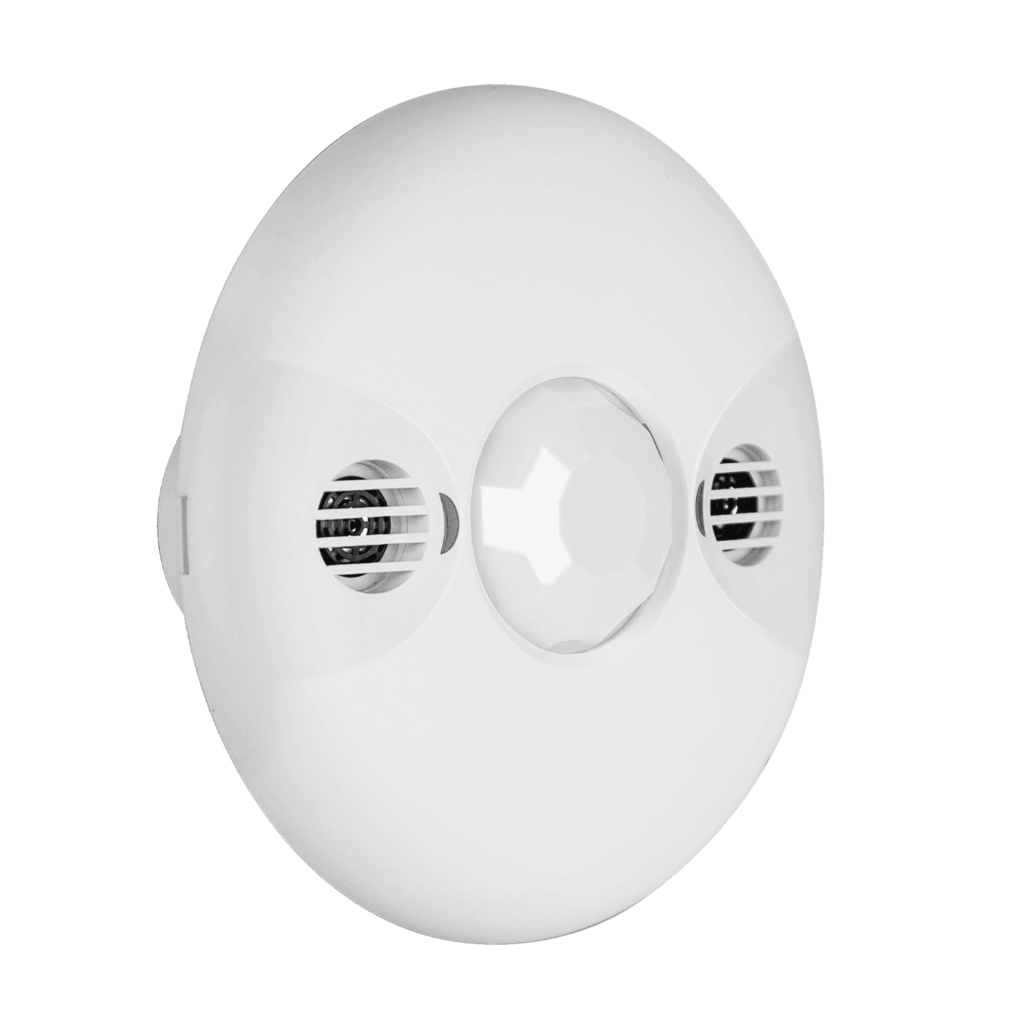
Dual Technology Occupancy Sensors: Smart Sensing for Efficiency
Dual technology occupancy sensors represent a significant advancement in building automation and energy management. These sensors combine two distinct technologies, such as passive infrared (PIR) and ultrasonic, to provide a […]
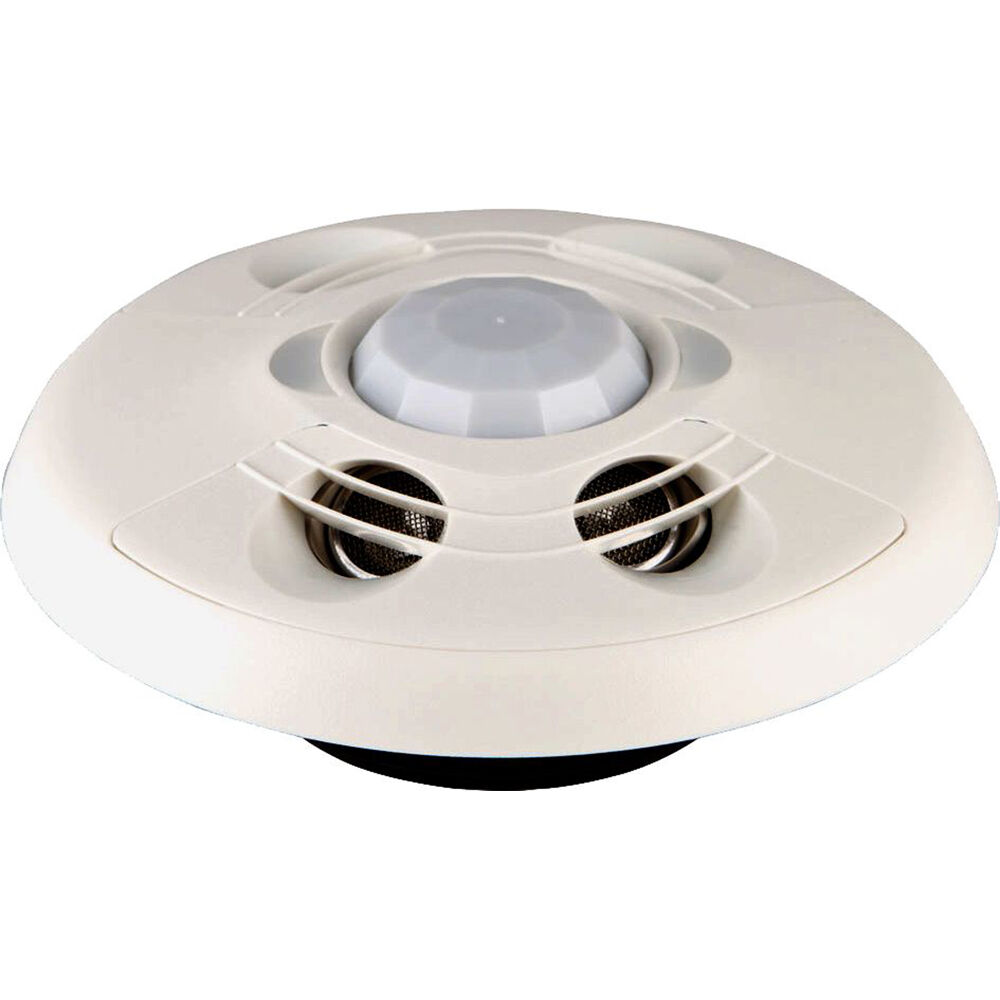

Dual technology occupancy sensors represent a significant advancement in building automation and energy management. These sensors combine two distinct technologies, such as passive infrared (PIR) and ultrasonic, to provide a more reliable and accurate detection of occupancy in a space. This dual approach addresses the limitations of single-technology sensors, offering a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of room usage.
By integrating these technologies, dual technology sensors can overcome the challenges associated with environmental factors like drafts, temperature fluctuations, and even the presence of pets. They can accurately detect movement and presence, regardless of the individual’s position or activity. This enhanced accuracy leads to greater efficiency in energy consumption, improved comfort for occupants, and a more sustainable approach to building management.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Dual Technology Occupancy Sensors
Dual technology occupancy sensors combine passive infrared (PIR) and ultrasonic detection to provide more accurate and reliable occupancy detection than single-technology sensors. This combination allows them to detect a wider range of movements and overcome limitations of each individual technology.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Dual Technology Sensors, Dual technology occupancy sensors
When selecting dual technology occupancy sensors, it is crucial to consider several factors that influence their effectiveness and suitability for specific applications. These factors include:
| Application | Space Size | Environmental Conditions | Budget | Integration with Other Systems |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occupancy detection for lighting control in offices, classrooms, and conference rooms | Small to medium-sized spaces | Normal ambient temperatures and humidity levels | Mid-range budget | Integration with building automation systems (BAS) and lighting control systems |
| Occupancy detection for HVAC control in large spaces, such as warehouses and retail stores | Large spaces | Extreme temperatures, humidity, and air movement | High budget | Integration with HVAC control systems and building management systems (BMS) |
| Occupancy detection for security systems in sensitive areas, such as data centers and laboratories | Small to medium-sized spaces | Controlled environment with minimal air movement | High budget | Integration with security systems, access control systems, and video surveillance systems |
Final Summary: Dual Technology Occupancy Sensors

Dual technology occupancy sensors have become an indispensable tool for modern buildings, offering a smarter and more efficient approach to managing energy consumption and optimizing space utilization. By combining the strengths of different sensing technologies, these sensors provide reliable and accurate occupancy detection, leading to significant cost savings, enhanced comfort, and a more sustainable built environment. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated dual technology sensors that further enhance building automation and energy efficiency, paving the way for a smarter and more sustainable future.
Dual technology occupancy sensors offer a reliable way to optimize energy efficiency in buildings. These sensors, combining both passive infrared (PIR) and ultrasonic technology, can accurately detect movement and adjust lighting and HVAC systems accordingly. This is just one example of how dealer automation technologies are transforming the way businesses operate.
By leveraging these technologies, dealers can enhance customer experiences, streamline processes, and ultimately, drive revenue growth. Dual technology occupancy sensors are a valuable tool for achieving these goals, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient future.