Intro to Surgical Technology: A Guide to the Operating Room
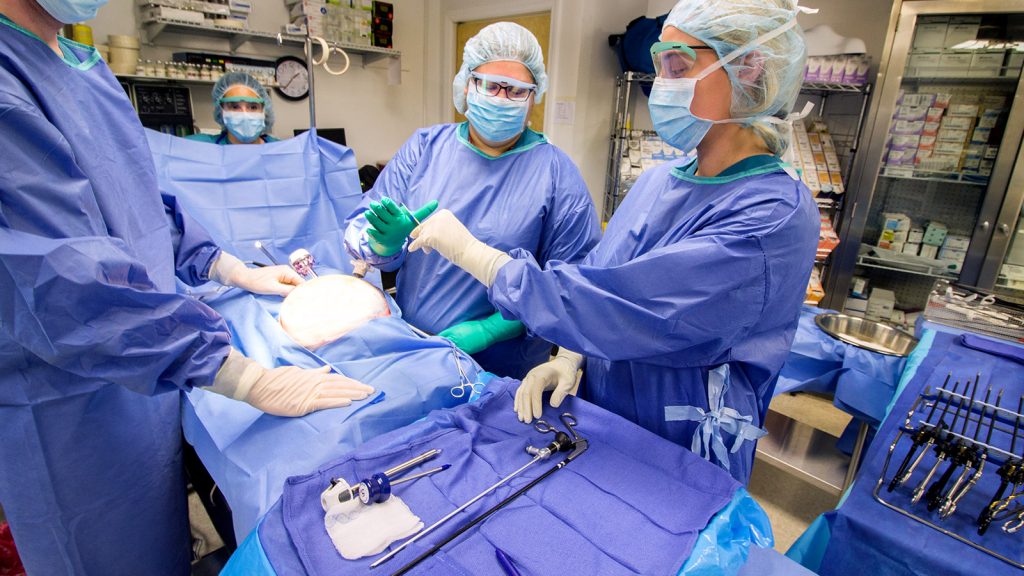
Intro to surgical technology opens a window into the fascinating world of the operating room, where precision, skill, and teamwork converge to improve patient lives. Surgical technologists play a vital […]

Intro to surgical technology opens a window into the fascinating world of the operating room, where precision, skill, and teamwork converge to improve patient lives. Surgical technologists play a vital role in this complex environment, ensuring the smooth and safe execution of surgical procedures. From preparing the operating room to assisting surgeons with instruments, these professionals are integral to the success of every surgery.
This guide delves into the diverse aspects of surgical technology, encompassing educational pathways, responsibilities, essential instruments and equipment, ethical considerations, and career advancement opportunities. By understanding the intricacies of this field, aspiring surgical technologists can gain valuable insights into the demanding yet rewarding career path that lies ahead.
Responsibilities and Duties of a Surgical Technologist
Surgical technologists play a crucial role in the operating room, ensuring a safe and sterile environment for surgical procedures. They work closely with surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to provide essential support during surgeries. This section delves into the specific responsibilities and duties of a surgical technologist.
Key Responsibilities of a Surgical Technologist
Surgical technologists have a wide range of responsibilities, which can be categorized as follows:
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparing the Operating Room | This involves setting up the operating room with all the necessary equipment and supplies, ensuring that the room is sterile and ready for surgery. |
| Sterilizing Instruments and Supplies | Surgical technologists are responsible for sterilizing all instruments and supplies used during surgery, using various methods like steam sterilization, gas sterilization, or chemical sterilization. |
| Assisting the Surgeon | During surgery, surgical technologists assist the surgeon by handing them instruments, supplies, and medications, as well as maintaining a sterile field. |
| Maintaining Sterile Technique | Surgical technologists must strictly adhere to sterile technique to prevent infections during surgery. This includes wearing sterile gowns and gloves, using sterile instruments and supplies, and maintaining a sterile field. |
| Documenting Procedures | Surgical technologists are responsible for documenting the procedures performed, including the instruments and supplies used, the time of the surgery, and any complications that occur. |
| Patient Care | Surgical technologists are responsible for providing basic patient care, such as monitoring vital signs and assisting with patient positioning. |
The Importance of Sterile Technique and Infection Control
Maintaining a sterile environment is paramount in the operating room to prevent infections. Surgical technologists are trained in strict sterile technique and infection control practices, which are essential to minimize the risk of postoperative infections. They must follow protocols meticulously, including:
- Wearing sterile gowns and gloves
- Using sterile instruments and supplies
- Maintaining a sterile field
- Proper hand hygiene
- Environmental disinfection
The Role of a Surgical Technologist in Preparing the Operating Room
Before a surgical procedure, the surgical technologist plays a critical role in preparing the operating room. This involves:
- Gathering and organizing equipment and supplies: The surgical technologist must ensure that all necessary equipment and supplies are available and in good working order, based on the specific surgical procedure.
- Sterilizing instruments and supplies: All instruments and supplies used during surgery must be sterilized to prevent infection. Surgical technologists are responsible for using appropriate sterilization methods, such as steam sterilization or gas sterilization, to ensure that all items are free of microorganisms.
- Setting up the operating room: The surgical technologist is responsible for setting up the operating room, ensuring that all equipment is in place and functioning correctly, and that the room is sterile and ready for surgery. This includes positioning the operating table, setting up the surgical lights, and ensuring that the room is properly ventilated.
- Preparing the patient: The surgical technologist may assist in preparing the patient for surgery, including transporting the patient to the operating room, positioning the patient on the operating table, and prepping the surgical site.
- Maintaining a sterile field: The surgical technologist is responsible for maintaining a sterile field throughout the surgery, ensuring that no contaminated objects or materials come into contact with the surgical site. This includes keeping the surgical team members sterile, monitoring the sterile field for any breaches, and promptly addressing any contamination.
Ethical Considerations and Professionalism
Surgical technologists play a crucial role in the operating room, ensuring the safety and well-being of patients. Their responsibilities extend beyond technical skills, encompassing ethical principles and professional conduct. Ethical considerations guide their actions, ensuring patient care is paramount and upholding the integrity of the profession.
Ethical Principles, Intro to surgical technology
Ethical principles serve as the foundation for surgical technologists’ conduct. These principles guide their decisions and actions, ensuring they prioritize patient well-being and maintain professional integrity.
- Beneficence: Surgical technologists are obligated to act in the best interests of their patients. They strive to provide safe and effective care, minimizing harm and maximizing positive outcomes.
- Non-maleficence: This principle requires surgical technologists to avoid causing harm to their patients. They must be meticulous in their work, ensuring instruments are sterile, and procedures are performed correctly to prevent complications.
- Autonomy: Patients have the right to make decisions about their own healthcare. Surgical technologists respect this right by ensuring patients understand the risks and benefits of procedures and by providing information in a way that facilitates informed consent.
- Justice: Surgical technologists treat all patients fairly and equitably, regardless of their background, beliefs, or socioeconomic status. They ensure equal access to care and avoid discrimination.
Patient Confidentiality and Privacy
Maintaining patient confidentiality is a cornerstone of ethical practice. Surgical technologists are entrusted with sensitive information about their patients’ health and personal lives.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates the protection of patient health information. Surgical technologists must adhere to HIPAA regulations, ensuring patient data is kept secure and disclosed only with appropriate authorization.
- Professional Boundaries: Maintaining professional boundaries is essential. Surgical technologists should avoid discussing patient information outside of the work environment and should never share it on social media or other public platforms.
- Respectful Communication: Surgical technologists should always communicate with patients and their families with respect and sensitivity, avoiding any language that could be perceived as disrespectful or intrusive.
Professional Organizations and Continuing Education
Professional organizations and continuing education play a vital role in maintaining competency and ethical standards within the surgical technology profession.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations such as the Association of Surgical Technologists (AST) provide a platform for professional development, networking, and advocacy. They offer resources, guidelines, and ethical codes that help surgical technologists stay informed and maintain high standards of practice.
- Continuing Education: The rapid advancements in surgical techniques and technology necessitate ongoing learning. Continuing education courses, workshops, and conferences allow surgical technologists to update their knowledge and skills, ensuring they remain competent and proficient in their field.
Final Thoughts: Intro To Surgical Technology

As we conclude our exploration of intro to surgical technology, it’s clear that this field requires a unique blend of technical proficiency, meticulous attention to detail, and unwavering commitment to patient care. Surgical technologists are essential members of the surgical team, ensuring the safety and success of every procedure. With its dynamic nature and diverse career paths, surgical technology offers a rewarding journey for those who are passionate about healthcare and dedicated to making a positive impact on patients’ lives.
An introduction to surgical technology covers a wide range of topics, from sterilization techniques to the intricacies of operating room equipment. Understanding the importance of a sterile environment is paramount, and companies like envirocare technologies play a crucial role in providing advanced solutions for medical waste management.
These solutions ensure the safety and efficiency of surgical procedures, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes.