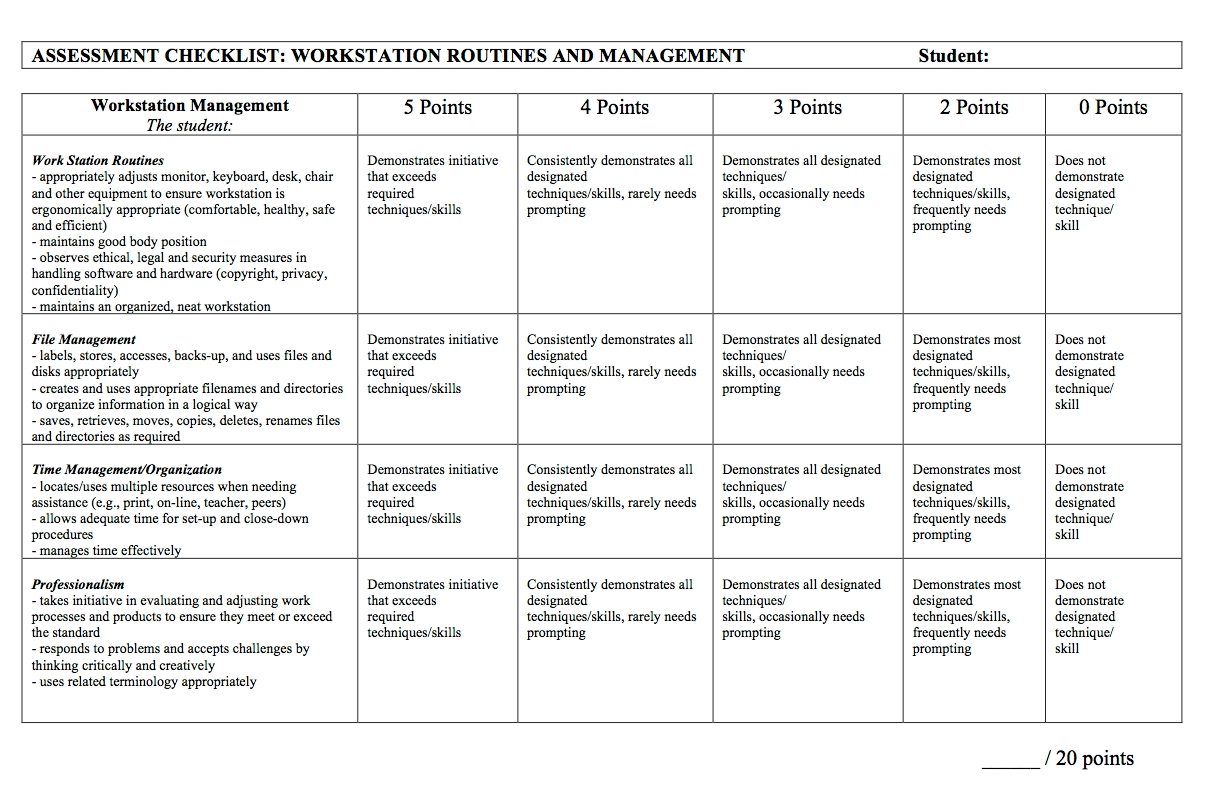
Technology Portfolio Management: A Strategic Approach
Technology portfolio management is the art of strategically aligning technology investments with business objectives. It’s not just about acquiring the latest gadgets; it’s about building a robust technology ecosystem that […]
Technology portfolio management is the art of strategically aligning technology investments with business objectives. It’s not just about acquiring the latest gadgets; it’s about building a robust technology ecosystem that fuels growth and innovation. From cloud computing to artificial intelligence, technology portfolio management ensures that organizations leverage the right tools to achieve their goals.
This strategic approach involves assessing the value and risk of different technology assets, prioritizing investments based on their potential impact, and optimizing the portfolio to maximize value and minimize risk. By taking a holistic view of technology investments, organizations can make informed decisions that drive sustainable success.
Key Components of a Technology Portfolio

A technology portfolio is a strategic tool that helps organizations manage and optimize their technology investments. It provides a comprehensive overview of all the technologies an organization uses, their current state, and their potential impact on the business. This portfolio is dynamic and evolves as the organization’s needs and the technology landscape change.
Technology Asset Categories
The technologies within a portfolio can be categorized based on their function, purpose, and impact on the business. This categorization helps organizations understand the various aspects of their technology landscape and make informed decisions about investments, prioritization, and optimization.
- Core Technologies: These are the fundamental technologies that support the core business operations and are critical for the organization’s survival. They often represent a significant investment and require ongoing maintenance and upgrades. Examples include enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and data management platforms.
- Enabling Technologies: These technologies facilitate and enhance the core business operations, improving efficiency, productivity, and customer experience. They are often less critical than core technologies but still important for achieving strategic goals. Examples include collaboration platforms, cloud computing services, and analytics tools.
- Emerging Technologies: These are new and innovative technologies with the potential to disrupt the industry or create new business opportunities. They are often characterized by rapid evolution and uncertainty, making them high-risk but potentially high-reward investments. Examples include artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Legacy Technologies: These are older technologies that are still in use but may be nearing the end of their lifecycle or no longer meeting the organization’s needs. They can be a significant source of technical debt and security risks, and organizations need to consider their migration or replacement. Examples include outdated operating systems, legacy databases, and mainframe systems.
Technology Portfolio Assessment and Prioritization
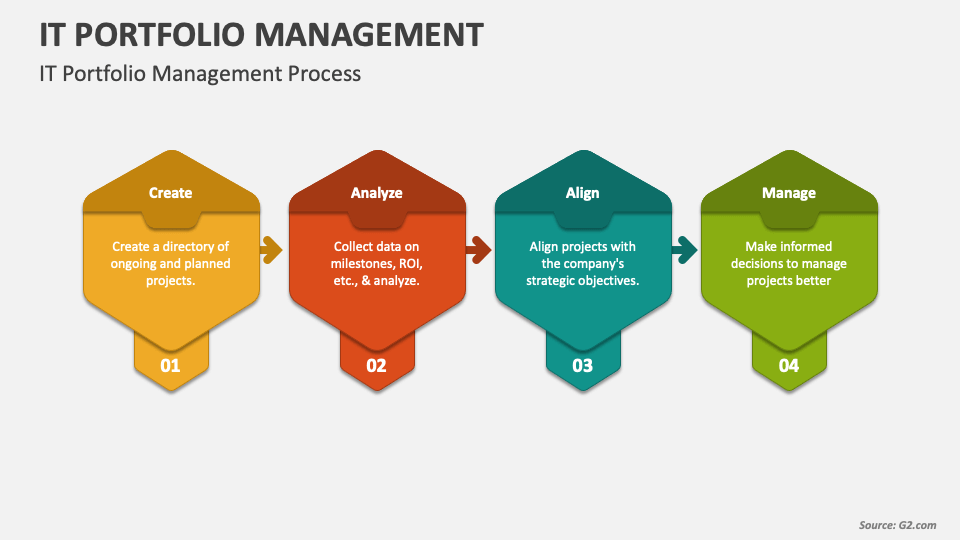
A well-structured technology portfolio is not just about having the right tools; it’s about ensuring those tools are aligned with your strategic goals and deliver the maximum return on investment. This involves continuously assessing and prioritizing your technology investments based on their value and risk.
Assessing Technology Value and Risk
A robust framework for assessing technology value and risk is essential for making informed decisions about your technology portfolio. This framework should consider both tangible and intangible aspects of each technology asset.
- Tangible Value: This includes quantifiable benefits such as cost savings, revenue generation, and improved efficiency.
- Intangible Value: This encompasses less quantifiable benefits such as enhanced customer satisfaction, improved employee productivity, and increased brand reputation.
- Risk: Technology investments involve inherent risks such as technological obsolescence, security vulnerabilities, and potential disruption to business operations.
Here’s a table outlining key factors to consider for each aspect:
| Aspect | Factors to Consider |
|---|---|
| Tangible Value |
|
| Intangible Value |
|
| Risk |
|
Prioritizing Technology Investments, Technology portfolio management
Once you’ve assessed the value and risk of your technology assets, it’s time to prioritize investments based on strategic alignment and return on investment (ROI).
- Strategic Alignment: Prioritize technologies that directly support your organization’s strategic goals and objectives. This ensures that your technology investments are driving your overall business strategy.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Evaluate the potential return on investment for each technology investment. This involves considering both tangible and intangible benefits, as well as the associated costs and risks.
A common method for prioritizing technology investments is to use a matrix that plots investments based on their strategic importance and potential ROI. This allows you to quickly identify high-priority investments that offer a strong combination of strategic alignment and return.
Evaluating Technology Impact
Evaluating the potential impact of technology investments on business outcomes is crucial for ensuring that your investments are delivering the expected results.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define clear and measurable KPIs that reflect the desired business outcomes for each technology investment. This helps you track progress and assess the effectiveness of your investments.
- Impact Analysis: Conduct regular impact analyses to assess the actual impact of your technology investments on your KPIs. This involves collecting data, analyzing trends, and identifying areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the insights gained from impact analyses to refine your technology portfolio, prioritize future investments, and ensure that your technology investments continue to deliver value over time.
Technology Portfolio Optimization
Technology portfolio optimization is the process of strategically managing and aligning your technology investments with your organization’s goals. It’s about ensuring that your technology resources are deployed in the most efficient and effective way, maximizing value and minimizing risk.
Optimizing Technology Portfolio for Value and Risk
Optimizing a technology portfolio is a continuous process that involves assessing the current state of your technology assets, identifying opportunities for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance value and mitigate risk. It requires a holistic approach, considering factors such as:
- Business Objectives: Aligning technology investments with the organization’s strategic goals and priorities. This involves understanding the key business drivers and identifying how technology can support their achievement. For example, if a company is focused on expanding into new markets, its technology portfolio should prioritize investments in tools and platforms that facilitate global expansion.
- Technology Landscape: Analyzing the current state of your technology assets, including their capabilities, limitations, and potential for future growth. This involves identifying redundant or outdated technologies, assessing the potential of emerging technologies, and understanding the dependencies between different systems.
- Cost Optimization: Identifying opportunities to reduce costs associated with technology, such as licensing fees, maintenance contracts, and energy consumption. This may involve negotiating better deals with vendors, consolidating systems, or adopting cloud-based solutions.
- Risk Management: Assessing the potential risks associated with your technology investments, such as security breaches, data loss, and system downtime. This involves implementing appropriate security measures, developing disaster recovery plans, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Innovation and Agility: Encouraging experimentation with new technologies and fostering a culture of innovation. This involves allocating resources for research and development, piloting new technologies, and adapting to rapidly evolving market trends.
Managing Technology Dependencies
Technology dependencies can arise from various sources, including:
- Software Interoperability: Different software applications may require specific versions or configurations to work together seamlessly. This can create challenges when upgrading or replacing systems, as compatibility issues may arise.
- Data Integration: Data from different systems may need to be integrated for reporting, analysis, or decision-making purposes. This can create dependencies between systems, requiring careful planning and coordination to ensure data consistency and accuracy.
- Infrastructure Dependencies: Systems may rely on specific hardware or network infrastructure components. This can create dependencies that need to be managed to ensure system availability and performance.
To manage technology dependencies effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Dependency Mapping: Create a comprehensive map of all technology dependencies within your organization. This will provide a clear understanding of the relationships between different systems and help identify potential risks associated with changes or upgrades.
- Standardization: Adopt industry standards and best practices for technology deployments. This will help reduce the complexity of managing dependencies and improve interoperability between systems.
- Change Management: Implement a robust change management process to ensure that all changes to technology systems are carefully planned, tested, and documented. This will help minimize the risk of unintended consequences and disruptions caused by dependencies.
- Vendor Management: Develop strong relationships with technology vendors and ensure that they are aware of your dependency requirements. This will help you negotiate favorable contracts and ensure that you have access to the support and resources you need.
Aligning Technology Portfolio with Evolving Needs
Organizations need to be agile and adaptable to keep pace with rapidly changing business environments and technological advancements. To ensure your technology portfolio remains aligned with evolving needs, consider the following best practices:
- Regular Portfolio Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of your technology portfolio to assess its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This should involve input from key stakeholders across the organization, including business leaders, IT professionals, and end users.
- Scenario Planning: Develop different scenarios for future business needs and assess how your technology portfolio would support each scenario. This will help you anticipate potential challenges and opportunities and make informed decisions about future investments.
- Innovation and Experimentation: Allocate resources for exploring new technologies and piloting innovative solutions. This will help you stay ahead of the curve and identify emerging trends that could provide a competitive advantage.
- Continuous Improvement: Establish a culture of continuous improvement and embrace feedback from all stakeholders. This will help you identify areas for improvement and ensure that your technology portfolio is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of your organization.
Technology Portfolio Governance
Technology portfolio governance ensures that technology investments align with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives. It provides a framework for managing technology risks, optimizing resource allocation, and driving innovation.
Key Elements of a Robust Technology Portfolio Governance Framework
A robust technology portfolio governance framework comprises several key elements that work together to ensure effective management and oversight.
- Clear Objectives and Alignment: The framework should be aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy, defining clear objectives for technology investments and ensuring they contribute to achieving strategic goals.
- Governance Structure and Responsibilities: Establishing a well-defined governance structure with clear roles and responsibilities for stakeholders involved in decision-making, oversight, and implementation is crucial.
- Portfolio Management Processes: Robust processes for identifying, evaluating, prioritizing, and managing technology investments are essential for optimizing resource allocation and achieving desired outcomes.
- Risk Management and Mitigation: The framework should include mechanisms for identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks associated with technology investments, ensuring a proactive approach to risk management.
- Performance Measurement and Reporting: Regular monitoring and reporting on the performance of technology investments against established metrics is essential for evaluating progress, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring accountability.
Stakeholder Roles in Decision-Making and Oversight
Effective technology portfolio governance requires the involvement of various stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in decision-making and oversight.
- Executive Leadership: Provides strategic direction and sets the overall vision for technology investments, ensuring alignment with business objectives.
- Technology Leadership: Leads the development and implementation of technology strategies, ensuring alignment with business goals and managing technology risks.
- Business Units: Identify technology needs and requirements, providing input on potential investments and ensuring alignment with business operations.
- Finance: Manages budget allocation, tracks spending, and ensures financial viability of technology investments.
- IT Operations: Manages the implementation and maintenance of technology solutions, ensuring efficient and effective operation.
Examples of Governance Processes and Reporting Mechanisms
Implementing effective governance processes and reporting mechanisms is crucial for ensuring transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making.
- Technology Portfolio Review Meetings: Regular meetings with stakeholders to review the technology portfolio, assess progress, and discuss upcoming investments.
- Technology Investment Approval Processes: Formal processes for evaluating and approving technology investments, including cost-benefit analysis, risk assessment, and alignment with strategic goals.
- Dashboards and Reports: Regularly updated dashboards and reports that provide insights into the performance of technology investments, key metrics, and areas for improvement.
Emerging Trends in Technology Portfolio Management
The landscape of technology portfolio management is constantly evolving, driven by the rapid pace of innovation and the emergence of disruptive technologies. Understanding and adapting to these trends is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their technology investments and maintain a competitive edge.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations access and manage their IT infrastructure. The shift towards cloud-based solutions has significantly impacted technology portfolio management. Organizations are now faced with the challenge of managing a hybrid environment consisting of on-premises and cloud-based resources. This requires a new approach to portfolio management, encompassing cloud service selection, cost optimization, and security considerations.
- Increased agility and scalability: Cloud computing allows organizations to scale their IT resources up or down as needed, providing greater flexibility and responsiveness to changing business demands. This agility enables organizations to quickly adapt to market shifts and seize new opportunities.
- Cost optimization: Cloud computing offers a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for upfront capital investments in hardware and infrastructure. This can significantly reduce costs and improve resource utilization.
- Enhanced security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, providing organizations with access to robust security infrastructure and expertise. This can help mitigate security risks and ensure data protection.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various aspects of business operations, including technology portfolio management. AI-powered tools can automate tasks, analyze data, and provide insights that can help organizations make informed decisions about their technology investments.
- Automated portfolio analysis: AI algorithms can analyze large datasets of technology data, identifying trends, risks, and opportunities. This enables organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their portfolio and make data-driven decisions.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can be used to predict equipment failures, allowing organizations to proactively address maintenance needs and minimize downtime. This can significantly reduce costs and improve operational efficiency.
- Intelligent resource allocation: AI-powered tools can analyze historical data and predict future resource requirements, enabling organizations to optimize resource allocation and ensure efficient utilization.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including technology portfolio management. Blockchain’s decentralized and secure nature can enhance transparency, accountability, and trust in technology investments.
- Secure technology asset management: Blockchain can be used to track and manage technology assets, ensuring their authenticity and provenance. This can help prevent counterfeiting and fraud, enhancing the security of technology investments.
- Improved supply chain management: Blockchain can streamline technology procurement processes by providing a secure and transparent platform for tracking and managing transactions. This can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Enhanced collaboration: Blockchain can facilitate collaboration among stakeholders in the technology portfolio, providing a shared and immutable record of decisions and actions. This can improve transparency and accountability.
Conclusion
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, effective technology portfolio management is no longer optional; it’s essential for organizations to thrive. By embracing a strategic approach that prioritizes alignment, optimization, and governance, businesses can unlock the true potential of their technology investments and gain a competitive edge in the digital age.
Technology portfolio management involves carefully selecting and managing a company’s technological assets. This includes assessing the potential of each technology, like the emerson climate technologies control board , and ensuring it aligns with strategic goals. By understanding the value and risks associated with each technology, businesses can optimize their portfolio for growth and efficiency.